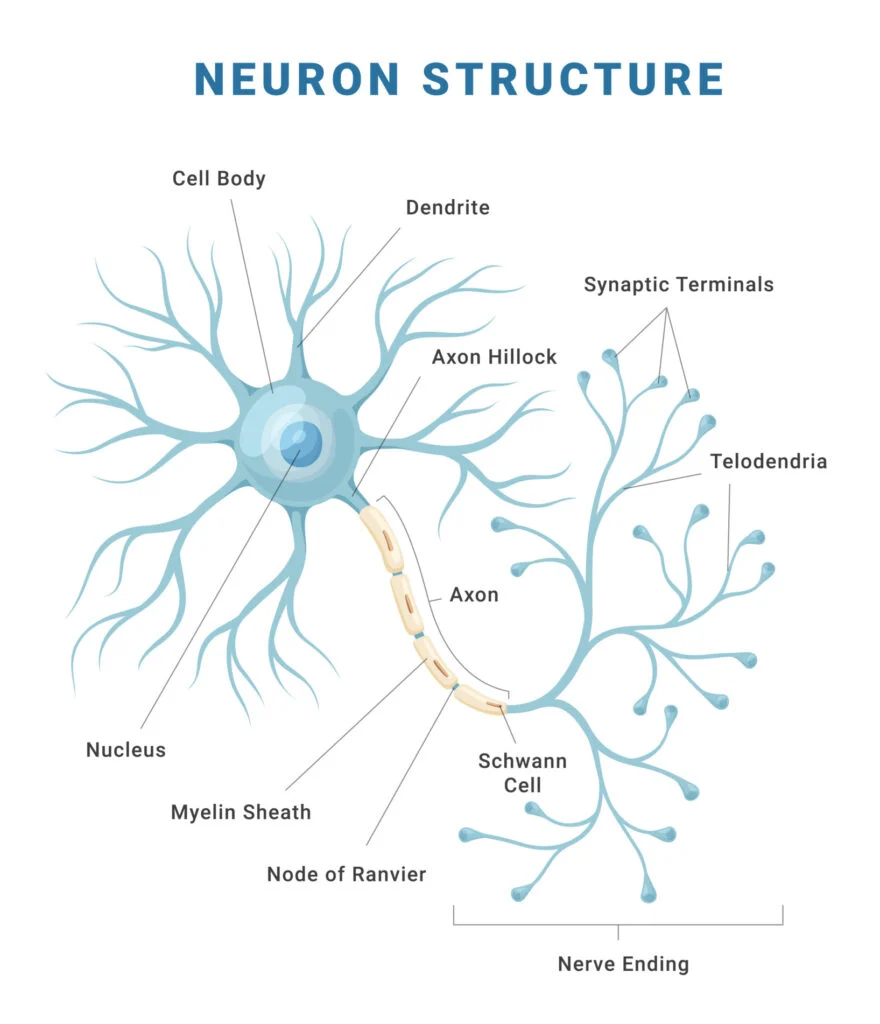
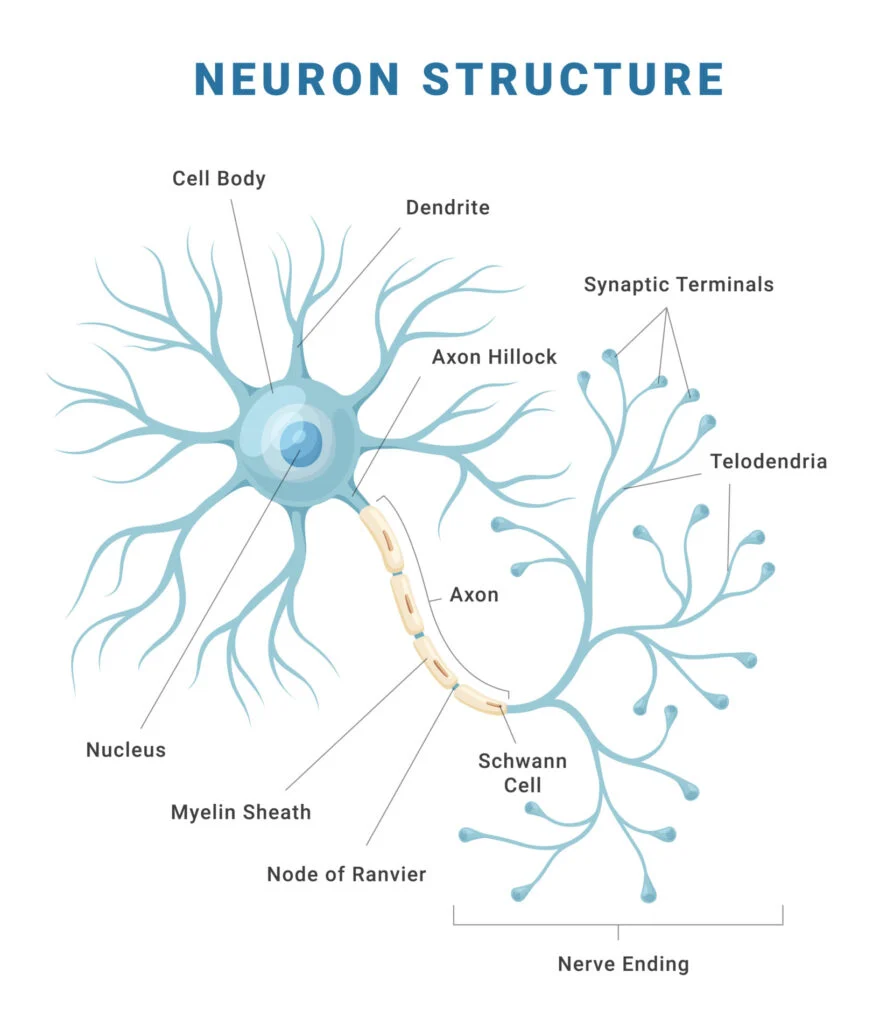
Parts of a Neuron
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
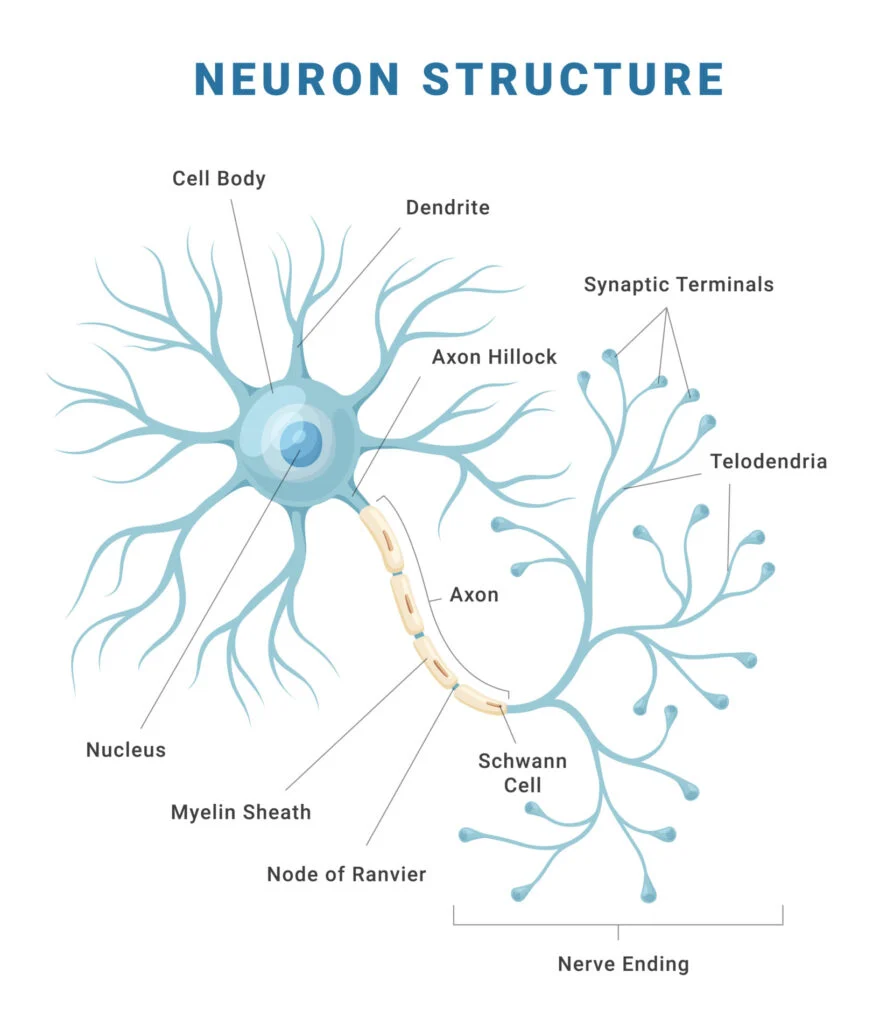
Dendrites
Receive information (either from RECEPTOR cells or other