Organismal Practical Practice
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
What is this?
Classification?
Found where?
Food habit?
Medical Information?
Trypanosoma Cruzi
Classification
D- Eukaryote
K- Protista
P- Euglenozoa
C- Kinetoplastea
O- Trpanosomatidae
G- Trypanosoma
Species: Trypanosoma cruzi
Found: warm places in humans/bugs
Food Habit: Hetertroph
Medical Importance: Causes Changas Disease, transferred through kissing bugs
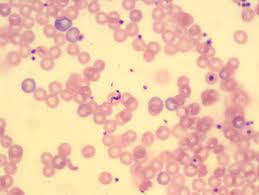
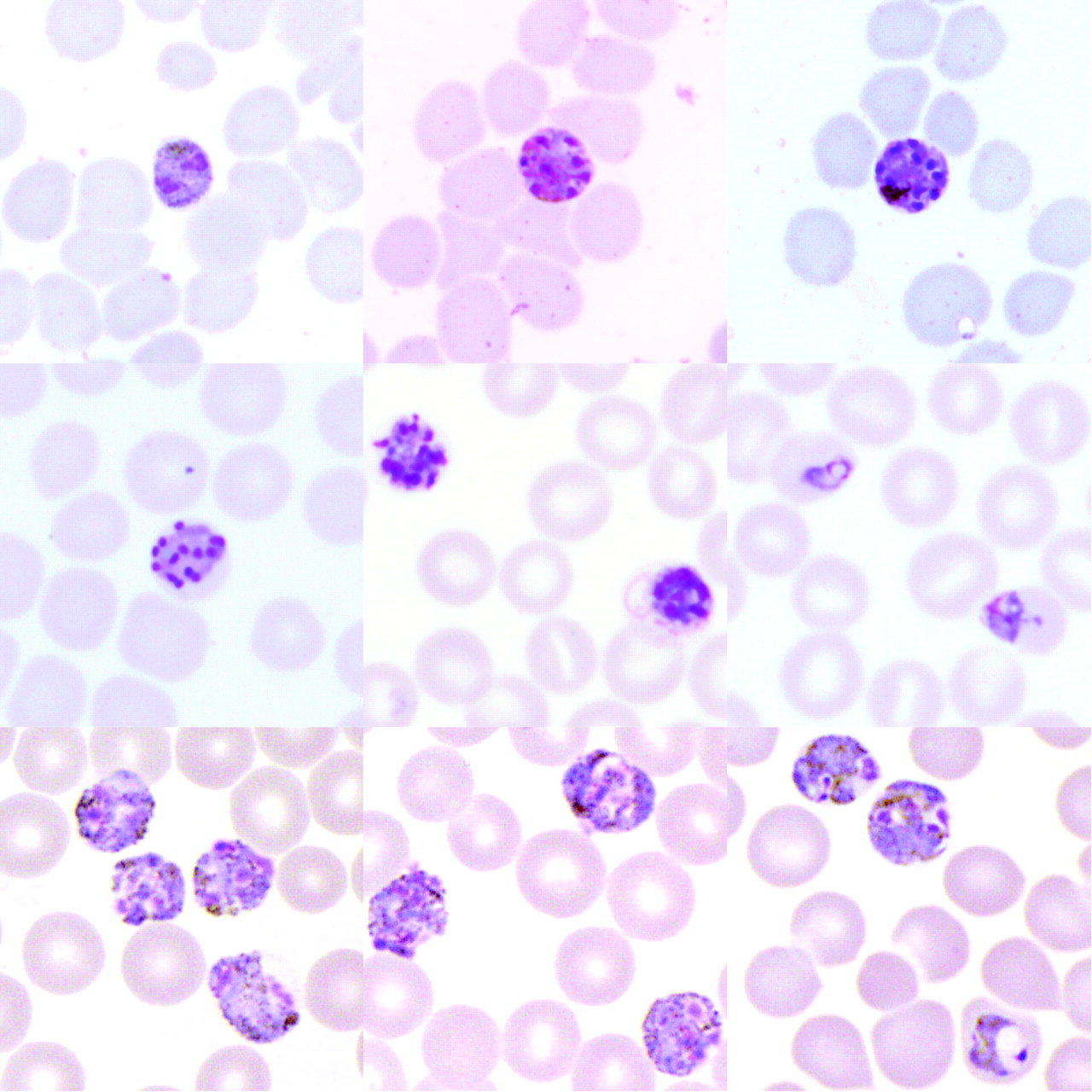
Plasmodium malariae
Classification:
D: Eukaryote
K: Protista
P: Apicomplexa
C: Sporozoa
O:Eucoccidiida
F: Plasmodiidae
G: Plasmodium
Species: Plasmodium malariae
Found: Mostly South America/Asia, parasites found in humans, and salvatory glands of mosquitoes.
Food Habit: Hetertroph, Feed on hemoglobin in RBC
Medical Importance: Causes Maleria in humans
Causes death in humans due to Anemia, kidney failure, and brain damage
Classification?
Found where?
Food Habits?
Medical Importance?
Identify Malaria Cell, and blood cell
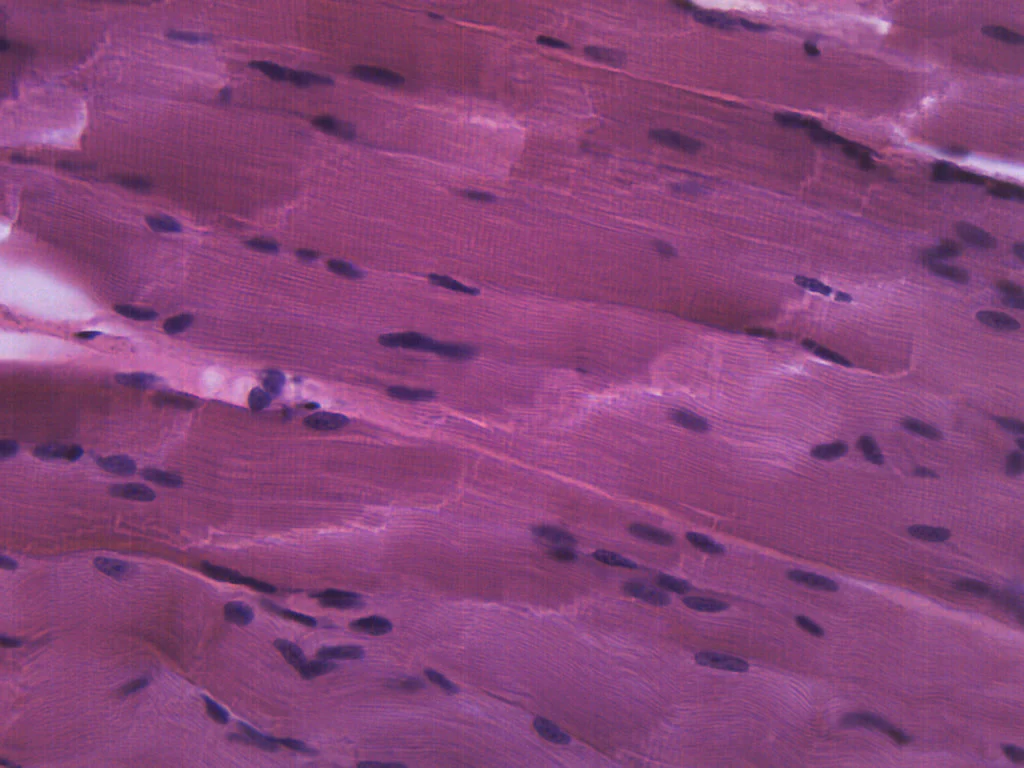
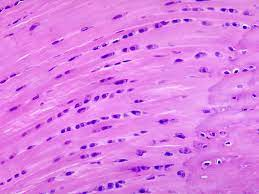
What type of tissue ?
