Neuromuscular NPTE
1/1748
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
1749 Terms
Meniere's disease
chronic vestibular disorder characterized by nausea and vomiting, episodic vertigo and fullness in the ear with low frequency hearing loss
BPPV
episodic vertigo, nausea, blurred vision and autonomic changes that occur with head movement.
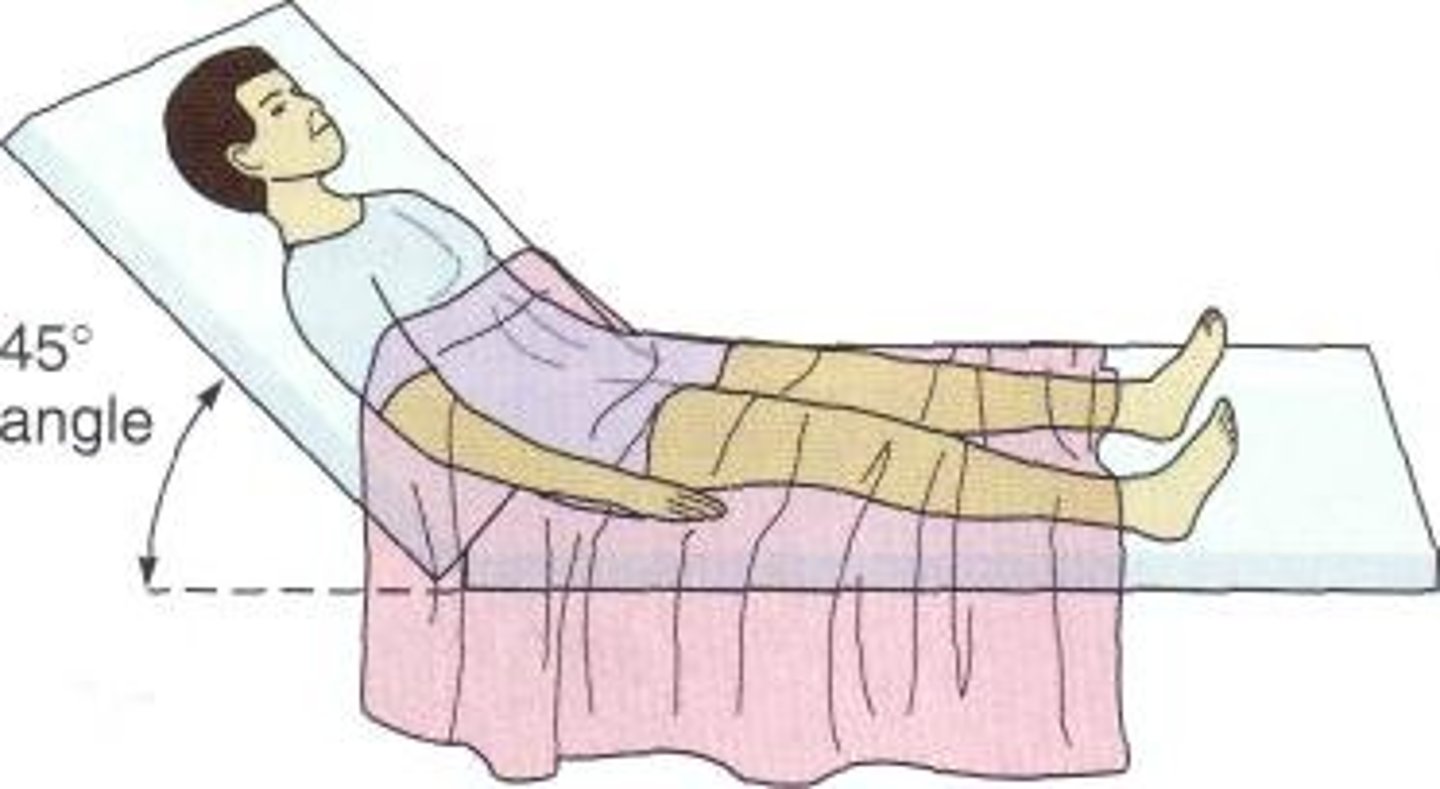
Optimal positions for ventilation of a patient with a C5 SCI
Supine, HOB flat
Semi-Fowler's position
head is raised between 15-45 degree
Extensor Spasticity - LE
Typically strong in antigravity muscles. In the LE, this is usually the hip and knee extensors, adductors and PFers, Strong extensor tone results in sacral sitting with the pelvis tilted posteriorly. This results in a rounded upper spine (kyphotic) and forward head.
