Domain 1: Topic A: Food and Nutrition and Supporting Sciences
1/230
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
231 Terms
water content range of fruits and vegetables
75-96%
what vegetable is at 96% water content
cucumber
what are some types of carbs found in fruits and vegetables
starches, sugars, polysaccharides, and fibers
define state of turgor (crispiness)
pressure insdie the cells of the fruits and vegetables due to osmotic pressure. Increased turgor causes fruits and vegetables to be crunchy and decreased turgor causes fruits and vegetables to wilt and become soft.
name good sources of potassium
baked white or sweet potatoes, cooked greens (spinach), winter (orange) squash, bananas, oranges, canteloupe, and honeydew
name good sources of calcium
dark, leafy greens, rhubard, broccoli, oranges
name good sources of iron
leafy greens (spinach, kale, Swiss chard, collard, beet greens), potatoes, mushrooms, olives, figs, dates, raisins, prunes, broccoli, cabbage, brussels sprouts
name good sources of zinc
white and sweet potatoes, green beans, mushrooms, spinach, garlic, broccoli
name good sources of phosphorus
potatoes, peas, asparagus, tomatoes, apples, cauliflower
name good sources of folic acid
broccoli, spinach, collards
name good sources of magnesium
avacados, bananas, leafy greens (kale, spinach, collard greens, turnip greens, and mustard greens)
name good sources of vitamin A
bright orange vegetables (carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkins), tomatoes, red sweet peppers, leafy greens, orange fruits (mangos, canteloupes, apricots, red or pink grapefruit)
name good sources of vitamin C
citrus fruits and juices, kiwi, strawberries, guava, papaya, cantaloupe, broccoli, peppers, tomatoes, cabbage, brussel sprouts, potatoes, leafy greens
name good sources of vitamin K
kale, mustard, greens, Swiss chard, collard greens, spinach, broccoli, brussels sprouts, green beans, prunes, kiwi, avacado
name good sources of vitamin E
spinach, green, leafy vegetables, (Swiss chard, collards), avacado, mango, butternut squash, red peppers
name some types of soybeans
miso, tofu, edamame, tempeh, and natto
Are soybeans complete proteins?
yes, although the limiting amino acid is methionine
protein concentrate information
over or equal to 70% protein, keeps some of the fiber, removes some of the carbs, found in baked good products, breakfast cereals, some meat and poultry products, and pet food
protein isolate information
over or equal to 90% protein, provides some functional properties to food
define textured protein products
meat extenter/meat substitute product made from soybeans (can extent number of servings and therefore reduce the cost)
What color is Chlorophyll?
green
Is Chlorophyll soluble or insoluble in water?
insoluble
What color is Chlorophyll in acid?
olive green (called pheophytin)
What color is Chlorophyll in alkaline conditions?
bright green (called chlorophyllin)
Where is the Chlorophyll pigment found?
produce; fibers are strengthened in an acidic environment and destroyed in a basic environment
Are carotenoids the most or least affected by changes in pH?
least affected
What is the color(s) of carotenoids?
yellow, orange
Are carotenoids soluble or insoluble in water?
insoluble in water
what type of carotenoid creates the red color in produce?
lycopnene
Which flavenoids are red, blue, or purple?
anthocyanins
Are anthocyanins soluble or insoluble in water?
soluble
What color are anthocyanins in acid?
bright red/magenta
What color are anthocyanins in an alkaline solution?
blue
Which flavonoids are white?
anthoxanthins/flavones
Are anthoxanthins/flavones soluble or insoluble in water?
soluble
What color are anthoxanthins/flavones in acid?
stays white
What color are anthoxanthins/flavones in alkaline or when cooked in aluminum
yellow
What makes corn and peas sweet?
sugar (sucrose)
Which amino acid provides an umami flavor, used in MSG, and found in high levels in tomato?
glutamic acid (glutamate)
Cabbage and onions are high in what?
sulfur (enzymes and sulfur are mixed when cabbage and onions are cut)
How should brussels sprouts be cooked for the best flavor
they should be cooked uncovered with a little bit of water
What are some components that add to the flavor of fruits?
acids, sugars, aramatic compounds
Define tannins.
polyphenols that give foods a bitter/astringent taste (examples include grapes, pomegranate, berries)
True or false: a controlled atmosphere can delay ripening by reducing the level of oxygen and increasing levels of carbon dioxide and nitrogen so that the respiration and ethylene production is reduced.
True
Define climacteric fruits.
fruits which ripen post-harvest (example: banana, tomato)
Define non-climacteric fruits
fruits that do not continue to ripen after harvest (examples: strawberries, grapes, raspberries)
What gas is produced during ripening of produce, which accelerates the process?
during ripening, ethylene gas is produced, accelerating the process
What happens during the ripening process?