Function ?
Found where?
Tissue: Muscle- Skeletal (Skeletal Muscle- Mammal)
Function: Contract to produce movement, maintains body temp, stabilizes joints
Location: Lungs
Only muscle that voluntarily contracts
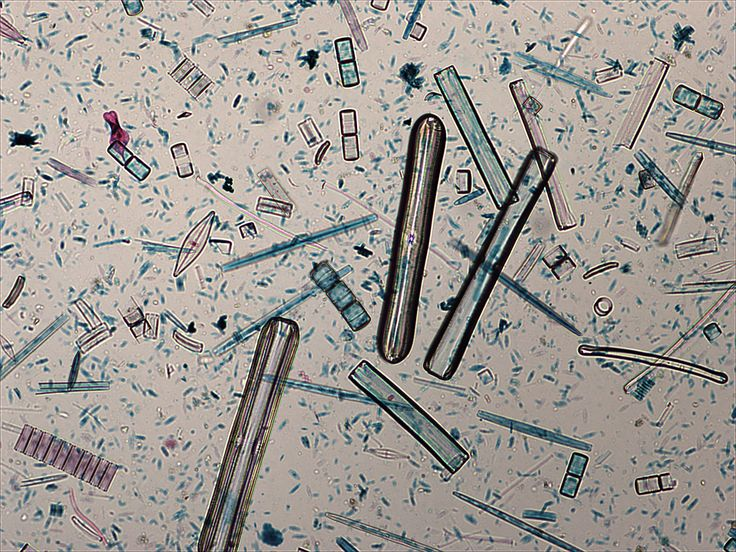
What is this?
Classification?
Found where?
Food Habits?
Other info?
Mixed Diatoms
Classification
D- Eukaryote
K- Protista
P- Bacillariophyta
Found: All aquatic enviroments, any type of water or moist enviroments
Food habits: Autotroph
Other: Test made of Silicic Dioxide (glass) & unicellular
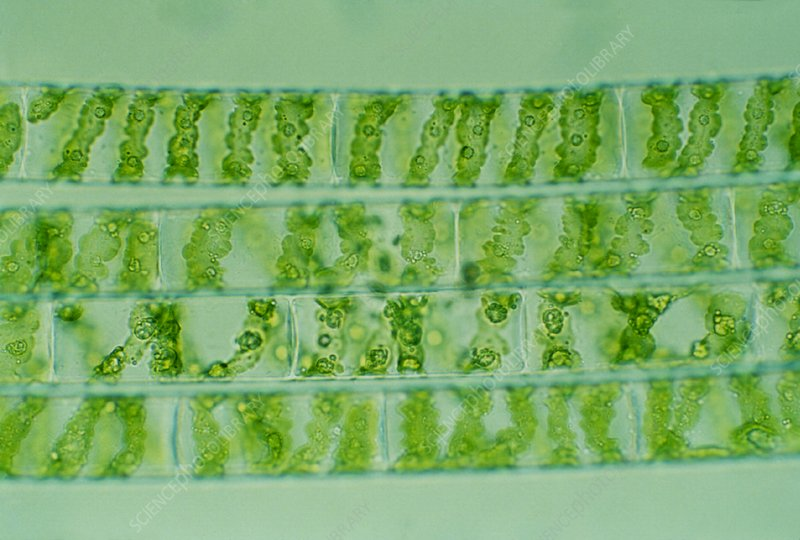
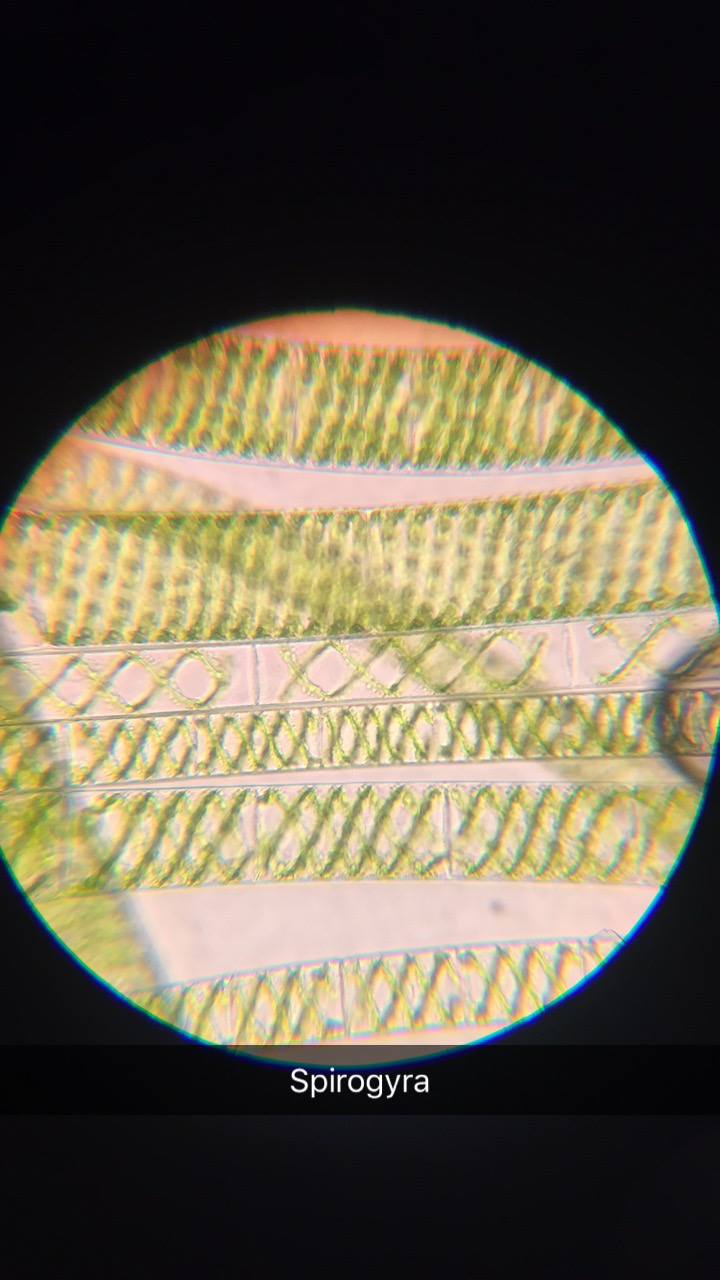
Classification?
