Terms list 7 and 8
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
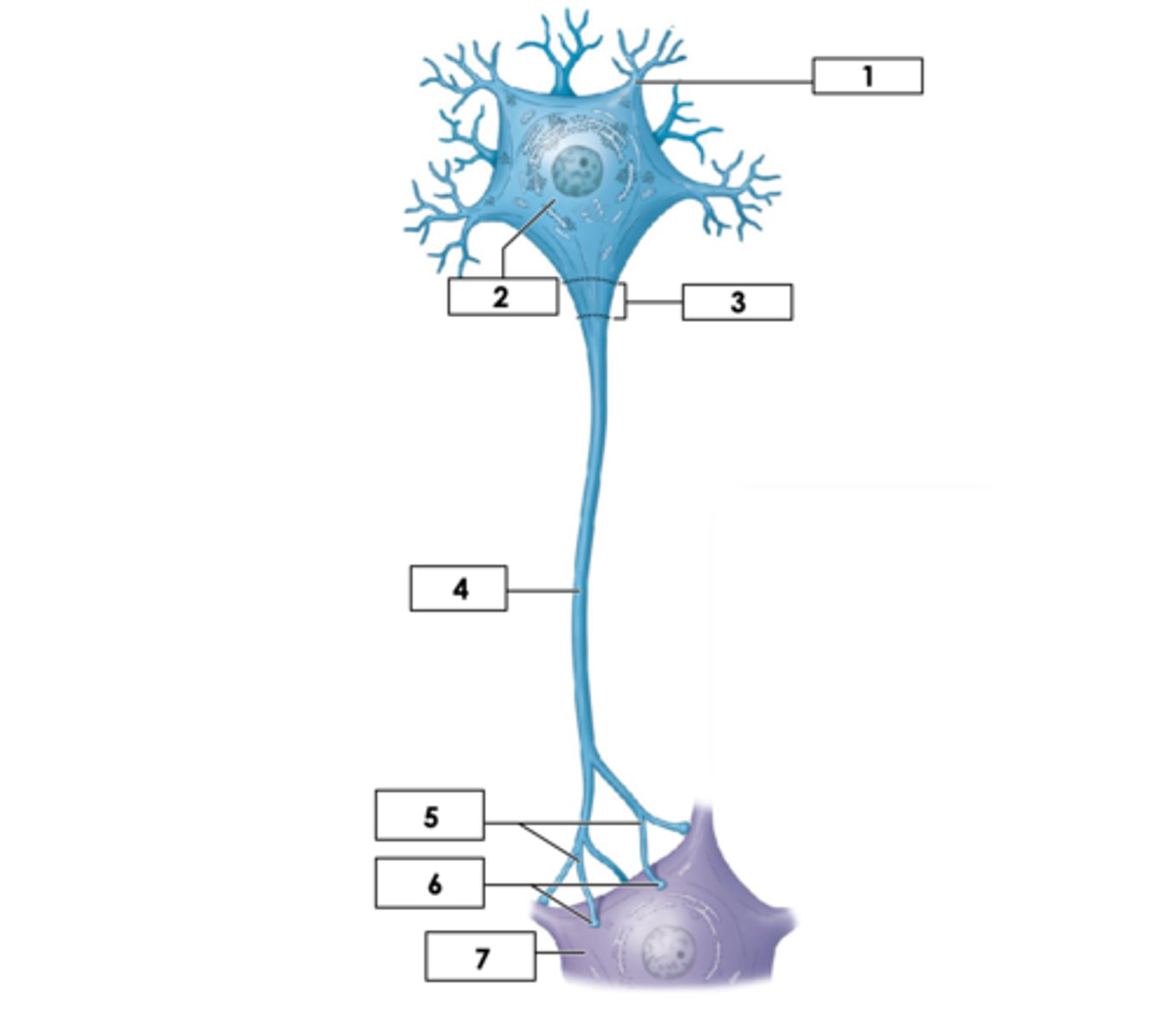
Cell body (soma)
2
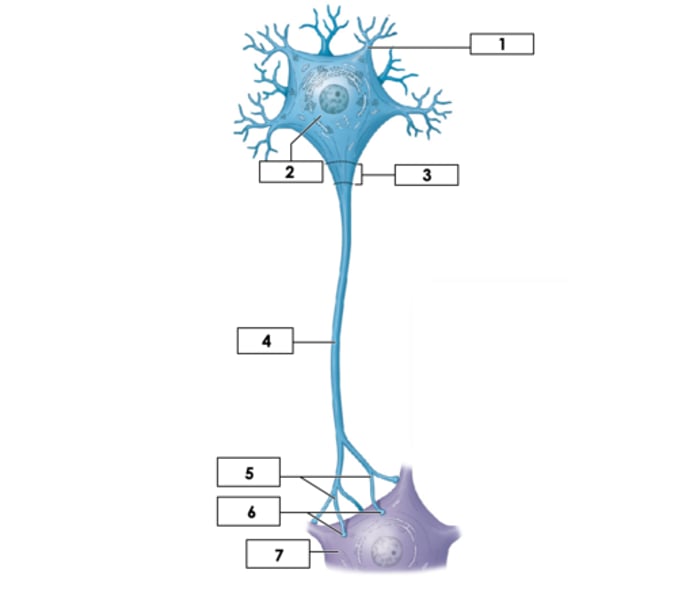
mitochondria of axon
Produces energy for the cell
Nissl bodies
Clusters of rough endoplasmic reticulum in neurons
Dendrites
1
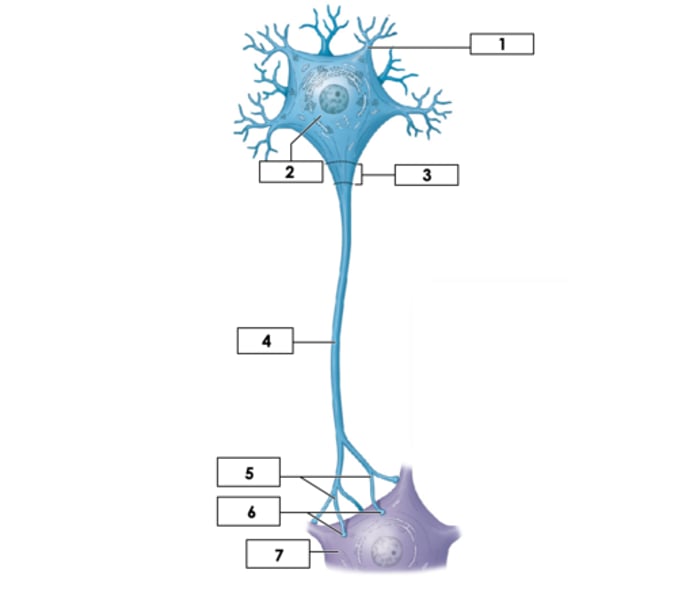
Axon: Unmyelinated
4
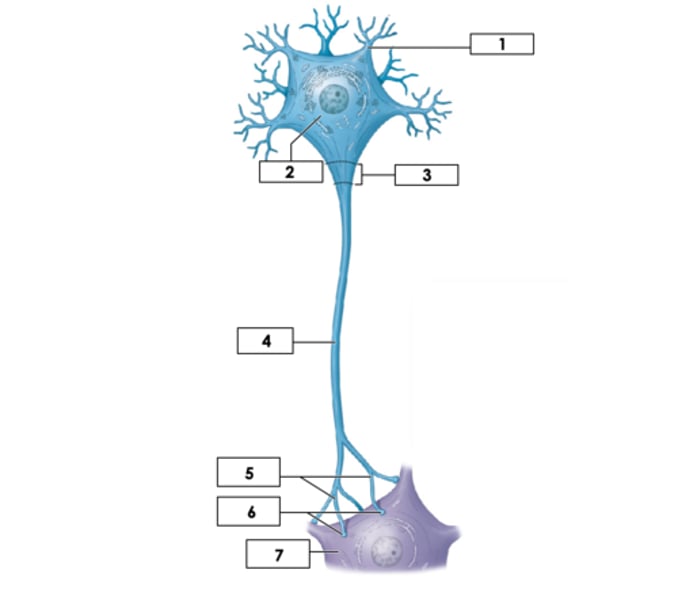
Axon Hillock
3
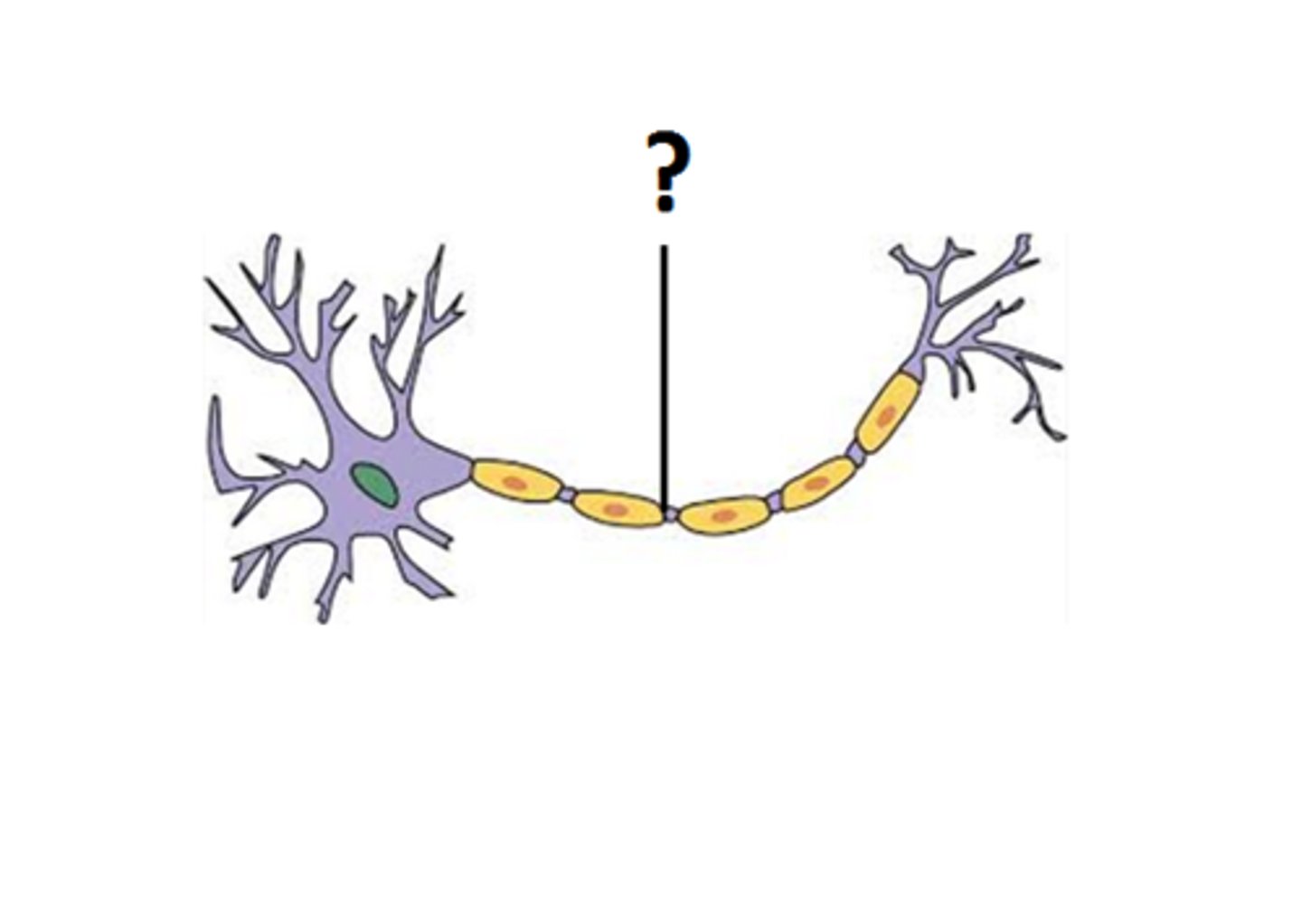
Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
Produce myelin in the central nervous system
Myelin sheath
Insulating layer around axons
Nodes of Ranvier
3
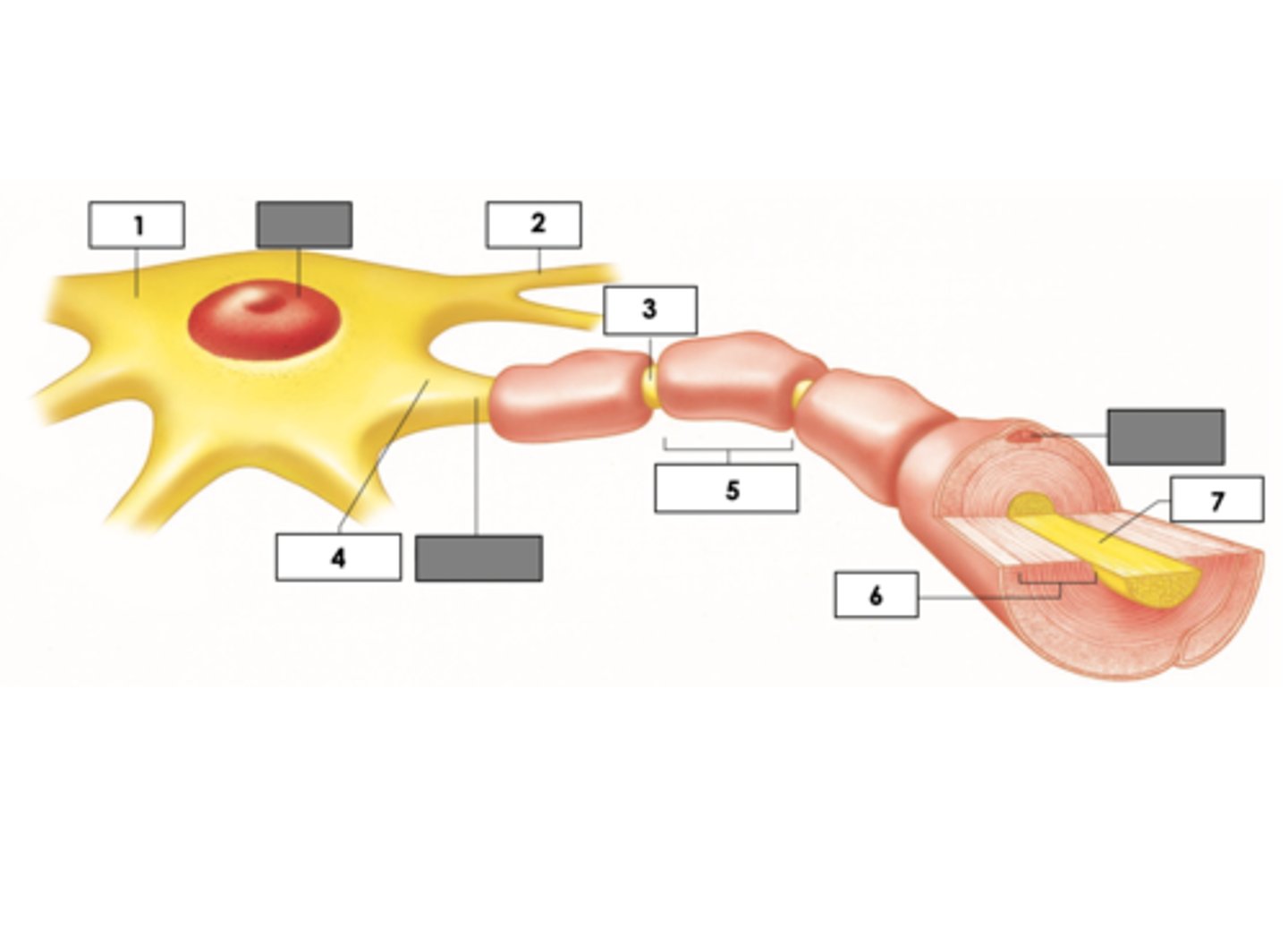
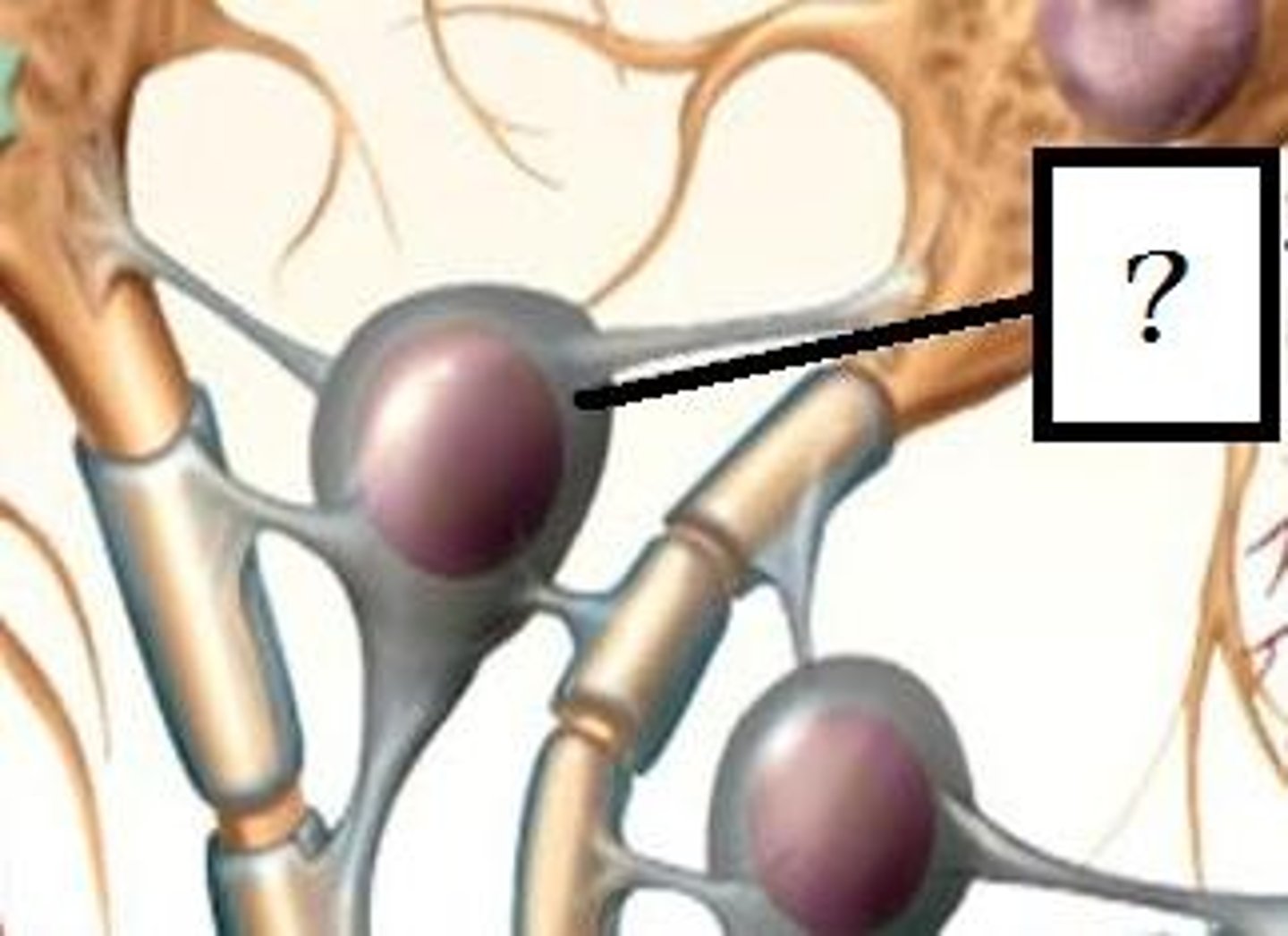
Schwann cells (PNS) = internode
5
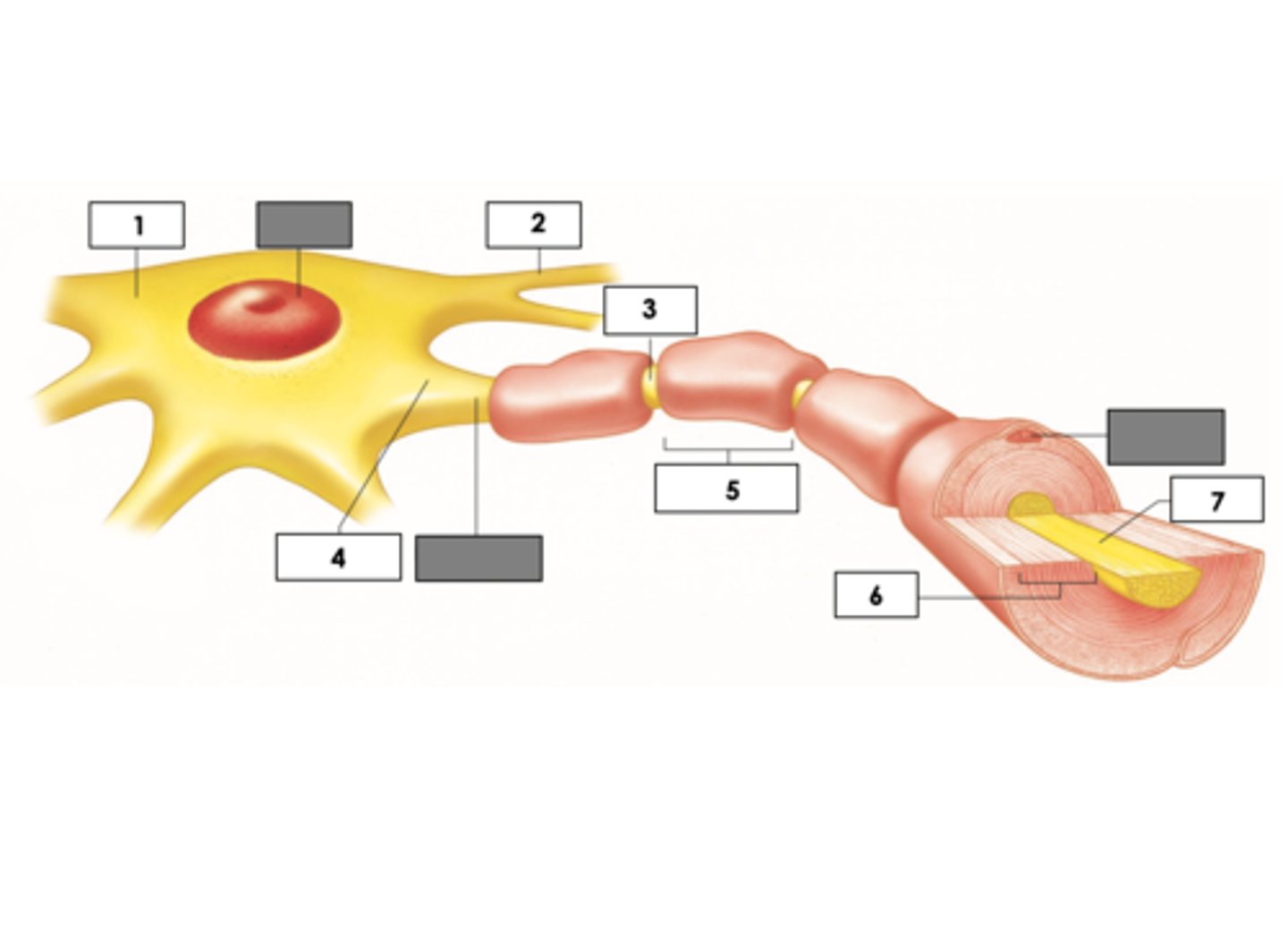
Telodendria
5
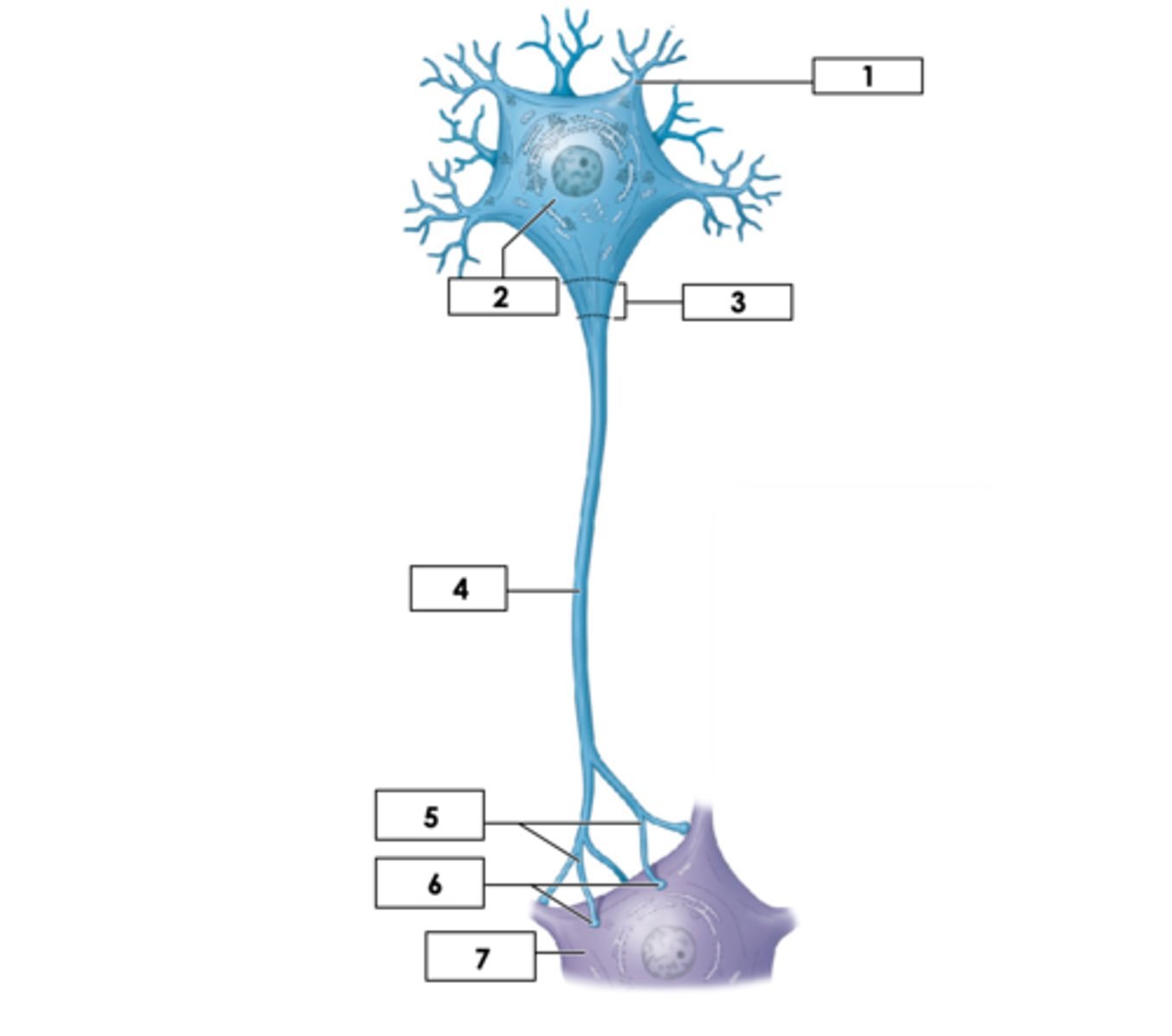
Synaptic knobs (ends of telodendria)
Enlarged structures that release neurotransmitters
