Lecture 1 - Infectious Diseases/Antimicrobial Stewardship
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
what is the definition of antibiotic
a substance created by a microorganism to inhibit or kill another microorganism
what is the definition of antibacterial
a substance that inhibits or kills bacteria (usually synthetic, more specific)
what are the 2 types of bacterial resistance
intrinsic resistance
acquired resistance
what is acquired resistance
transfer of resistant genes from other bacteria by transduction, transformation, or conjugation
what are the 4 mechanisms of bacterial resistance
decreased permeability
enzyme modification
target site changes
active efflux
what are ways bacteria can decrease the permeability of antibacterials
cell wall changes (e.g. vancomycin)
porin channel changes (e.g. imipenem)
biofilm production
what are ways bacteria modify enzymes to decrease the effectiveness of antibacterials
beta-lactamases (e.g., penicillin)
aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes
methylation (e.g. clarithromycin)
what are target site changes that can decrease the effectiveness of antibacterials
alteration of penicillin binding proteins
ribosomal modification (e.g. clindamycin)
what are ways bacteria actively efflux antimicrobials
tetracycline efflux
fluoroquinolone efflux
what are the consequences of antibacterial resistance
increased use of broad-spectrum antibacterials
increased use of IV antibacterials
increased hospitalization
increased costs of hospitalization
increased infection control
diminished quality of life
increased morbidity and mortality
what are issues with antibacterials in agriculture
level required to promote growth has increased 20-fold since 1950
high rates of resistance in intestinal flora of farm animals and farmers
molecular methods show resistant organisms in farm animals reach consumers in meat products
>90% of antibacterials given to animals excreted in urine/stool → excreted into soil, surface runoff, widely dispersed through fertilizer
what are ways to practice antimicrobials stewardship
use antibacterials only when necessary
do not use antibacterials for viral infections
use antibacterials for appropriate duration
ensure patient adherence
use antibacterials with the narrowest spectrum of activity possible
prevent the spread of infections - handwashing, cleaning services
prevent infections - vaccinate
what is a common myth about reducing antibacterial resistance (exam question)
stopping antibacterial treatment early results in bacterial resistance development - FALSE
longer durations are more likely to do this (selective pressure)
what are other ways to reduce antibacterial resistance
strict infection control procedures
antibacterial cycling?
regulatory policies