Where can be found?
Food Habits?
Classification:
Domain: Eukaryote
Kingdom: Protista
Phylum: Chlorophyta
Class: Zygnematales
Family: Zygnemataceae
Genus: Spirogyra sp
Found in: Freshwater
Foot Habits: Autotroph, performs photosynthesis

Classification?
Found?
Food Habits?
Medical Importance?
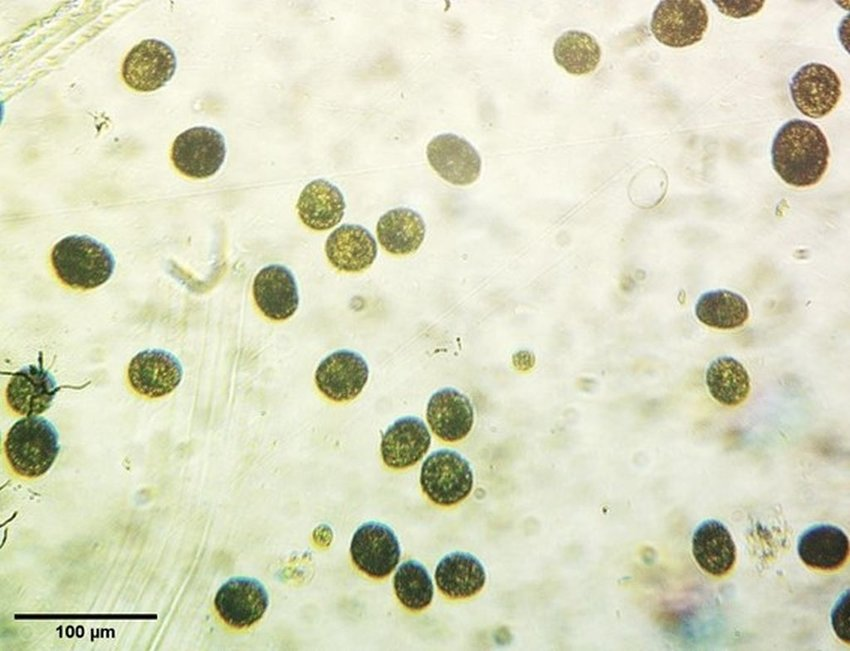
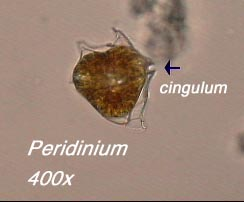
Classification:
D-Eukaryote
K- Protista
P- Pyrrophyta
C- Dinophyceae
O- Peridiniales
G- Peridinium
Found: Common in North America, Fresh or Marine water (cannot tolerate high salinity levels)
Food: Mostly Autotroph
Medical Information: Humans can ingest through molluscs, causes paralyzation of respiratory tract
Dinoflagellates blooming releases toxins into the water killing fish, birds, and more marine mammals
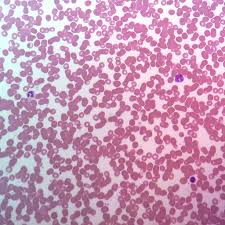
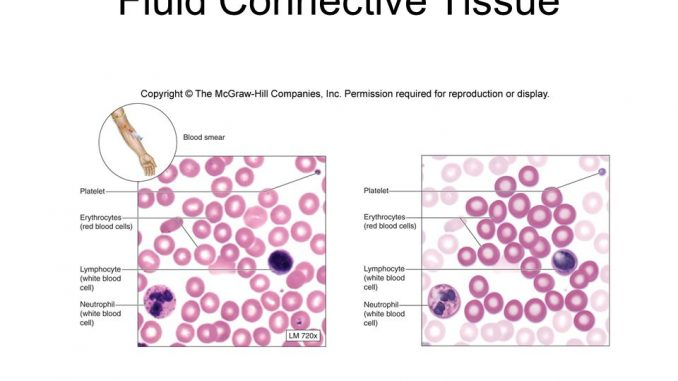
What type of Tissue is this?
What is the Function?
Where can this tissue be found?
Type: Connective Tissue- Fluid
Function: Transport fluid, nutrients, waste, acts as a messenger
Found: In blood
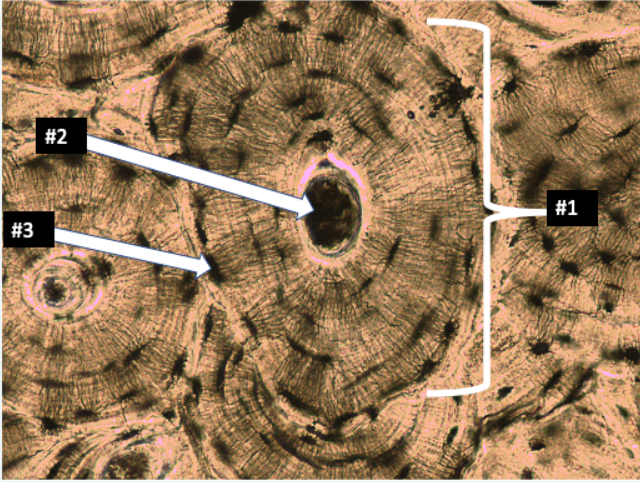
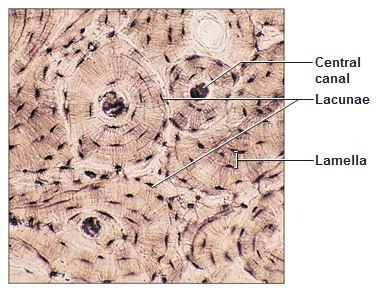
What type of tissue is this?