Synapse
Junction between two neurons
Synaptic vesicles
3
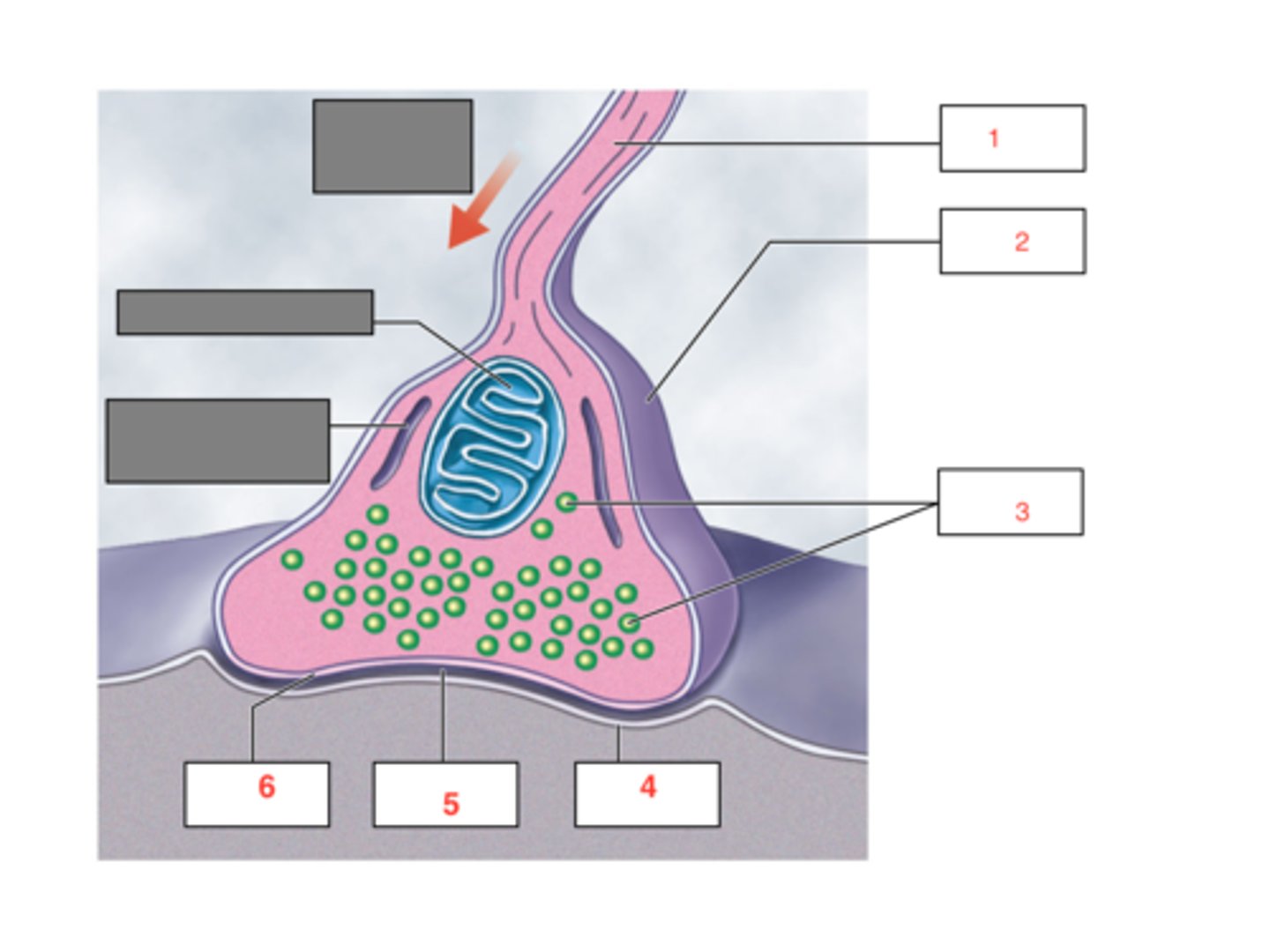
Neurotransmitter
Chemical messenger that transmits signals between neurons
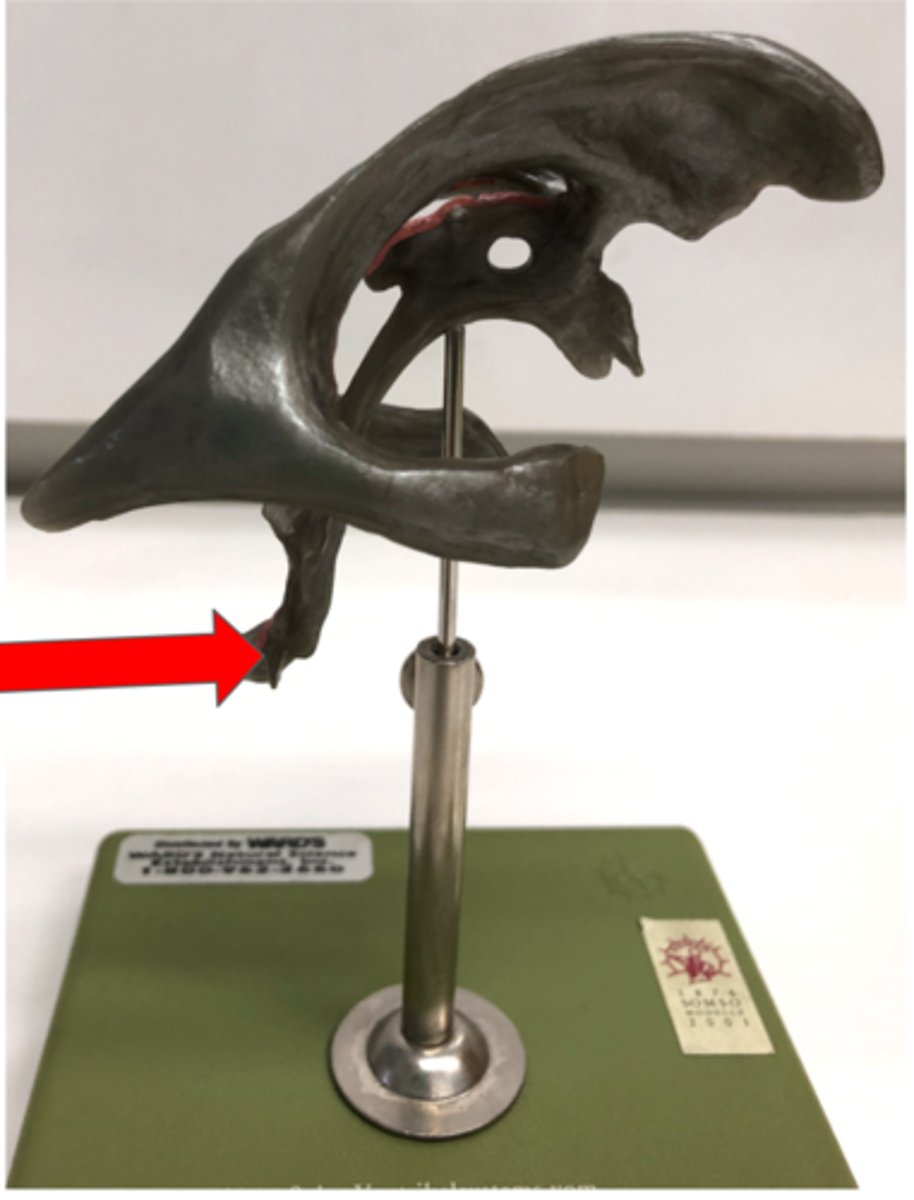
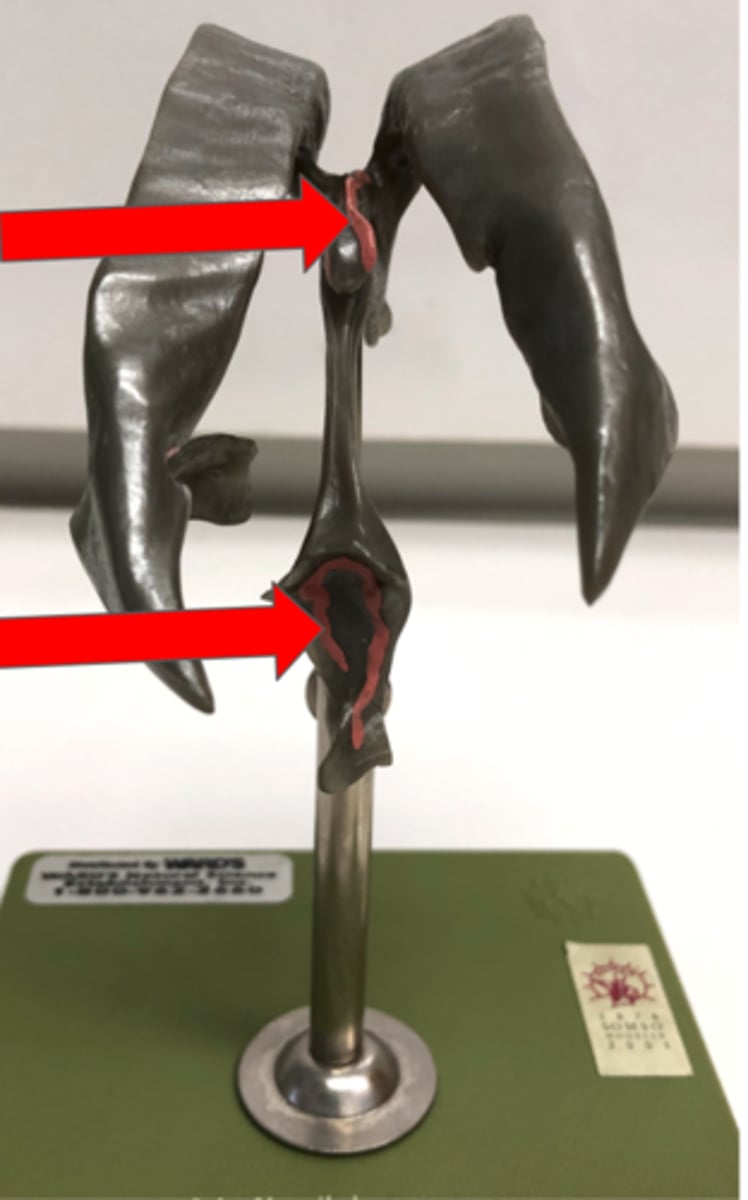
Spinal Nerve
Anterior (ventral) root
Contains motor neurons
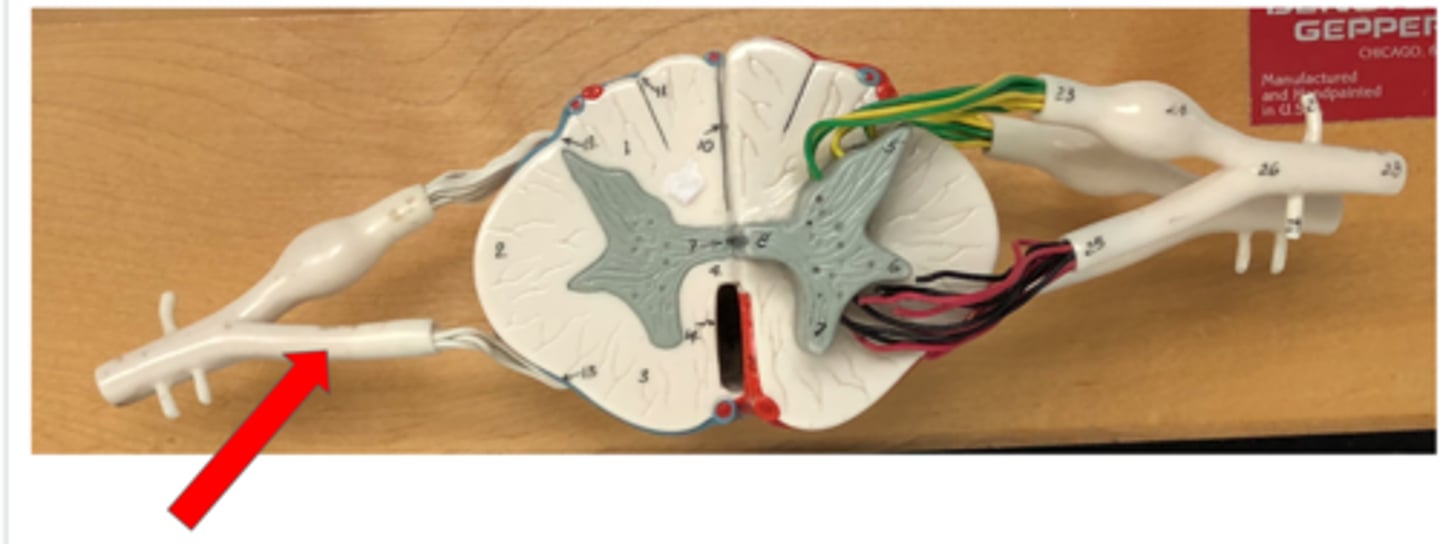
Posterior (dorsal) root
Contains sensory neurons
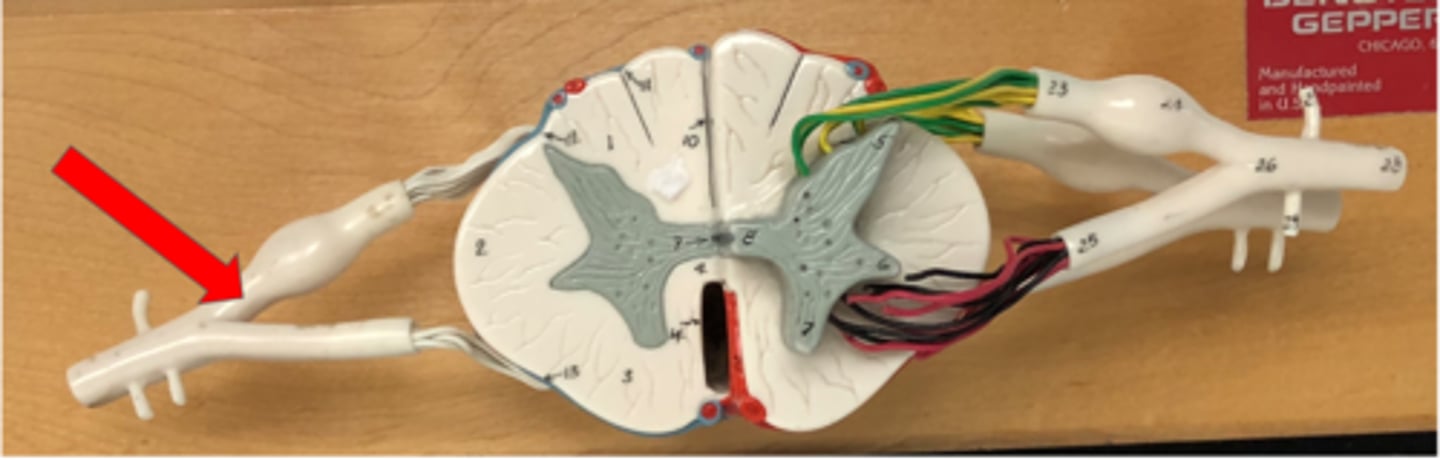
Posterior (dorsal) root ganglion
Contains cell bodies of sensory neurons
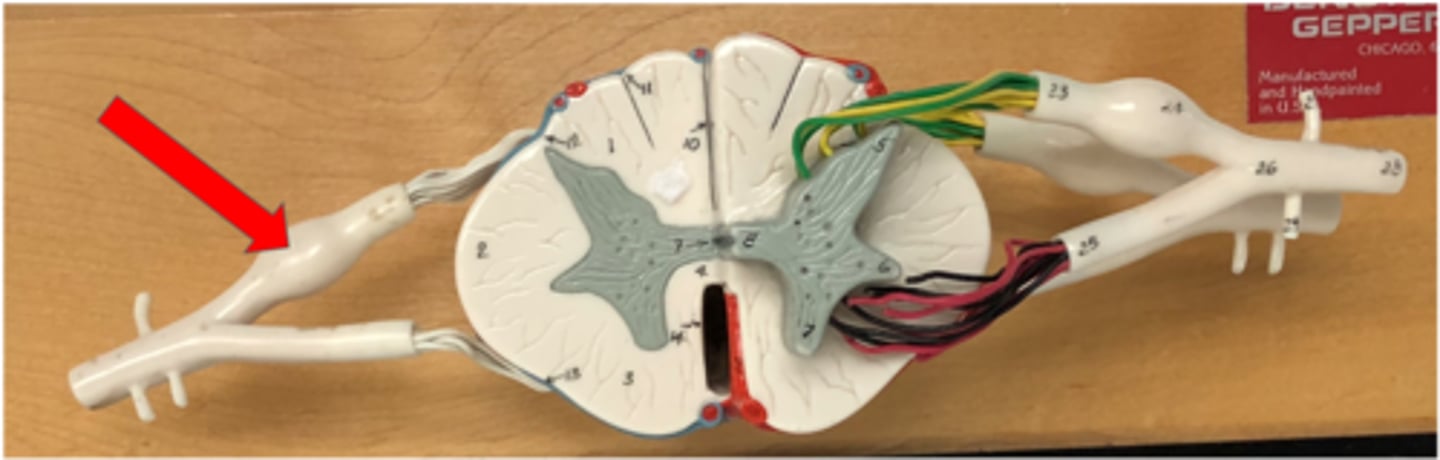
Anterior median fissure
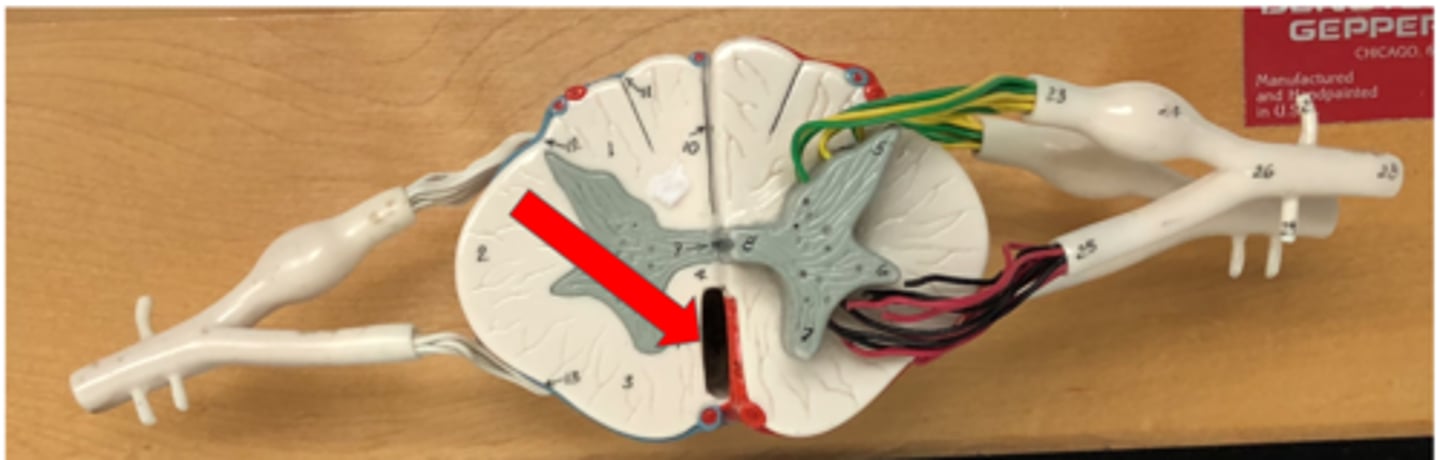
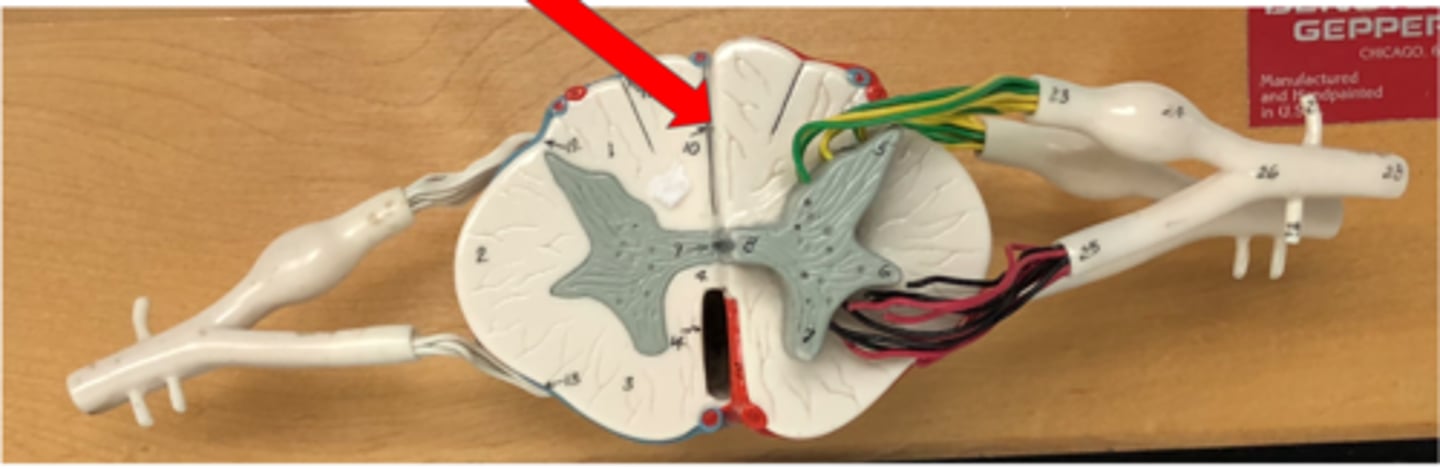
Posterior median sulcus
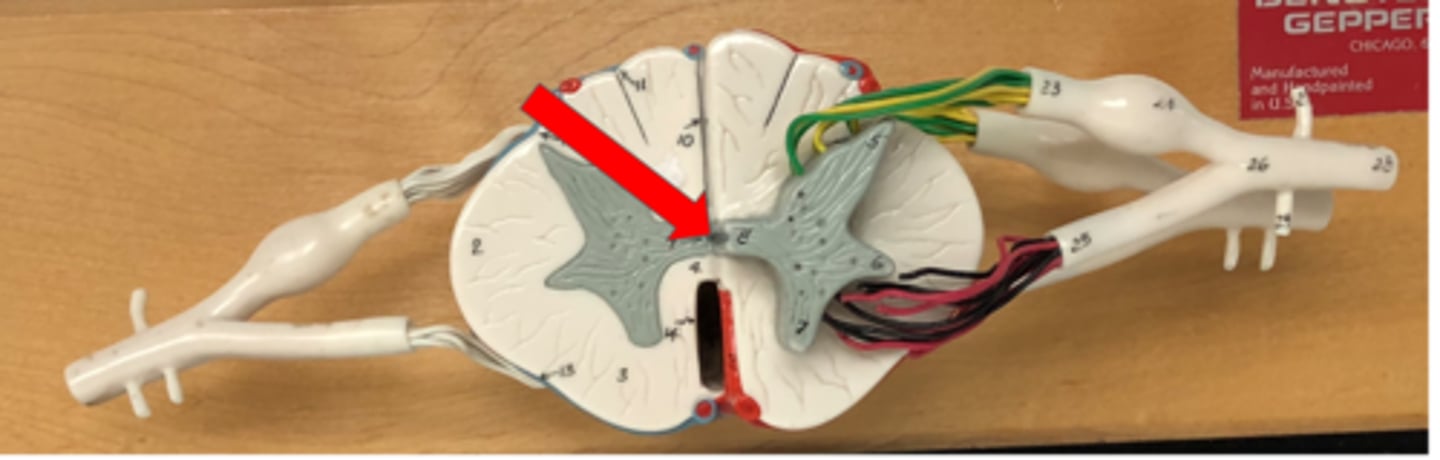
Central canal
Contains cerebrospinal fluid in the spinal cord
Gray matter
Inside of spinal cord, outside of brain
Anterior horn