Predisone - use and side effects
For MS, corticosteroids to suppress the normal immune system response during an MS attack. Chronic treatment leads to adrenal suppression, muscle wasting, pain, weakness and osteoporosis.
MCA stroke
contralateral hemiparesis and sensory deficits, UE involvement > LE involvement
Romberg Test
Ask person to stand up w/ feet together and arms at sides. Once in stable position, ask person to close eyes and hold position. Wait about 20 seconds. Normally, person can maintain posture and balance even w/ visual orienting information blocked, although slight swaying may occur. (Stand close to catch the person in case they fall)
commonly seen in dorsal column disease
Spina Bifida
Neural tube defect characterized by defective closure of the vertebral column. HKAFO's are often employed to assist pediatric patients with ambulation activities.

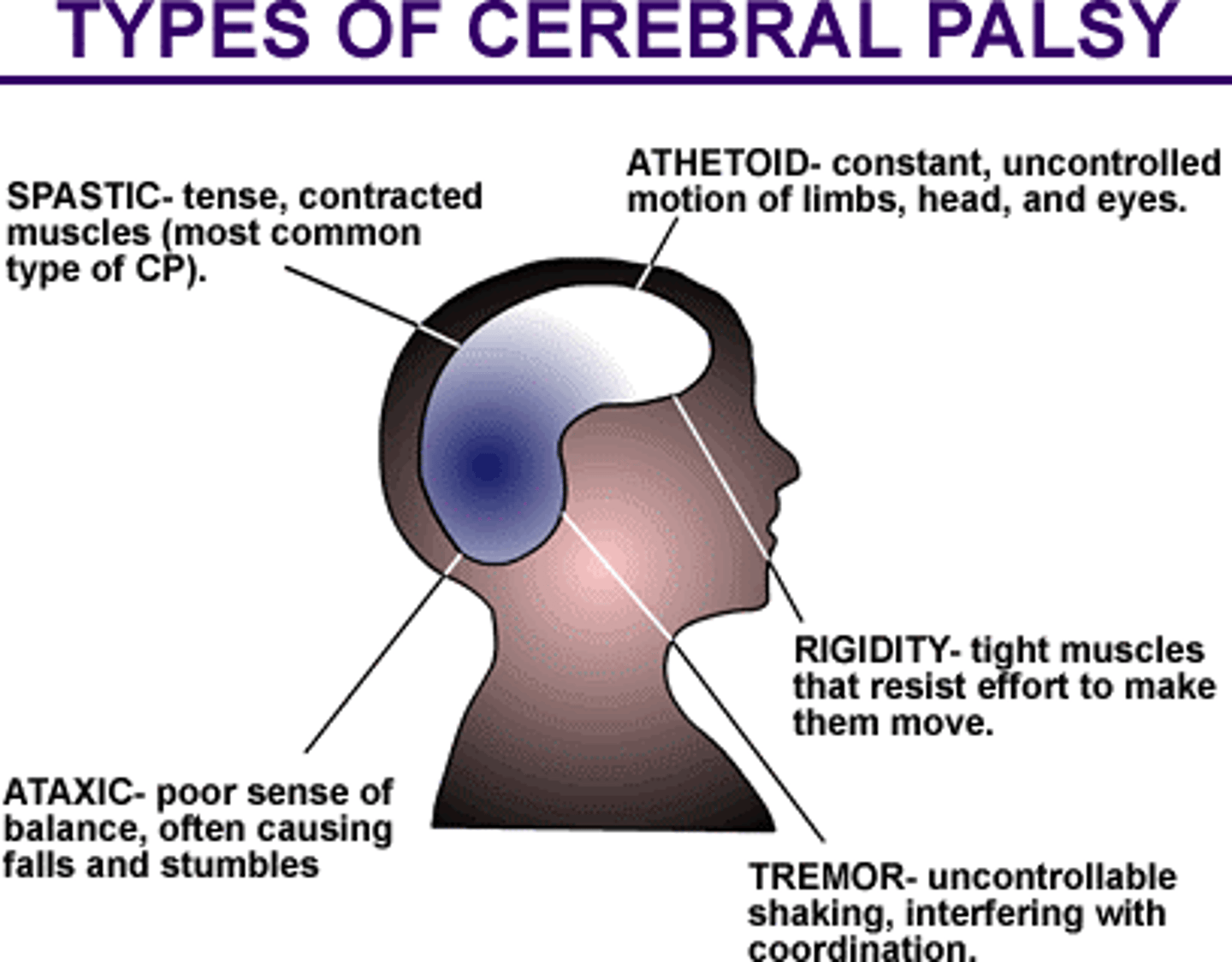
Cerebral Palsy
Umbrella term used to describe a group of non-progressive movement disorders that result from brain damage.