Ethylene gas is produced, accelerating the process. Also, starch will be degraded into soluble sugars (mainly fructose), the cell wall will be degraded and as a result the fruit will become soft and sweet
Define protopectin.
protopectin is an insoluble form of pectin found in the cell walls of unripe fruits and vegetables. it is a large, complex polysaccharide. It is a precursor to pectin.
Define Pectin.
soluble fiber found in ripe fruits, used as thickener in cooking and baking. Gives gel-like consistency to jams and jellies
Define pectic acid.
more degraded form of pectin. Contributes to softening of over-ripe/rotting fruits. Less effective at gelling.
What are tips for storing produce?
store most fresh produce in the refrigerator except for bananas, pears, tomatoes, and avacados. Temps to store frozen produce must be 0 degrees F
True or false: you should wash berries and mushroom RIGHT before eating or cooking them.
true
washing raw produce removes ___
dust and spray residues
True or false: enzymatic action in fruits low in what vitamin cause darkening
vitamin C
what are some ways to prevent darkening of produce?
coating the produce with acidic juice (lemon, orange and pineapple juice) and/or using anti-darkening on the produce
true or false: cooking produce breaks down the walls of cells to help in the digestion process and cooks the starch
true
when sweetener is added to canned fruit, the density of syrup is expressed as % weight of sucrose, which is expressed as ___, ____, ____, and ____.
extra light, light, heavy, or extra heavy syrup
Define coulis
thin puree of fruit or vegetable with added water and sugar
define compote
fruit cooked in syrup; thicker than a coulis
Define polyphenol oxidase (aka tyrosinase)
the enzyme and compound that causes color changes in raw, peeled potatoes
True or false: potatoes can have a green pigment (chlorophyll) that is found under the skin which develops when potatoes are exposed to sunlight
true, also, solanine is a toxicant that may accompany the pigment. During storage, the starch in potatoes changes to sugar, causing older potatoes to be sweeter and cook gto a darker color (Maillard reaction)
can sizes
image
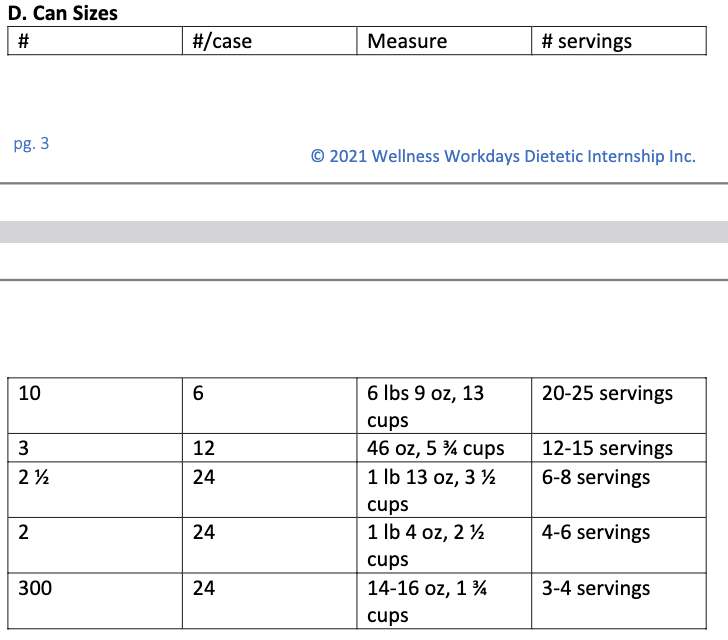
What shoudl you be sure to do when boiling more acidic vegetables?
They should be cooked with more water and no lid for a longer period; other vegetables shoudl be cooked for a brief period with a covered lid
How should you boil cabbage?
cook in a large amount of water with the lid off for a breif period of time to prevent the development of a strong flavor
Define steaming
a moist-heat method of cooking that works by boiling water which evaporates into steam. Use a covered perforated container over boiling water.
What are the benefits of microwaving?
may reduce the formation of harmful compounds in certain foods and doesn’t heat up as much as it does with other cooking methods. Has slightly better retention of color, vitamin C, no difference in quality of taste
What are the benefits of pressure cooking?
food retain most of their nutrients and quality, saves energy, saves time, kitchen is cooler, less cleaning required, pressure cookers can also be used to preserve food
Define baking
cook food with dry heat without direct exposure to a flame, typically in an oven or on a hot surface
What are the best consistency of vegetables to stirfry?
tender vegetables
Define dried cooking
any cooking technique where the heat is transferred to the food item without using extra moisture
tips for frozen veggies
frozen vegetables are blanched before freezing, which has made them tender
What organization oversees the grading of produce?
USDA
In termds of grading produce, what is it based on?
color, consistency, absence of defects, uniformity of size and shape, flavor, and color
In terms of grading produce, what it the highest quality?