Contains cell bodies of motor neurons in the spinal cord
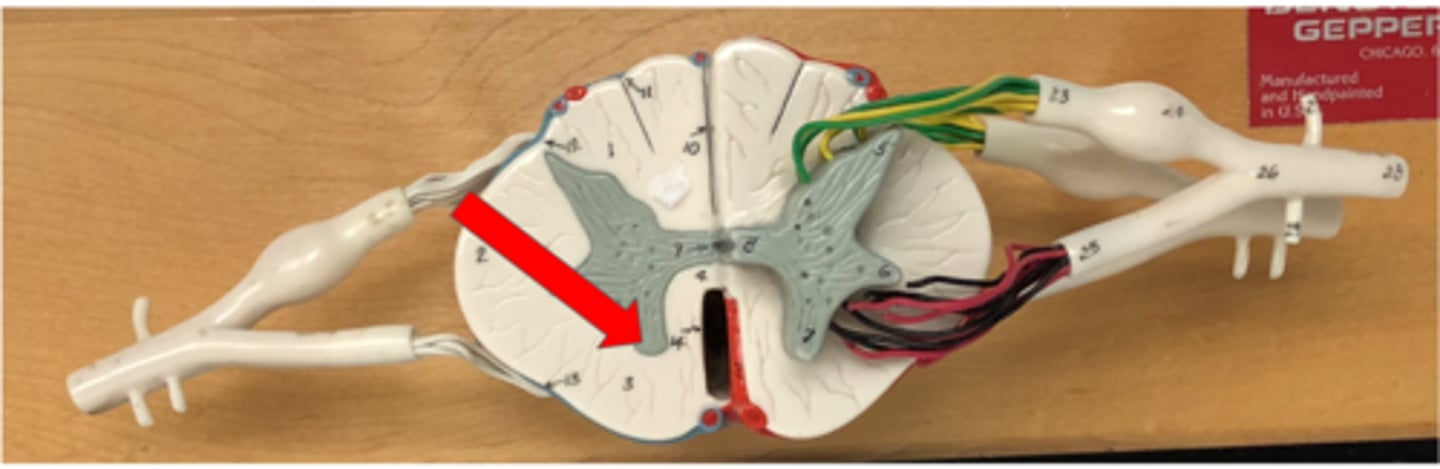
Lateral horn
Contains cell bodies of autonomic motor neurons in the spinal cord
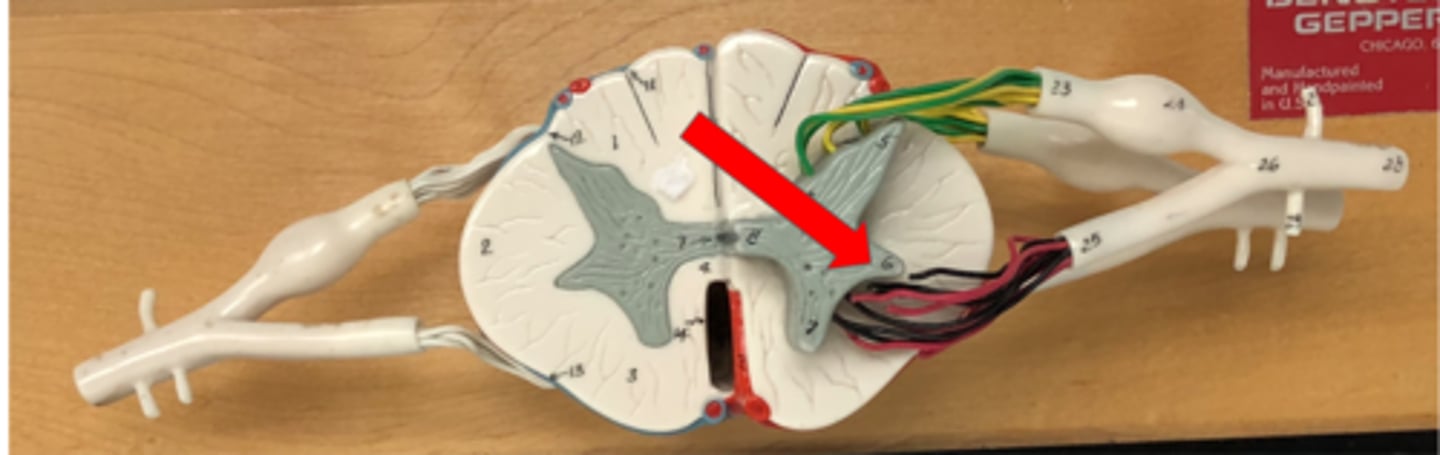
Posterior horn
Contains axons of sensory neurons in the spinal cord
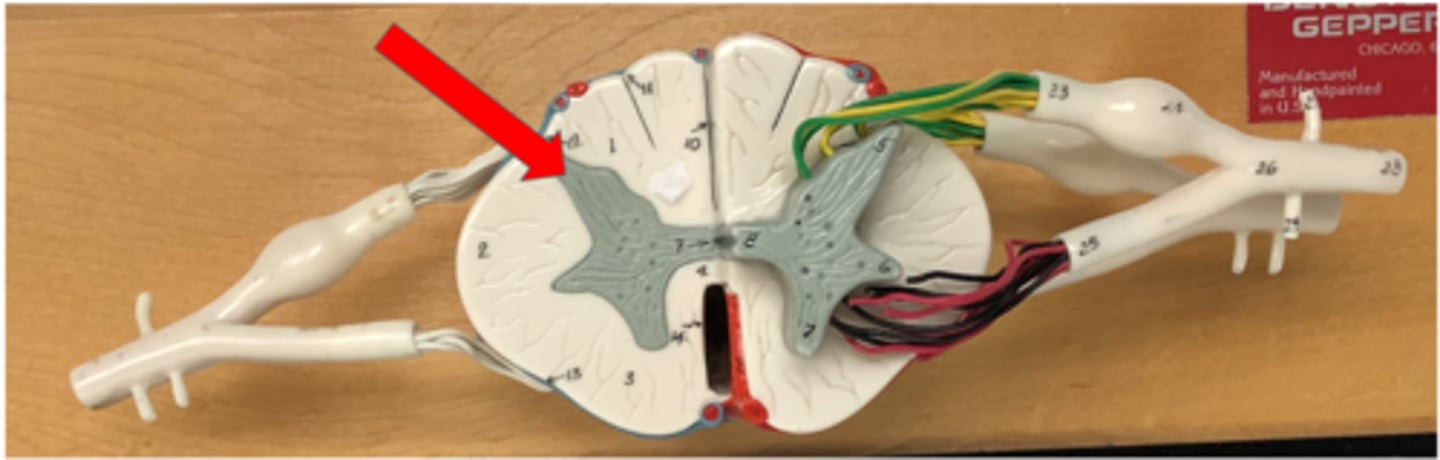
White matter
outside of spine, inside of brain
Anterior white column (funiculus)
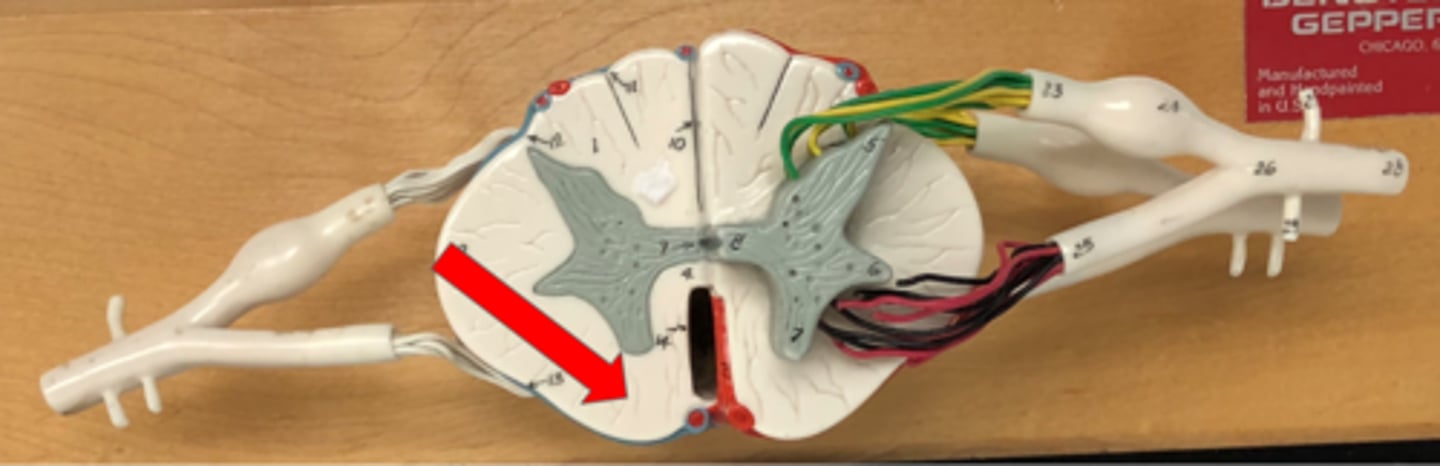
Posterior white column (funiculus)
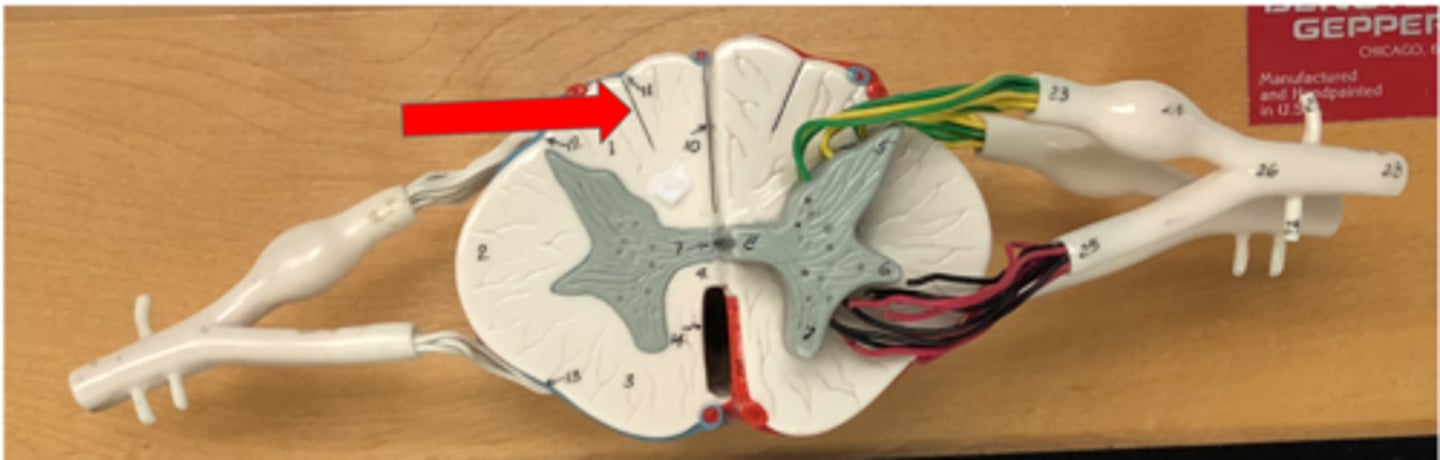
Lateral white column (funiculus)
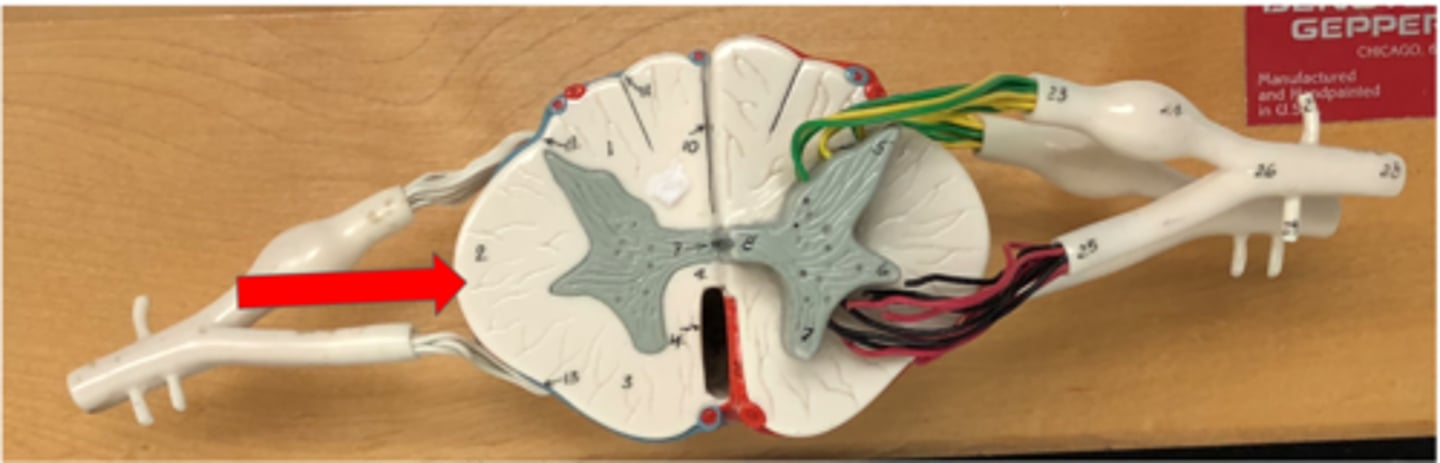
Pia mater (spine)
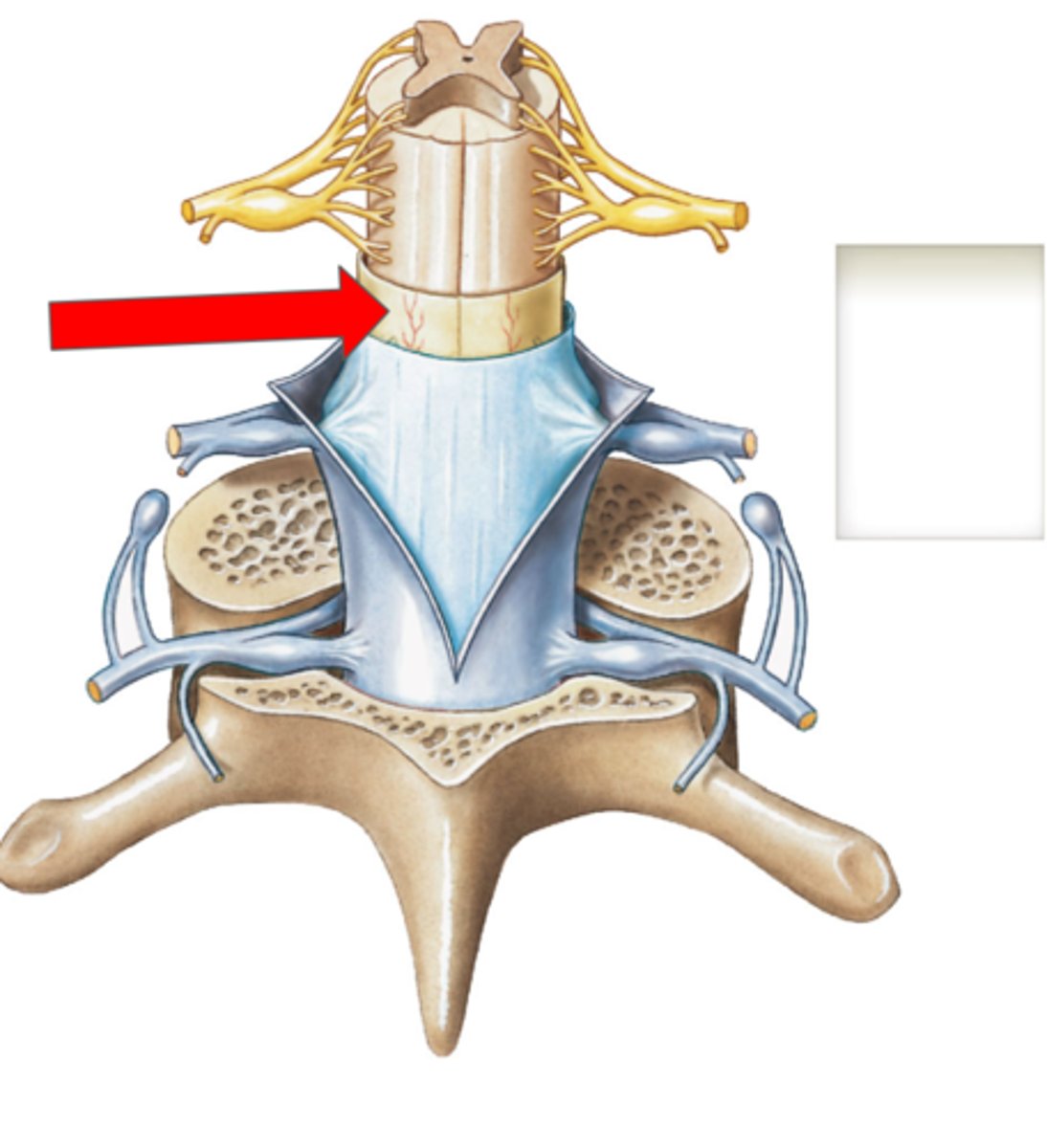
Subarachnoid space (spine)
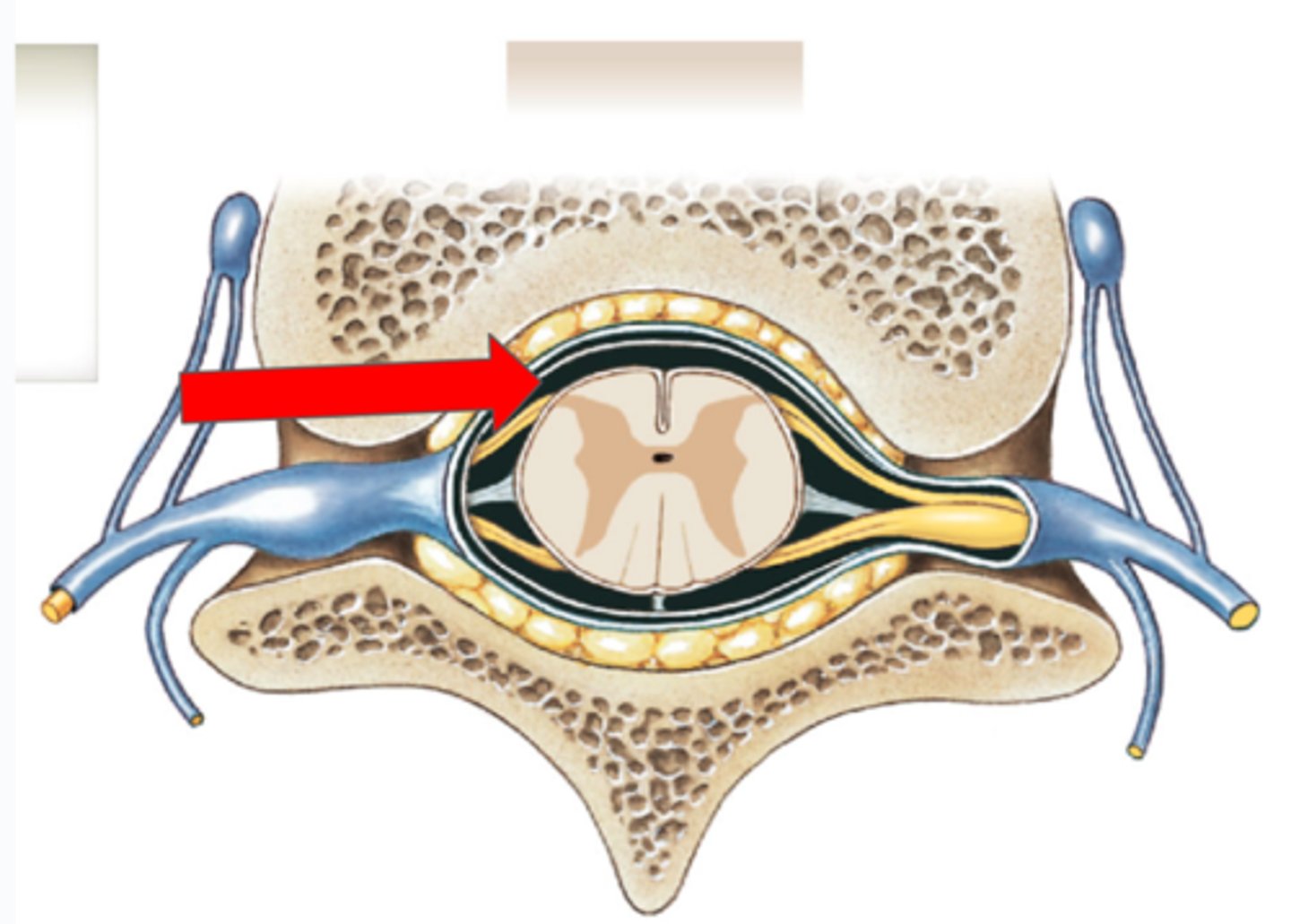
Arachnoid mater (spine)
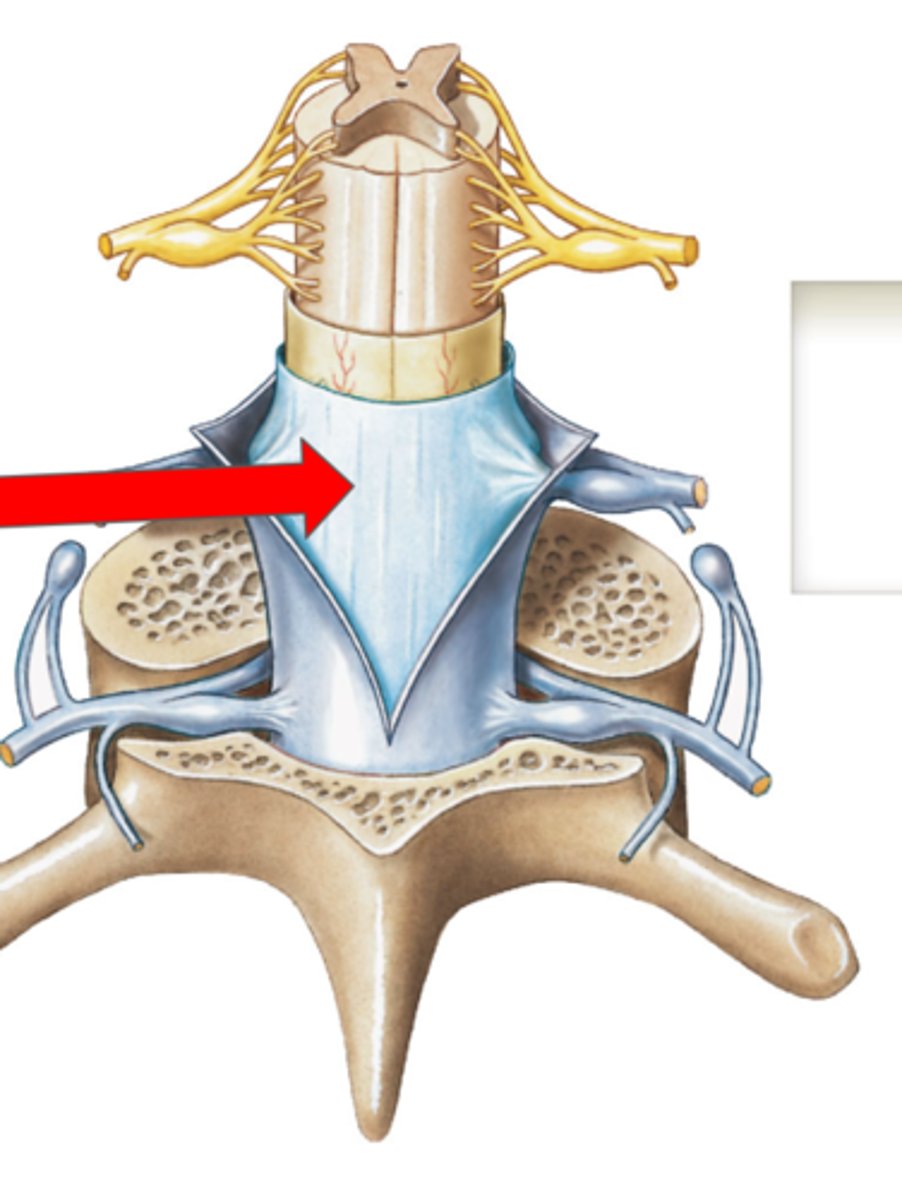
Subdural space (spine)
(space)
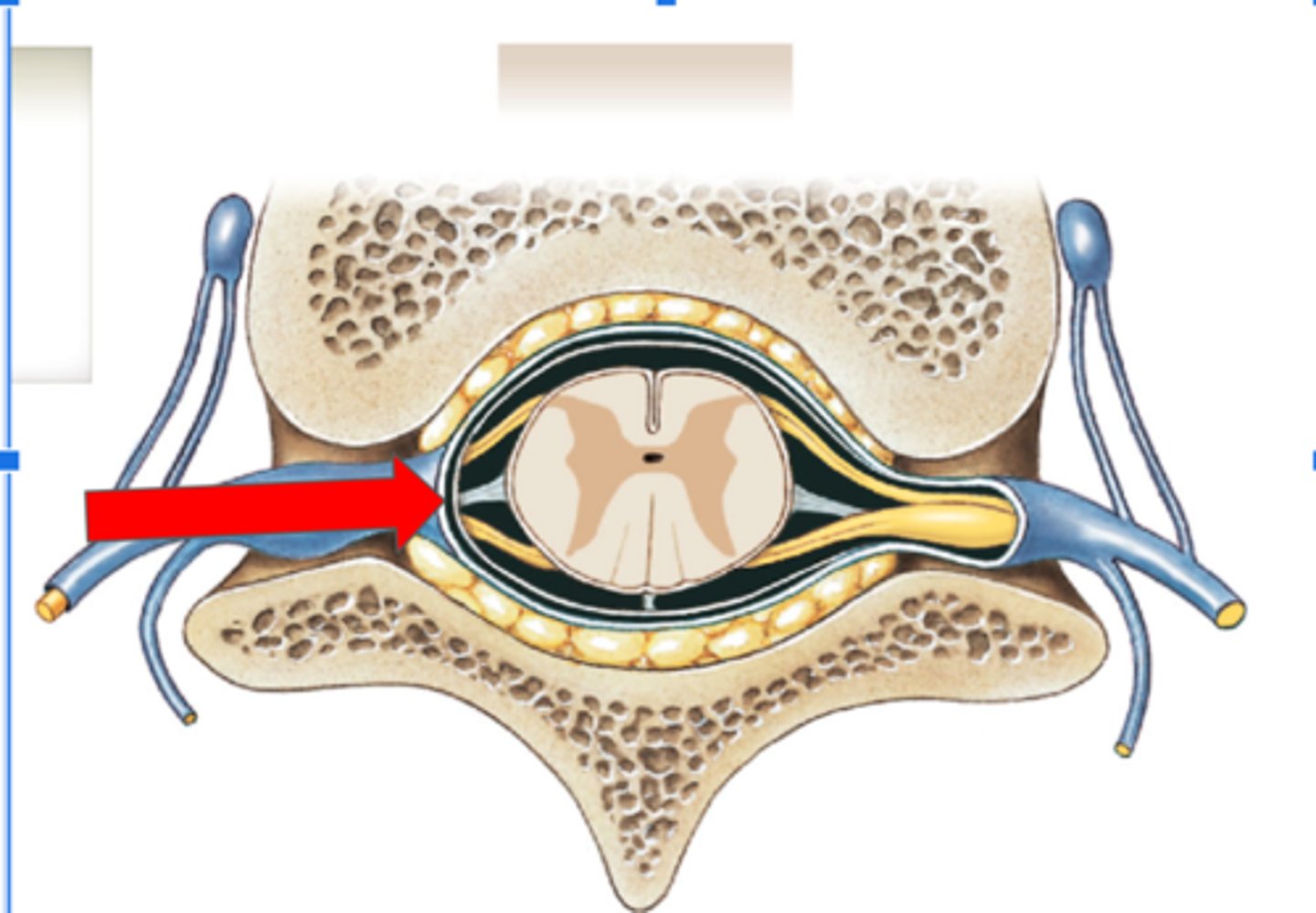
Dura mater (spine)
Outermost layer of the meninges in the spinal cord
