Pulmonology
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
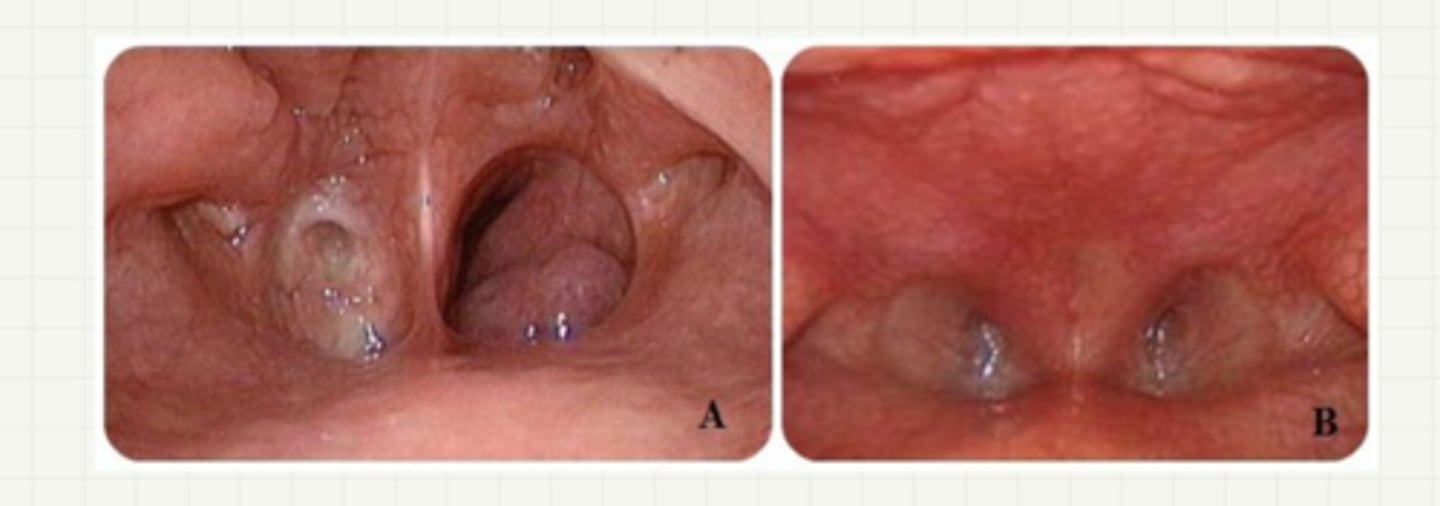
-congenital condition choanea are occluded
-failed recanalization
-unilateral
-female
-trisomy 21
choanal atresia
-feeding difficulties
-uilateral: mucopurlent discharge
-bilateral: unstable to breate, choking and airway obstruction, releived with crying, paradoxical cyanosis
choanal atresia sx
-dx: nasal endoscopy, CT scan
-tx: surgical correction
choanal atresia dx/tx
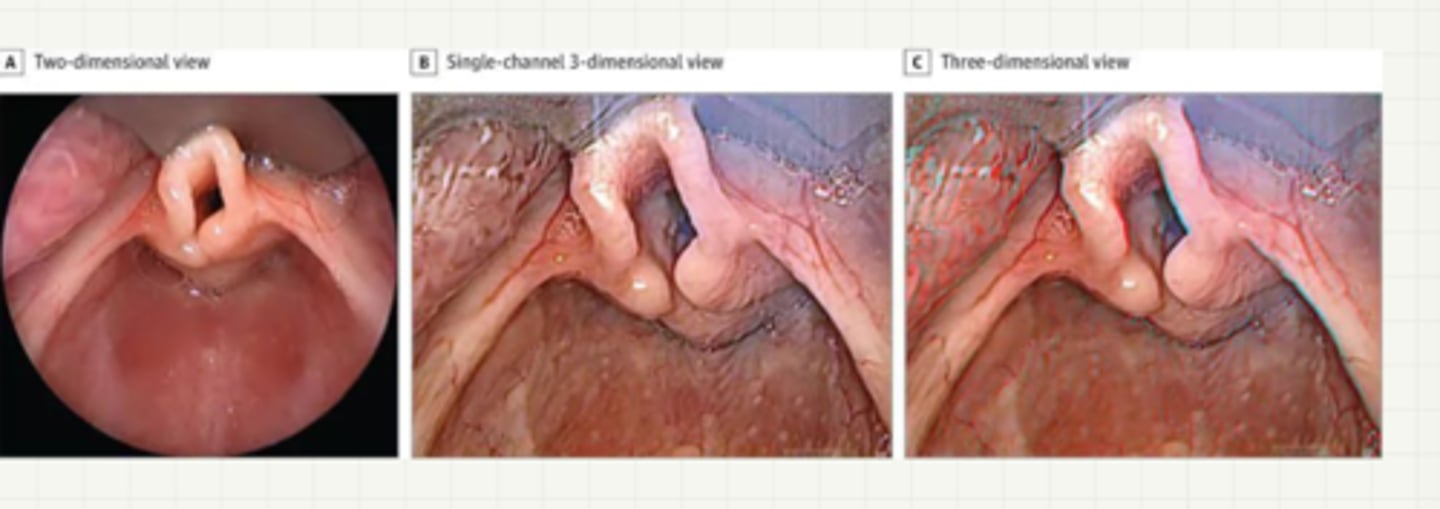
-congenital
-cartiaginous support of the supraglottix structure is underdeveloped and collapses with inspiration
-sx: intermitten stridor, within 6 mons of life
-dx: clinical, laryngoscopy
-tx: self limiting by age 2
-severe: surgical
laryngomalacia
-MCC: parainfluenza 1
-patho: infection leads to inflammation and edema in subglottic space
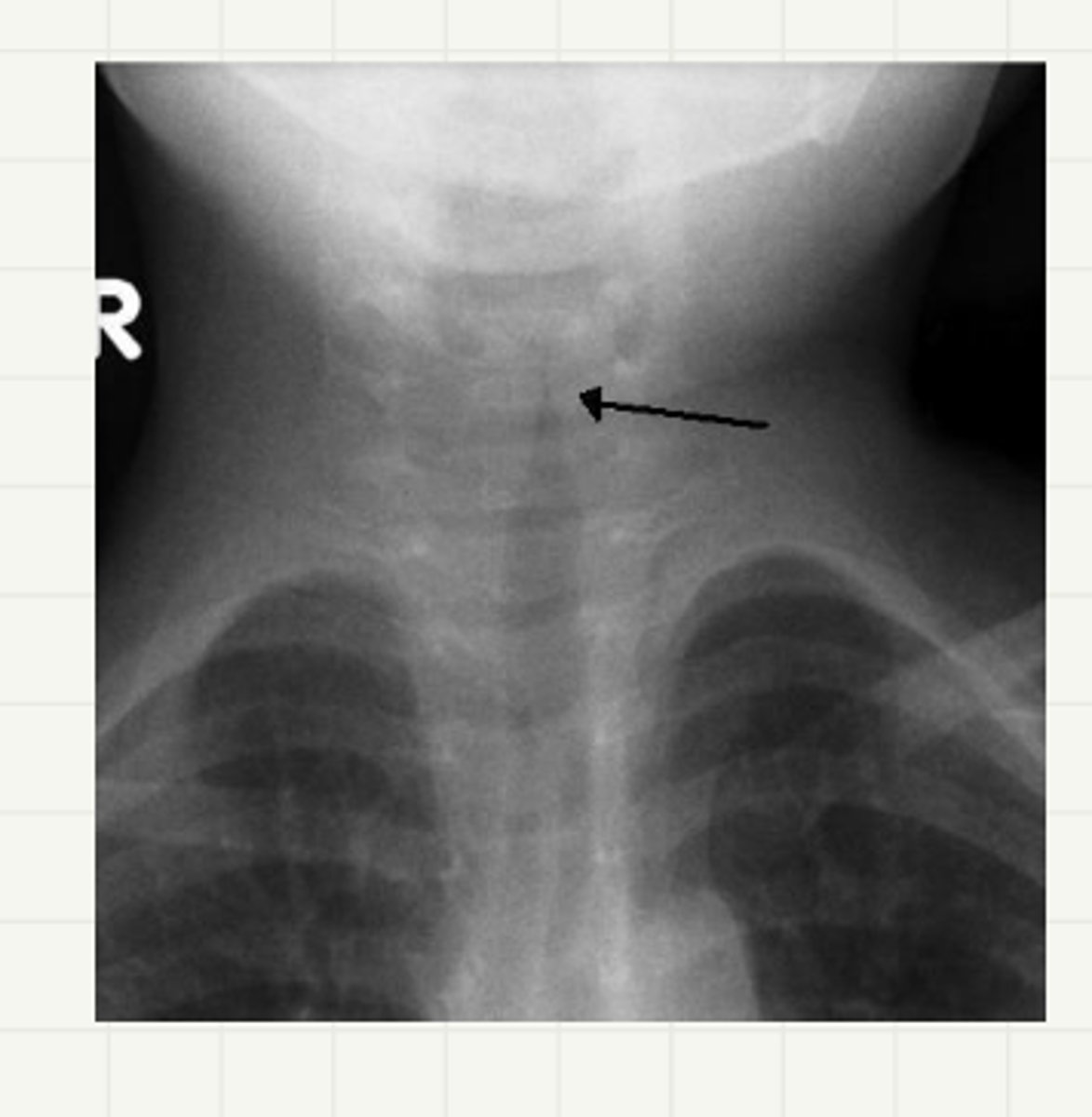
laryngotracheitis (croup)
-seal like cough (worse at night)
-stridor, hoarseness, absent or LG tempus, URI sx
-airway obstruction and edema progress, stridor occurs at rest