NERVE cells), conducting towards the cell BODY (about 200 dendrites/cell body)
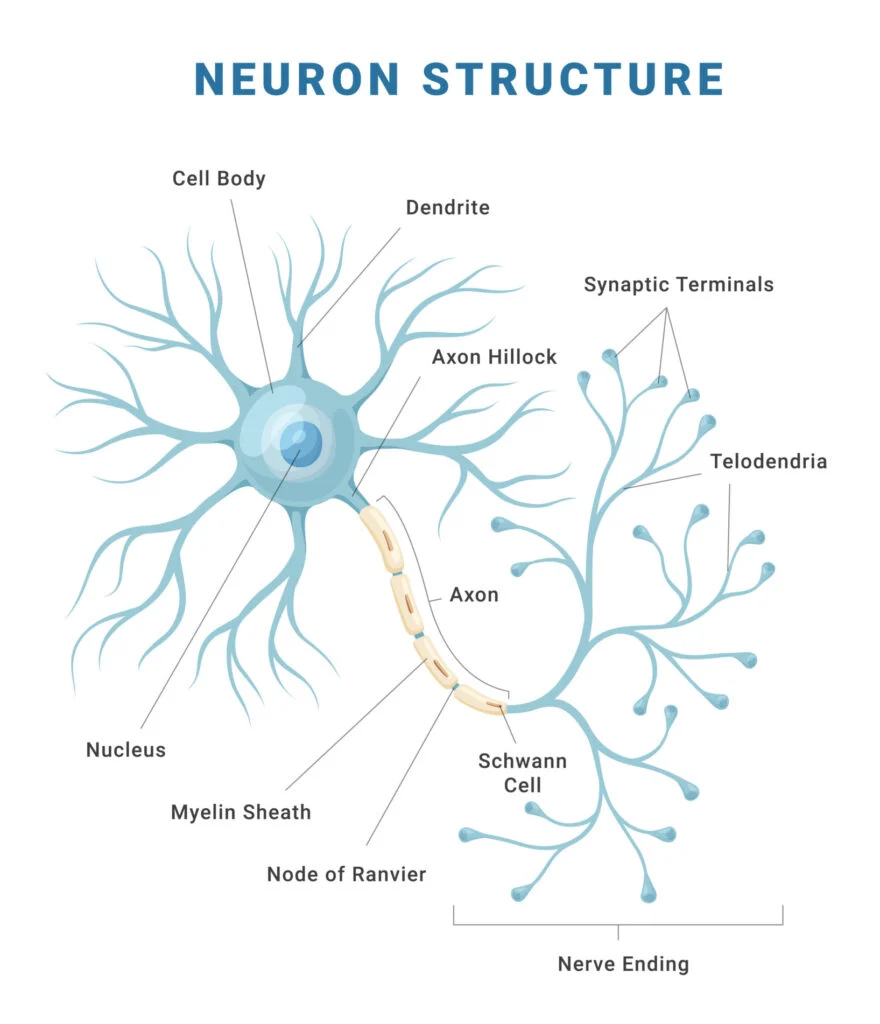
Cell body
Location of NUCLEUS, high metabolic rate (contains MITOCHONDRIA)
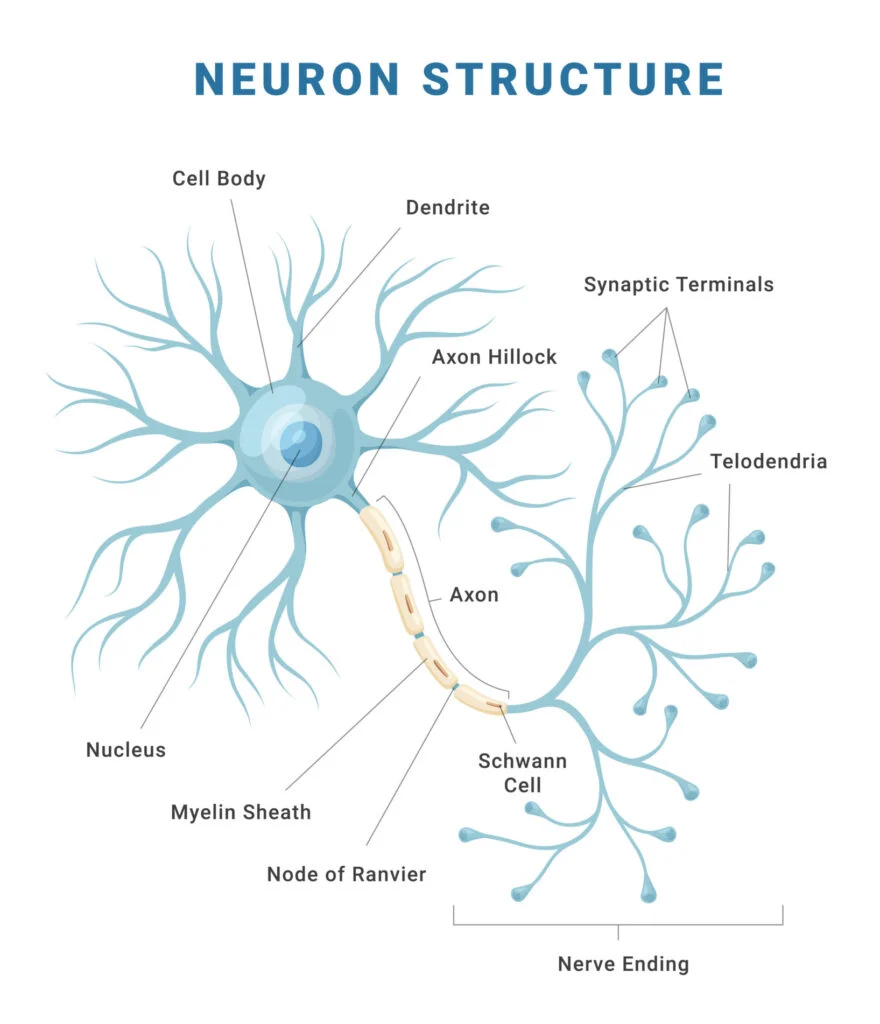
Axon