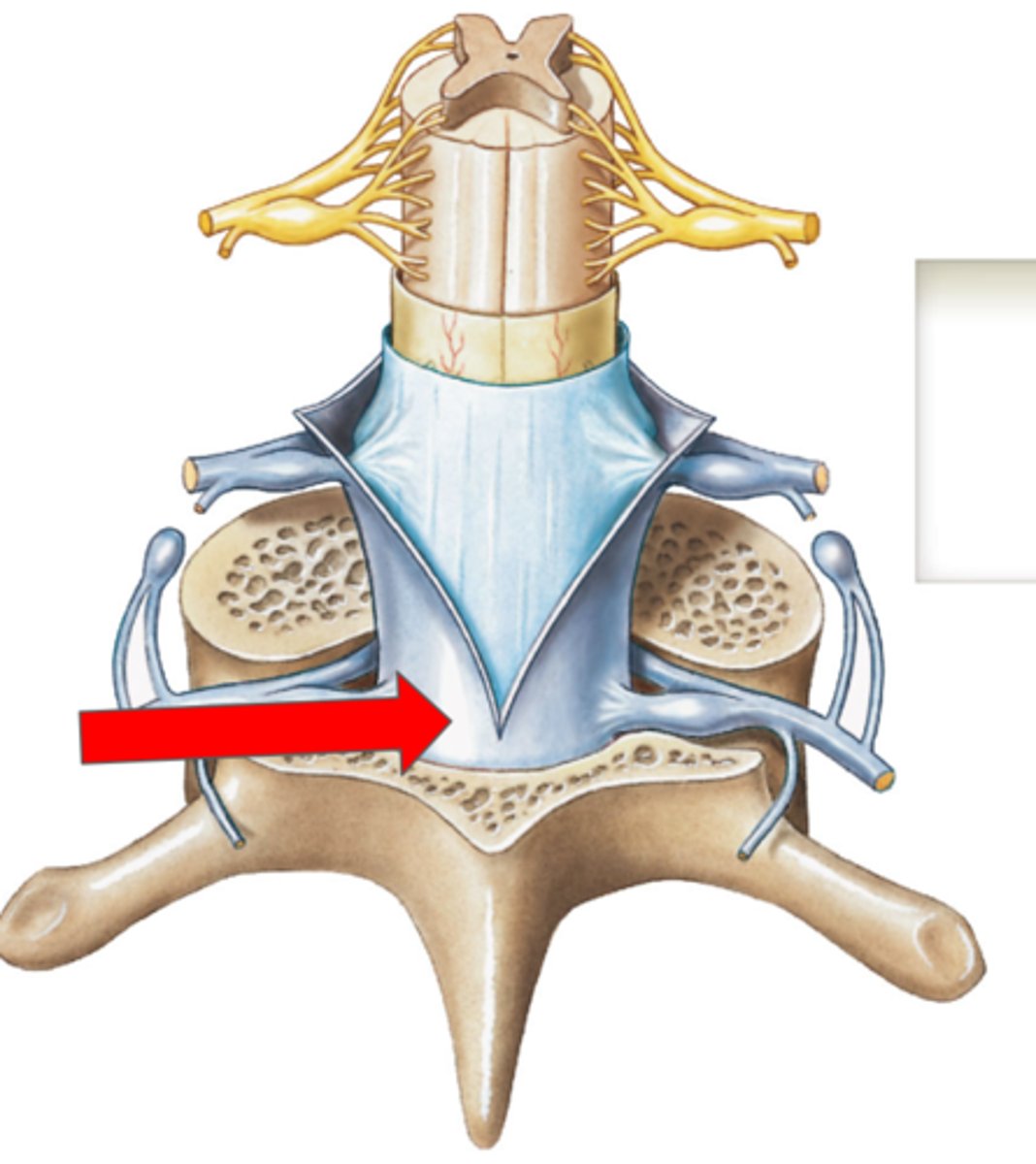
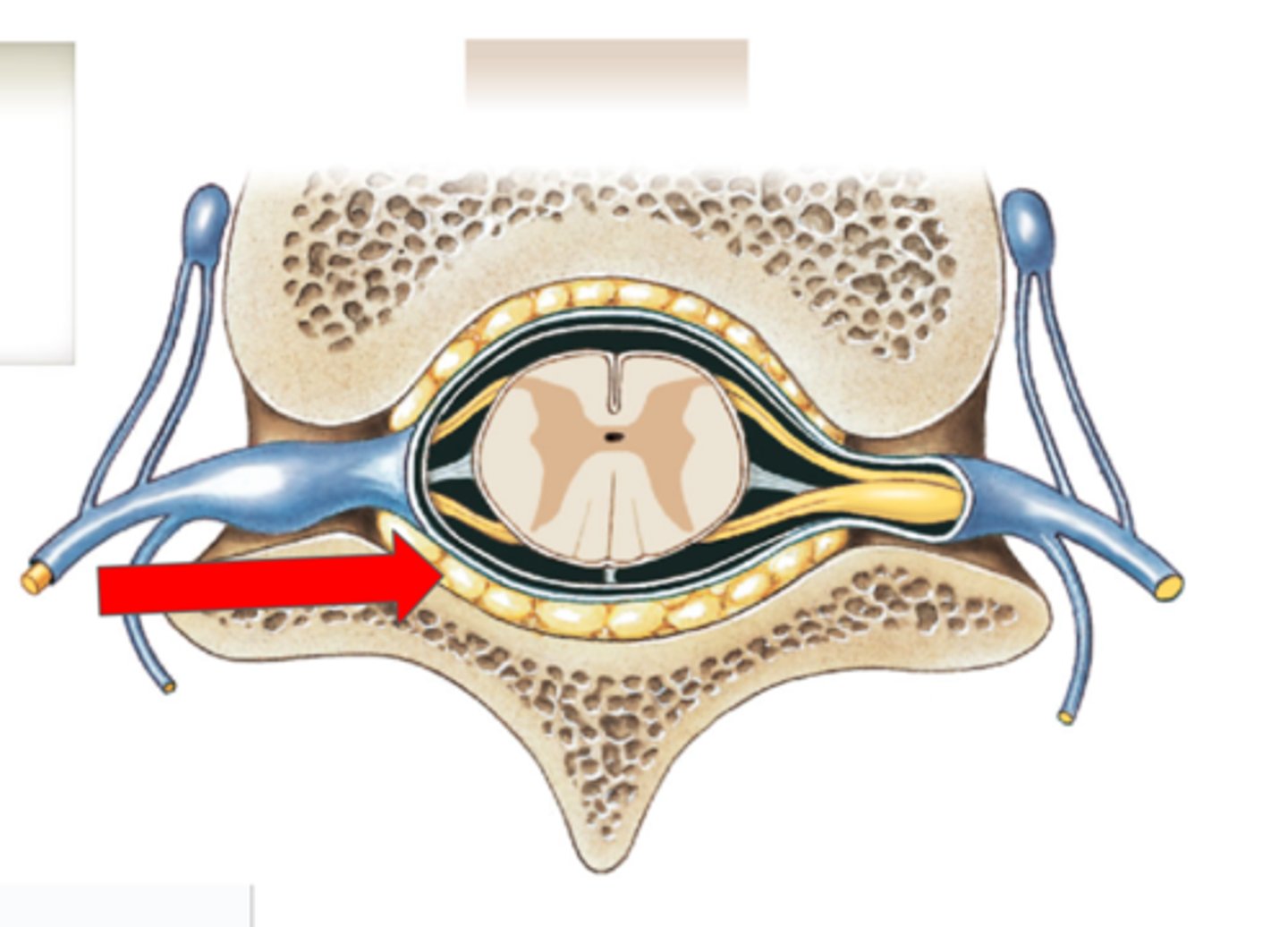
Epidural space (contains fat) (spine)
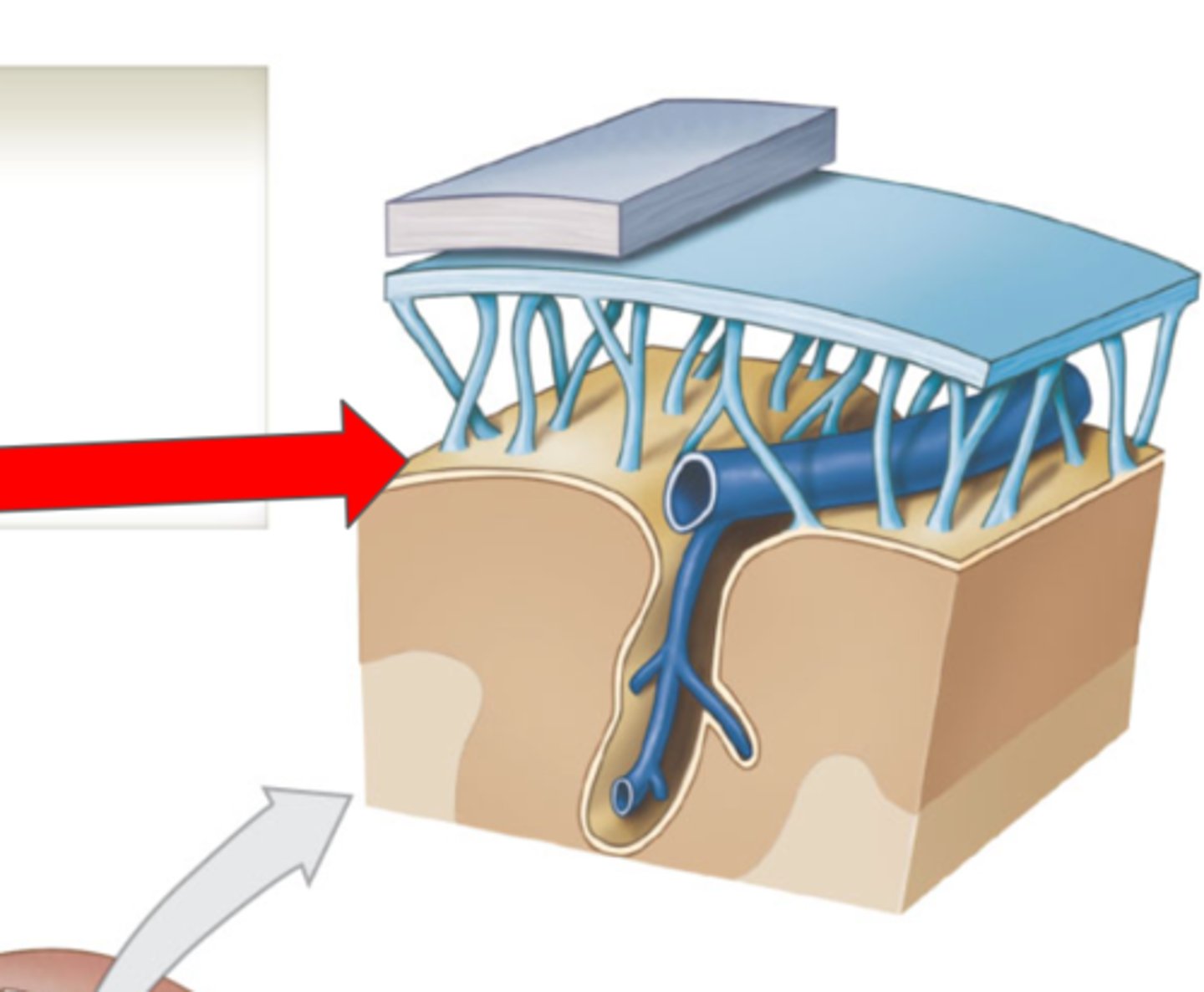
Cranial Meninges
Protective layers around the brain
Dura mater
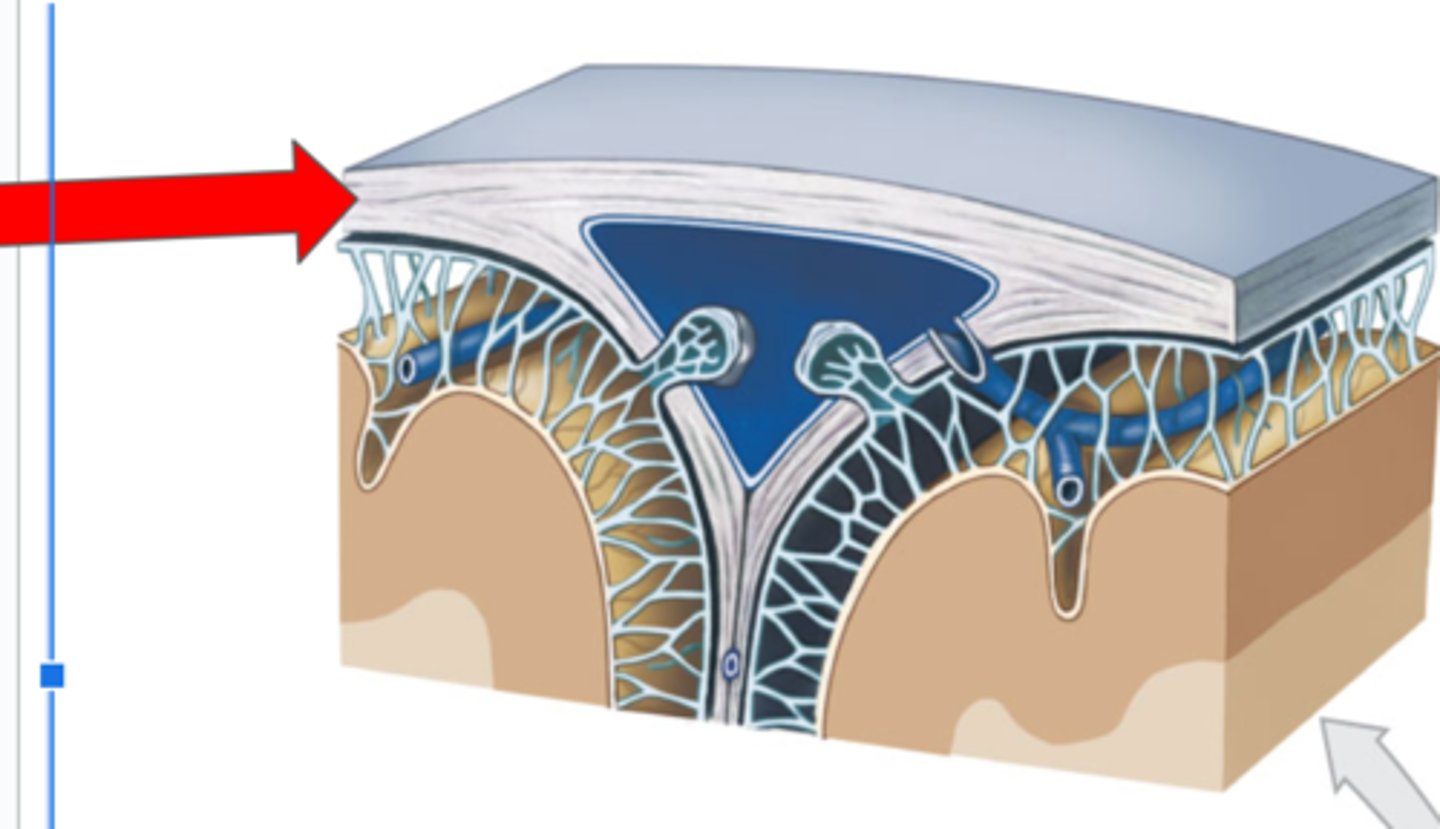
Arachnoid mater
Middle layer of the cranial meninges
Subdural space
(space)
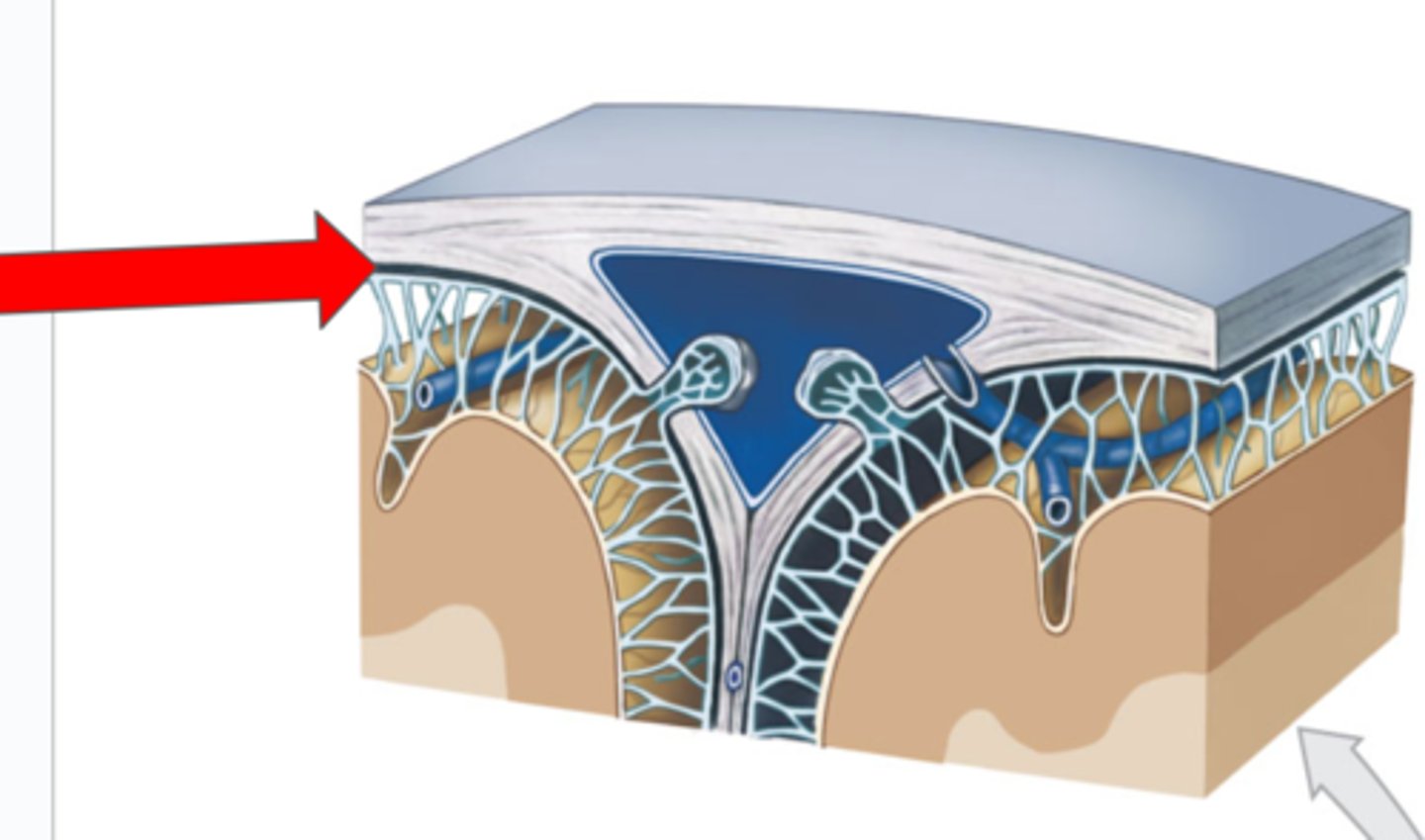
Subarachnoid mater
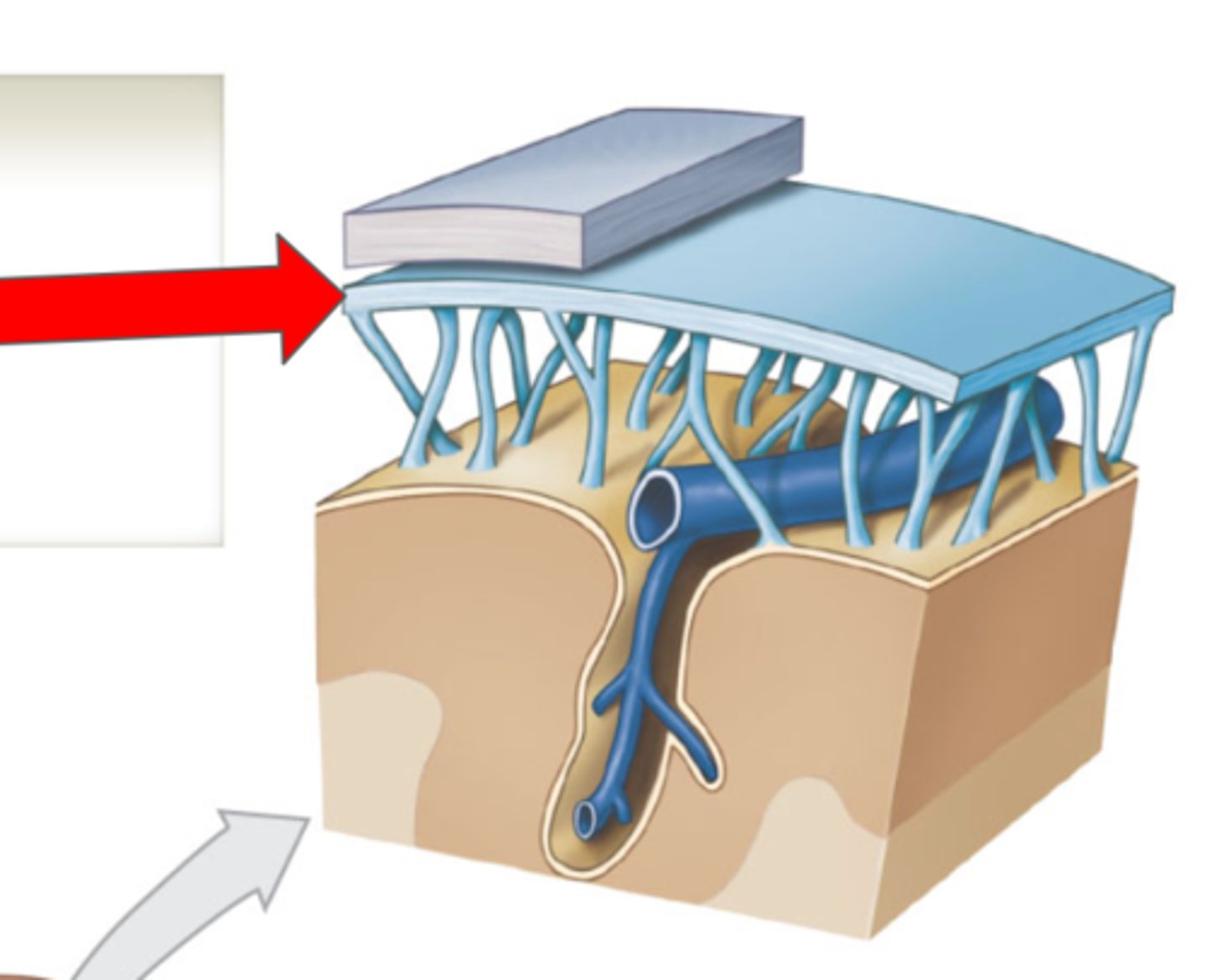
Arachnoid trabeculae
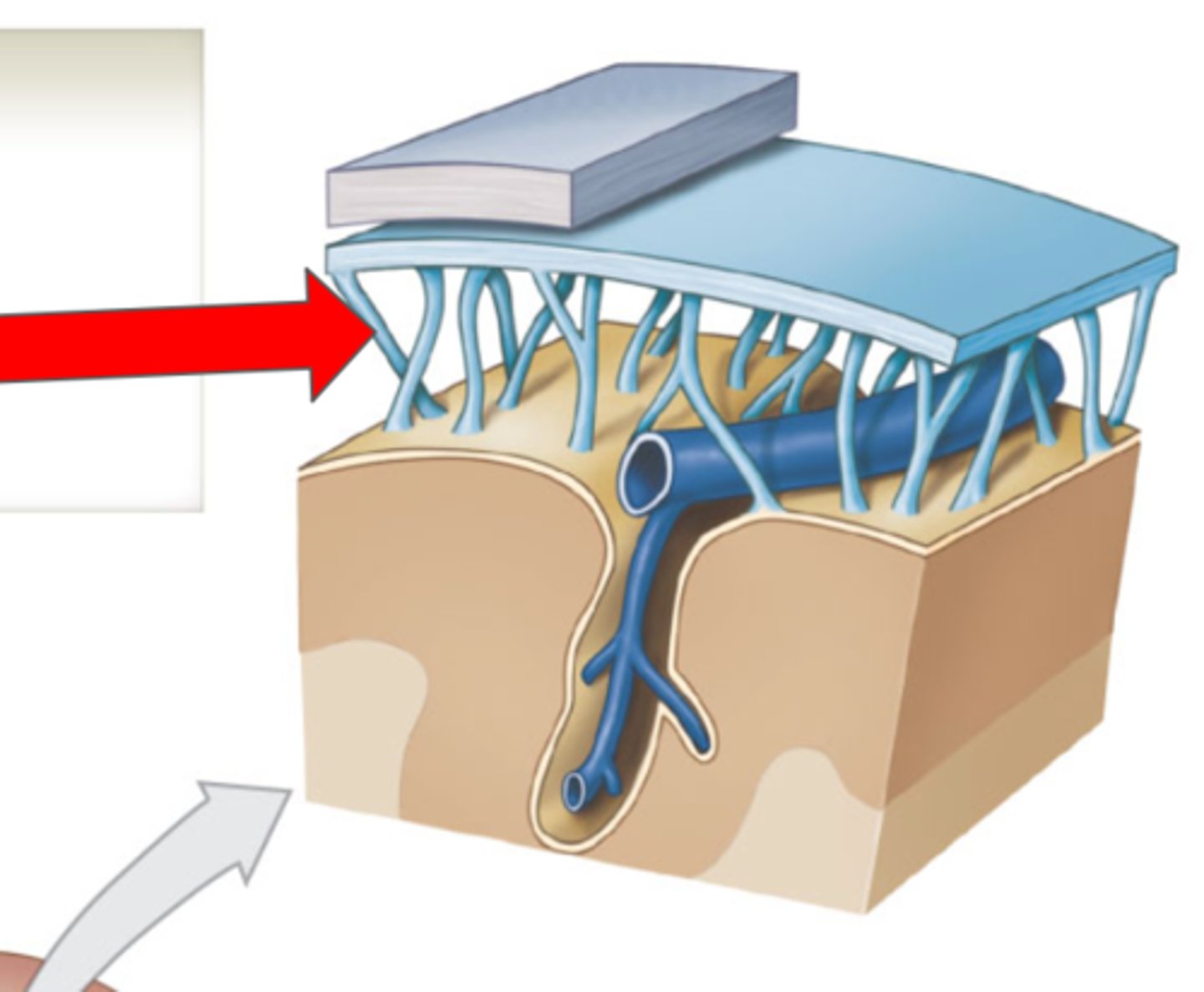
Pia mater
Cerebrum (Two Cerebral Hemispheres)
Cerebral cortex
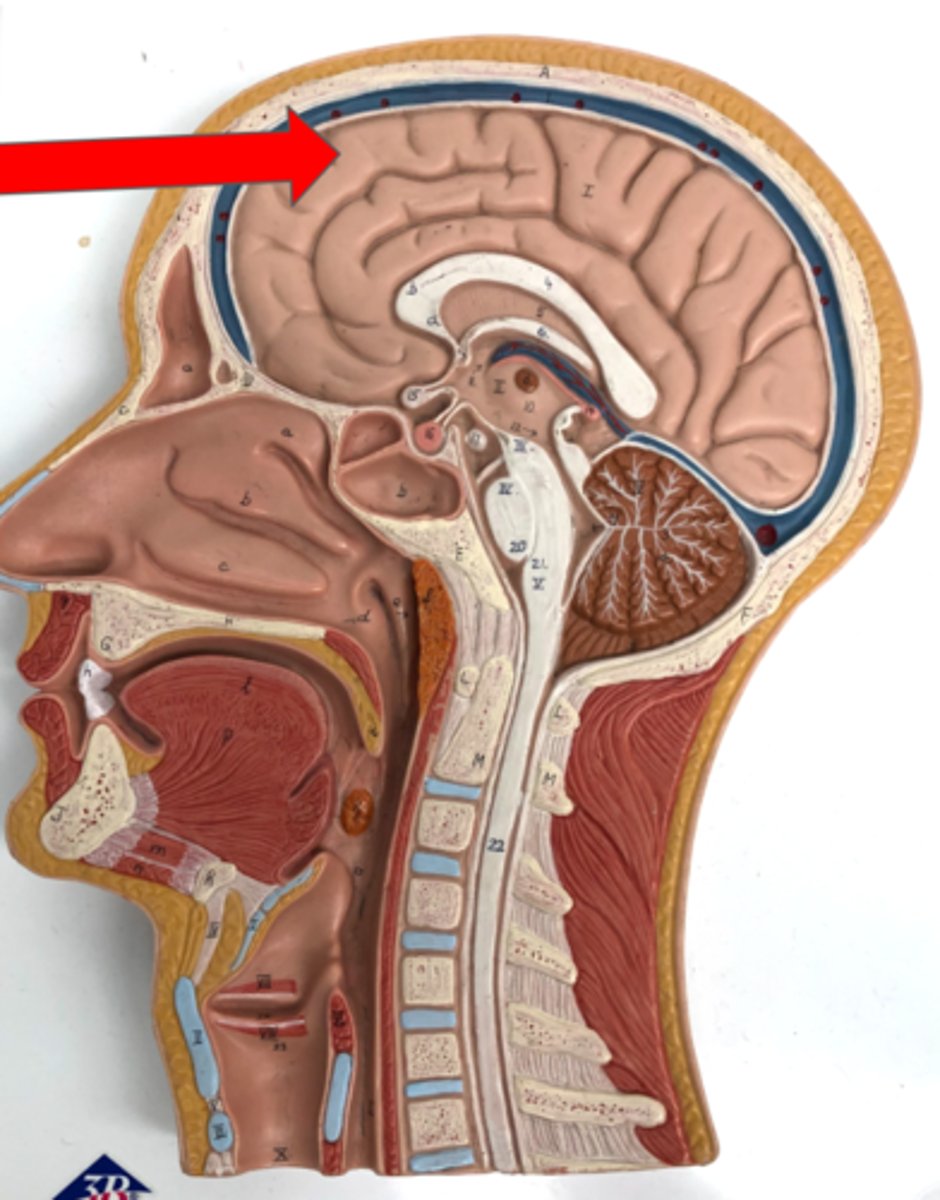
Ventricles
Fluid-filled cavities in the brain
Lateral ventricles

Cerebral aqueduct

Third ventricle

Fourth ventricle

Choroid plexus
Produces cerebrospinal fluid

Fornix
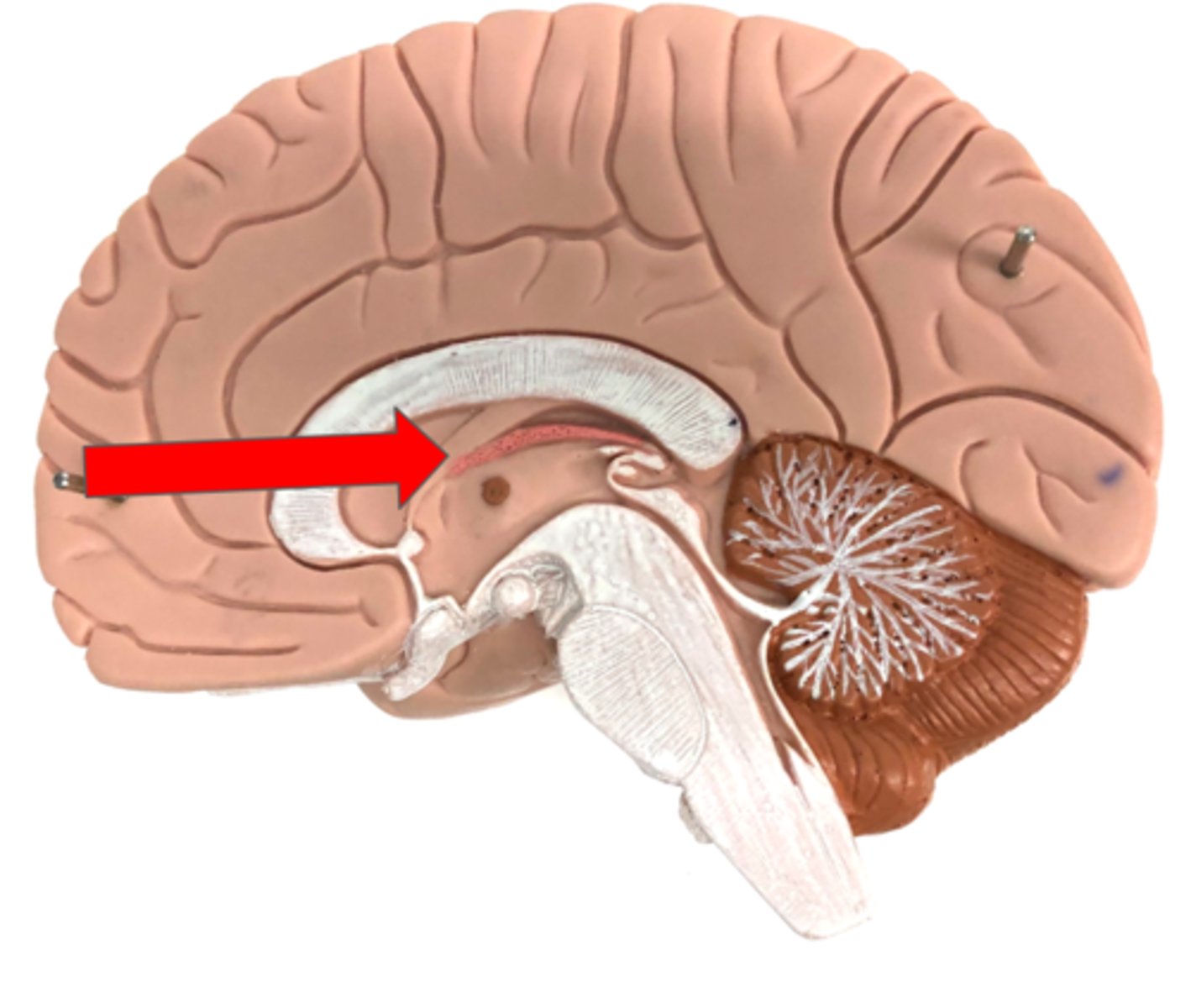
Epithalamus
contains the pineal gland
Pineal gland
Produces melatonin