Clinical presentation includes motor delays, abnormal muscle tone and motor control, reflex abnormalities, poor postural control, and balance impairments.
Down Syndrome
Occurs when there is an error in cell division
Clinical presentation include hypotonia, flattened nose bridge, simian line, epicanthal folds, enlargement of the tongue, and developmental delay.

Legg-Calve-Perthes
Idiopathic osteonecrosis of the capital femoral ephysis of the femoral head
Clinical presentation include short limb, high greater trochanter, quad atrophy, and adductor spasm.
Bracing using a Scottish-rite brace may be used in an attempt to contain the femoral head in the acetabulum.

ALS
chronic degenerative disease, motor weakness typically presents distal to proximal progression. Unlikely to ambulate.
Neurogenic arthropathy
rapidly destructive arthropathy d/t impaired pain perception and position sense, which can result from various underlying disorders, MC diabetes and stroke.
Symptoms include joint swelling, effusion, deformity and instability.
Treatment often consist of joint mobs which slows the disease progress
Peripheral Neuritis
refers to the inflammation of nerves and is synonymous with peripheral neuropathy.
Symptoms include: numbness, tingling, paresthesia, sensitivity to touch, and muscle weakness.
Cerebeller degeneration symptoms
dysmetria, nystagmus, dysdiadochokinesia
Basal Ganglia damage symptoms
athetosis, slow, writhing,
S/S of intracranial pressure
increased intracranial pressure secondary to cerebral edema and brain hernation include creasing consciousness with slowing of pulse and Cheyne-Stokes respirations.
Barthel Index
consists of 10 ADLs and is often used as a screening tool in rehab, long-term care settings and home care. Scores range from 0-100 in increments of 5. 100 = independent
Functional Index Measure
tests a subject in multiple areas to determine the overall degree of disability experienced by an adult rehabilitation patient. A 7 point scale is used to examine 18 areas, which include self-care, transfers, locomotion, communication, etc. Commonly used to examine changes in disability status that occur over time.
Functional Status Index
developed as a comprehensive ADL assessment for adults living in the community. 18 items include: gross mobility, social/role activities, hand activities and home chores. Scores are generated in 3 areas: dependence, difficulty, and pain.
Katz Index
The Katz index of ADLs uses nominal scale index to ID self-care problems and the level of assistance required within six areas: bathing, dressing, toileting, transfers, continence and feeding.
CVA Gait
hemiplegia/hemiparesis. Gait deviations are secondary to weakness which include foot drop and decreased stability at the ankle, knee and hip.
Parkinson's Gait
decrease in stride length and velocity. As the disease progresses, pt appears to be catching up with their COG as step length becomes smaller, termed festination. Festination places the patient at high risk for falls.
Post-polio gait
asymmetrical gait secondary to weakness, fatigue and pain.
MS Gait
impaired trunk control and balance. There is often circumduction to assist with foot clearance and ataxia d/t weakness and tonal influence.
Construct ability
copying drawn figures of varying size and shape.
Abstract ability
commonly tested using two specific methods. First is by asking a patient to describe how two items such as a cat and mouse are similar. The other method is by asking a patient to interpret the meaning of a proverb such as "rolling stone gathers no moss." Patients with difficulty in abstract thinking may provide answers that tend to be literal or concrete.
Graphesthesia
ability to recognize symbols, letters or numbers traced on the skin. Patients with language and speech disorder secondary to stroke can identify the correct figure by pointing at an image located in a table instead of through verbal identification.
EMG
asses the health of a muscle and the nerves controlling the muscle.
A normally innervated muscle is electrically silent at rest.