What is the function?
Where can it be found?
Identify Haversian Canal, Osteocytes, Lucuna, Osteon
Type: Connective Tissue- Supportive (Name:Compact Bone)
Function: To support organs & Cells, Serves as framework
Found: Bone; Femur; Shoulder blade
Classification?
Found where?
Food Habits?
Medical Importance?
Classification:
D:Eukaryote
K: Protista
P: Rhizophoda
C: Lobosea
O: Eumoebida
F: Entamoebidae
G: Entamoeba
Species: Entamoeba histolytica
Found: throughout world, most common in tropical place. Moist warm, found in mucosa of large intestines
Food: Heterotroph, eats cells off of host (Parasitism relationship)
Medical: spreads through feces, can cause diarhhea
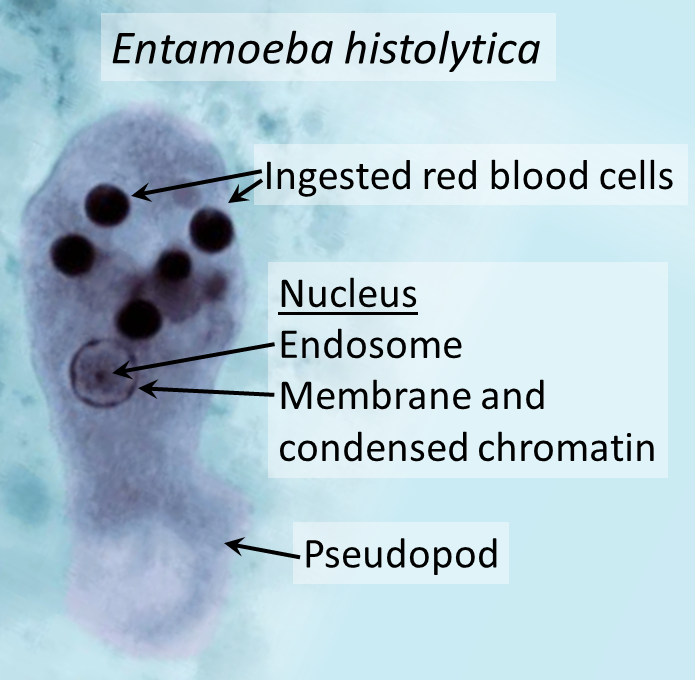
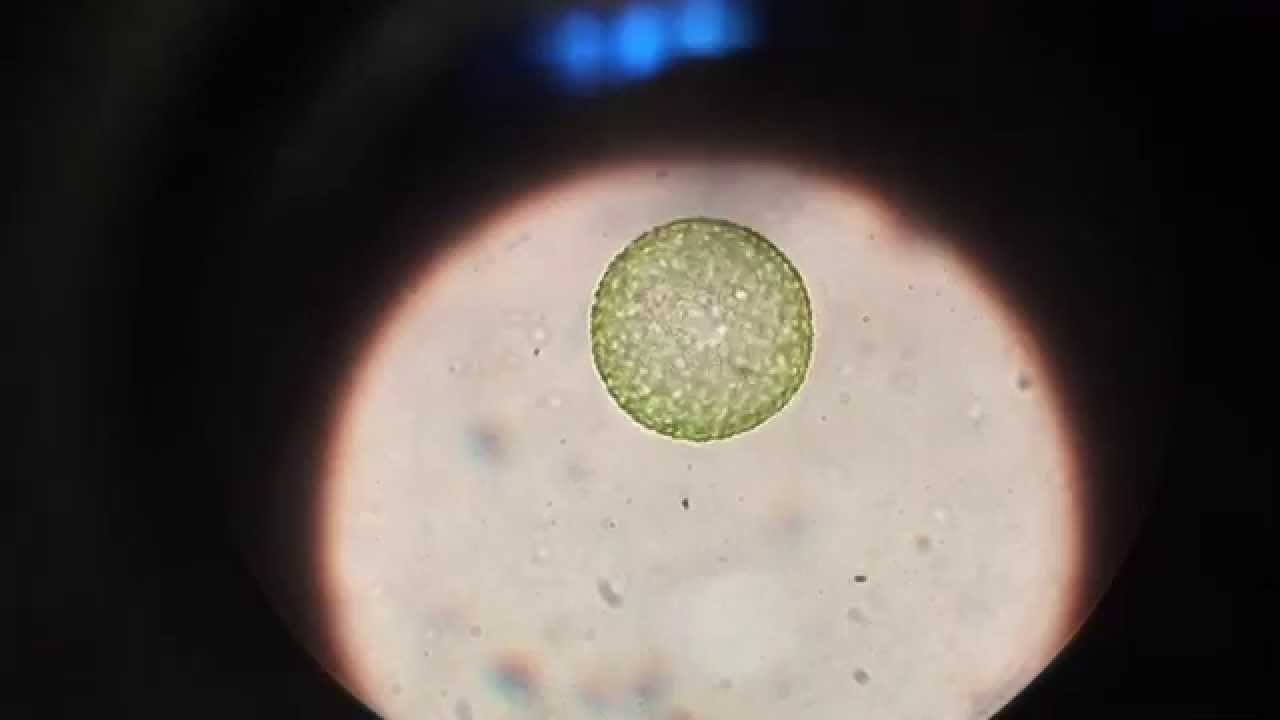
What is this?
Classification?
Food habit?
Habitat?
Other?