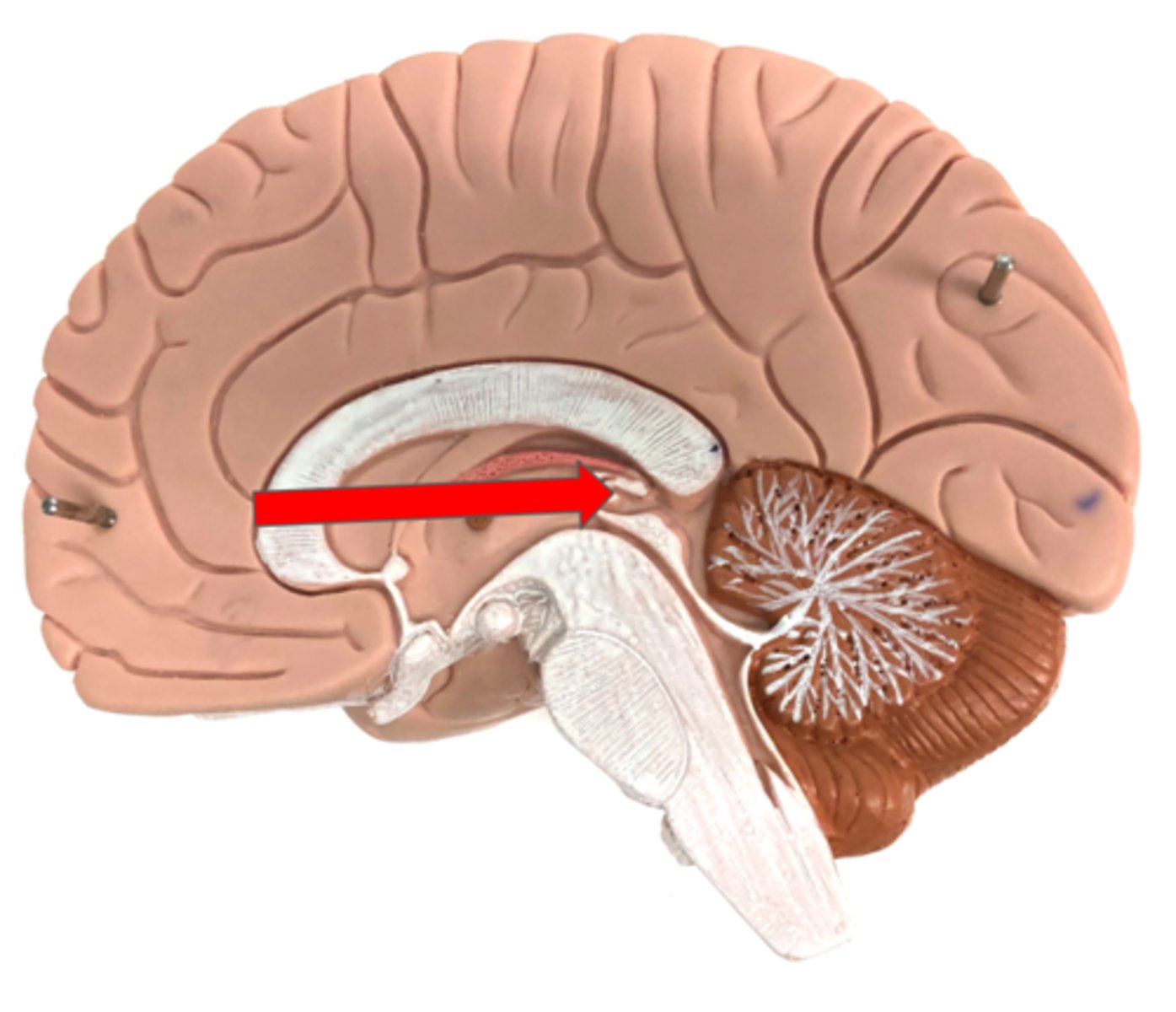
Thalamus
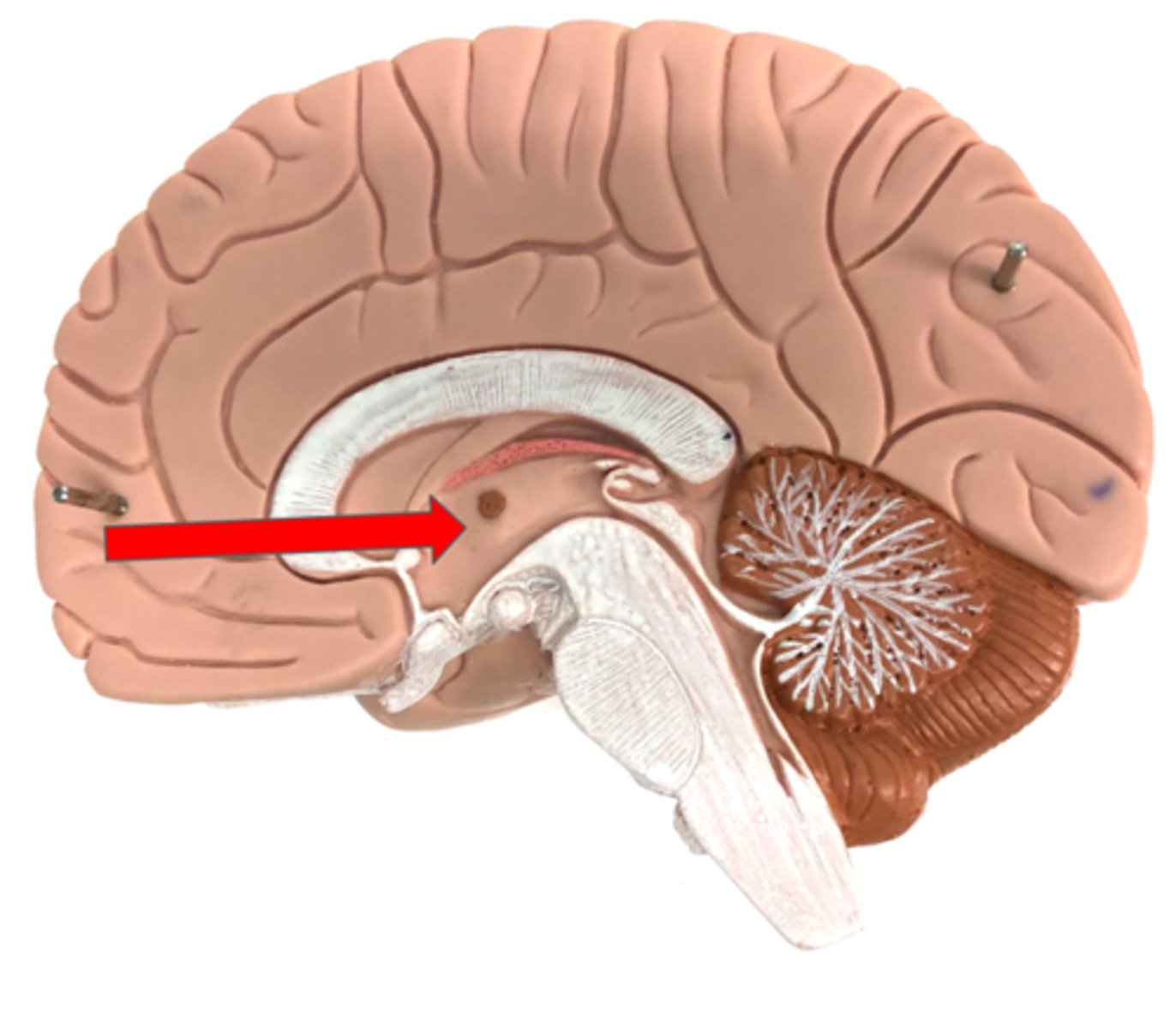
Interthalamic adhesion
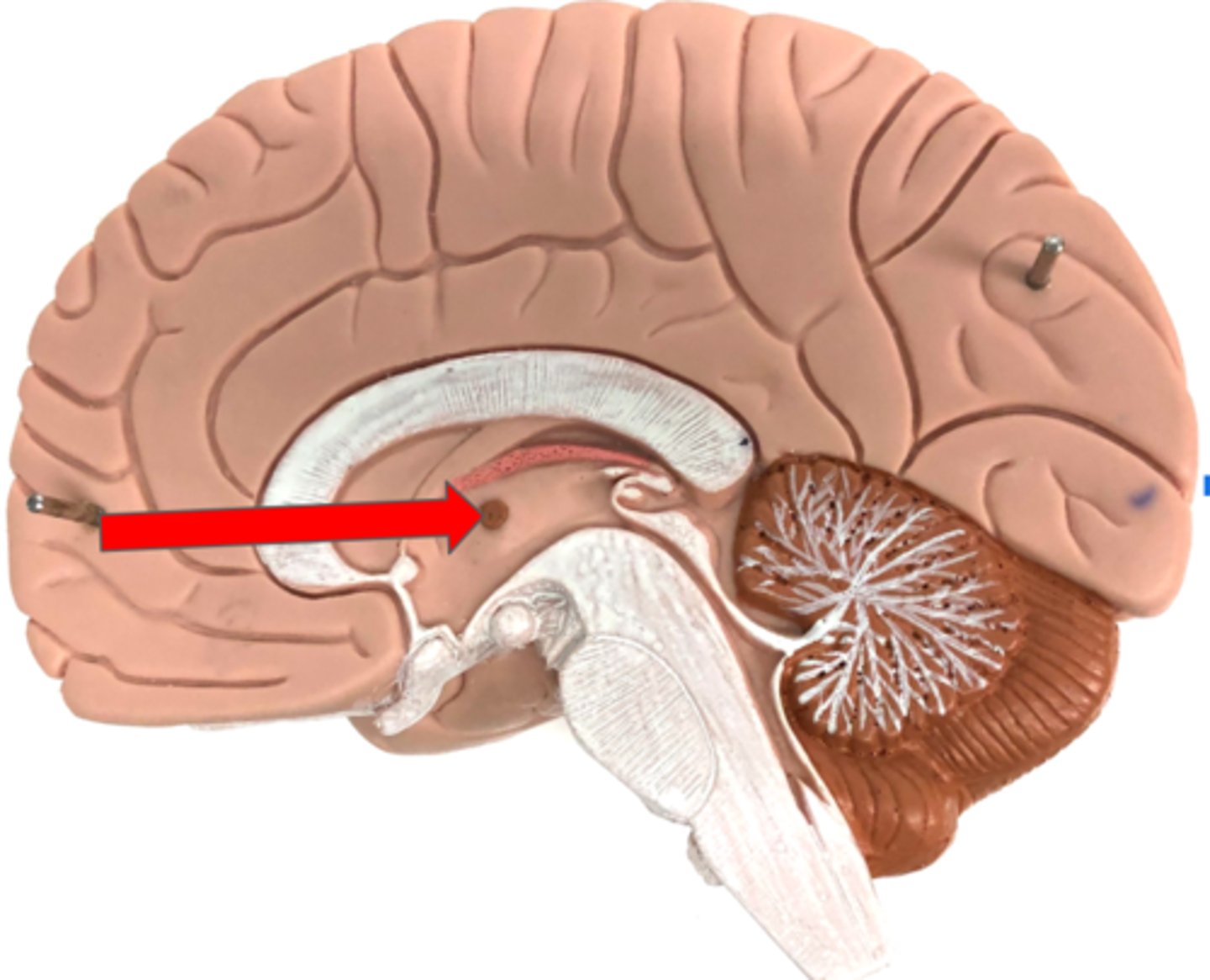
Hypothalamus
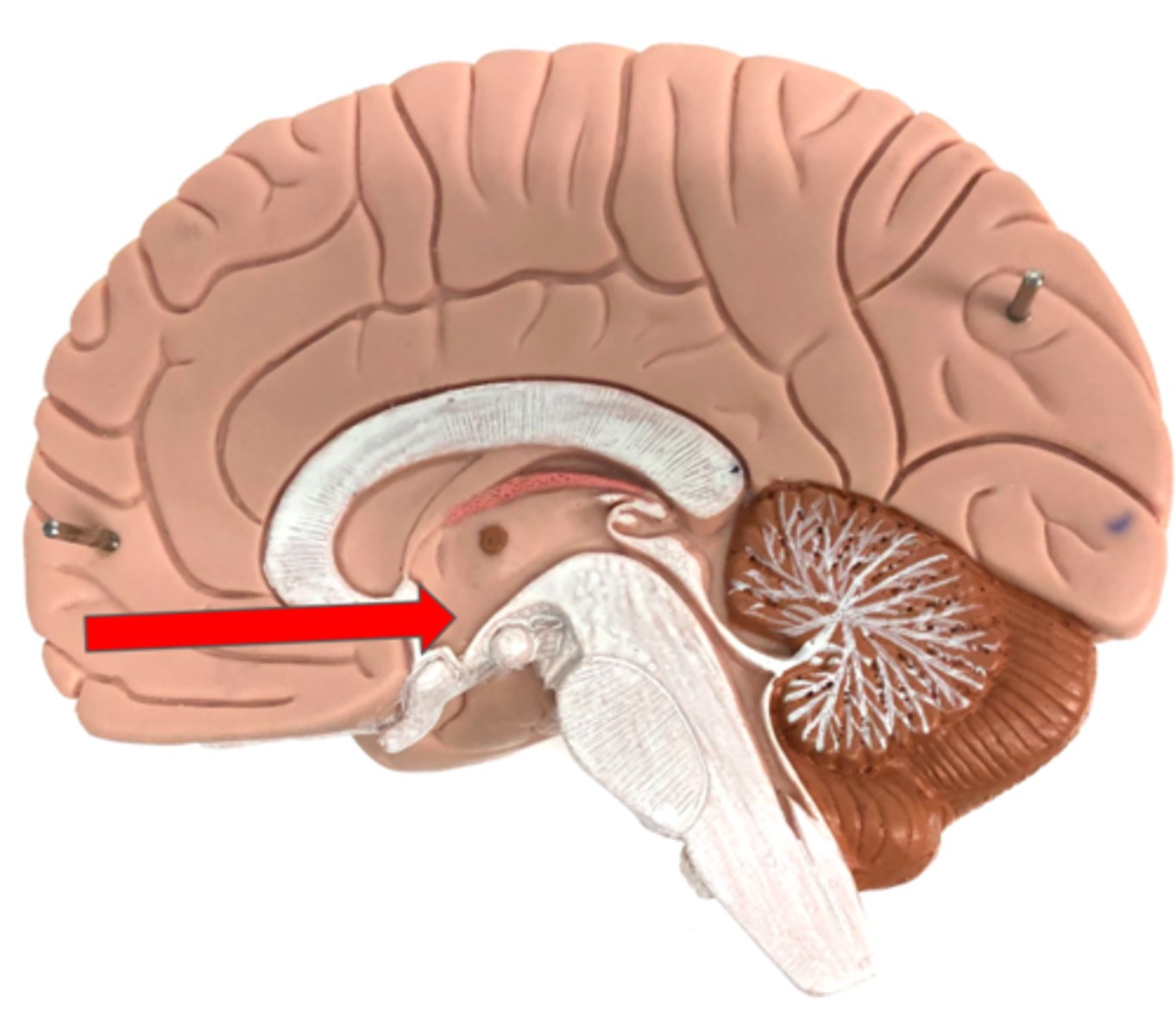
Infundibulum
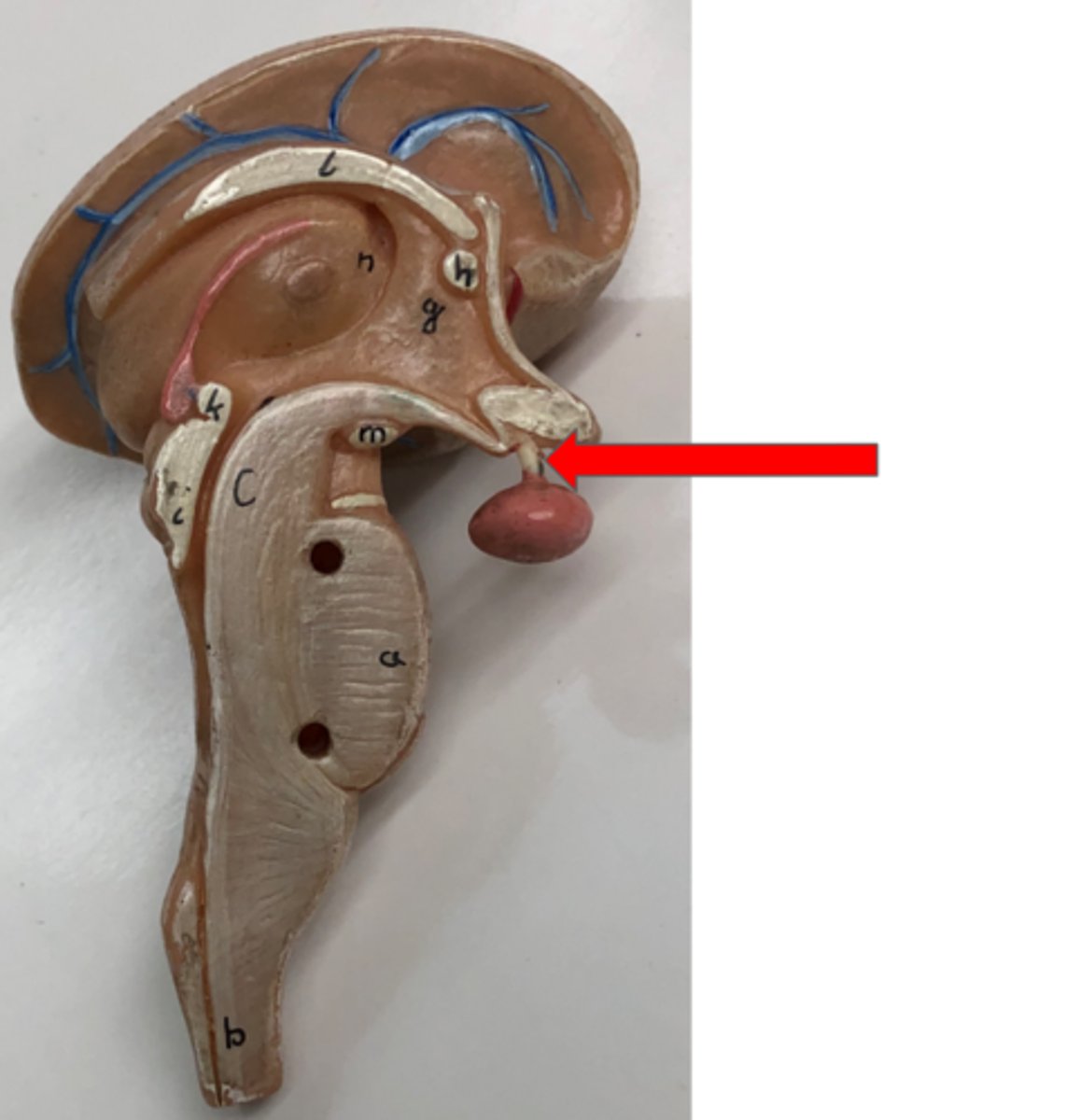
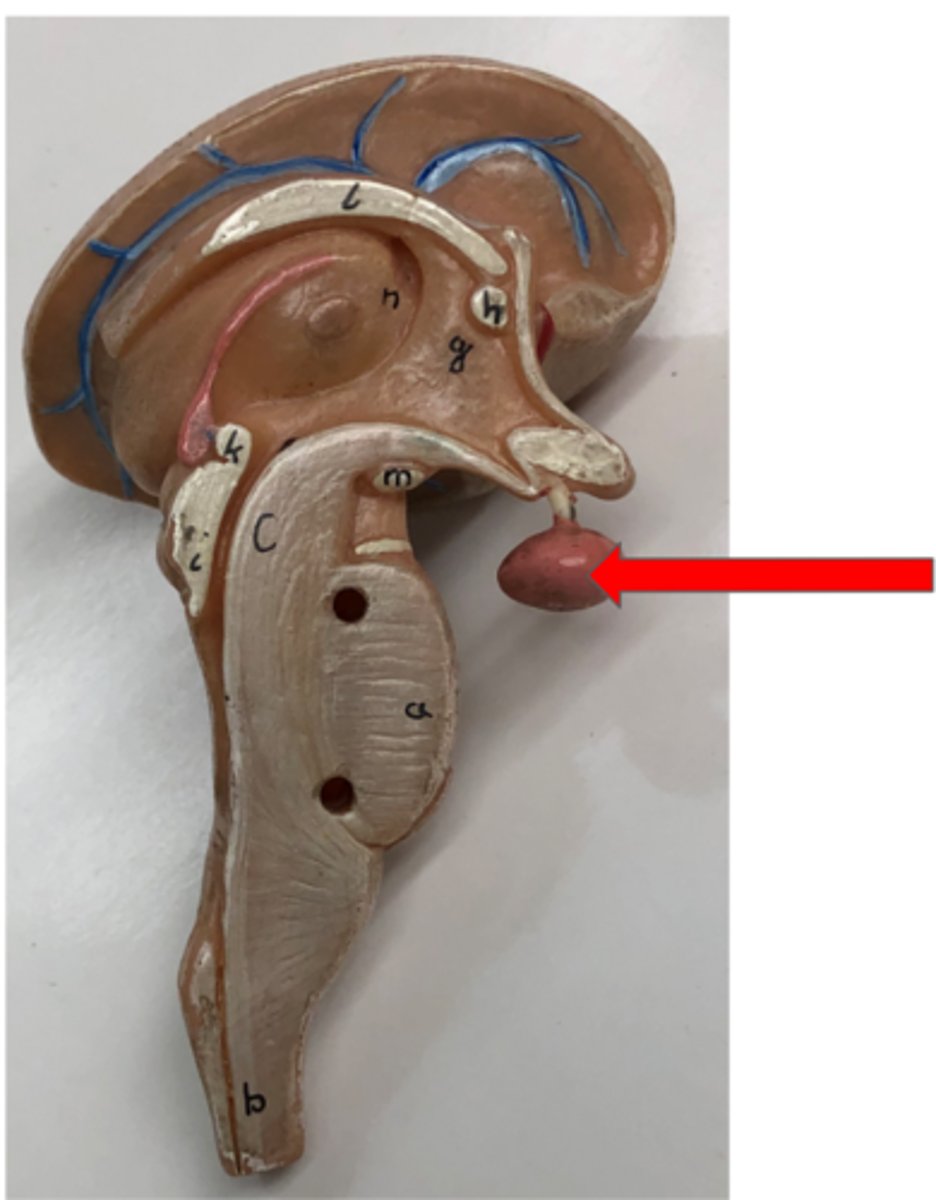
Pituitary gland
Produces and releases hormones
Optic chiasm
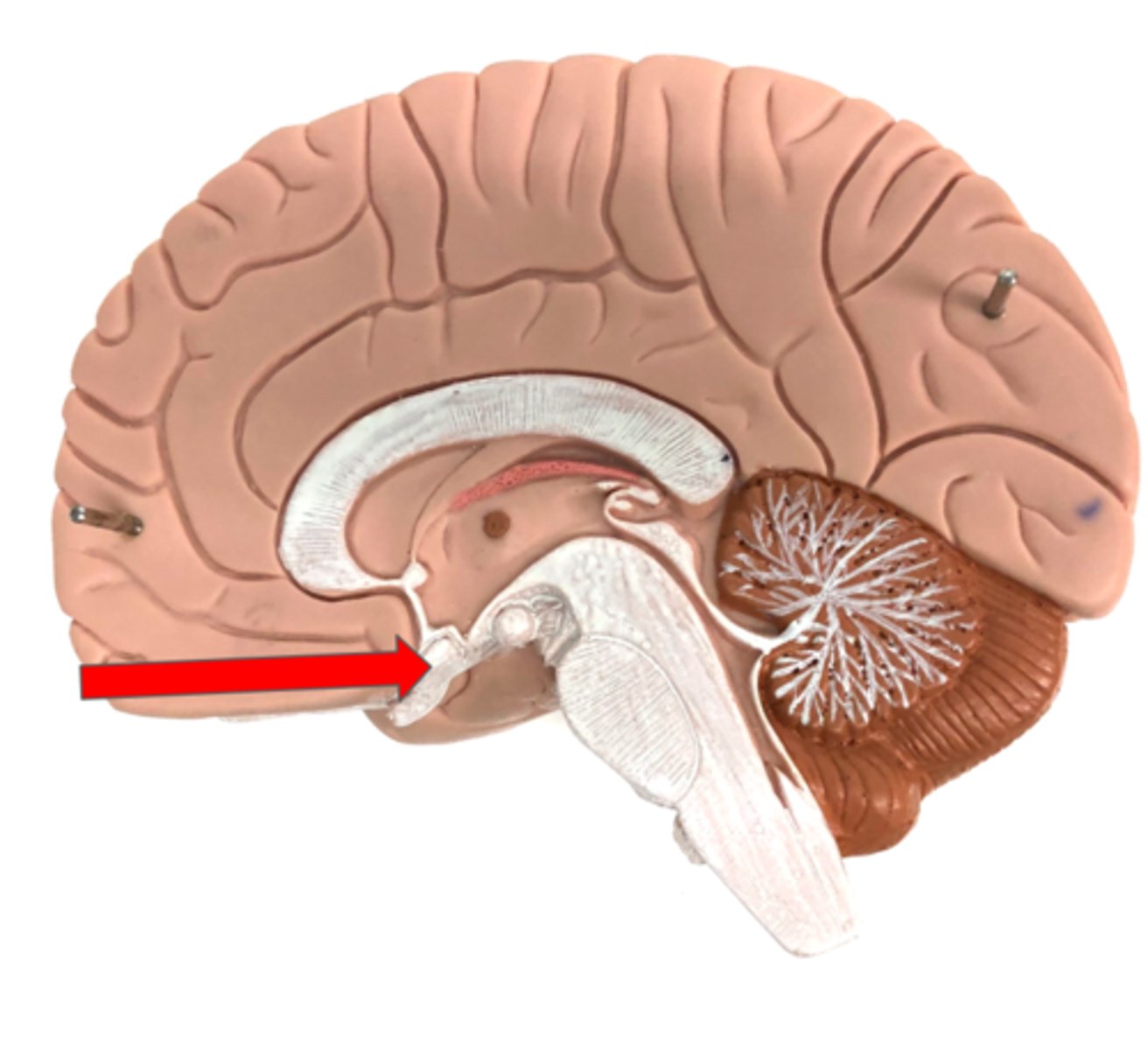
Brain Stem
Connects the brain and spinal cord
Pons
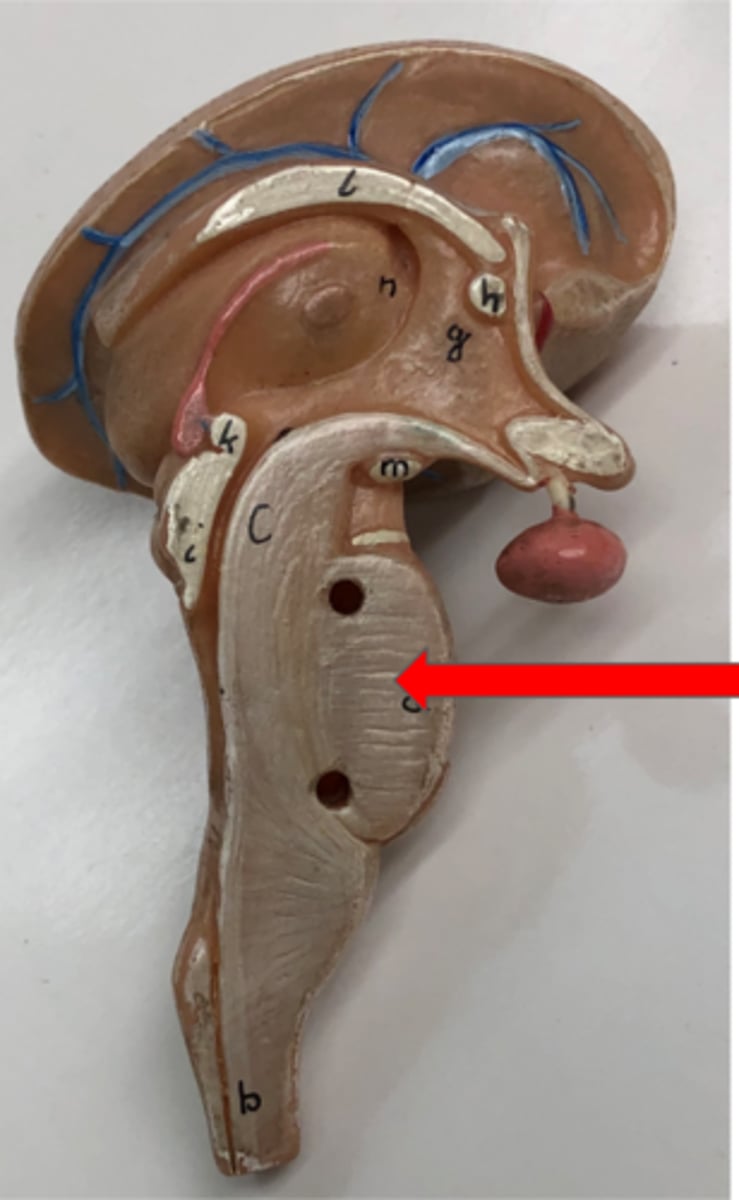
Medulla oblongata
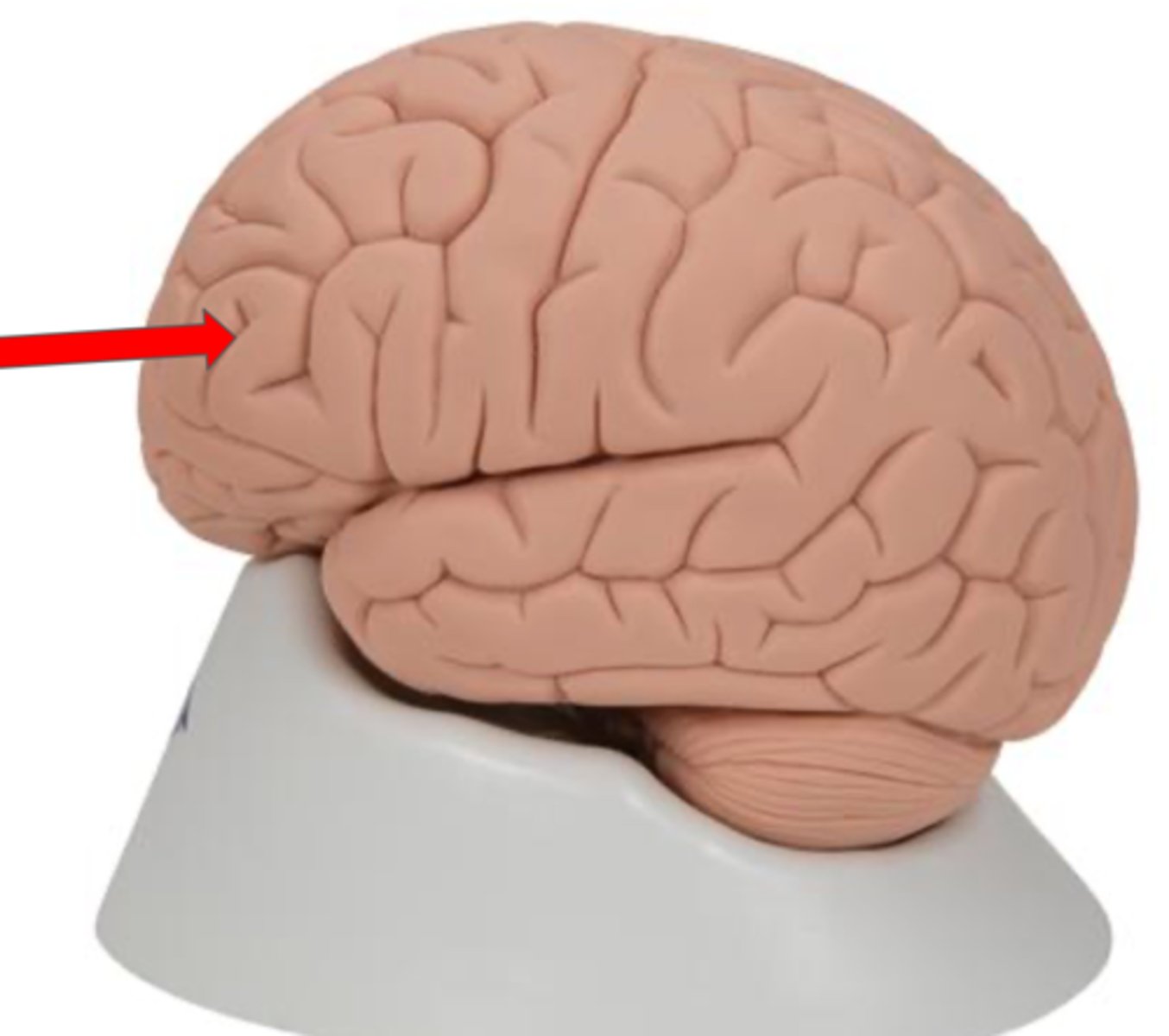
Frontal lobe
Part of the cerebrum responsible for decision making and motor control
Parietal lobe
Part of the cerebrum responsible for sensory processing
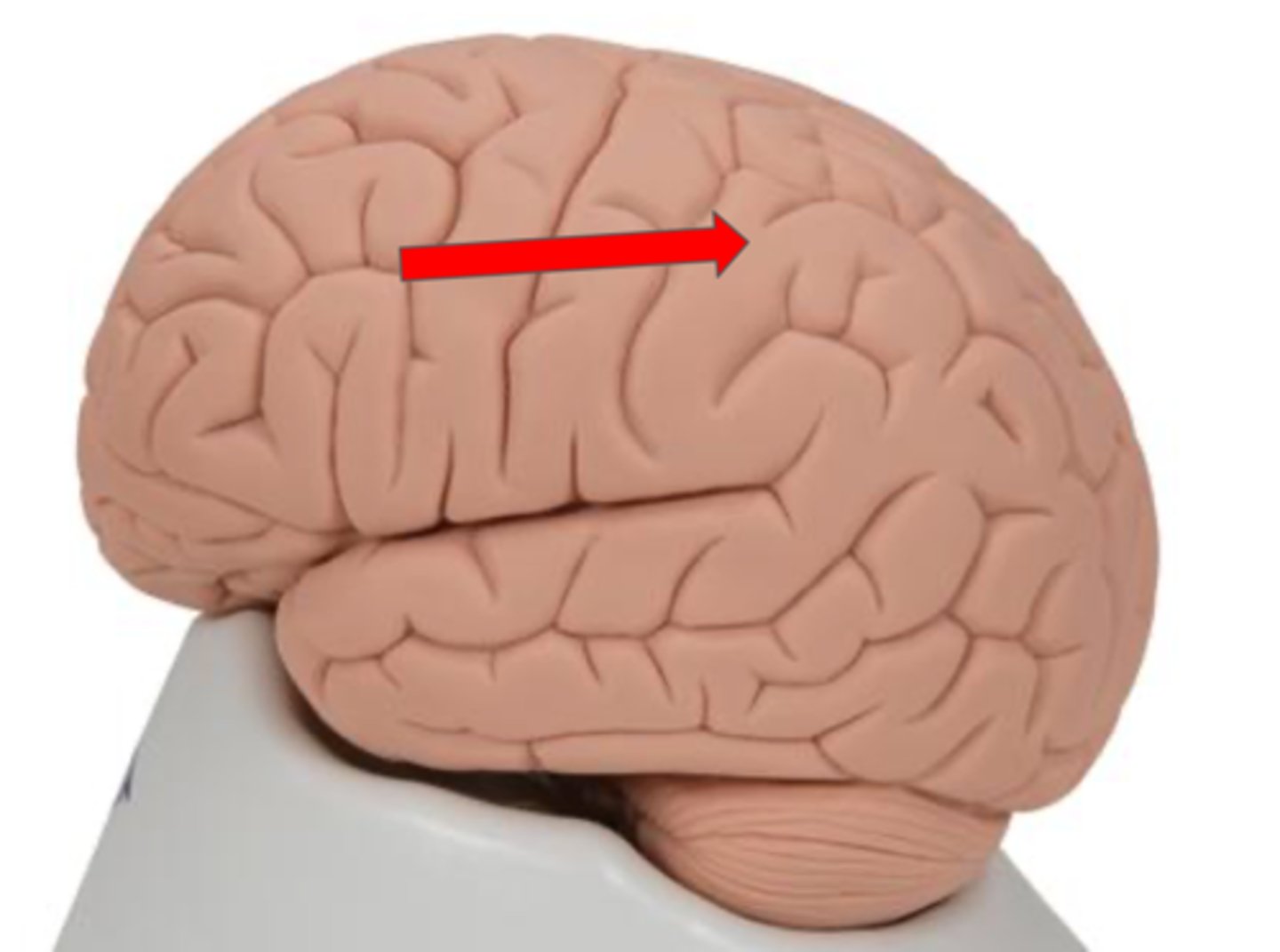
Central sulcus
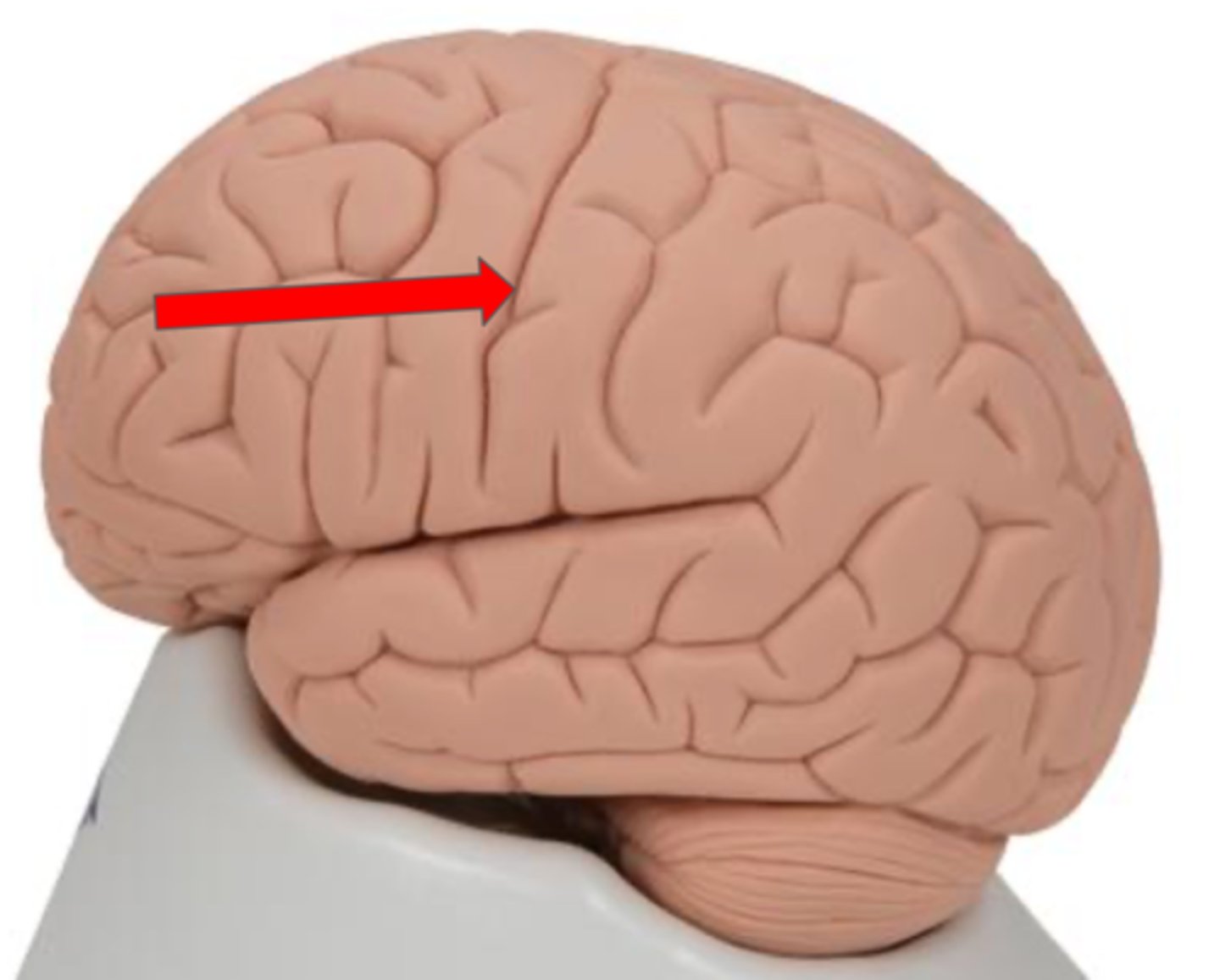
Precentral gyrus
Primary motor cortex located in the frontal lobe
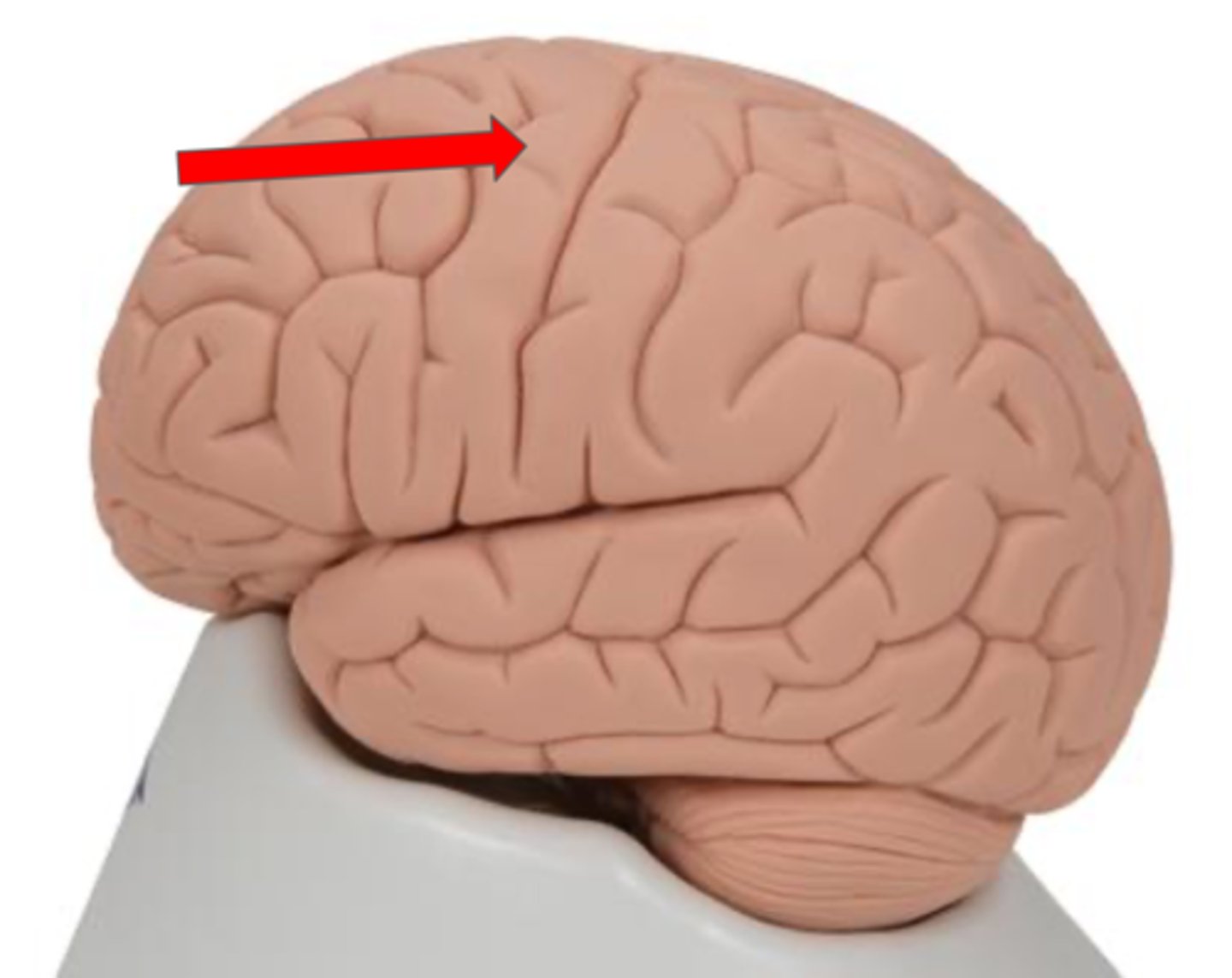