EMG - Spontaneous fibrillation means what
Spontaneous fibrillation potentials, like fibrillations and positive sharp waves, are seen in an acutely denervated muscle. Fibrillation and positive sharp waves are the result of spontaneous discharge of a single muscle fiber.
EMG - polyphasic motor units of low amplitude and short duration are evidence of
reinnervation
Neurapraxia
class 1 peripheral nerve injury with a local compression or blockage. EMG typically reveals no spontaneous activity.
Occasional motor unit potentials occurring during minimal effort muscle contractions two or three weeks after injury
suggest neurapraxia (a temporary failure of nerve conduction in the absence of structural nerve changes due to blunt injury, compress, or ischemia)
Transferring objects from one hand to the other
8-9 monts
Pincer Grasp
11 months
Stacking 2 blocks
12-15 months
Stacking 6 blocks
16-24 months
Holding a cup by the handle while drinking
12 months
Levodopa - used for, side effects
(Sinemet)
Used for Parkinson's
Dyskinesias (involuntary movement) care caused by an adverse effect of prolonged use of dopamine.
Other side effects include GI disturbances (nausea, vomiting), mental disturbances.
Analgesia
complete loss of pain sensibility
Anesthesia
more global term referring to loss of sensation
Open Skills
movement skills that can be performed in a variable, changing environment.
Externally placed skills
must comply with timing demands from the environment (e.g. walking through the revolving door)
Closed motor skills
movement skills that are performed in a stable, nonchanging environment.
Serial skills
movements that combine a series of discrete elements elements, with a specific order of elements.
Continuous Skills
movement skills that appear to have no recognizable beginning or inherent beginning and end.
Ideomotor apraxia
patient cannot perform a task upon command but can do the task when on his/her own.
Ideotional Apraxia
patient cannot perform the task at all.
Alternating isometrics
designed to facilitate isometric holding first in agonists acting on one side of the joint, followed by holding the antagonist muscle groups. Used when there is instability in weight bearing, poor static postural control, and/or weakness.
Approximation
is a therapeutic exercise technique designed to facilitate contraction and stability through joint compression. The compression force is most often applied to joints through gravity acting on body weight, manual contacts or weight belts.
Rhythmic initiation
begins with voluntary relaxation followed by passive movement through increments in range. This is followed by active-assisted movements progressing to resisted. The technique is indicated when there is a need to relax, hypertonicity, inability to initiate movement, motor learning deficits and communication deficits.
Timing for emphasis
uses max resistance to elicit a sequence of contractions from major muscle components of a pattern of motion. This technique allows overflow to occur from strong to weak muscles. The technique is indicated when there is weakness and/or incoordination and is commonly used in conjunction with repeated contractions.
CVA - Homonymous Hemianposia initial treatment
Best initial strategy to assist the patient in compensation for this deficit is to teach the patient to turn to the affected side. This is so the patient can be made aware of the deficit and instructed to turn the head to the affected side.
Ankle strategy
first to be elicited by a small range and small velocity perturbation when the feet are on the ground.
Suspensory strategy
used to lower the COG during standing or ambulation in order to better control the COG. Examples include knee flexion, crouching or squatting. This strategy is often used when both mobility and stability are required during a task (i.e. surfing)
Stepping strategy
is elicited through unexpected challenges or perturbations during static standing or when the perturbation produces a movement that displaces the COG beyond the BOS.
Deep sensory receptors
are sensory receptors that are located in the muscles, tendons and joints. Muscle and joint receptors are both classified as deep sensory receptors include Golgi tendon organs, pacinian corpuscles, muscle spindle, ruffini endings, free nerve endings and joint receptors. They evaluate position sense, proprioception, muscle tone and movement.
Mechanoreceptors
are sensory receptors responsible for touch, pressure, vibration, and discriminative touch.
Nociceptors
specialized peripheral free nerve endings that respond to noxious stimuli and result in the perception of pain.
Aversive Conditioning
reduces the appeal of a behavior by associating the behavior with a physical or psychological discomfort.
Extinction
withholding of reinforcement for a previously reinforced behavior which decreases the future probability of that behavior.
Operant Conditioning
learning that takes place when the learner recognizes the connection between the behavior and its consequence
Rational Emotive Imagery
form of intense mental practice for learning new emotional and physical habits. Focuses on uncovering irrational beliefs which may lead to unhealthy negative emotions and replacing them with more productive rational alternatives.
