Experiment 3: Analysis of Proteins
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
DENATURED
any change that alters the unique three-dimensional configuration of protein molecules without causing a concomitant cleavage of peptide bonds.
PROTEINS
one of the major constituents of living cells.
Macromolecules
that contain amino acids (as building blocks joined together by peptide bonds).
Functions of Proteins
Denatured proteins aggregate and become visible as a precipitate, catalyze biochemical reactions, regulate the activity of various organs in the body, counteract the adverse effects of antigens, transport molecular oxygen, and serve as structural materials of the muscle, skin, and hair.
Denaturation
Collectively refers to reactions such as salting out and heat coagulation due to the colloidal nature of proteins.
Color Tests
Different color tests are used to identify the amino acid or proteins due to the presence of specific chemical groups in the protein molecule.
Denaturation Reaction
Occurs due to the presence of specific chemical reagents such as strong mineral acid, salt of heavy metal, or alkaloidal reagents.
a-helix
The structural pattern of polypeptides at the secondary level maintained by weak hydrogen bonds between amino acids.
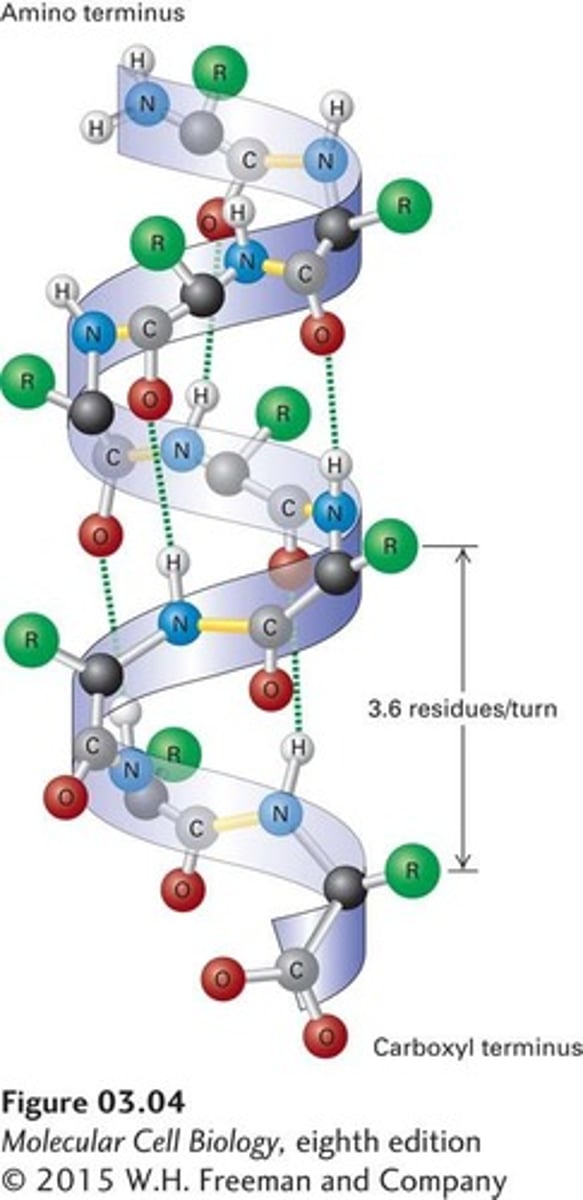
Tertiary Structure Stabilization
The linkages responsible for the tertiary structure of protein are a function of the nature of amino acid side chains within the molecule.
Bonds Stabilizing Tertiary Structure
Include salt linkages, hydrogen bonds, disulfide linkages, and hydrophobic interactions.
Denatured Proteins
Proteins that have undergone disruption of secondary and tertiary structure due to various physical and chemical methods.
BIURET TEST
A protein detection test that gives a characteristic purple color, positive for all compounds that contain two or more peptide bonds.
NINHYDRIN TEST
A test to detect and identify the presence of amino acids and amines, forming a blue violet colored complex when heated with amino acids.
XANTHROPROTEIC TEST
A test positive for those amino acids that contain a benzene ring or aromatic ring, involving nitration of the amino benzene ring with concentrated nitric acid.
Positive for Biuret Test
All compounds that contain two or more peptide bonds.