laryngomalacia sx
-dx: clinical
-AP/lat neck XR: steeple sign
-tx: single dose of dexamethasone
-severe: nebulized racemic epi (monitor), oral dexamethasone, O2
laryngomalacia dx/tx
-inflammation of bronchioles
-muscous in tinest lung tubes (chest cold)
-etiology: RSV
-2mon to 2 years
acute bronchiolitis
-viral prodrome (fever, URI sx) for 1-2 days following URI
-wheezing, scattered rhonchi, grunting, nasal flaring
-striodor and wheezing prominent
acute bronchiolitis sx
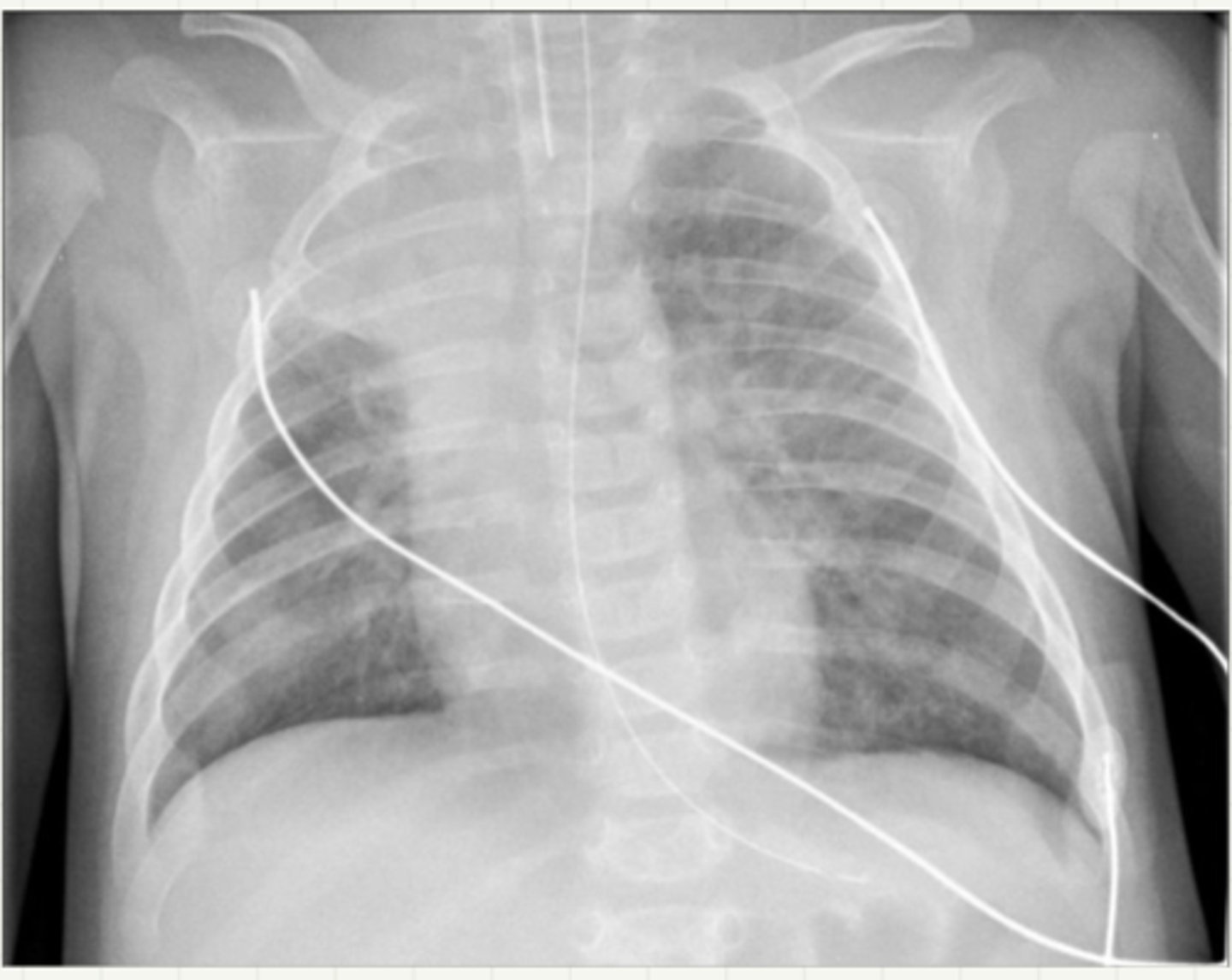
-dx: clinical, viral testing
-CXR: hyperinflammation, peribronchial, cuffing, patchy infiltrates
-tx: support measures
acute bronchiolitis dx/tx
-hypoemia on room air, hx of apnea, tachypnea with feeding difficulties, respiratory distress
-higher risk: <6 mon that are premature, children with cadiopulm disorder
-impatient tx: supportive, O2, intubation
acute bronchiolitis admission
-MCC- RSV
-most will get by age 3
respiratory syncytial virus
-abrysvo: 1 dose 32-36 weeks of pregnancy
-beyfortus: 1 dose 8 months
respiratory syncytial virus vaccine