Postcentral gyrus
Primary sensory cortex located in the parietal lobe
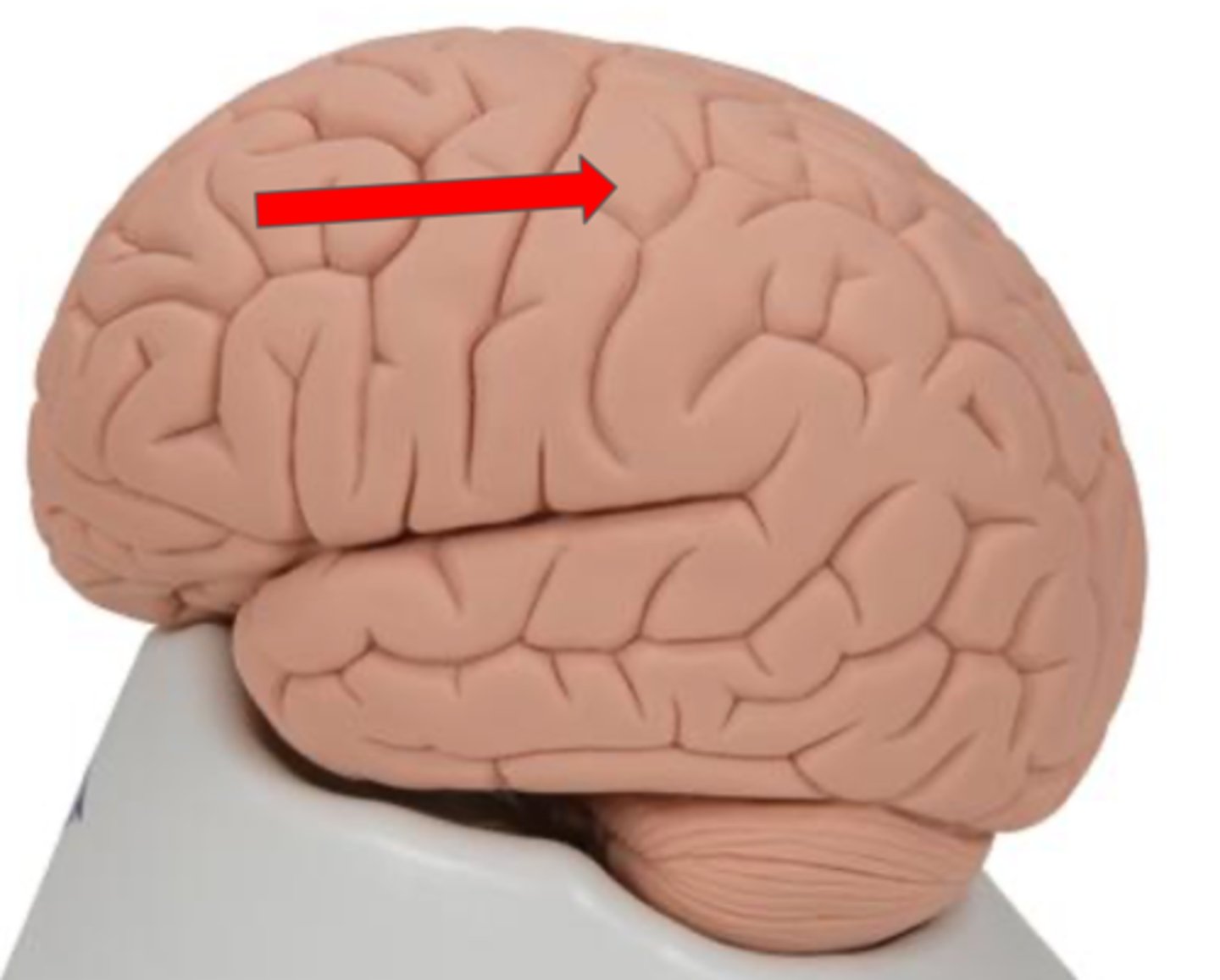
Lateral sulcus
Groove that separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes
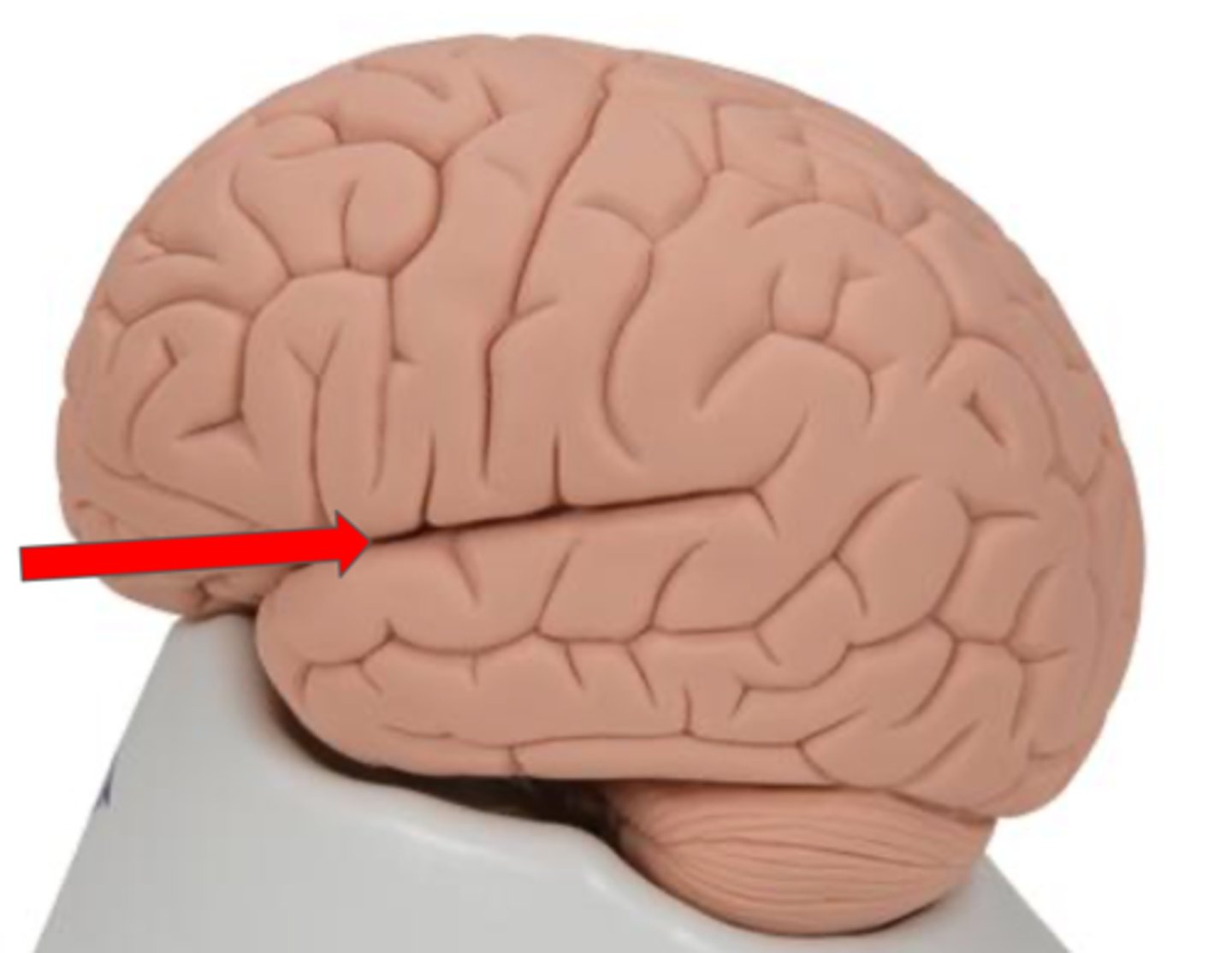
Temporal lobe
Part of the cerebrum responsible for auditory processing and memory
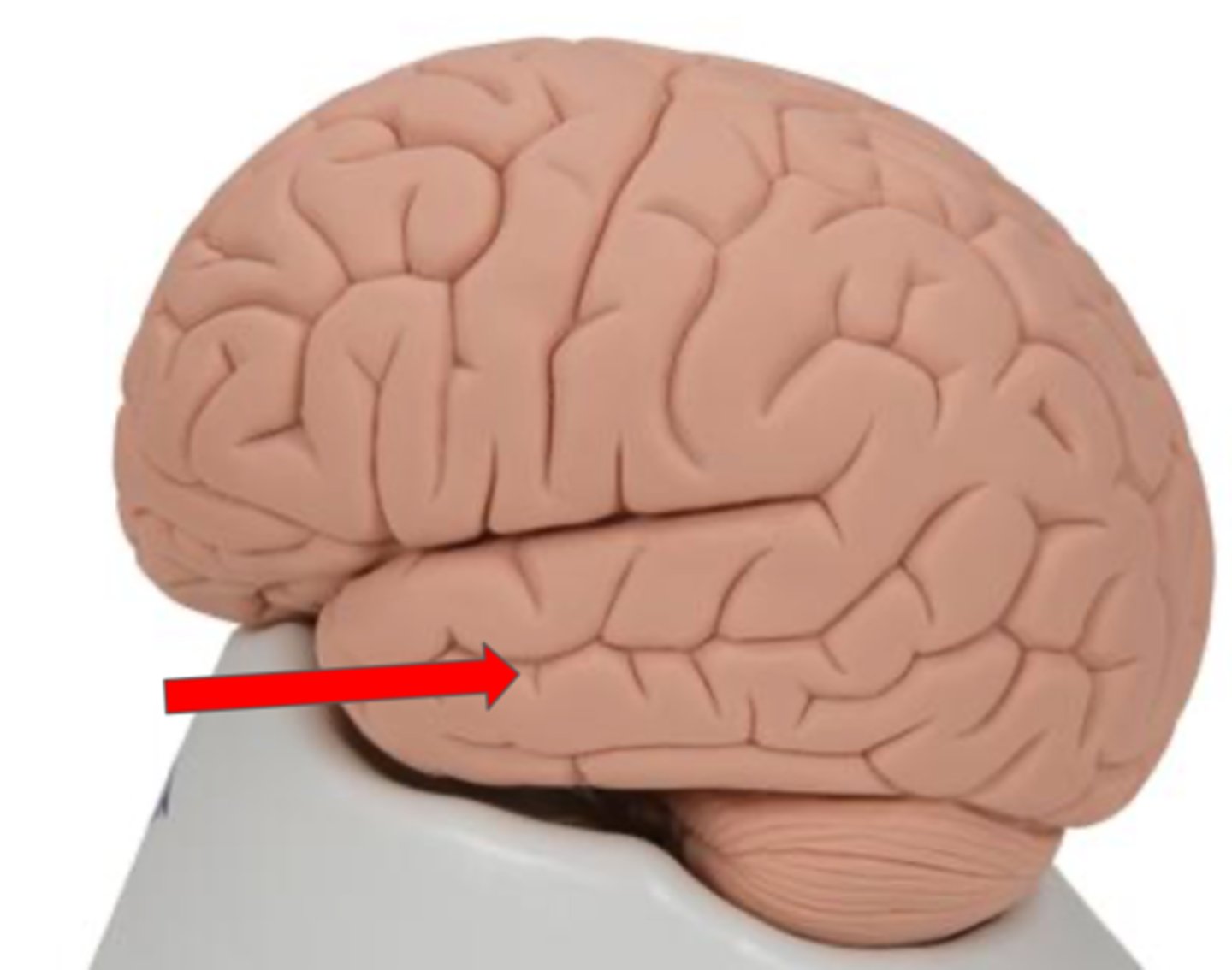
Occipital lobe
Part of the cerebrum responsible for visual processing
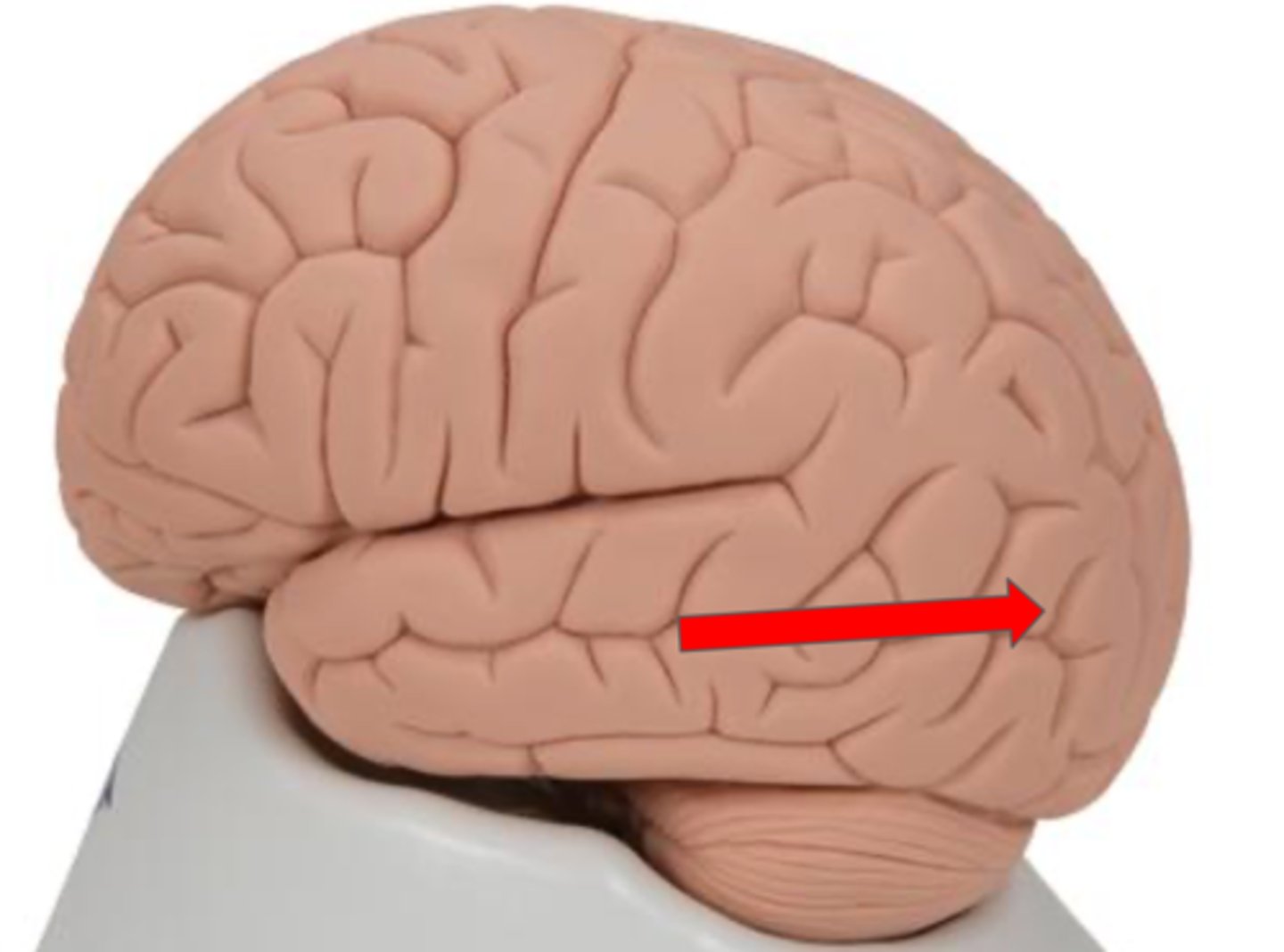
Insula
deep to temporal lobe
Corpus Callosum
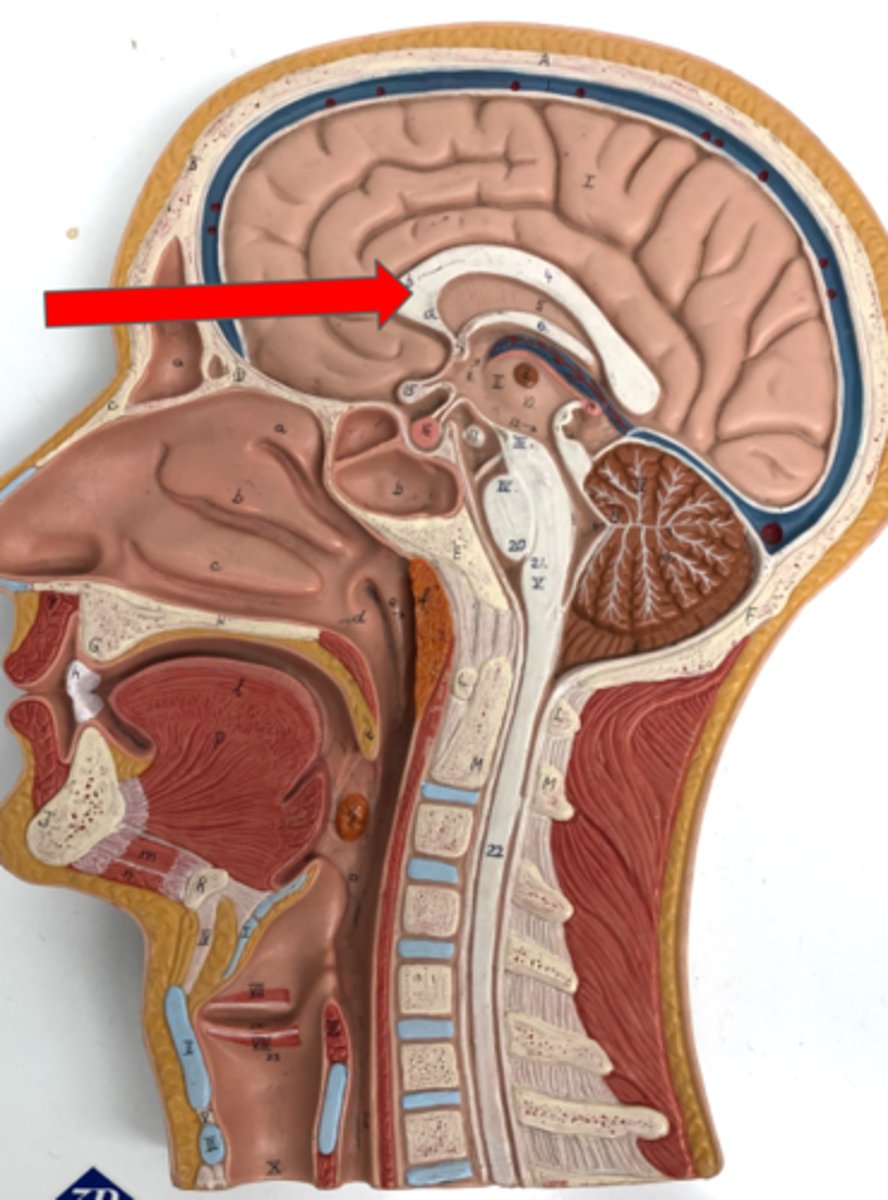
Septum pellucidum
Thin membrane that separates the lateral ventricles
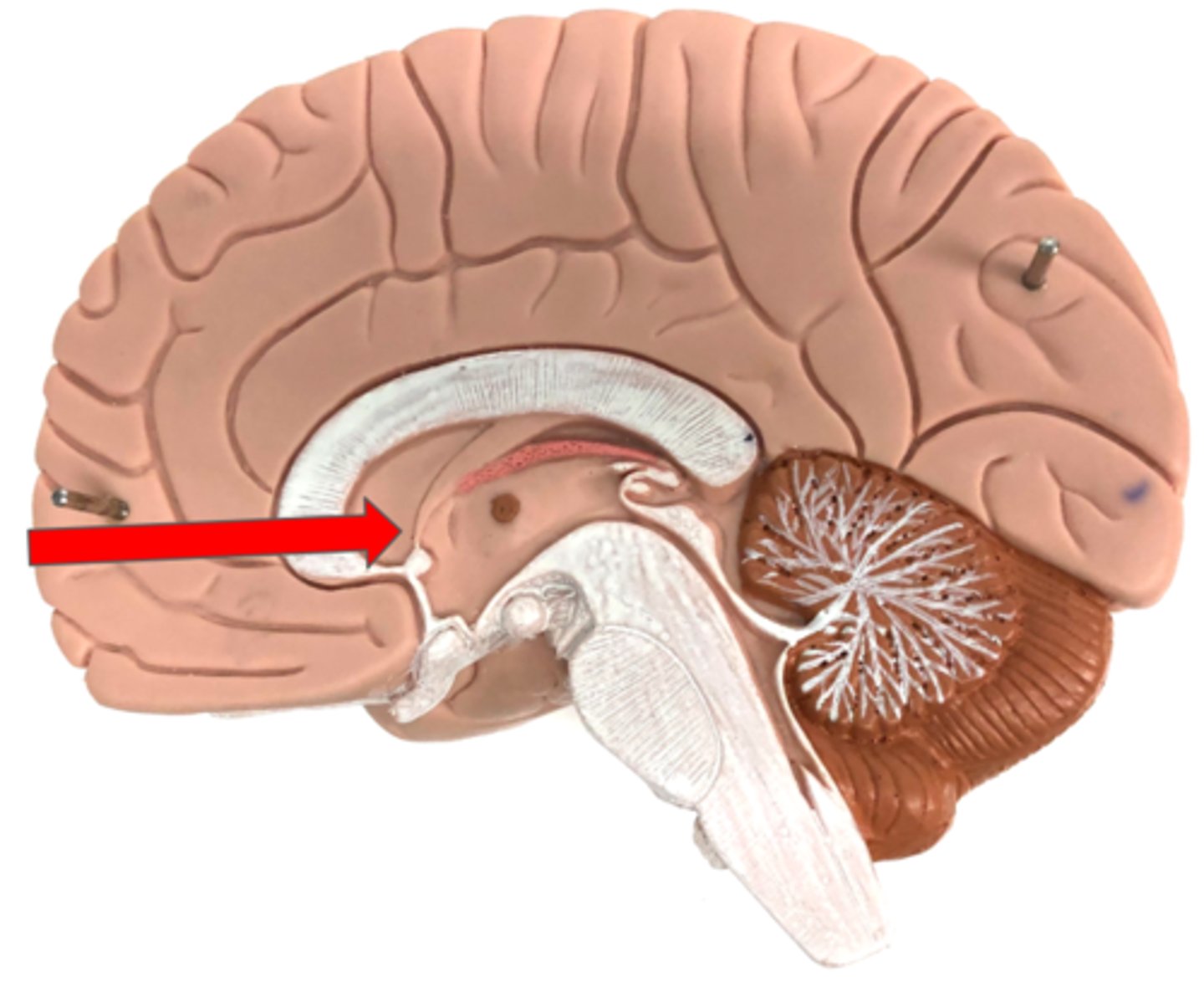
central canal (brain model)
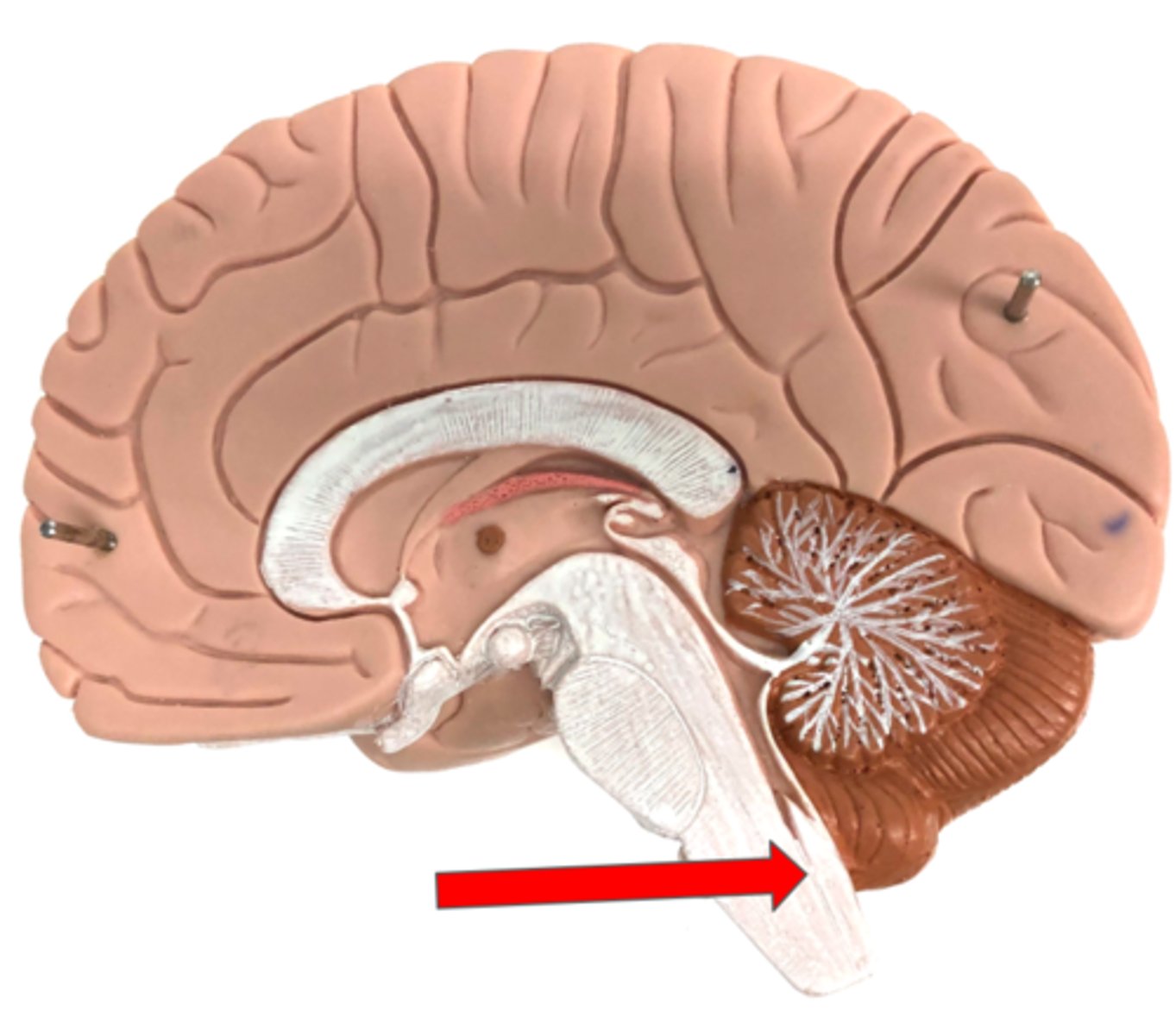
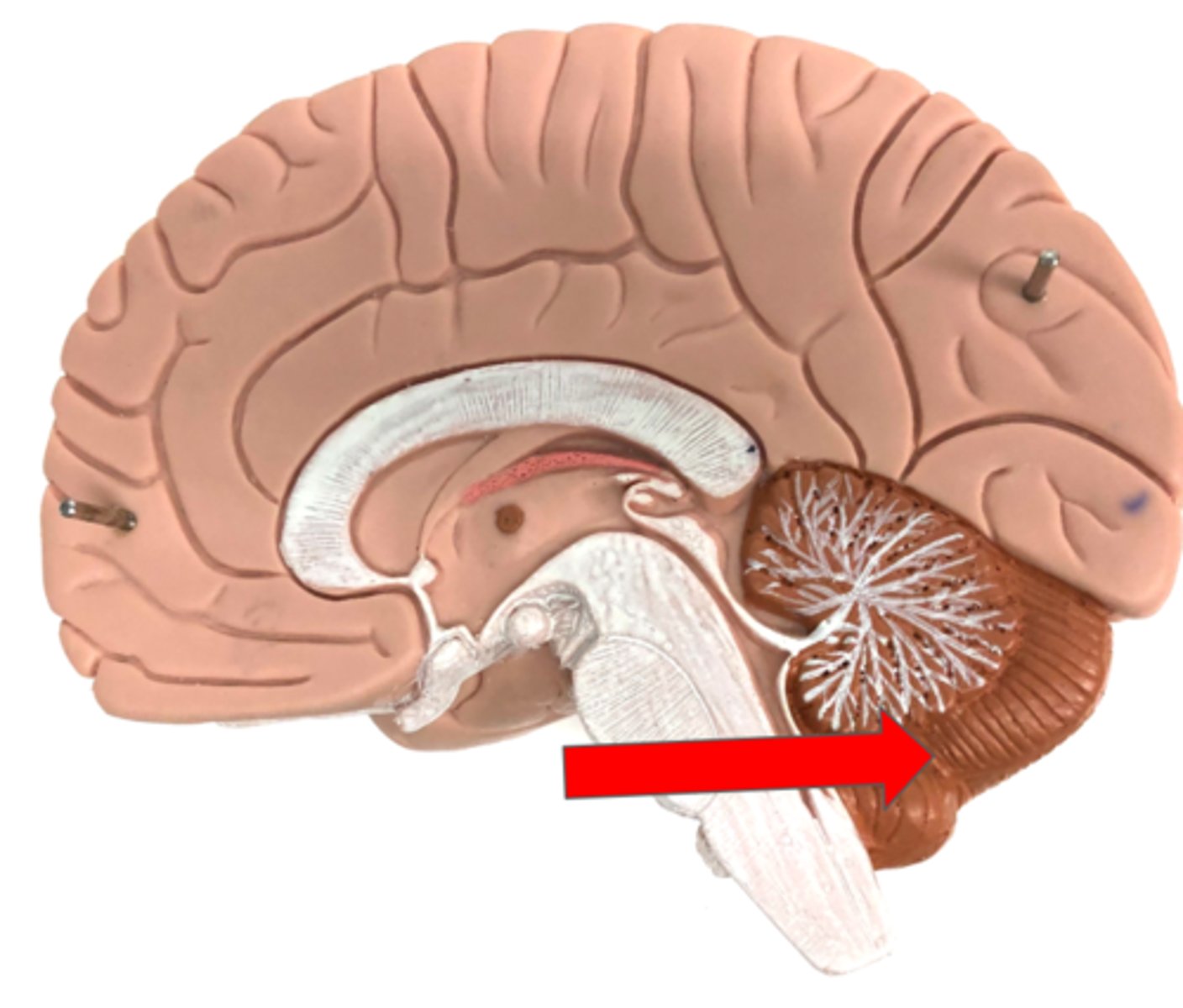
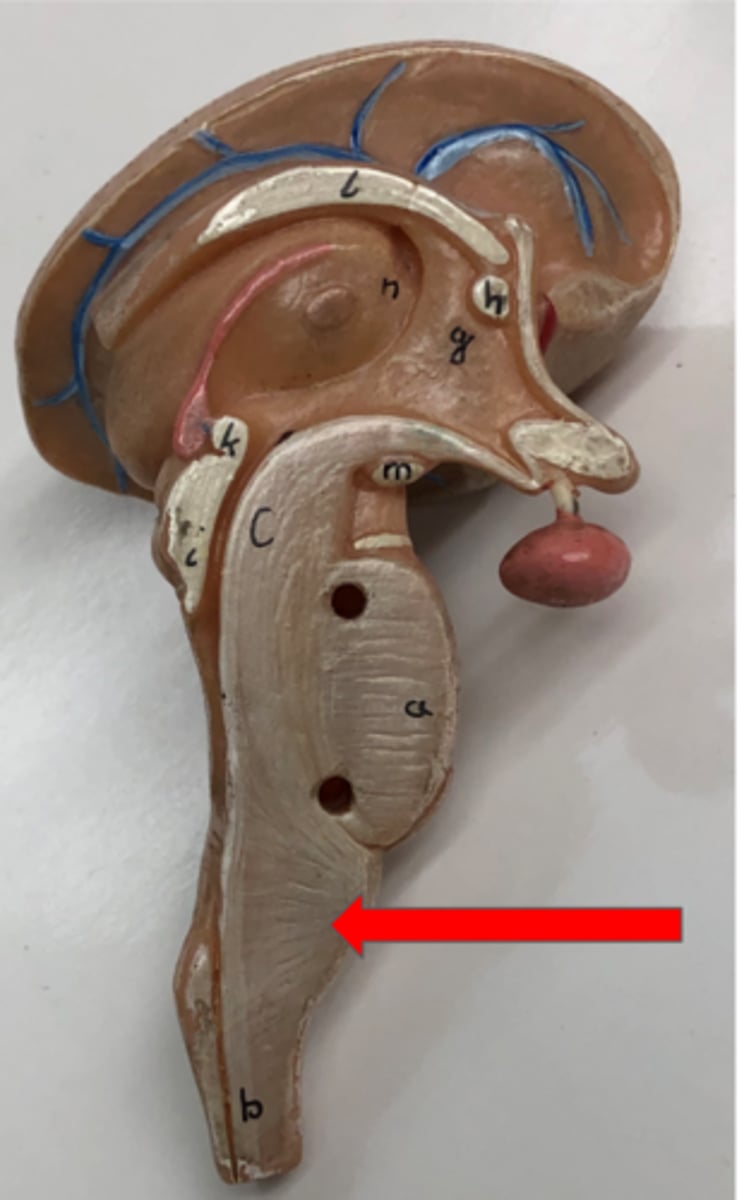
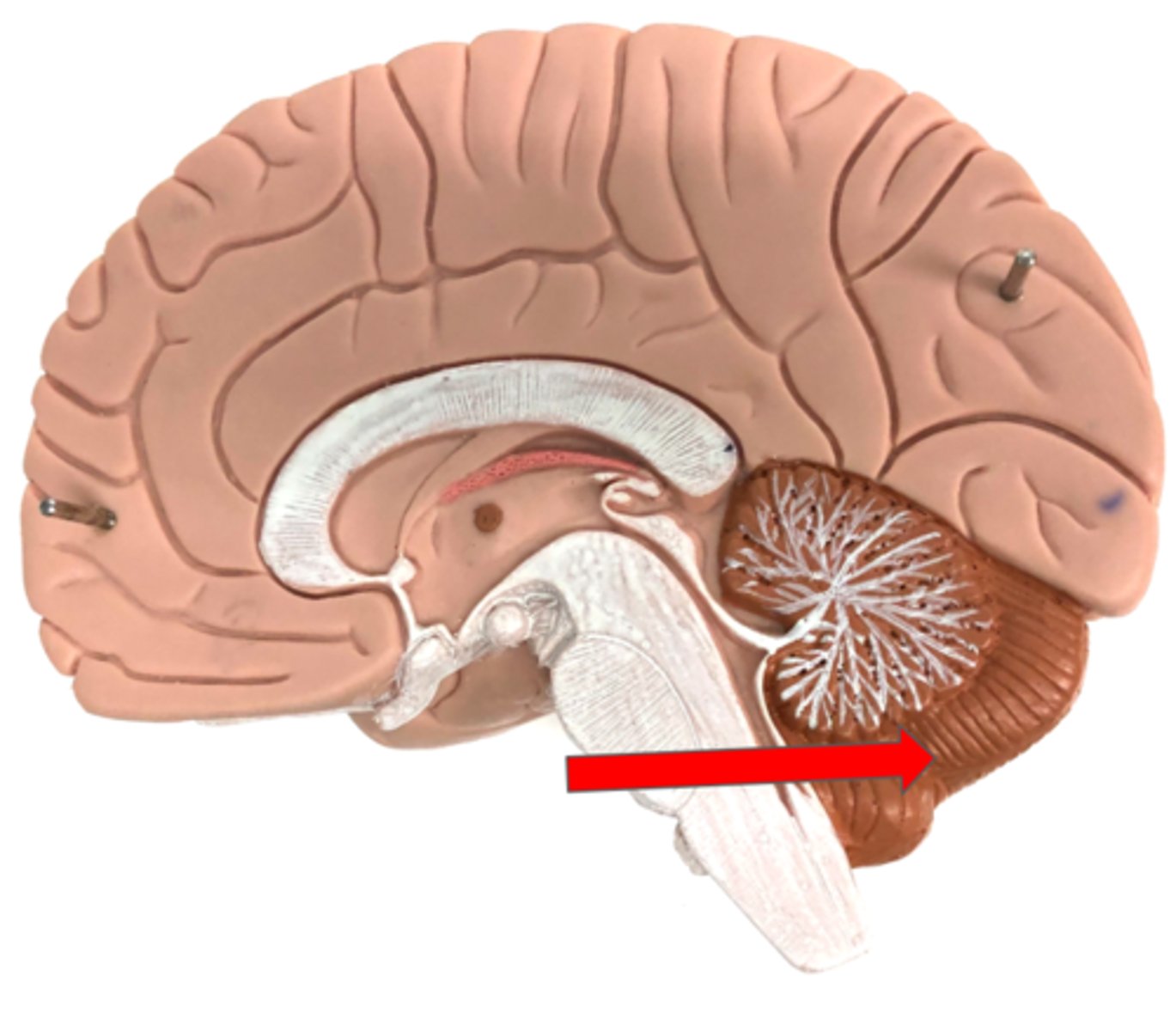
Cerebellum