Positive Except for Biuret Test
Threonine and serine.
Positive for Ninhydrin Test
All proteins or protein derivatives, as well as ammonia and amines.
Positive for Xanthoproteic Test
Amino acids that contain a benzene ring or aromatic ring.
Color for Ninhydrin Test
Blue violet for most amino acids, yellow for proline and hydroxyproline.
Color for Xanthoproteic Test
Yellow orange derivatives of nitrobenzene.
Coordination in Biuret Test
Due to the coordination of complex formed by cupric ions (in the reagent) and the amino groups.
A-amino group
Responsible for the positive results in the Ninhydrin Test.
Chemical Reagents for Denaturation
Strong mineral acid, salt of heavy metal, or alkaloidal reagents.
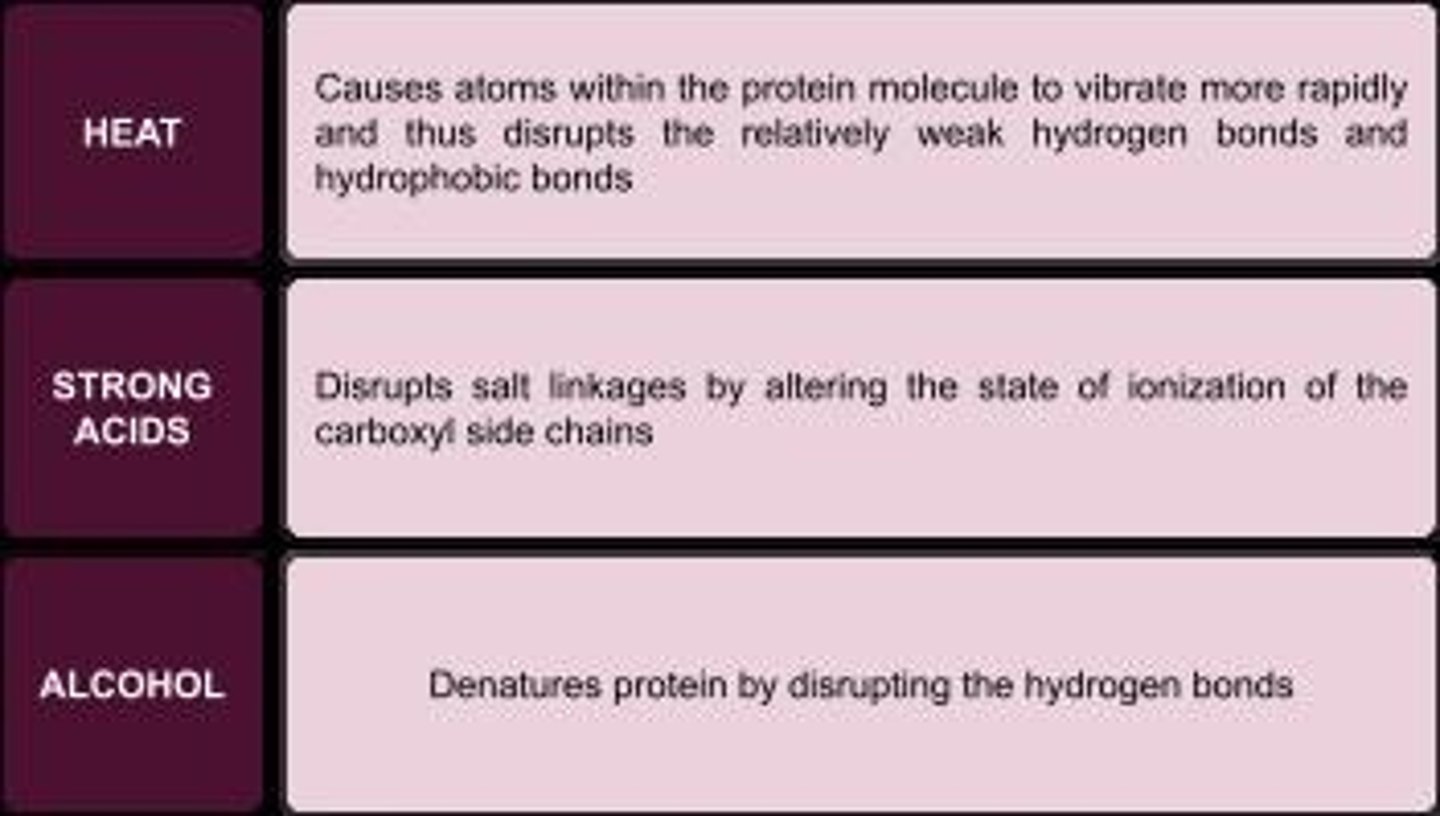
Heat Coagulation
Many proteins are coagulated by heat, strong acids, and alcohol.