A; other grades have increasing amounts of less desirable characteristics
In terms of grades of canned fruits and vegetables, what is grade A?
highest quality level, used in desserts, salads; aka Fancy
In terms of grades of canned fruits and vegetables, what is grade B?
excellent quality but are usually slightly more mature and have a slightly different taste. Aka Choice; best when baked, stewed
In terms of grades of canned fruits and vegetables, what is grade C?
standard; not as uniform in color and flavorful as the higher grades and usually more mature. Best used in puddings and pies.
In terms of fresh fruits and vegetables, what is “Fancy; Extra Fancy; #1”:
all indicate highest quality level; which one is used depends on the commodity
In terms of fresh fruits and vegetables, what is “Combination” mean:
contain increasing amounts of product with less desirable characteristics in appearance and/or marketability
In terms of fresh fruits and vegetables, what is “#2”:
contain increasing amounts of product with less desirable characteristics in appearance and/or marketability
Name the three parts of a whole grain.
bran, germ, and endosperm
What is the bran portion of a whole grain?
the fiber-rich outer layer, filled with B-vitamins and minerals
What is the endosperm portion of a whole grain?
the interior layer, mainly carbs (75% with some protein and vitamins
What is the germ portion of a whole grain?
the core of the seed, filled with healthy fats (2%), vitamin E, B-vitamins, and phytochemicals
What is the scutellum?
the portion of the germ; contains most of the Thiamin
Picture of anatomy of a grain
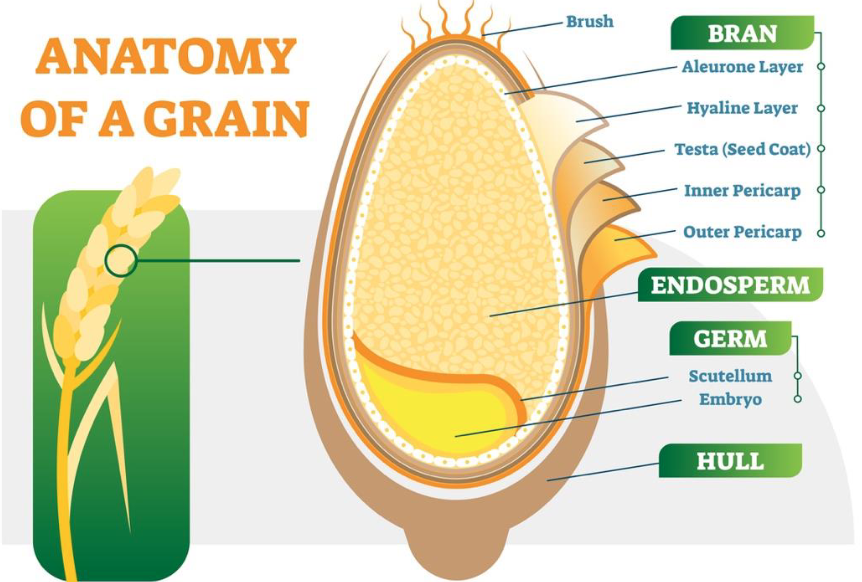
What are some vitamins and minerals found in whole grain?
B-vitamins, iron, copper, zinc, phosphorus, E vitamins, B vitamins, thiamin, and magnesium
Define milling.
Milling is a process used to break solid particles into smaller ones by force of shears, compression, friction, collison, or impact. Breaks the grain into its 3 main parts: germ, endosperm, and bran. Frshly milled flour results in more flavorful, nuanced breads and pastries, with more intense aromas.
Define farina.
A type of milled wheat made from both the endosperm and germ of the wheat (bran is removed); example: cream of wheat.
Define quick-cooking cereals.
disodium phosphate is added to create an alkaline environment, which causes particles to swell faster. Not a good choice for those on a low sodium diet.
Define whoel wheat flour.
contains all parts of the grain; whole grain flour spoils more quickly because the fat from the germ gets oxidized and becomes rancid.
What % protein (gluten) is bread (hard wheat) wheat?
12-14%
What % protein (gluten) is all purpose wheat (blend of hard and soft)?
8-11%
What % protein (gluten) is pastry wheat (soft wheat)?
8-9%
What % protein (gluten) is cake wheat (soft wheat)?
7-9%
What kinds of flours have thiamin, riboflavin, miacin, iron, and folic acid added back; these nutrients were lost as the flour was refined?
refined/enriched flours
Define self-rising flour.
baking powder, baking soda, and salt added to it, so it rises.
Define alimentary paste.
A shaped and dried dough (macaroni, noodles, spaghetti, etc.) prepared from semolina, farina, or wheat flour or a mixture of these with water or milk and with or without egg or egg yolk.