May be up to 1m long, very thin, conducts the IMPULSE towards other neurons or effectors, starts at AXON HILLOCK; the smaller the neuronal diameter, the FASTER the neuronal TRANSMISSION
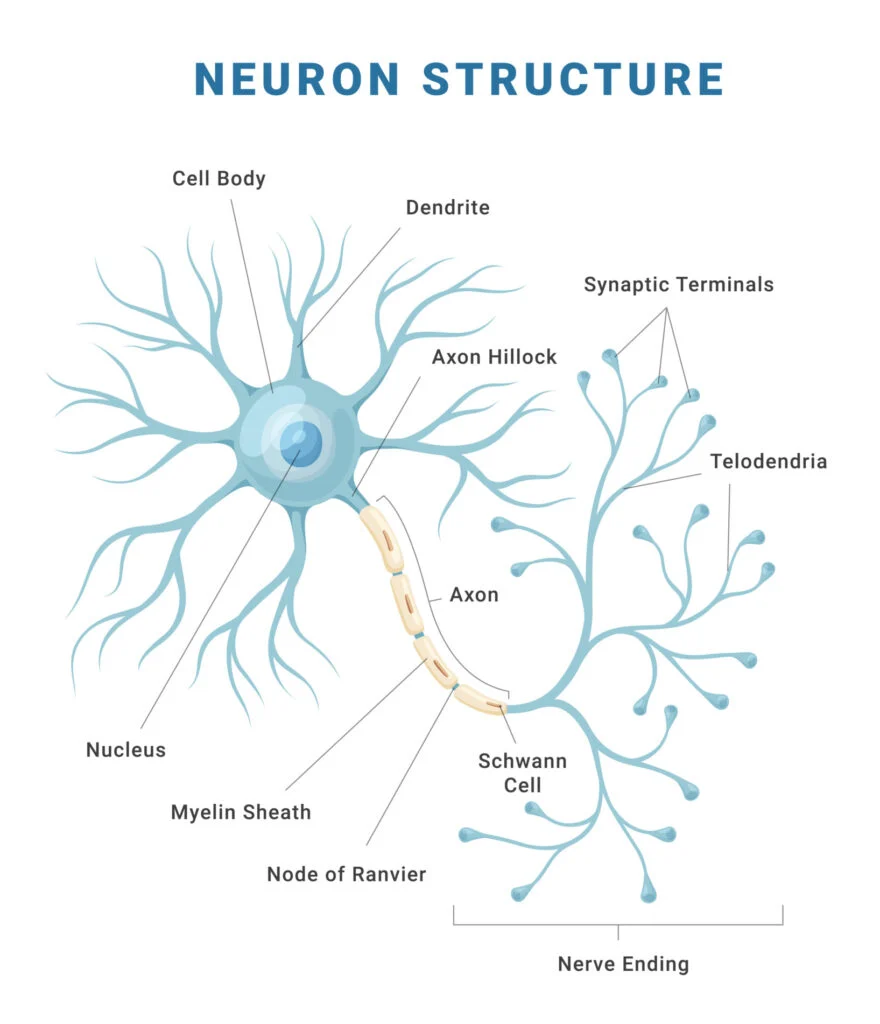
Myelin sheath
Fatty PROTEIN encasing many NEURONS, made by a