HOPKIN'S COLE TEST
This test is due to the presence of the indole ring of the tryptophan.
Violet colored complex
Formed when glyoxylic acid condenses with indole derivatives in the presence of strong acids like sulfuric acid.
MILLON'S TEST
Test for the detection of tyrosine-containing proteins in a given sample.
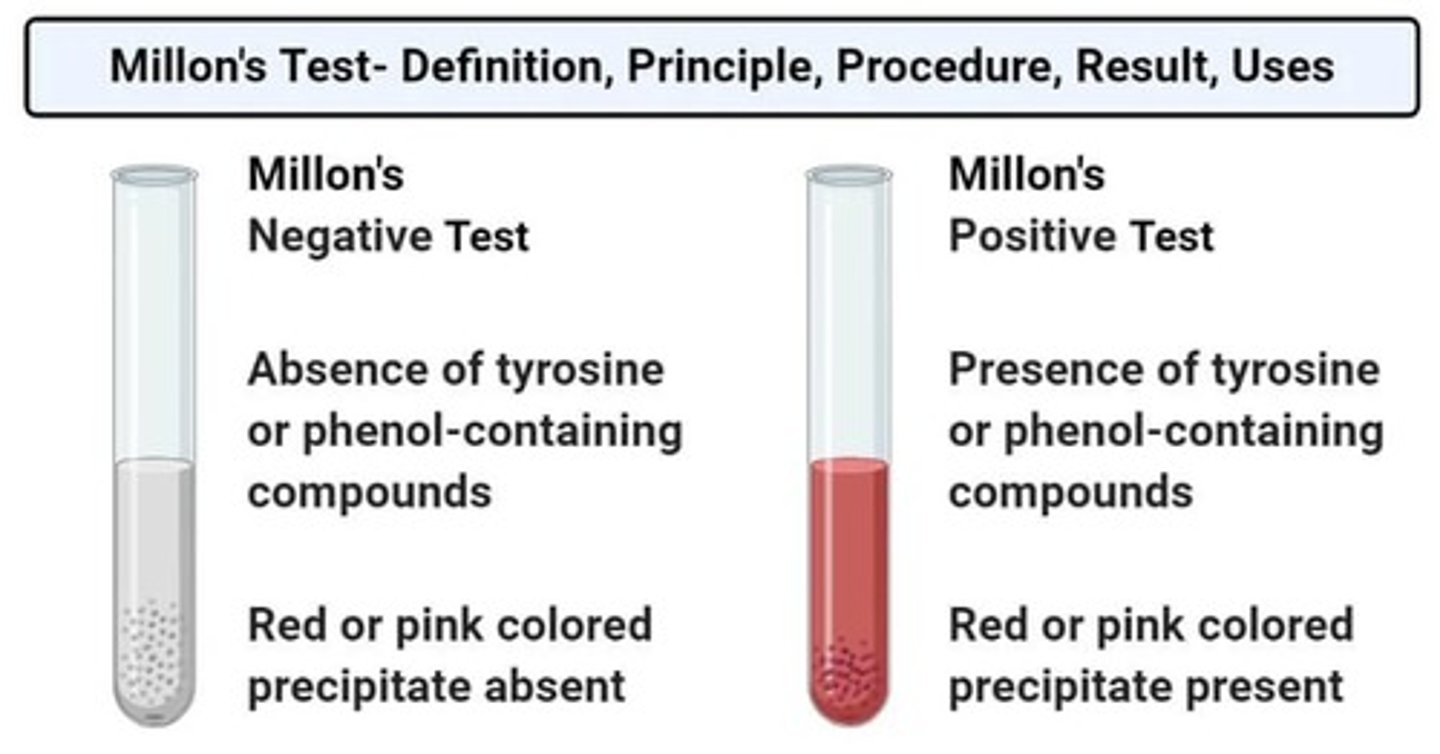
White precipitate
Produced in the MILLON'S TEST which becomes brick red upon prolonged heating.