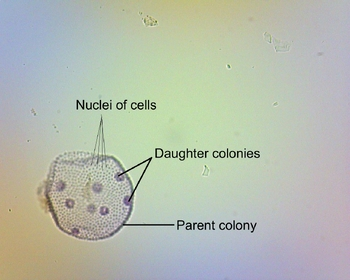
Identify- Daughter Colonies, Vegetative cells, Flagella
Volvox globator
Classification
D- Eukaryote
K- Protista
P- Chlorophyta
C- Chlorophyceae
O- Chlomydomonodales
F- Volvocaceae
G- Volvox
Species- Volvox globator
Food Habit- Heterotroph
Habitat- Aquatic/moist terrestrial areas. Freshwater
Other- Composed of daughter colonies
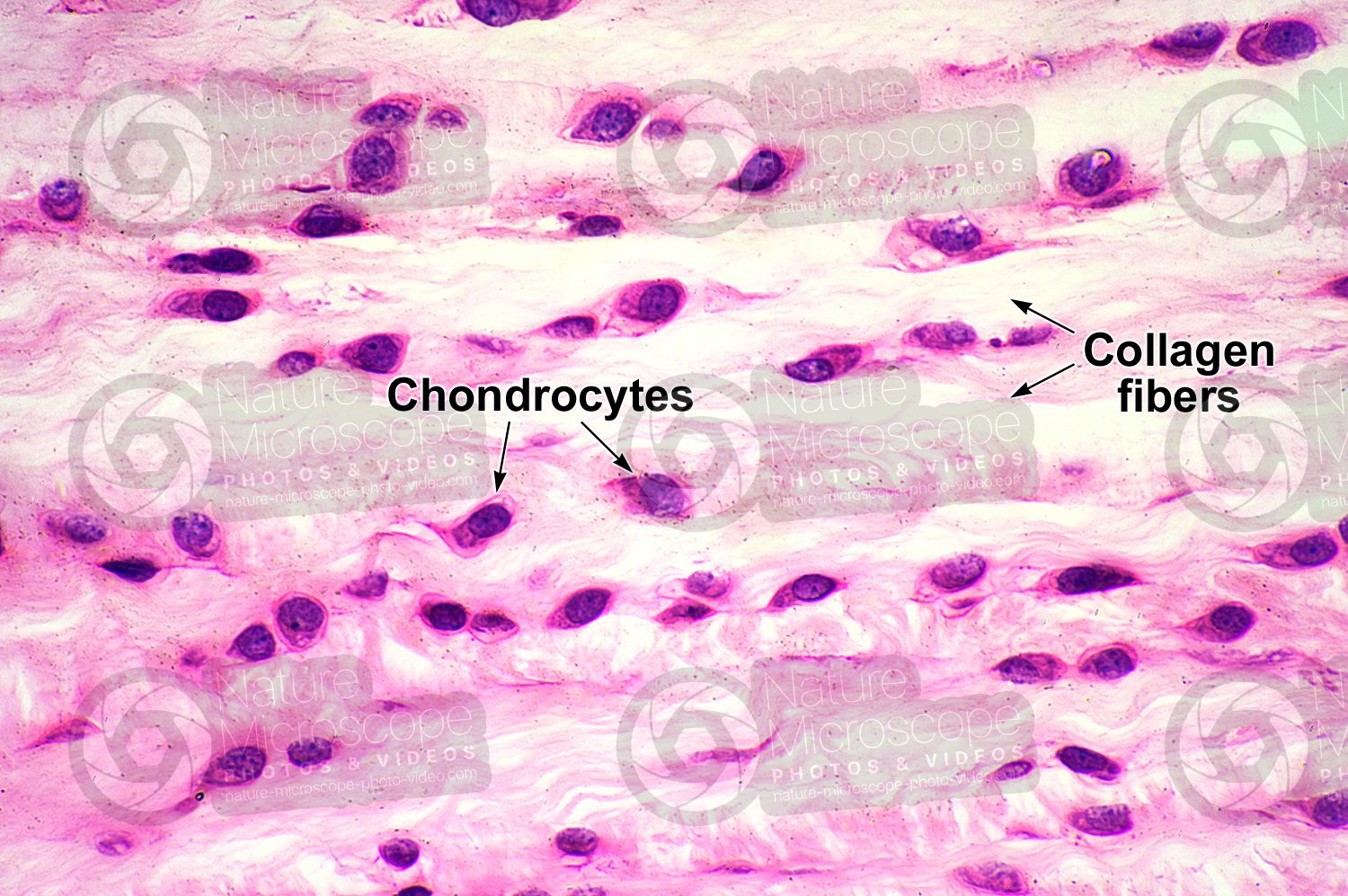
What type of Tissue is this?
Function?
Found where?
Identify Chondrocytes, Elastic Fibers, Matrix
Type: Connective- Supportive (Fibrous Cartilage)
Function: Protects joints, reduces friction between bones
Found: Between joints in fingers, between bones in knees
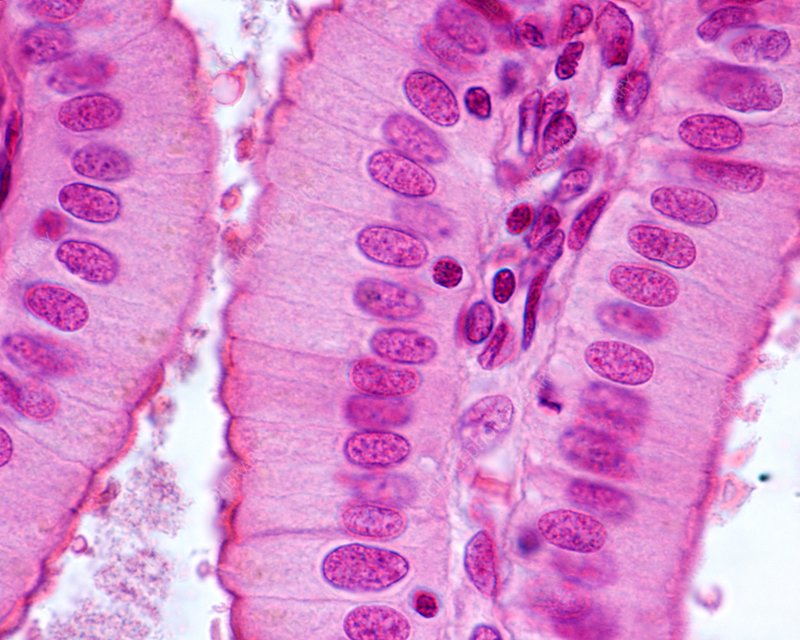
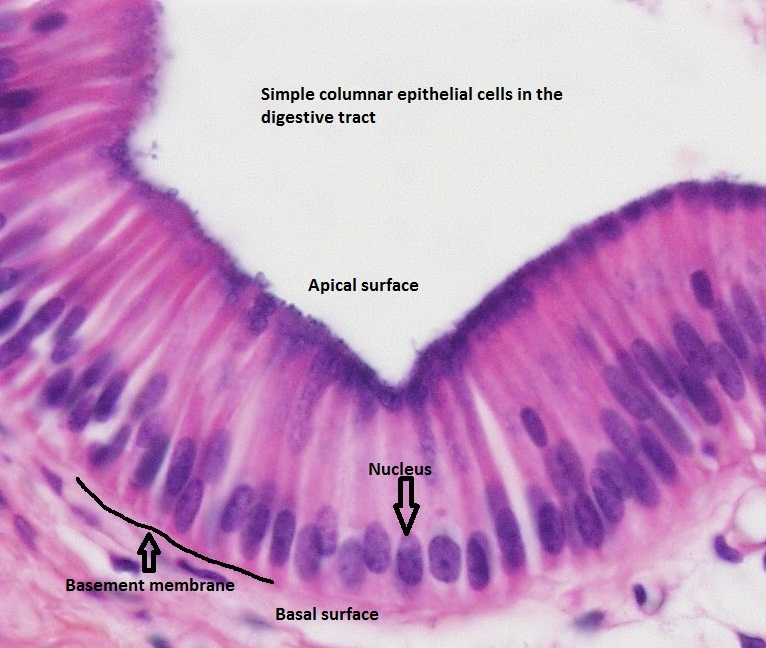
What type of Tissue is this?