SCHWANN CELL, acts as an INSULATOR (myelinated neurons are encased in myelin)
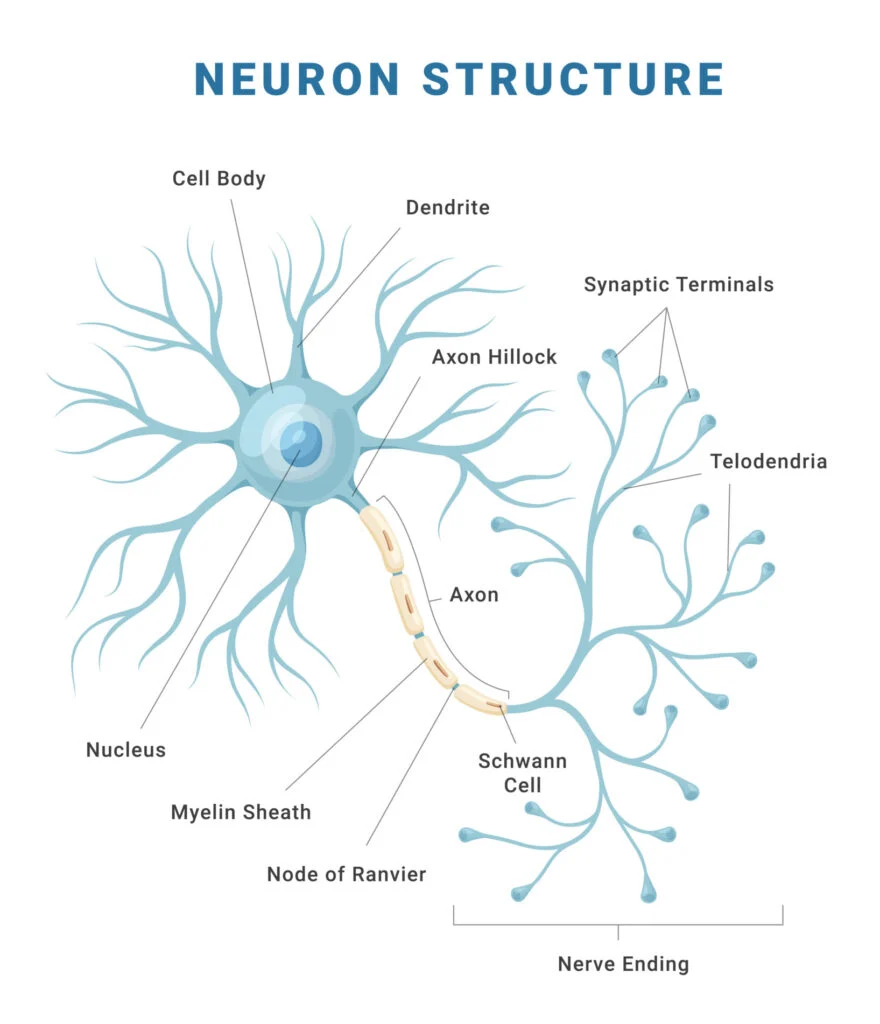
Nodes of Ranvier
The UNMYELINATED sections of a myelinated neuron, impulses “jump” between the nodes of Ranvier
Neurilemma