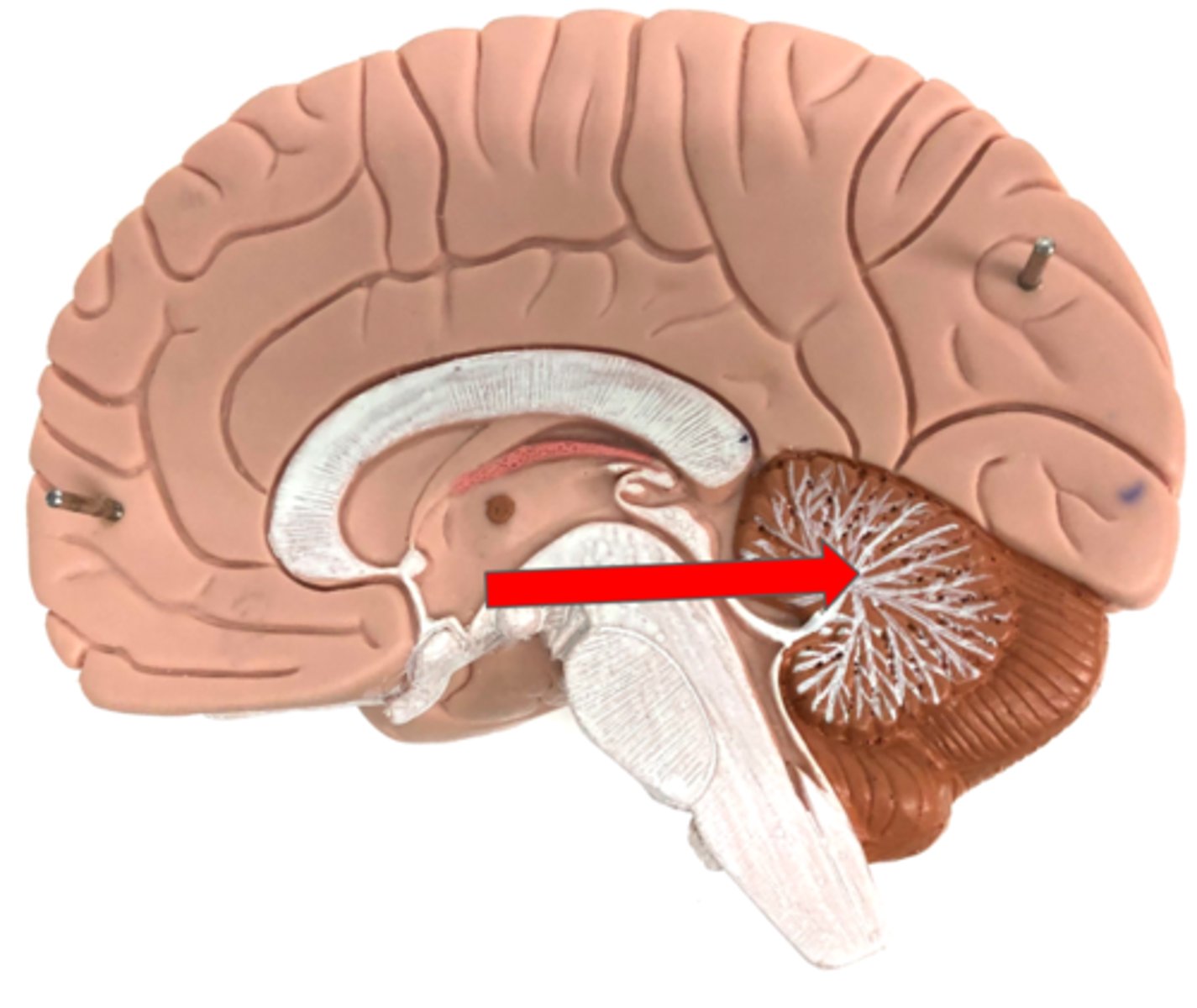
Arbor vitae
I olfactory- smell
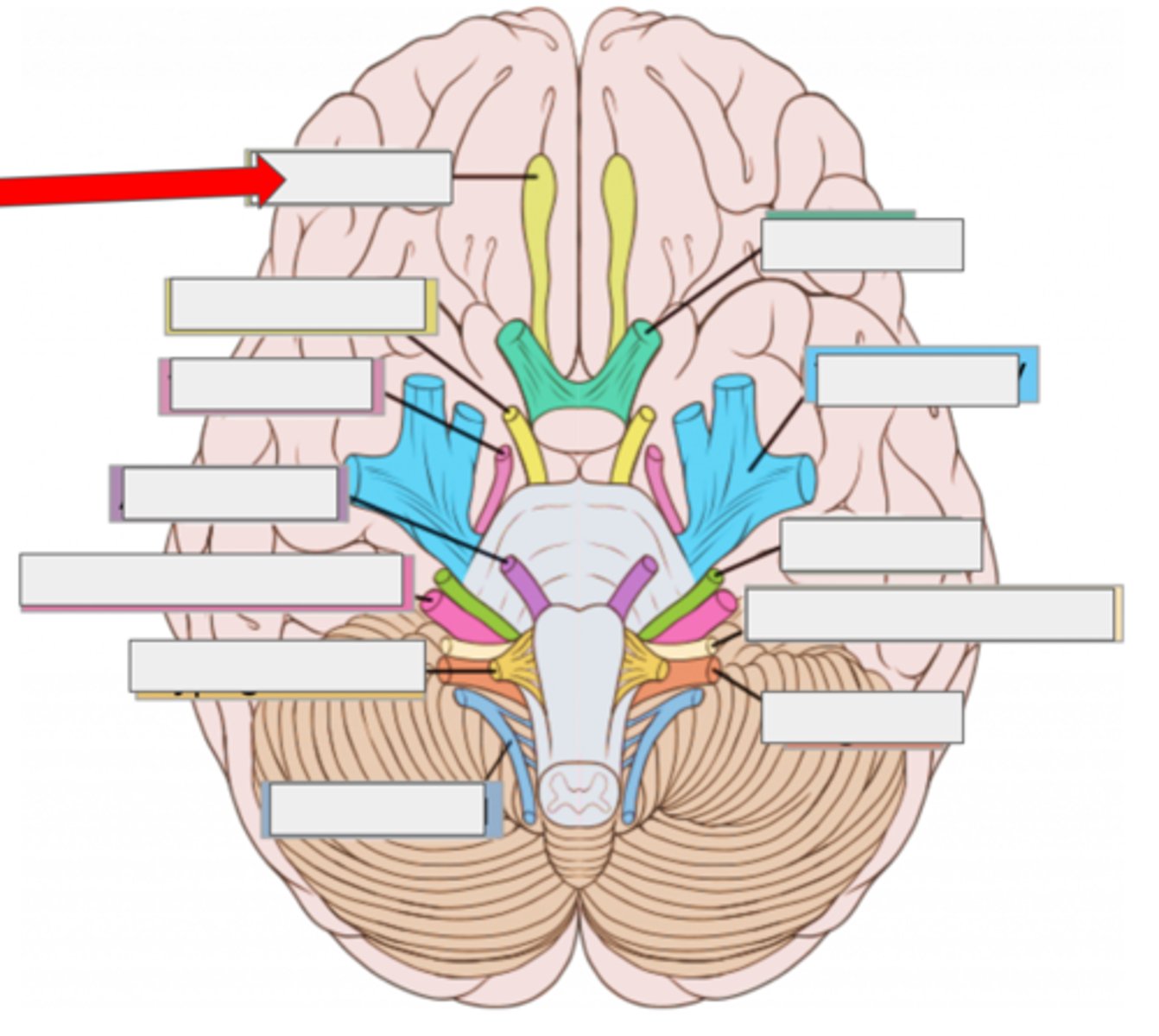
II optic- sight
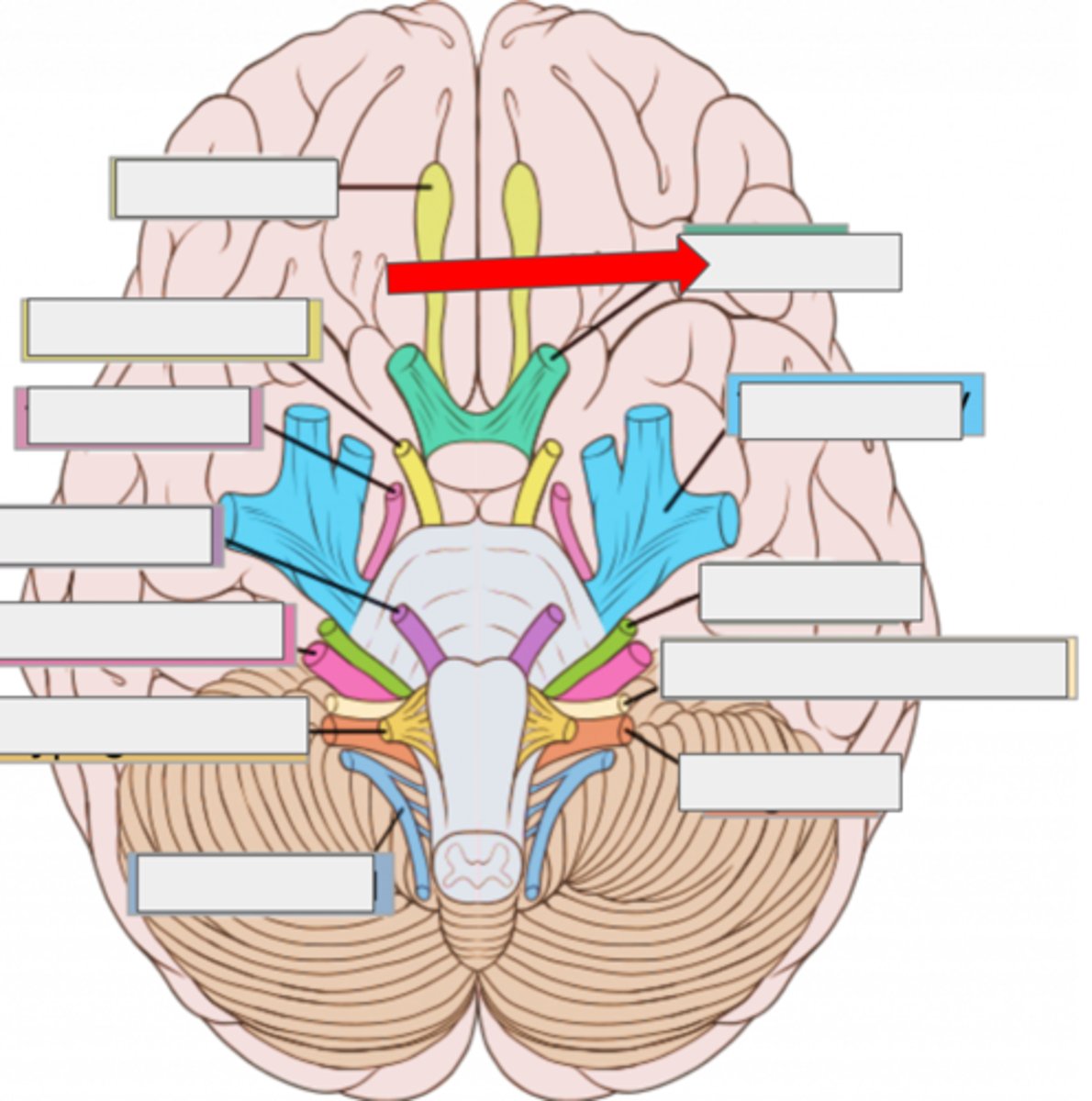
III oculomotor- moves eye
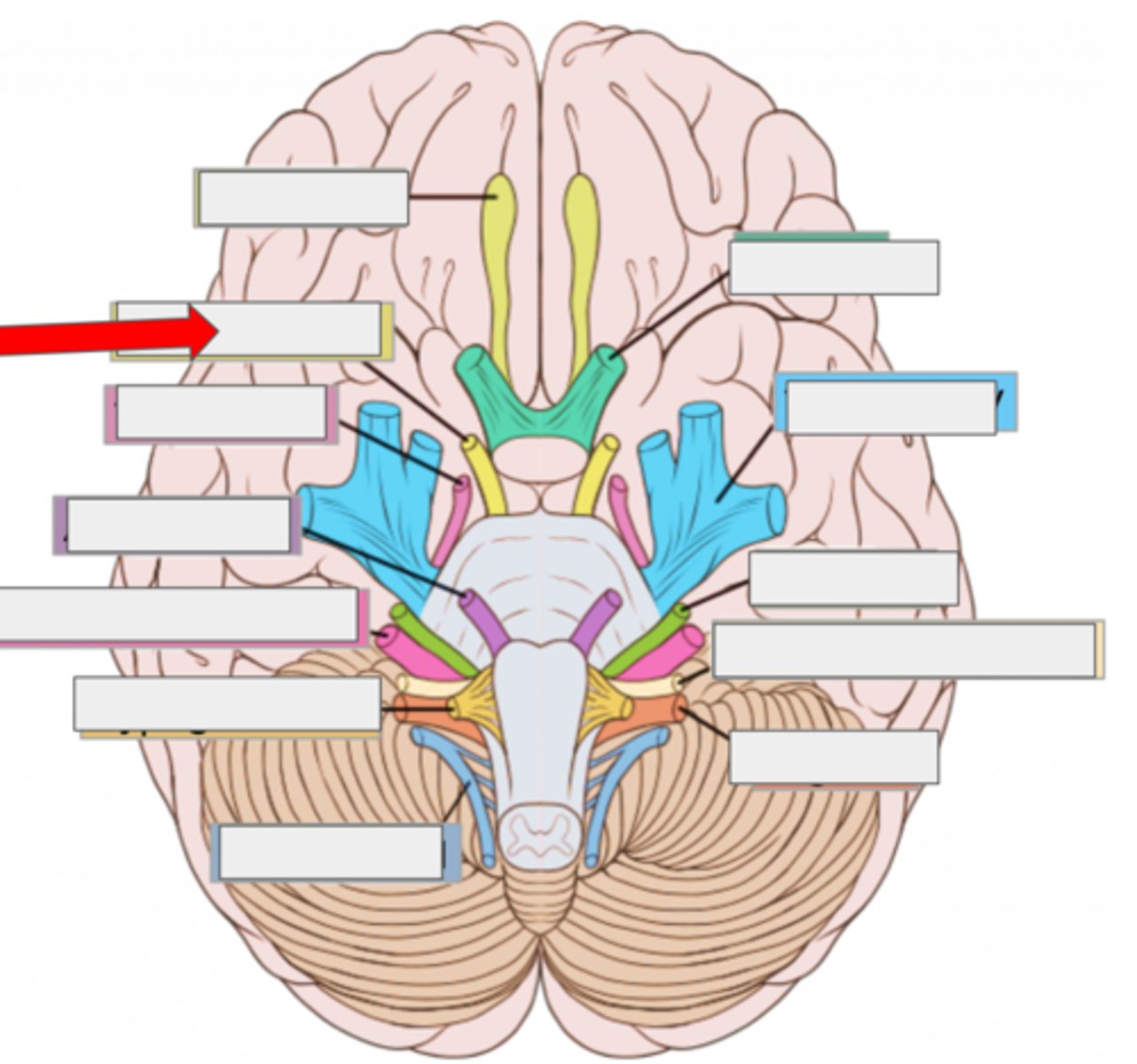
IV trochlear- moves eye
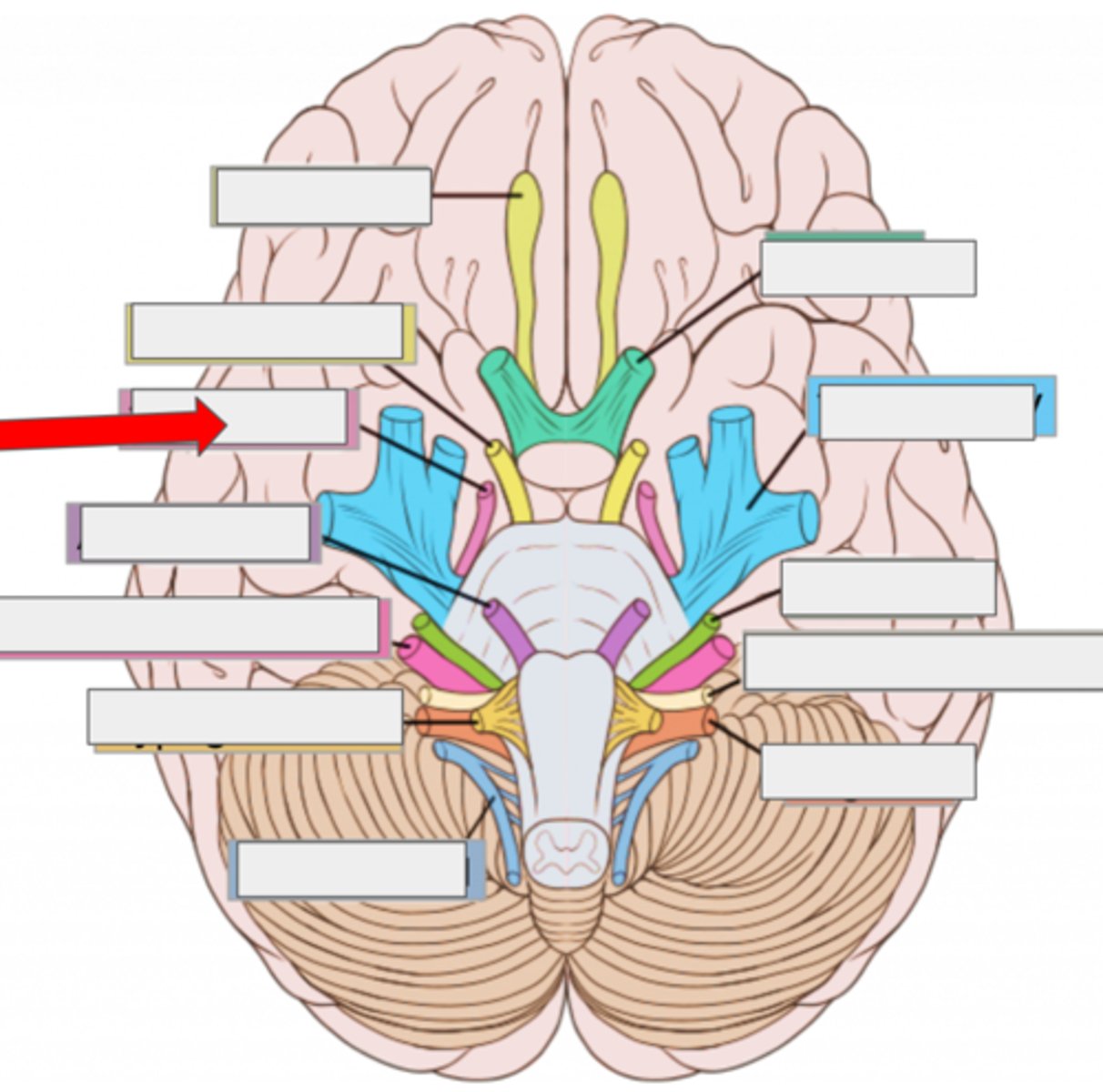
V trigeminal- face sensation
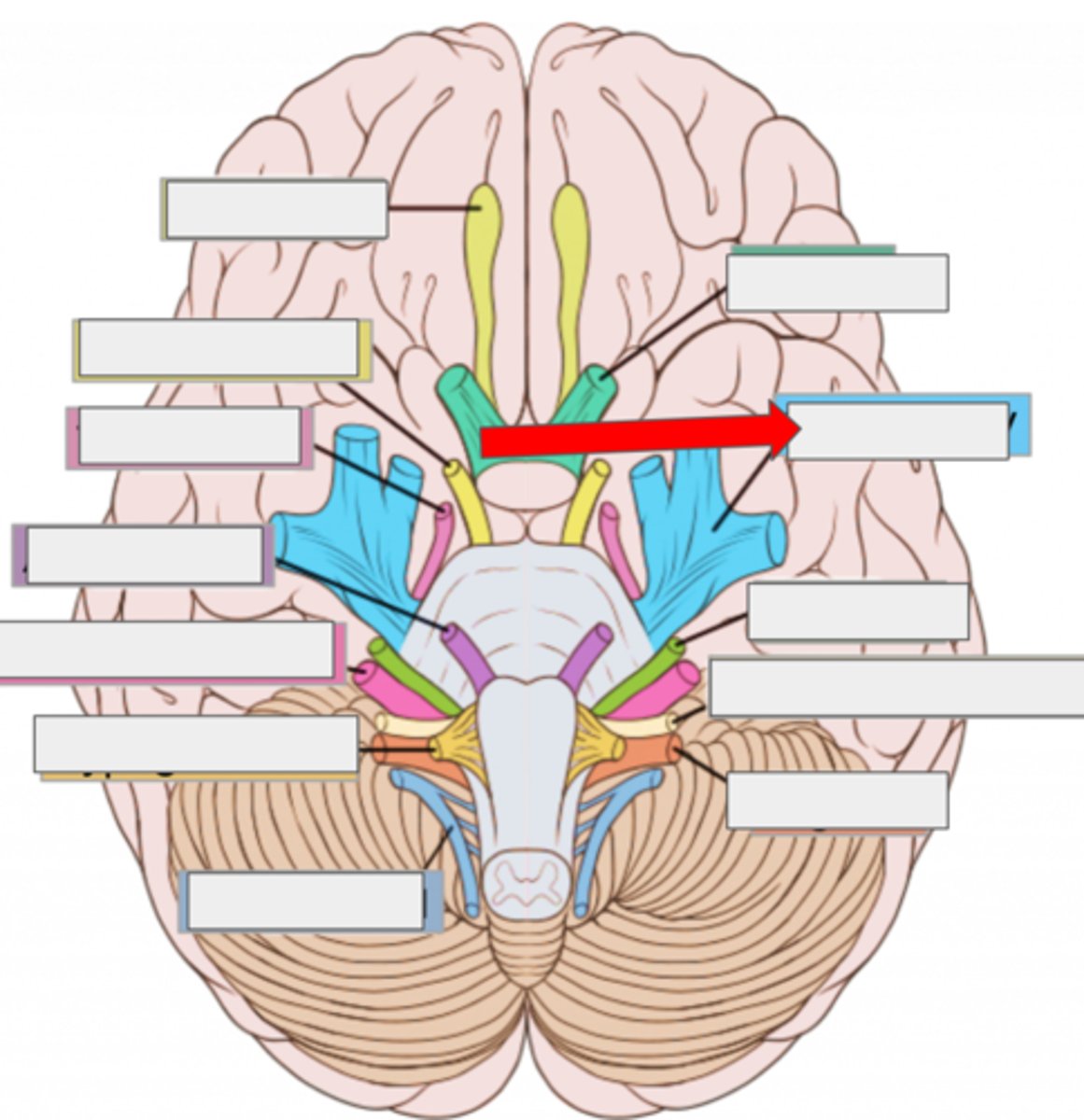
VI abducens- moves eye
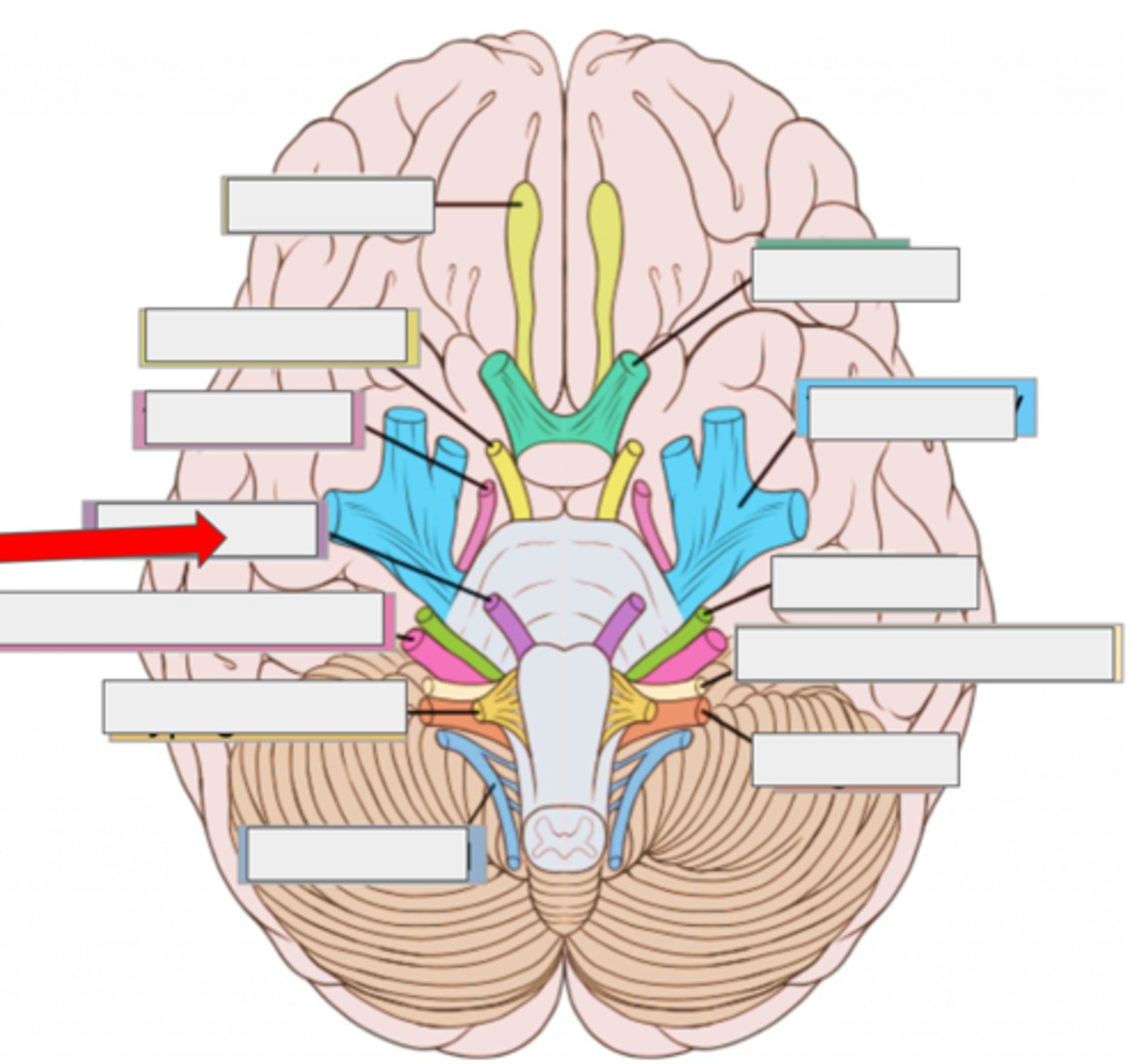
VII facial- moves face, salivate
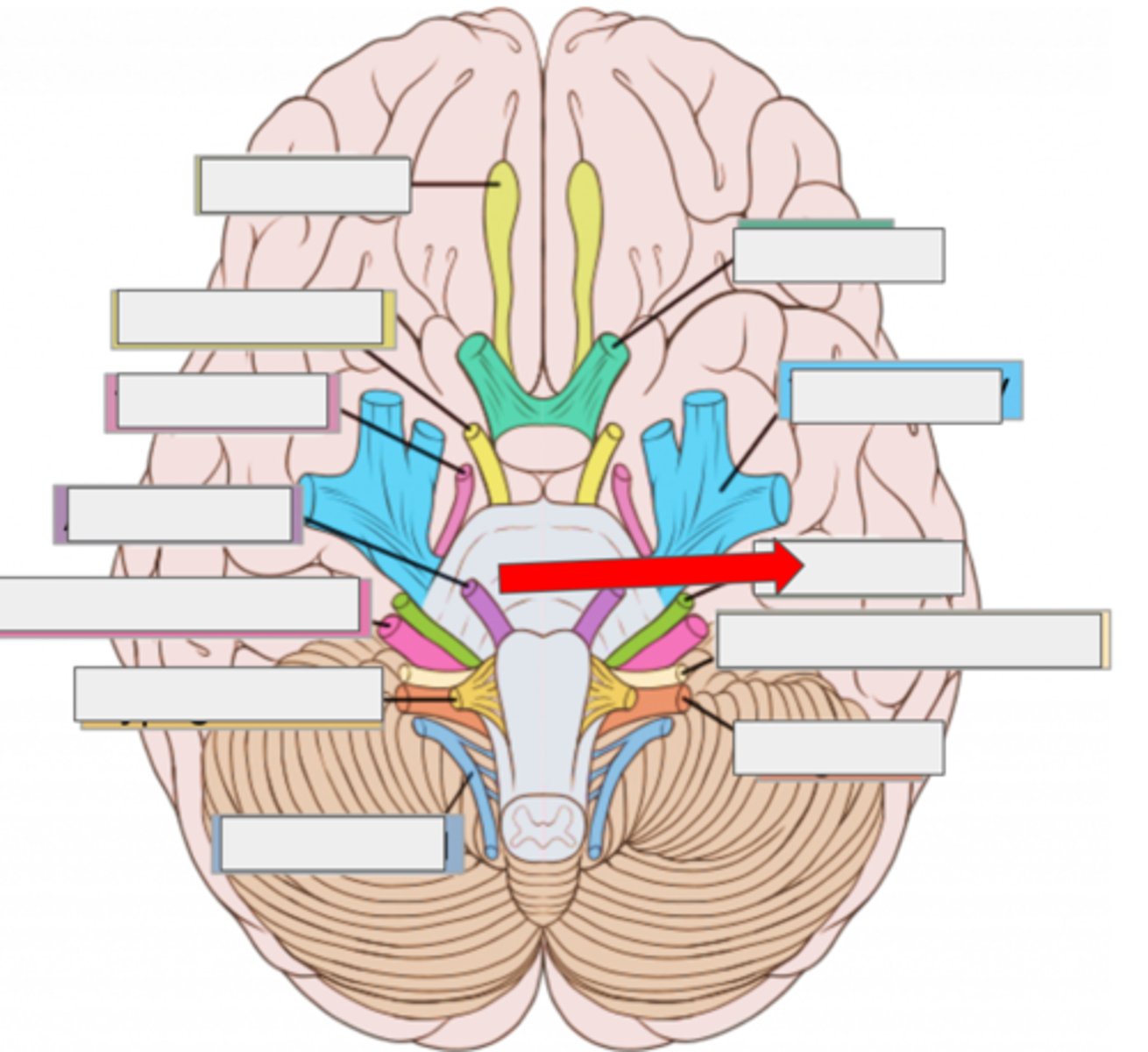
VIII vestibulocochlear- hearing, balance
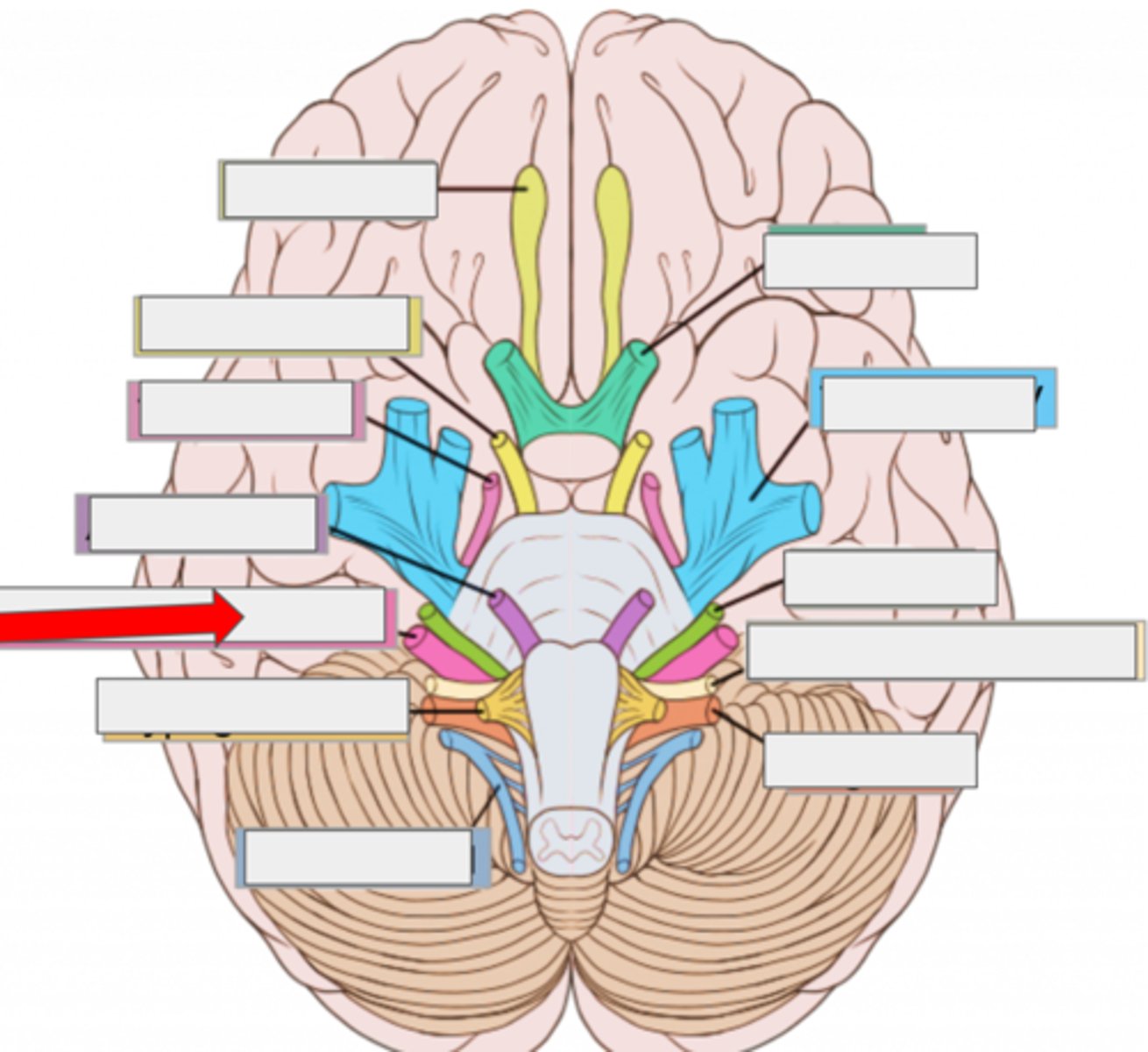
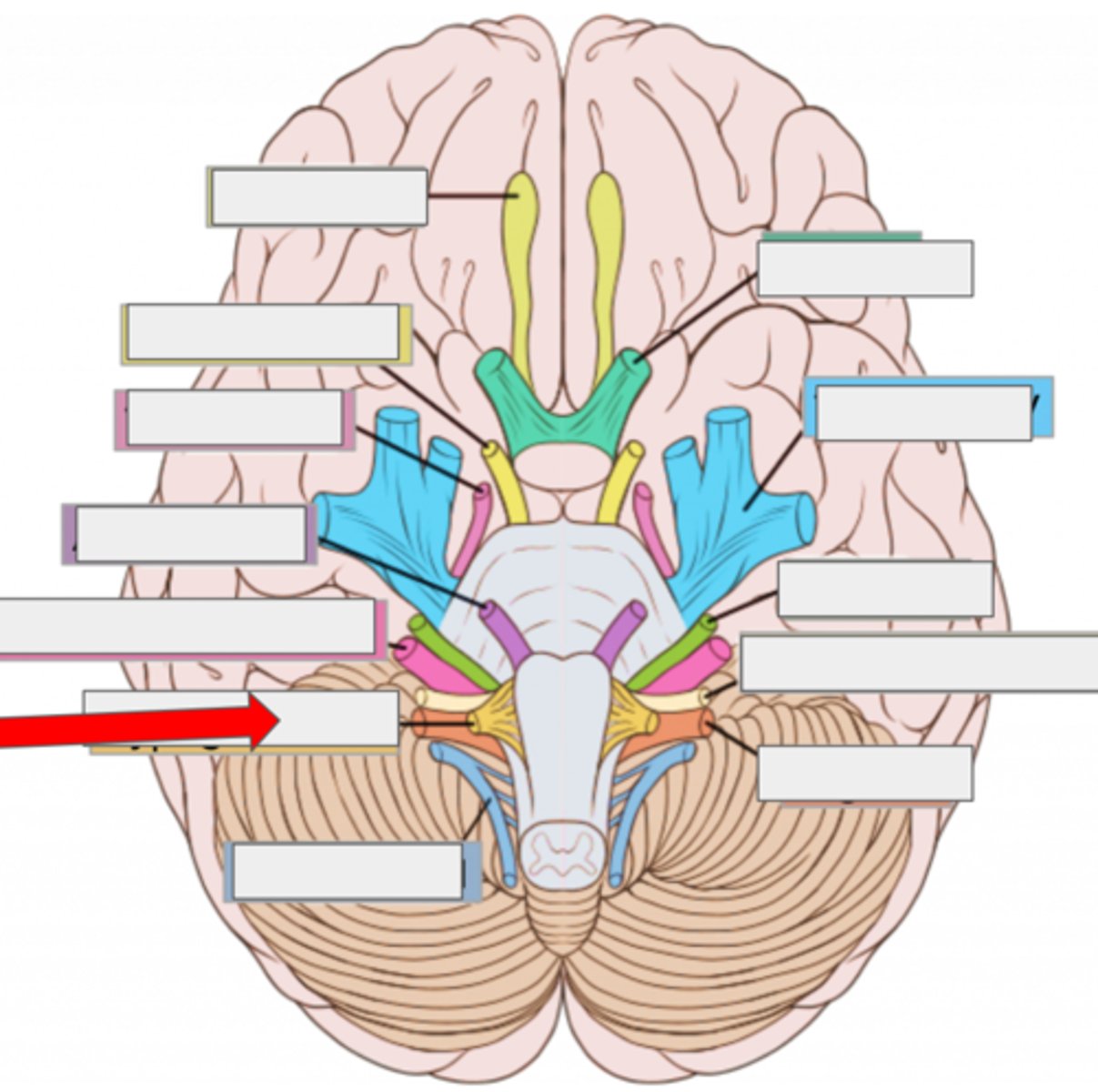
IX glossopharyngeal- taste, swallow
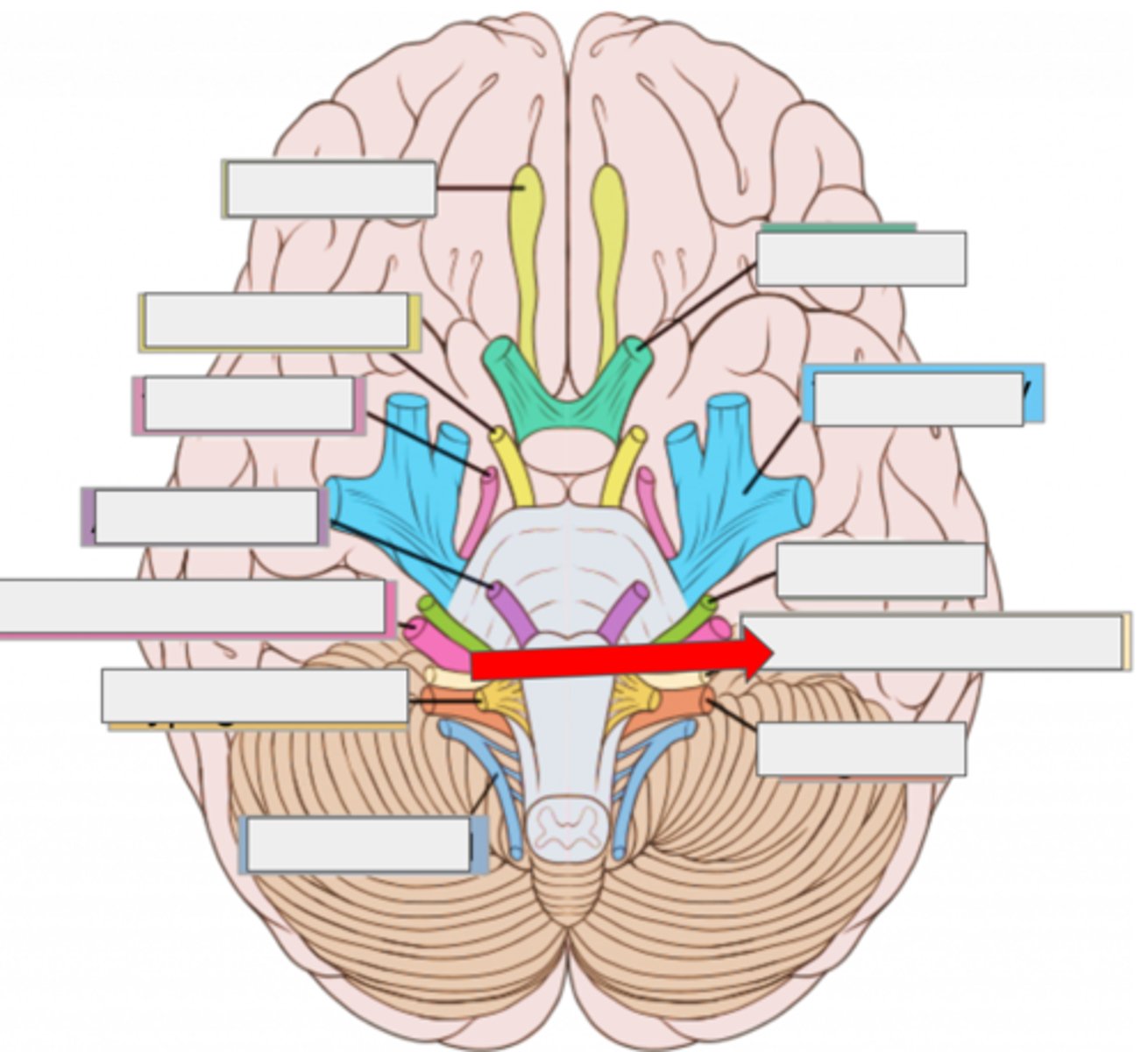
X vagus- heart rate, digestion
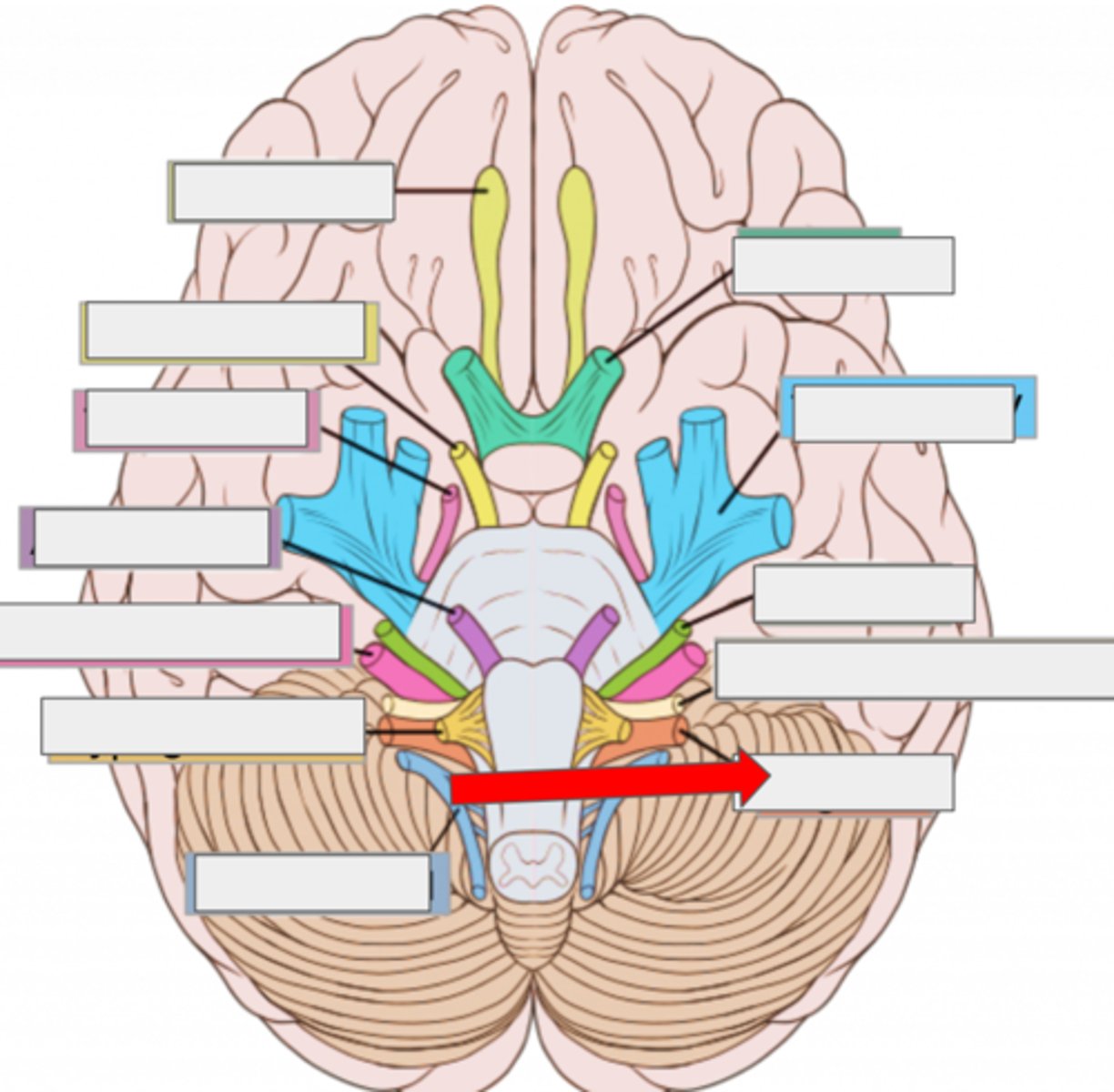
XI accessory- moves head
XII hypoglossal- moves tongue
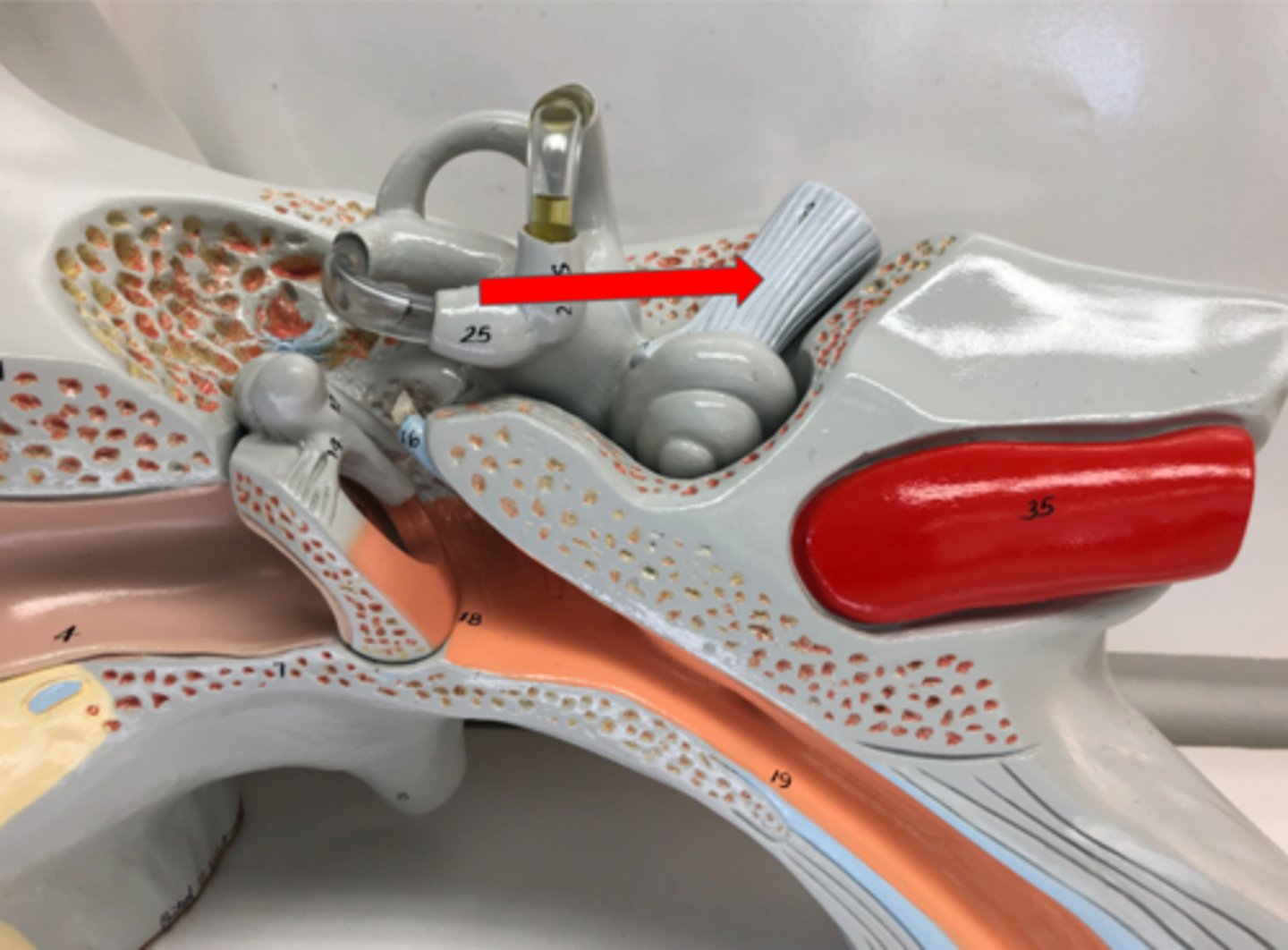
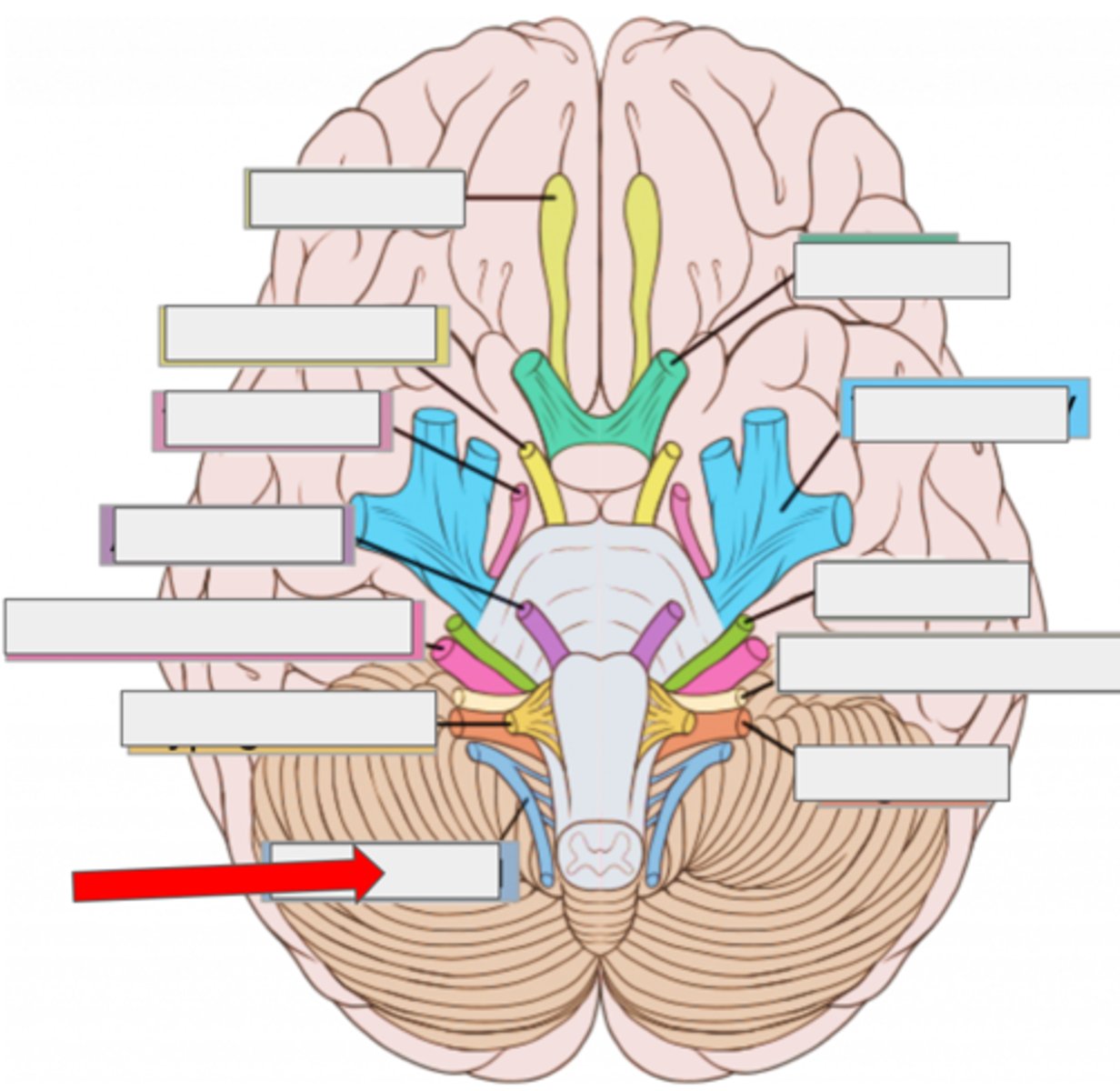