What is the function?
Where can this Tissue be found?
Type: Simple Columnar Epithelium
Function: Secretion, absorption
Found: Parts of gut lining, parts of respiratory tract lining
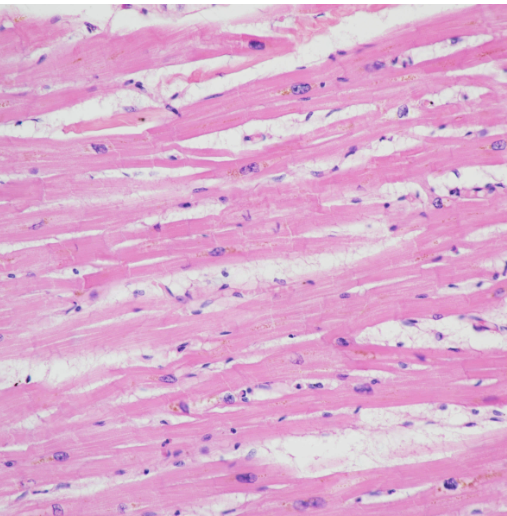
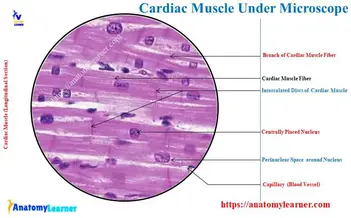
What type of tissue is this?
Function?
Location?
Identify Nucleus, Striation, Intercalated disc
Type: Muscle-Cardiac
Function- Contracting the Heart (Involuntary)
Location- Heart
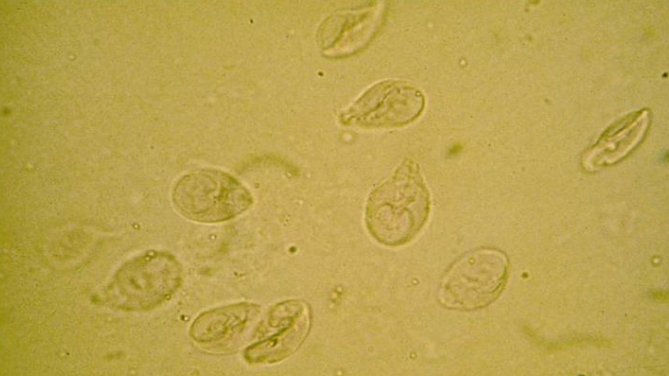
What is this?
Classification?
Found where?
Food Habits?
Medical Importance?
Giardia lamblia
Classification
D- Eukaryota
K- Protista
P- Sacromastigophora
C- Zooflagellate
O- Diplimonadida
F- Hexamitidae
G-Gardia
Species- Giardia lamblia
Found: World-wide, Freshwater
Food Habits: Heterotroph
Medical Importance: Infects small intestines (bloating, cramps, diarrhea, vomiting)
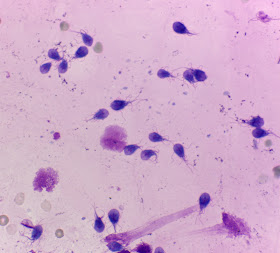
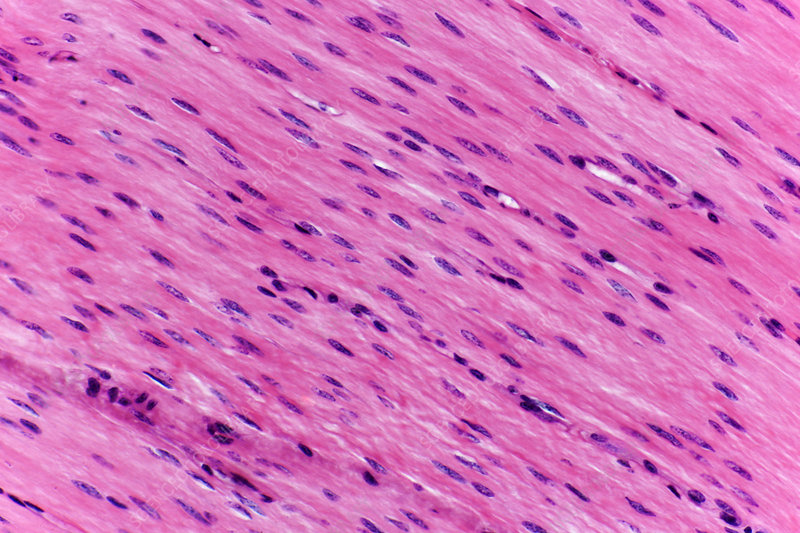
What type of tissue is this?
Function?
Location?
Type: Muscle- Smooth
Function: Involuntary contractions; helps with digestion, swallowing
Found: Trachea, digestive tract
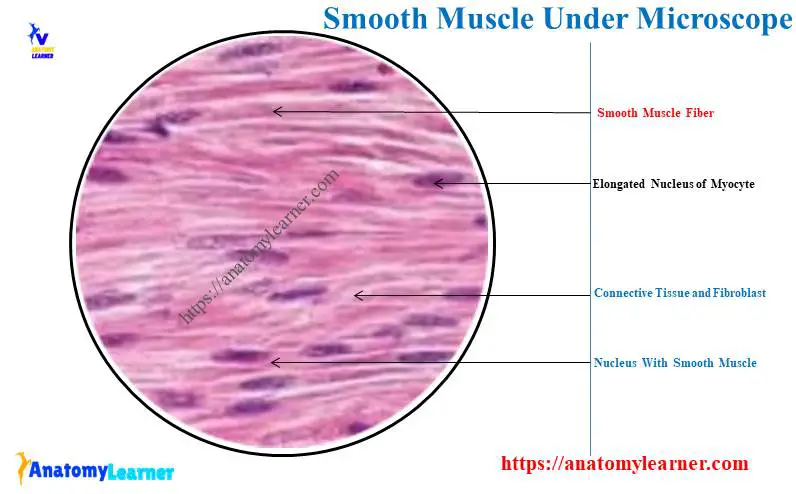
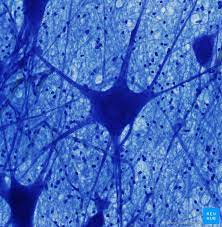
What type of Tissue is this?