-synagis: 1x month for high risk 0-24 mon
-high risk: premature, cardiopulm conditions
respiratory syncytial virus prophylaxis
-inflammation of lungs
-virus most common
-s. pnu most common bacteria
pneumonia
-usually follows viral LRTO
-most common strep pnu
-sx: fever over 39C, tachypnae, cough, abdominal pain
community acquired pneumonia
-etiology: RSV
-sx: fever, productive cough, pleuetic chest pain, dyspnea
-tachypnea, tachycardia, bronchia breath sounds, inspiratory rales
-dx: CXR- bilateral interstitial infiltrates
-tx: SABAs. fluids, rest
viral pneumonia
->5 years
-2-3 week inoculation
-M pnu, C pnu
-sx: cough dry onset, sputum production bulbous myringitis
-afebrile, conjuctivitis and staccato cough
atypical pneumonia
-clinically in kids with fever and exam
-CXR: asymmetrial lung exam, respiratory distress, >101F, hospital addmission
-bacterial: gram stain, PCR
-viral: viral respiratory panal
-atypical: PCR
pneumonia dx for all types
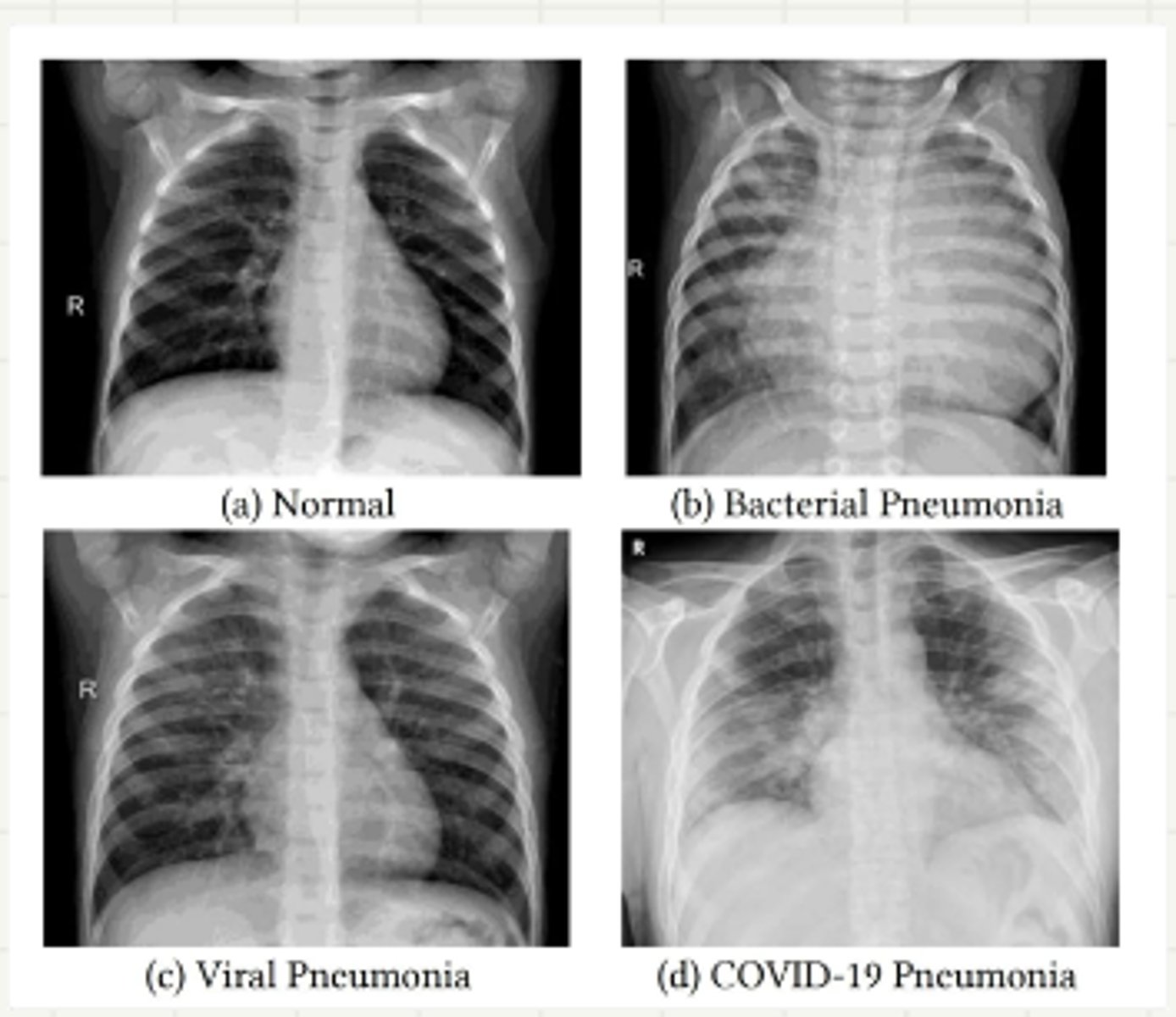
-supportice care in all
-mild to mod: bacterial: amoxicillin 90mg/kg/day 5-7 days
-atypicals: macrolides