improved diagnostics
educate the public, healthcare professionals
reduce agricultural use of antibacterials
what are factors to consider when choosing antimicrobial therapy
disease is being treated? should it be treated with antibacterials?
suspected organisms? cultures to direct antibacterial choice? current susceptibility patters by site?
how ill is the patient? is the patient immunocompromised?
what are the advantages/disadvantages of the available choices of susceptible antibacterials? cost considerations?
route of administration? issues limiting route of administration (severity, site, NPO, etc)?
evidence? evidence based guidelines?
dose (renal/hepatic function)? duration of treatment? monitoring?
drug toxicity/alergies? pregnancy?
prevention?
what are site-specific factors for eye, brain, prostate
non-fenestrated capillaries - impede drug diffusion making antibacterial delivery difficult
need to consider PK of the antibacterial - may required direct injection
when are biofilms formed in humans
on foreign substances inserted or implanted into the body if they come in contact with bacterial organisms
e.g. IV catheters, urinary catheters, dialysis catheters, artificial joints, artificial heart valve
may form on some tissues resulting in infections that are difficult to treat e.g. lung tissues in cystic fibrosis
what are concerns with antibacterial resistance for biofilms
sessile bacteria within biofilm become resistant to antibacterial therapy
when might antibacterial combinations be needed
to broaden empiric coverage
for polymicrobial coverage
to prevent emergence of resistance (less commom, sometimes in TB)
synergy
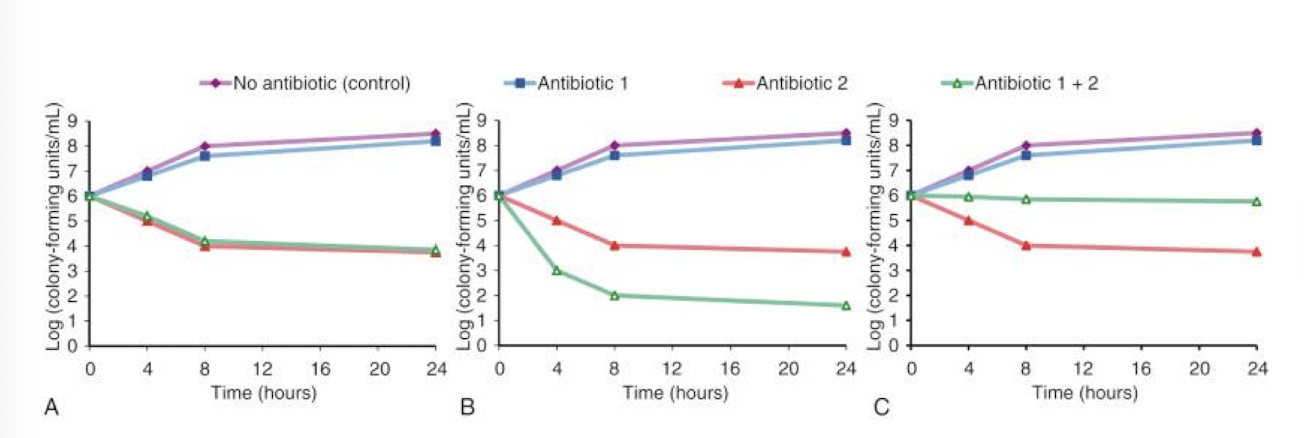
what is synergy
combination is superior to the sum of effects of both antibacterials given separately
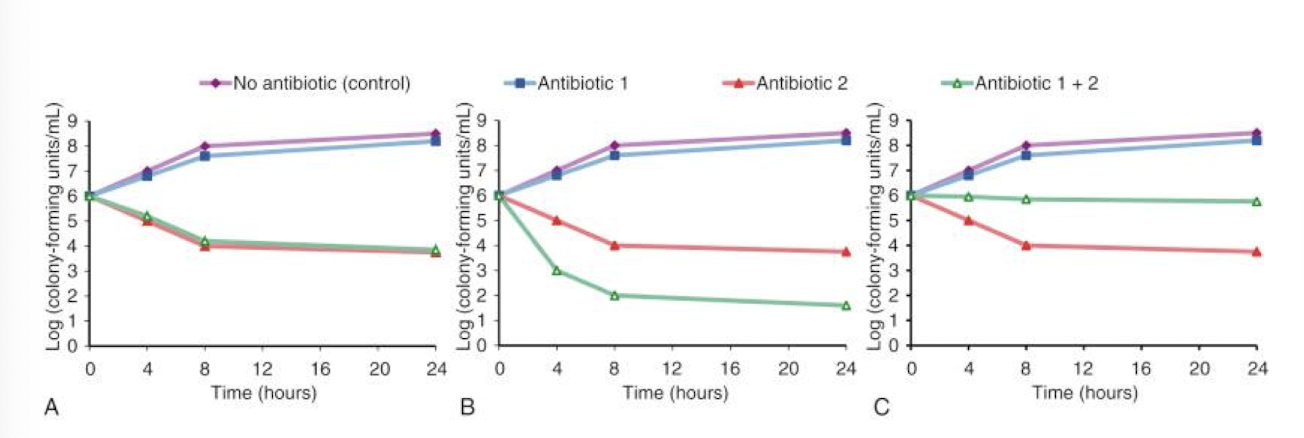
what is addition
combination is superior to either antibacterial given seperately but less that the sum of effects)
what is indifference
combining is equal to either antibacterial alone

what is antagonism
combination is inferior to either antibacterial alone
what are disadvantages of antibacterial combinations
antagonism - e.g. penicillin + tetracycline, gentamycin + chlormphenicol
cost
adverse effects
what are considerations for anticoagulants in antimicrobial therapy
antibacterial inhibits vitamin K synthesis in GI tract - risk of increased anticoagulant effect
monitor INR
what is the drug interaction of oral contraceptives with antimicrobial therapy
free estrogen is reabsorbed in GI by enterohepatic recycling
antibacterials may reduce bacteria in GI tract and interfere with enterohepatic recycling
some antibacterials cause increased metabolism of estrogens
some antibacterials cause diarrhea or vomiting that may decrease absorption