Function?
Location?
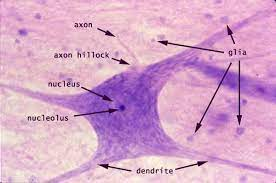
Label cytoplasm, dendrite, nucleus, axon
Type: Nerve Tissue (Motor Neuron)
Function: Carries signals from central nervous system, produces desired movement
Location: Brain, spinal cord
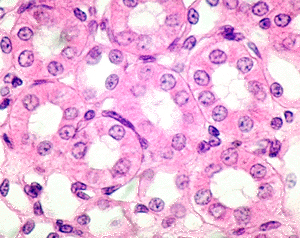
What type of Tissue is this?
What is the function?
Where can you find this tissue?
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Function: Secretion and absorption
Found: Lining kidney tuboles, salvitory glands (mouth), bronchioles in lungs.
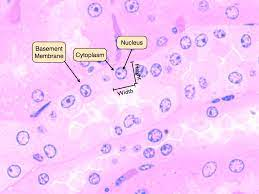
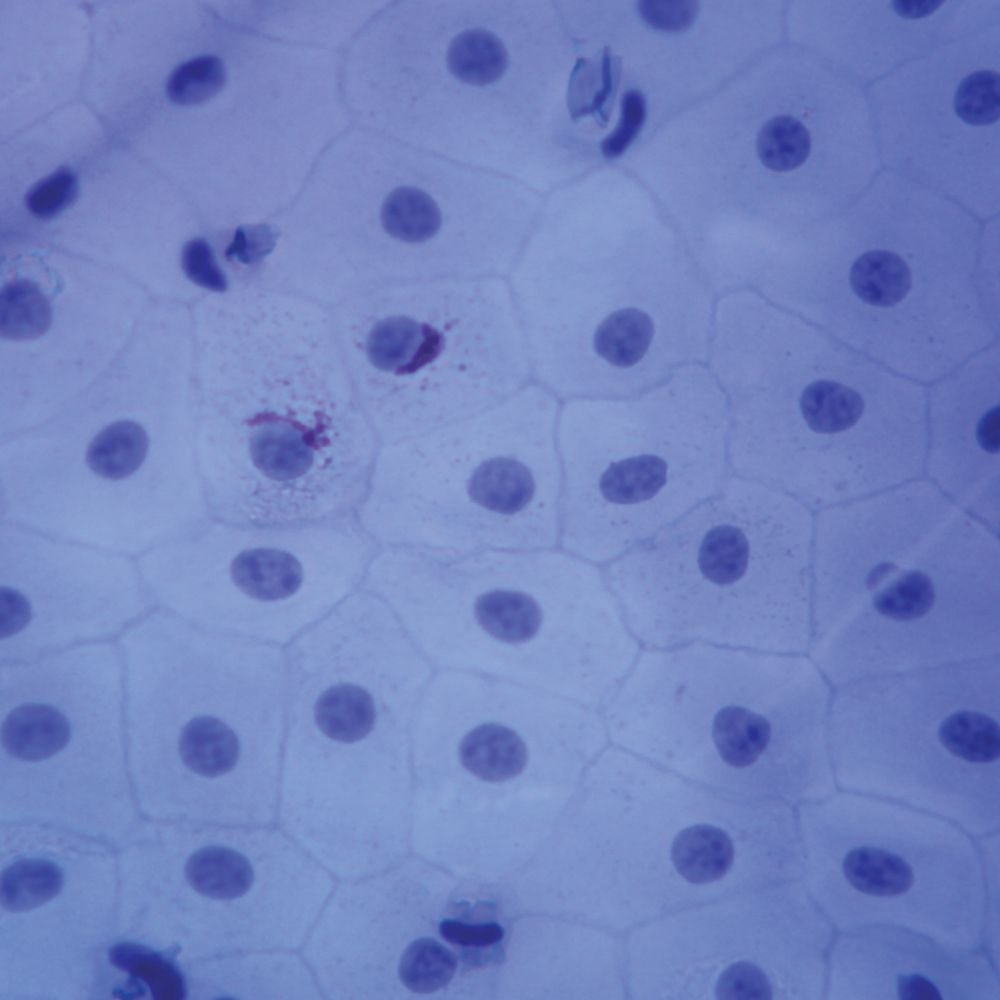
What type of tissue is this?
What's its function?
Where is it found?
Tissue: Simple Squamous Epithelium
Function: Diffusion
Found: Blood vessel walls, air sacs of lungs
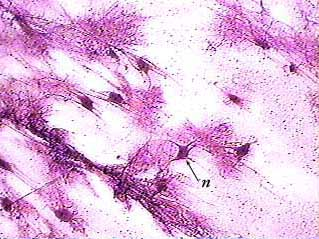
What type of Tissue is this?
Function?
Location?
Type: Nerve
Function: Processing information from external & internal environments
Location: Spinal Cord, Brain
what is this?
classification?
Habitat?
Food Habits?
Other?
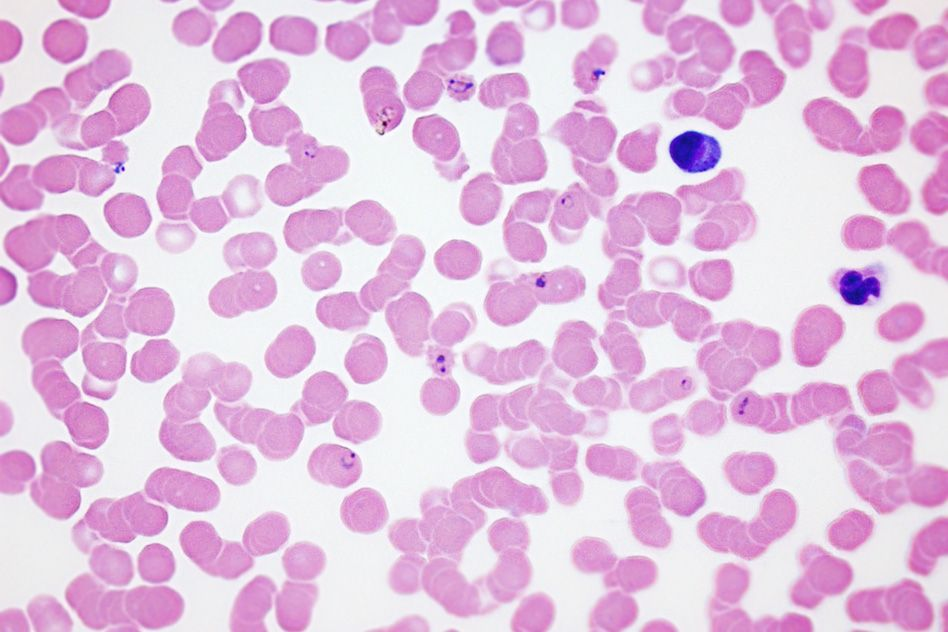
Plasmodium malariae
Classification:
D: Eukaryote
K: Protista
P: Apicomplexa
C: Sporozoa
O:Eucoccidiida
F: Plasmodiidae
G: Plasmodium
Species: Plasmodium malariae
Found: Mostly South America/Asia, parasites found in humans, and salvatory glands of mosquitoes.