-viral: antiviral therapy
pneumonia tx outpatient
-supportive care
-O2
-hydration and electrolytes
-nutrition
-IV ampicillin or ceftriaxone
-IV marolide for walking pnuemona
-antivirals
pneumonia tx inpatient
-most common lethal genetic disease
-chronic sinopulmonary infection, malabsorption, nutritional abnormalities
-lung disease is major cause of morbidity
-most develop obstructive lung disease
-autosomal recessive
cystic fibrosis
-mutation of CFTR gene on chromosome 7 > abnormal chloride, water transports aceross exocrine gands > thick viscous secretion of lungs pancreas sinus intestine liver
cystic fibrosis patho
-infancy: meconium ileus, FTT, diarrhea
-pulmonary: bronchiestasis
-GI: malabsorption, steatorrhea, diarrhea, pancreatitis
-cough, wheezing, recurrent pnumonia, exercise intolerance, hempotysis
cystic fibrosis patho sx
-dx: sweat chloride testing = >60 greater
-tx: managed by CF foundation accredaiated CR care center
-supplementation, nutrition, airwasy, abx, lung transplant
cystic fibrosis dx/tx
-autosomal recessive
-impaired mucocilliary clearance leads to chronic sunopulmonary disease
primary ciliary dyskinesia
-respiratory distress and often require supplemental O2
-year round nasal drainage, chronic sinutsitis, nasal polyps, chronic serous otitis media
-year roudn productive cough, reccurent bronchitis, reccurent pnuemonia
-situs inversis totalis
primary ciliary dyskinesia sx
-dx: phenotypic findings year round + confirmation of pathogenic mutation + defects noted in cillia
-tx: no specific therapy
-routine pulm monitor, airway clearance, nebulization, aggresive upper and lower airways tx
primary ciliary dyskinesia dx/tx
-most commonly on right side
-sx: sudden onset of cough, shokinh, dyspnea
-wheezing, asymmetic breath sounds, inspiratory stridor if FB is high in airway
-dx: chest xray, ct chest,
-difinitive: rigid bronchoscopy
foreign body aspiration
-infants younger than 1 year, apnea or irregular breathing, cyanosis, pallow, marked change in muscle tone, decreased responsiveness
-nervous system immaturity
-most hospitalized
-not a precursor of SIDS
-most with BRUE have serious underlying condition
brue