Phenolic groups
These groups are easily nitrated by a solution of mercuric and mercurous nitrates and nitrites in concentrated nitric acid.
Mercury complex of nitrophenyl derivatives
The color produced in MILLON'S TEST is due to this complex.
SAKAGUCHI TEST
Test for arginine-containing proteins in a given sample.
Red to an orange colored complex
Formed when compounds containing guanidine or guanido group combine with a-naphthol and sodium hypobromite or hypochlorite.
LEAD ACETATE TEST
Detect the presence of sulfur-containing amino acids, particularly cysteine and cystine, in proteins.
Brownish-black precipitate of lead sulfide, Pbs
Formed when inorganic sulphide reacts with lead acetate in LEAD ACETATE TEST.
BIURET TEST
Test that indicates the presence of proteins.
NINHYDRIN TEST
Test that detects free amino groups in proteins.
XANTHROPROTEIC TEST
Test that detects aromatic amino acids by nitration.
Albumin
Contains proteins and aromatic amino acids like tyrosine and tryptophan.
Gelatin
Lacks or has very low levels of aromatic amino acids.
Tyrosine
Has a phenol ring that is easily nitrated.
Phenylalanine
Benzene ring is less reactive than tyrosine; weak or no reaction.
Cysteine and cystine
Sulfur-containing amino acids detected by LEAD ACETATE TEST.
Urea
Has amino groups, but they are involved in a stable structure and do not react strongly with ninhydrin.
Phenol
Directly reacts with Millon's reagent.
Ammonium Water
Has ammonia/amines; result is blue rather than purple.
Trypthopan
Direct source of tryptophan; strong positive reaction in HOPKIN'S COLE TEST.
Biuret test
A test that detects proteins and produces a violet/purple color when proteins are present.
Ninhydrin test
A test that detects amino acids and produces a blue-violet color.
Xanthroproteic reaction
The nitration of aromatic amino acids like tyrosine.
Lead acetate test
A test that reacts with sulfhydryl groups (-SH) in albumin, forming lead sulfide (PbS), which is insoluble.
Mercuric chloride test
A test that reacts with thiol groups (-SH) of albumin, forming mercury salts that precipitate out of solution.
Silver nitrate test
A test that reacts with sulfide groups in albumin, forming silver sulfide (Ag₂S), which is a black precipitate.
Picric acid test
A test that precipitates albumin by forming complexes with the protein, resulting in a yellow precipitate.
Tannic acid test
A test that reacts with albumin to form an insoluble complex, resulting in a brown precipitate.
Sterilization by heat
A method that denatures proteins and disrupts hydrogen bonds, effective against microorganisms.
Disinfection by alcohol
A method that denatures proteins and disrupts hydrogen bonds, effective against microorganisms.
Heavy metal poisoning antidote
Egg white and milk are used as they bind to heavy metals (Chelation) and prevent toxicity.
Ethanol effect on albumin
Ethanol causes albumin to denature and coagulate by disrupting hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonds.
HCl effect on albumin
HCl denatures albumin by disrupting ionic and hydrogen bonds, causing it to coagulate.
Sulfur test colored precipitate
The formula of the colored precipitate obtained in the sulfur test or lead acetate test is PbS (lead sulfide).
Albumin + distilled water + Biuret reagent
Produces a violet/purple color indicating the presence of proteins.
Albumin + HCl
Results in a white precipitate due to denaturation of albumin.
Albumin + ethanol
Results in a white precipitate due to denaturation of albumin.
Gelatin + ethanol
Results in little or no visible change as gelatin is less structured and more heat-stable.
Albumin + picric acid
Results in a yellow precipitate indicating the presence of albumin.
Albumin + tannic acid
Results in a brown precipitate indicating the presence of albumin.
Albumin + lead acetate
Results in a white precipitate indicating the presence of lead sulfide (PbS).
Albumin + mercuric chloride
Results in a white precipitate indicating the formation of mercury salts.
Albumin + silver nitrate
Results in a white precipitate indicating the formation of silver sulfide (Ag₂S).