A thin layer encompassing neurons in the PERIPHERAL nervous system, promoting their regeneration
Schwann cell nucleus
Responsible for the myelin synthesis, type of GLIAL cell (supporting and nourishing cell found in the nervous system)
Myelin
lipid-based insulator surrounding AXONS. Insulates against ION flow speeding up neuronal transmission (about 200m/s for myelinated neurons, 1-5 m/s for non-myelinated neurons)
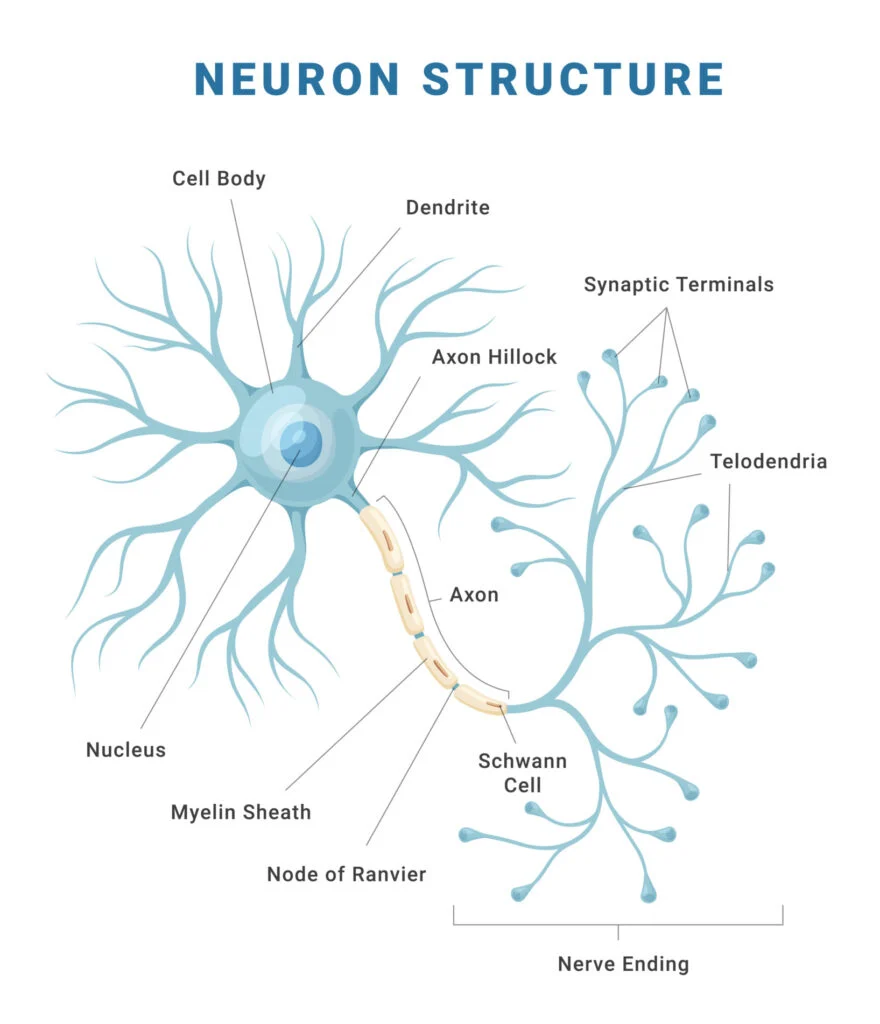
Terminal branches
Either at a SYNAPTIC BULB or end PLATE to muscle, contain NEUROTRANSMITTER