Gray Matter
Consists of unmyelinated neurons and contains capillaries, glial cells, cell bodies and dendrites
White Matter
Consists of myelinated axons and contains nerve fibers without dendrites
Sympathetic System - ANS
Prepares the body for emergency responses, norepinephrine neurotransmitter, STIMULATING response
Parasympathetic System - ANS
Conserving and restoring energy, acteylcholine neurotransmitter, generally an inhibitory response
Somatic Nervous System
-peripheral nerve fibers sends sensory information to the CNS
-motor fibers send information to the muscles
-somatic motor neurons travel DIRECTLY to muscle without intervening synapses, controls voluntary movement
-ALL FIVE SENSES INFLUENCED BY SOMATIC
Limbic System
-involved in control and expression of mood, emotion, memory, olfaction, appetite, responses to food
-lesions to the limbic system can be result in aggression, extreme fearfulness, altered sexual behavior, change in motivaiton
Brainstem
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
Frontal Lobe Functions
Complex thinking, emotion, voluntary movement, intellect
Broca's area: speech and concentration
Frontal Lobe Impairment
Broca's aphasia, contralateral weakness, personality changes, impaired concentration, personality changes
Parietal Lobe function
sensation, temperature, vibration, touch, interprets language and words, spatial and visual perception
Temporal Lobe Function
listening, smelling, interpret human emotions
Wernicke's area: ability to understand and produce speech, verbal and general memory
Temporal Lobe impairment
learning deficits, Wernike's aphasia, difficulty with facial recognition, difficulty with memory
Occipital Function
Visual- colors, shapes, light
Hippocampus
responsible for forming and storing new memories. Learning language.
Basal Ganglia
Voluntary movement, regulation of autonomic movement, posture, muscle tone, control of motor responses
Amygdala
emotional and social processing, involved in fear and pleasure responses
Thalamus
main processing station for information that goes to cerebral cortex
Hypothaalmus
Responsible for thirst, hunger, sex drive, temperature, sleeping
Subthalamus
regulating movement produced by skeletal muscles
Epithalamus
circadian rhytms
Cerebellum
balance
Pons
regulation of respiration rate, associated with orientation of the head in relation to visual and auditory cues - CN 5-8
Medulla oblongata
Influenced autonomic nervous activity and the regulation of respiration and HR. Reflex centers for vomiting, sneezing, and coughing.
ACA - CVA issues
Bilateral occlusion will produce paraplegia. Also will find incontinence, aphasia, FRONTAL LOBE symtpoms such as personality changes, potential akinetic mutism
MCA CVA issues
MOST COMMON SITE OF CVA, Bilateral occlusion will produce contraleral hemiplegia and sensory impairment. Dominant hemisphere includes global, Wernicke's and Broca's aphasia.
PCA CVA issues
Bilateral occlusion will produce thalamic pain syndrome and coritcal blindness. Thalamic pain presents with abnormal sensation of pain, touch, temperature, proprioception.
Vertebral Basilar Artery
Loss of conscioussness, hemiplegia or tetraplegia, locked in snydrome, comatose or vegeative statem dysphagia, dyssarthriat
Meninges
3 layers of connective tissue covering the brain and spinal cord. DAP - dura, arachnoid and pia from outter most to inner most.
Meningitis
Inflammation of meninges of the brain and spinal cord. Acute meningitis is a medical emergency. S/S include fever, vomiting, headache, stiff/painful neck, Brudzinski's skin (flexion or neck facilitates flexion of the hips and knees), Kernig's sign (pain with hip flexion combined with knee extension), light sensitivity
Gold standard for meningitis diagnosis
lumbar puncture
Ventricular System
designed to protect and nourish the brain, has CSF in it.
Blood Brain Barrier
responsible for exchanging nutrients with the CNS and vascular system
Hydrocephalus
Increase of CSF within the ventricles of the brain.
Associated conditions with hydrocephalus
spina bifida, choroid plexus neoplasm, meningitis, CP, tumor, encephalocele.
S/S of hydrocephalus
enlarged head, headache, change in vision, seizures, sun setting sign or downward deviation of eyes, incontinence
Spinothalamic Tract (anterior) - ascending
sensory tract for light touch and pressure