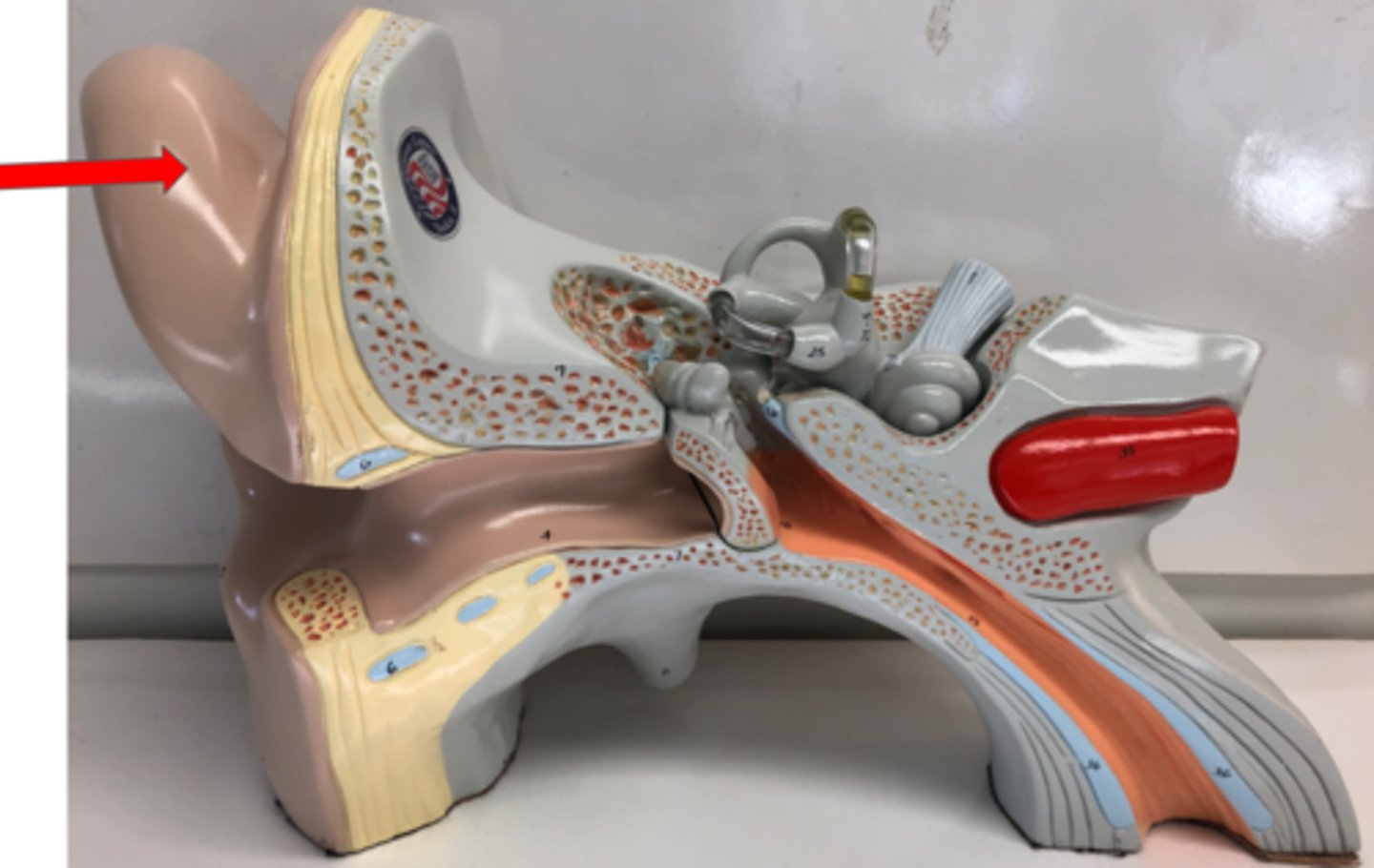
Auricle (OR pinna)
External auditory canal OR external acoustic meatus
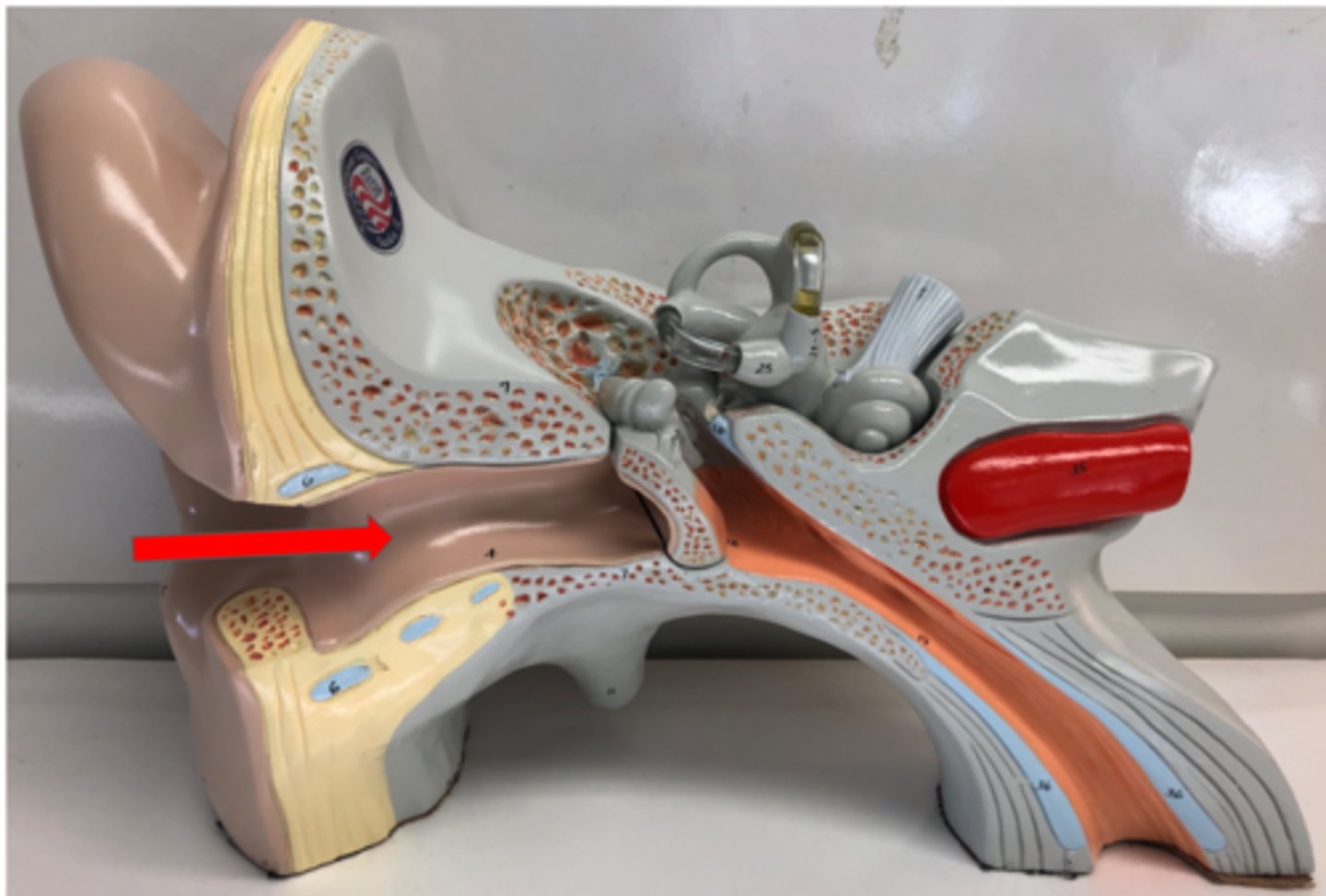
Tympanic membrane
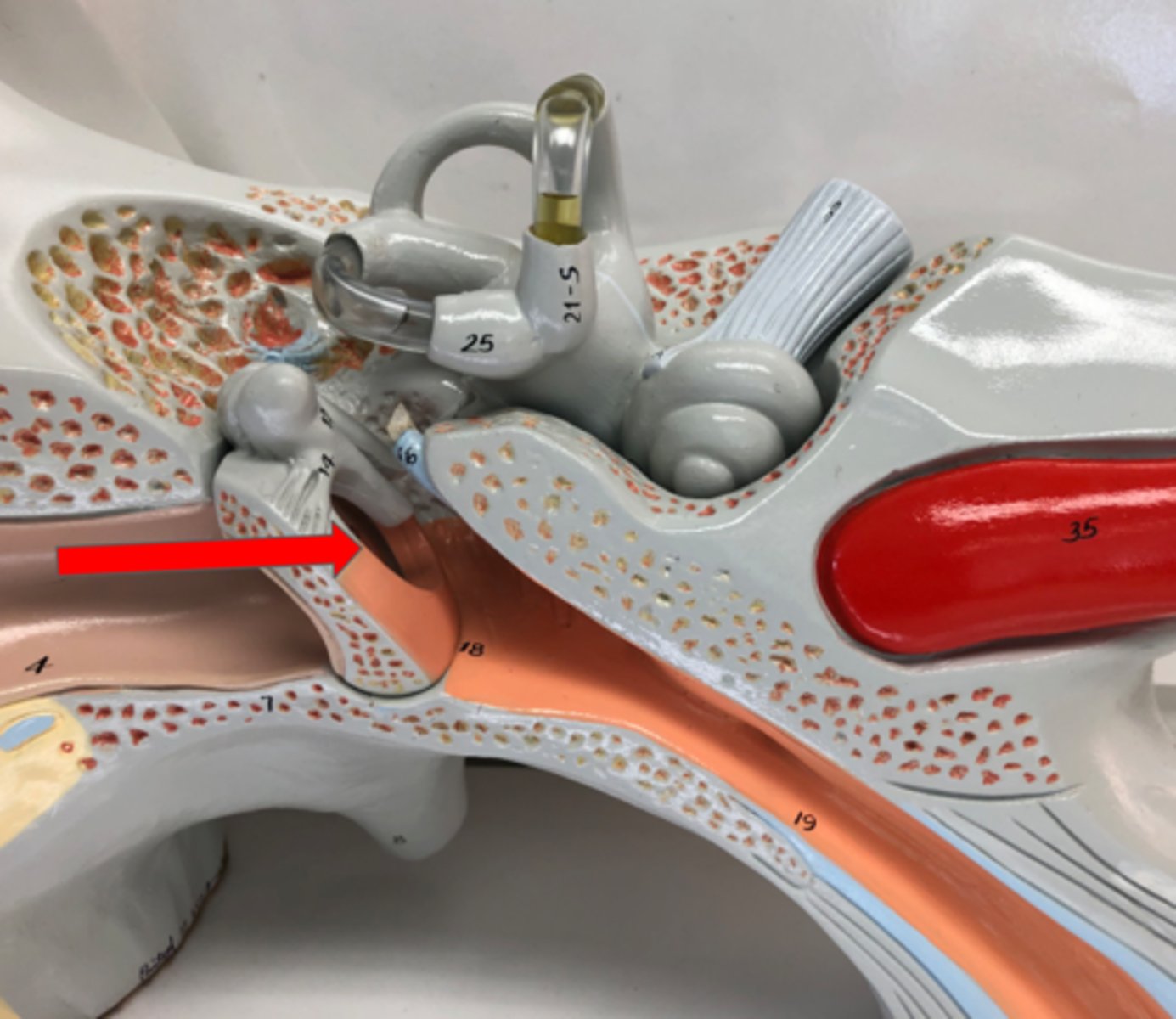

Middle ear
Cavity between the eardrum and inner ear
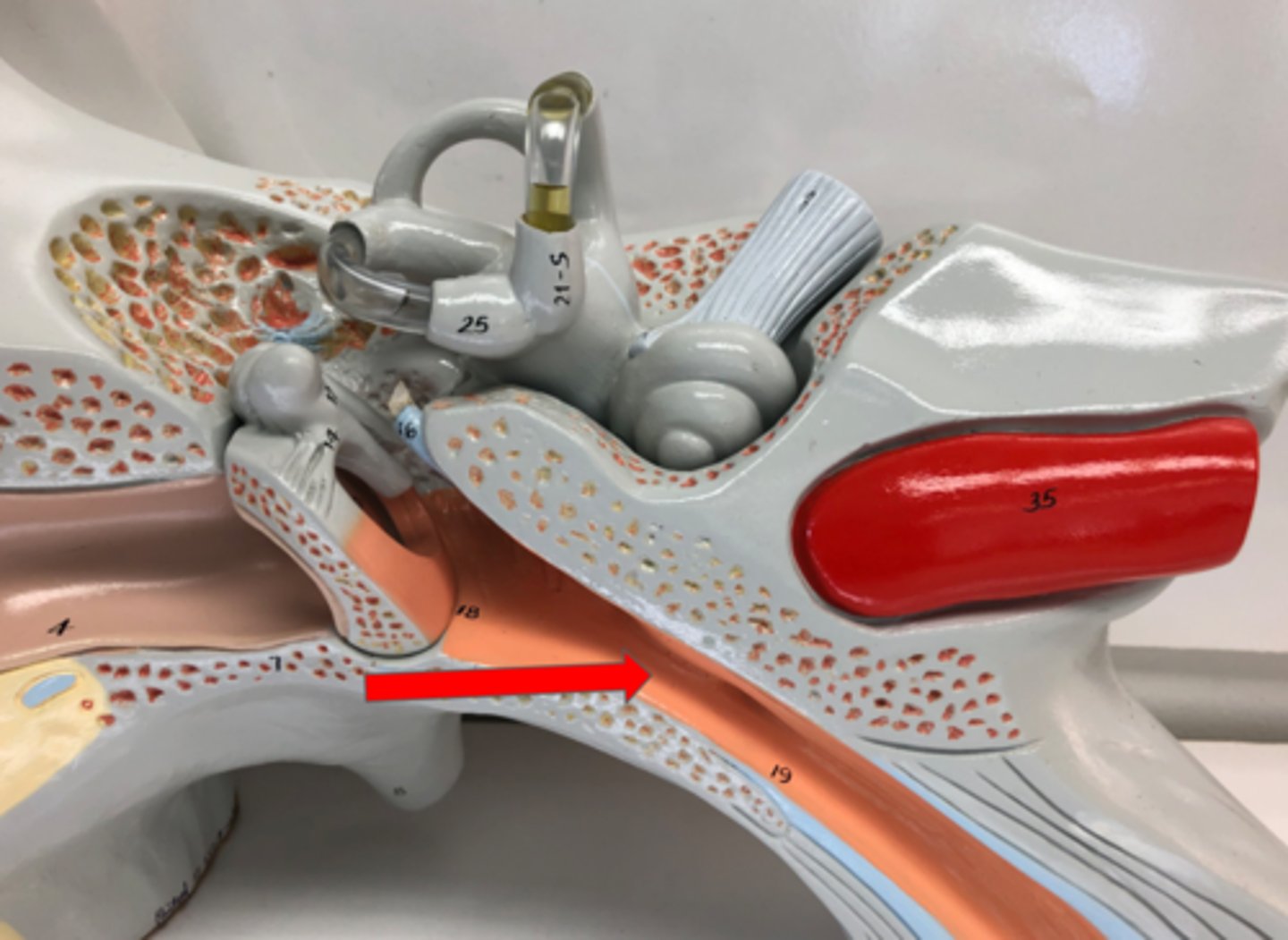
Pharyngotympanic tube
Connects middle eat to throat
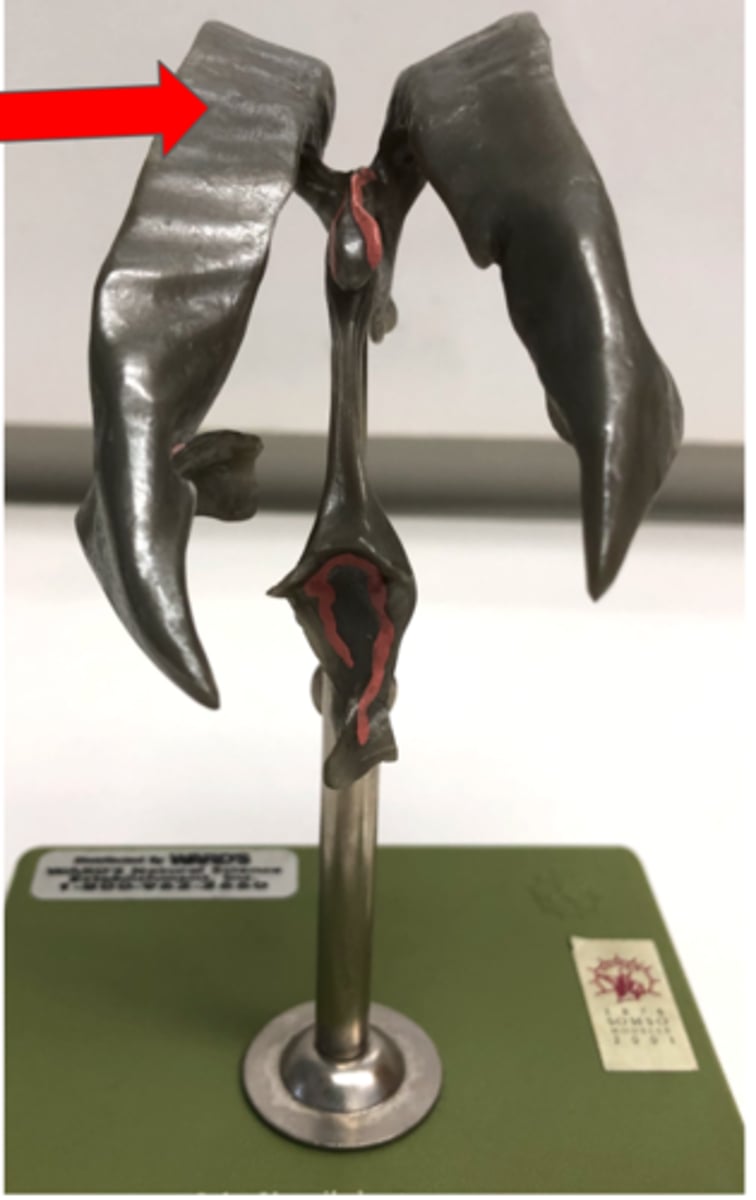
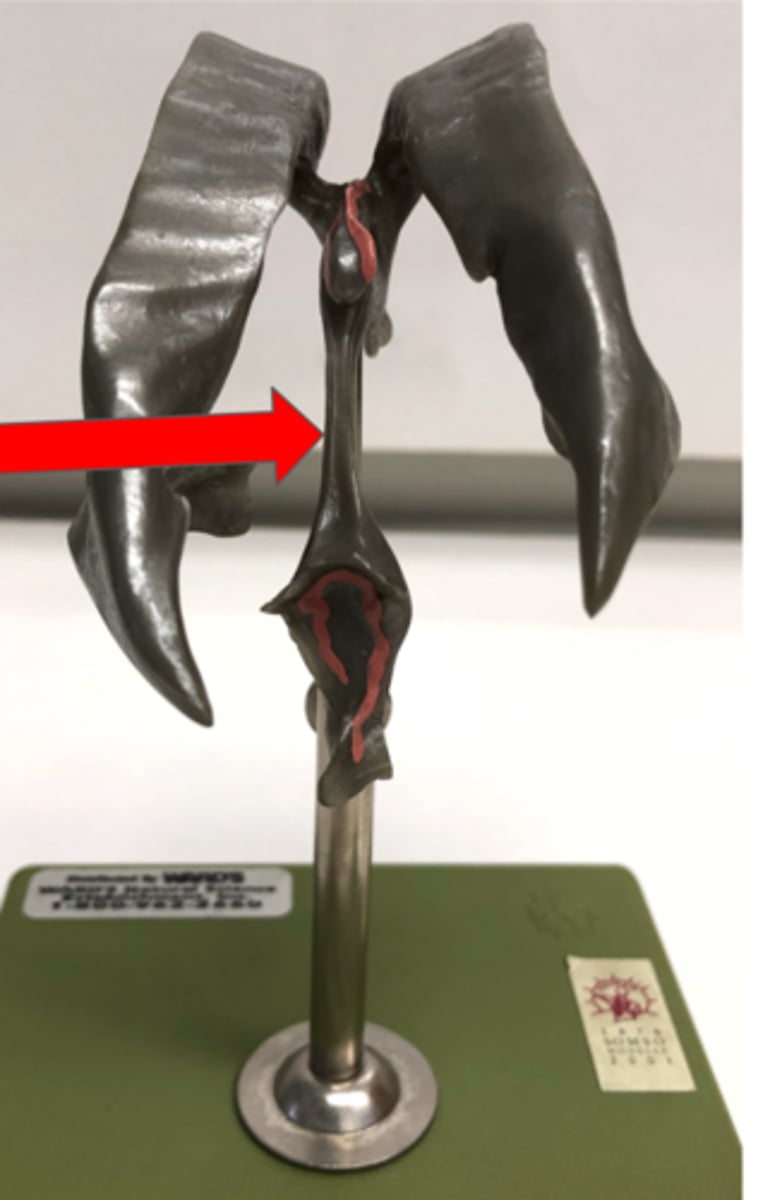
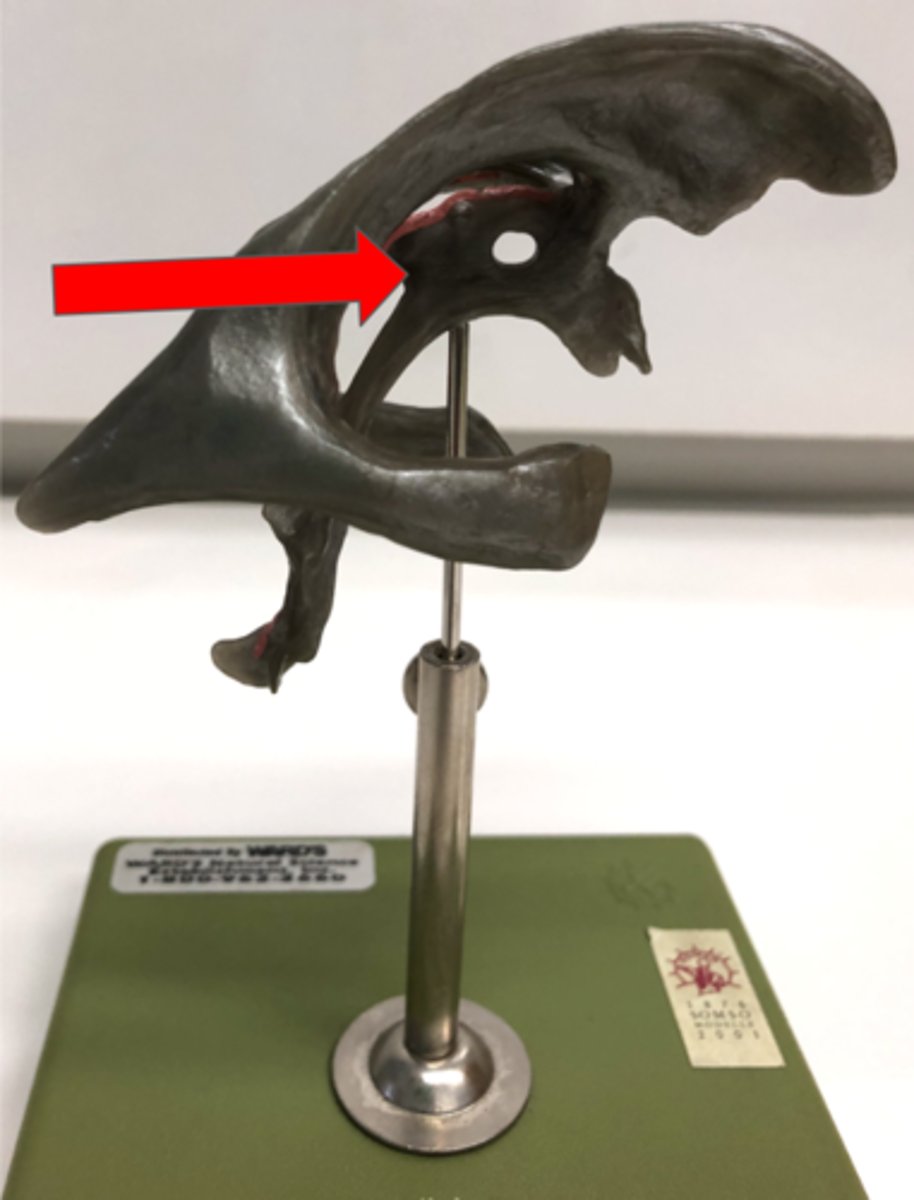
Auditory Ossicles
Three small bones in the middle ear
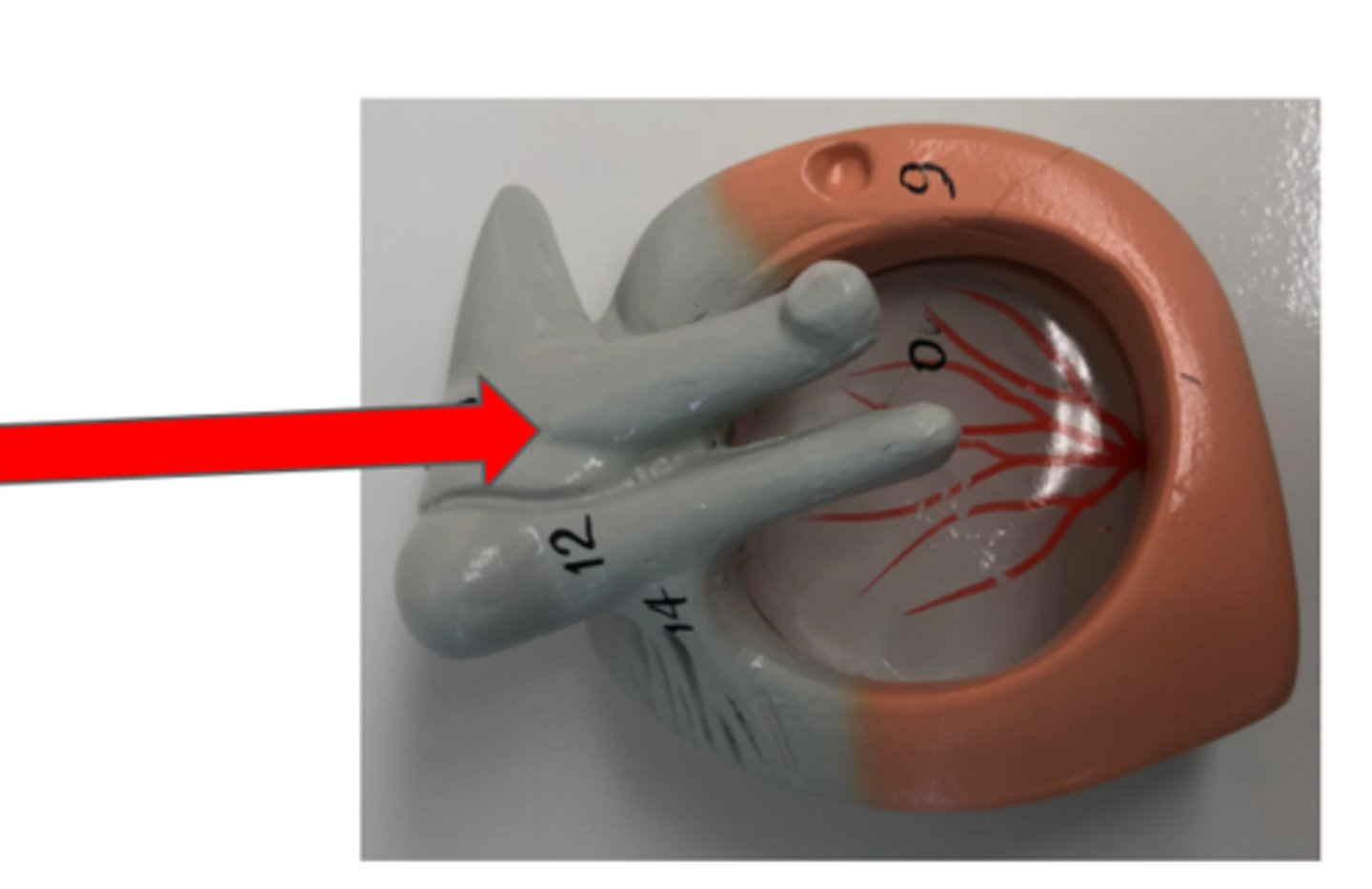
Malleus
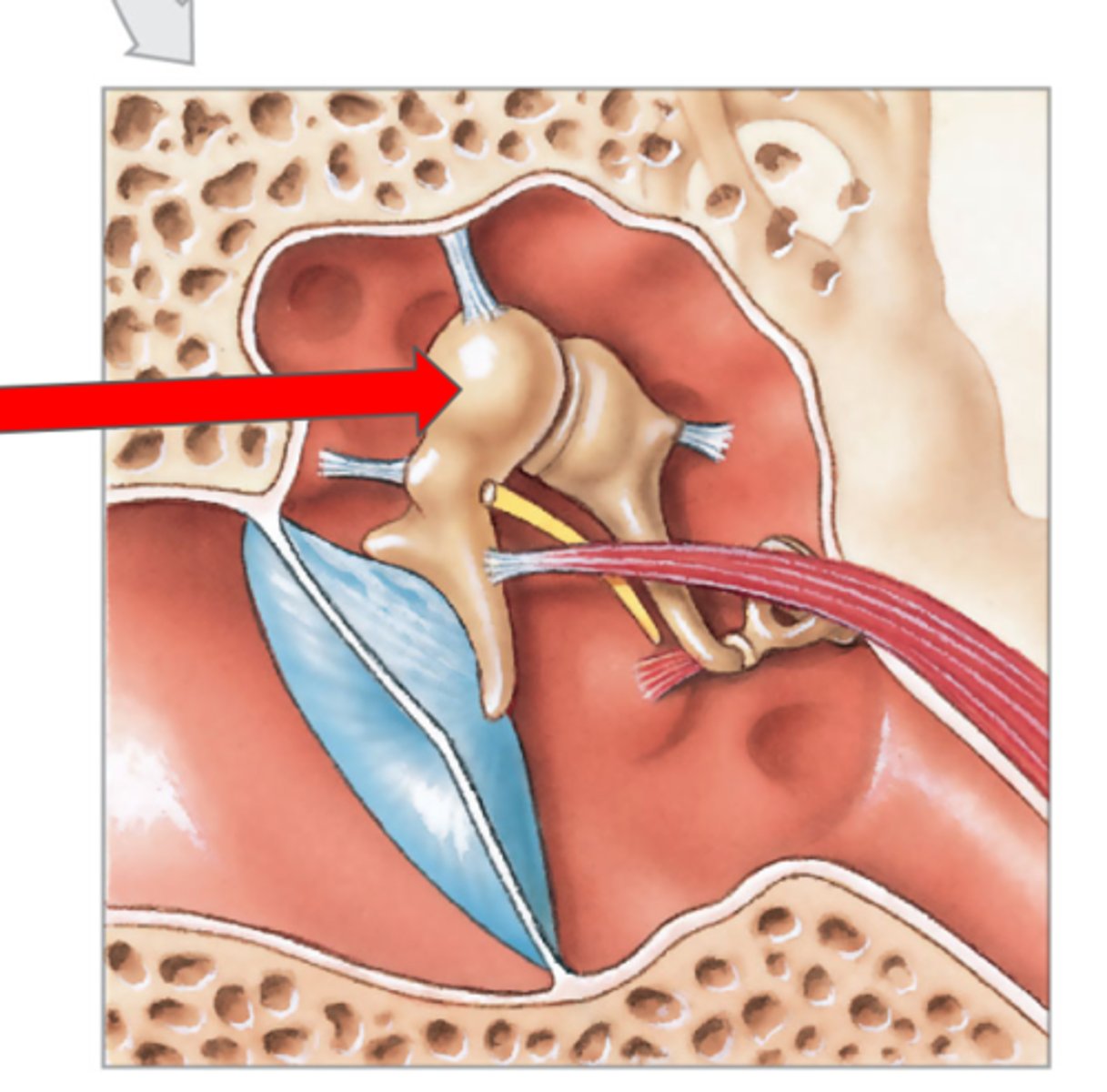
Incus
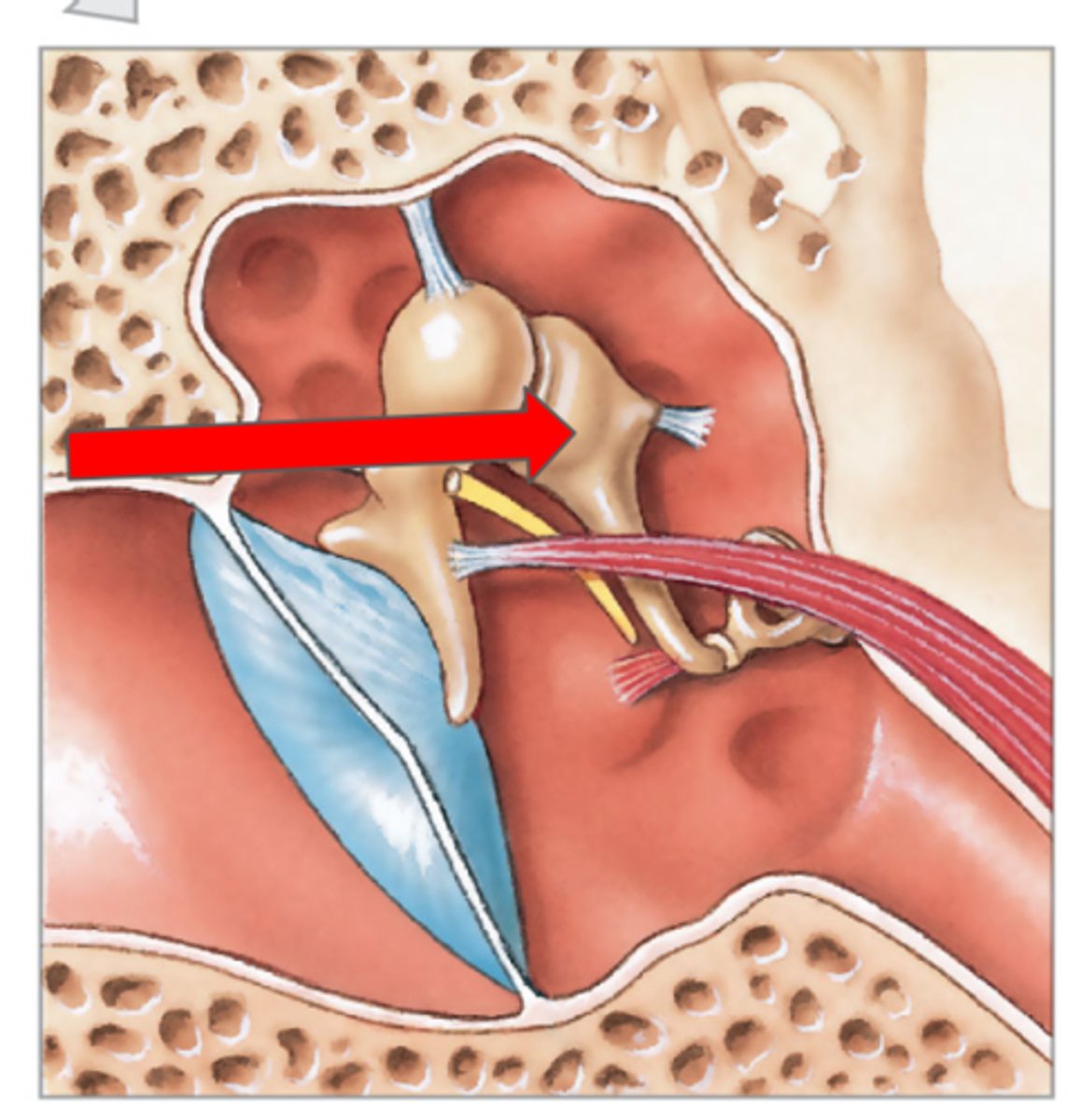
Stapes—connects to oval window
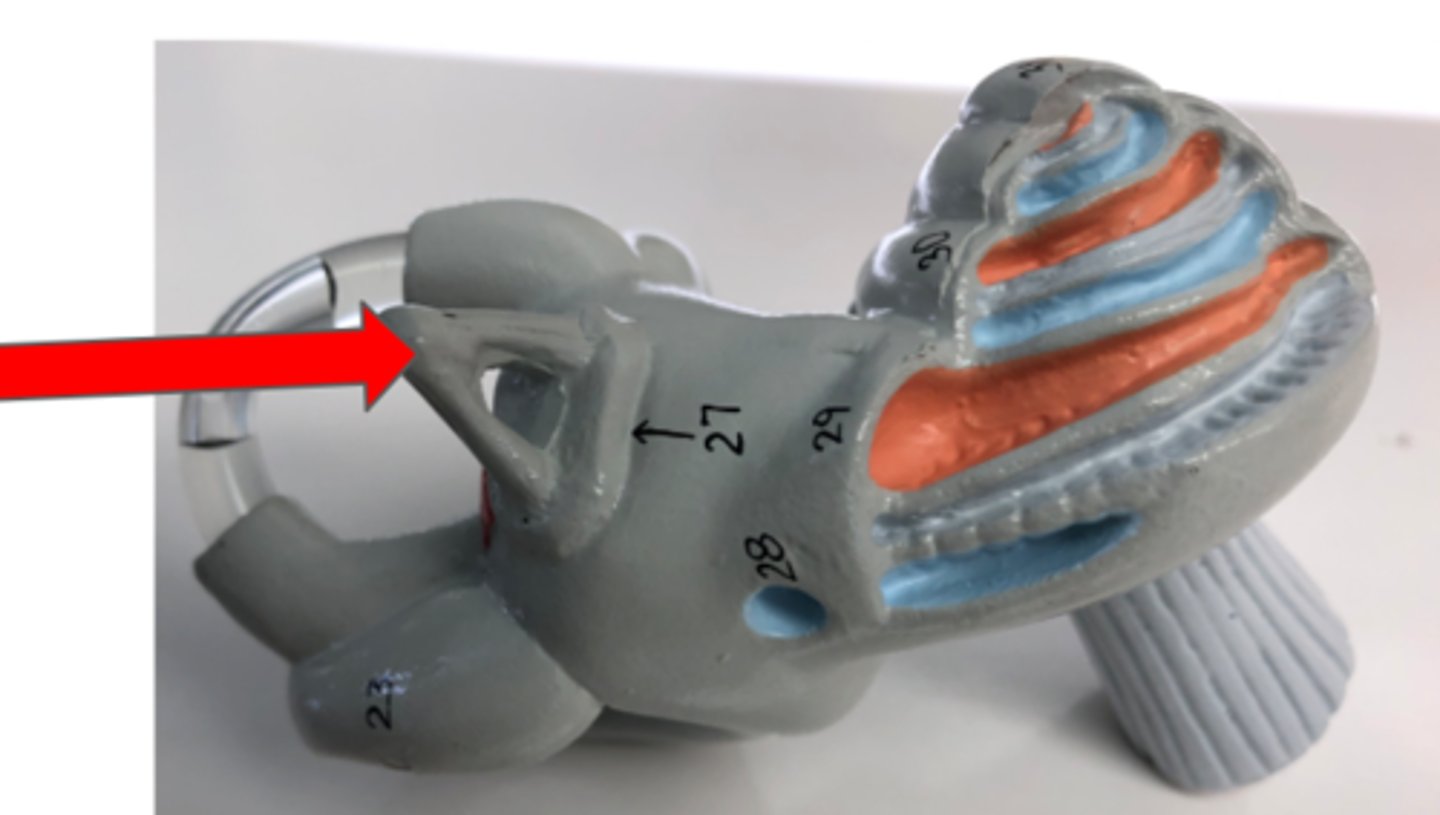
Semicircular canals
Fluid-filled canals in the inner ear for balance
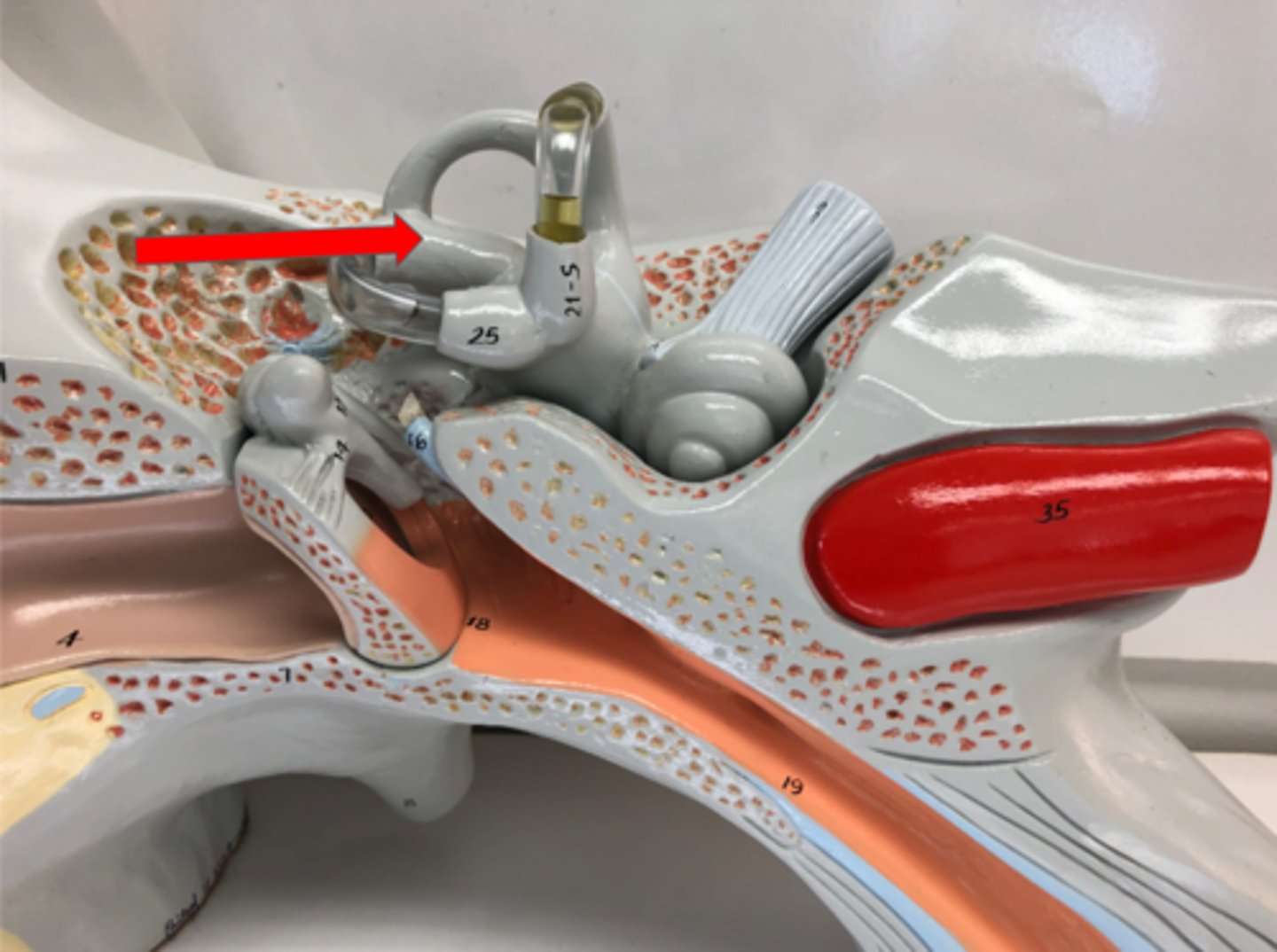
Vestibule
Part of the inner ear for balance