Food Habit: Heterotroph, Feed on hemoglobin in RBC
Medical Importance: Causes Maleria in humans
Causes death in humans due to Anemia, kidney failure, and brain damage
Other: Test made of silica dioxide (glass)
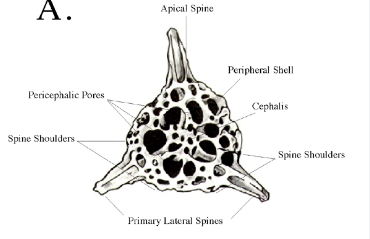

What is this?
Classification?
Habitat?
What is on surface ?
Paramecium caudatum
Classification:
D- Eukaryote
K- Protista
P- Ciliophora
C- Oligohymenophorea
O- Peniculida
F- Parameciidae
G- Paramecium
Species: Paramecium caudatum
Habitat: Freshwater, Marine Water, found attached to surface of water
Other: Cilia covering surface
What is this?
Classification?
Habitat?
Food Habits?
Other?
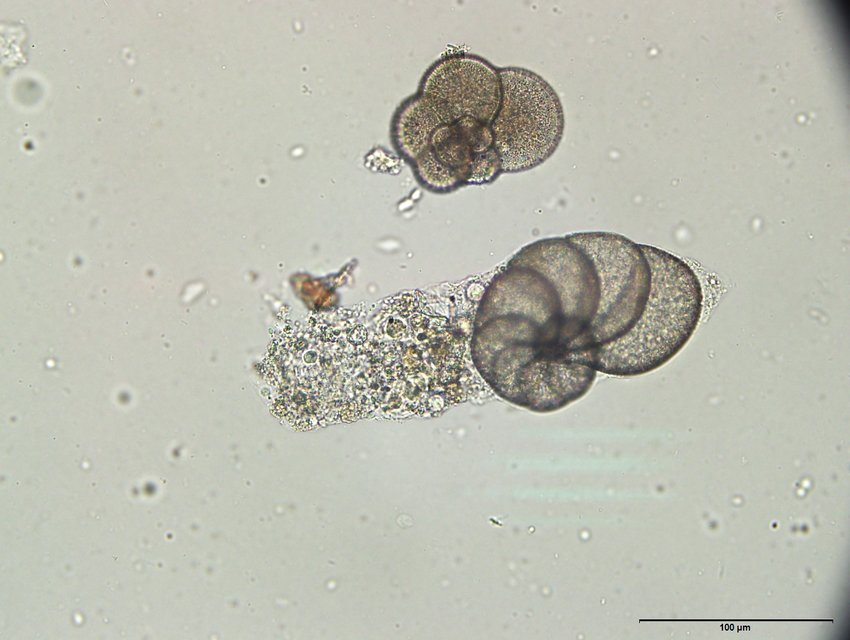
Classification:
D- Eukaryote
K- Protista
P- Foraminifera
Habitat: Lives on seafloor or float in the water column
Food Habits: Heterotrophs (gathers food from external environment)
Other: Test made of Calcium Carbonate (Natural Chalk), Single-celled, granular ectoplasm to catch food
What is this?
What kind of veins?
Flower parts?
What kind of roots?
Examples?
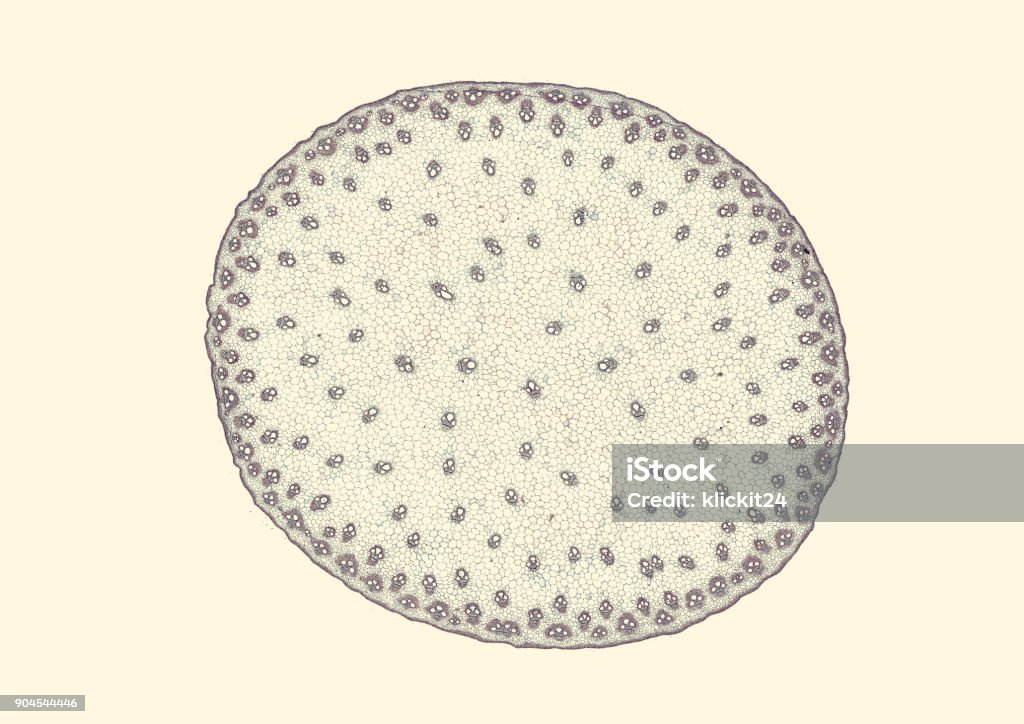
Monocot stem cross-section
parallel or up & down veins
Flower parts in 3s
Adventitious roots
Examples: Bamboo, onion, palm tree, grass
What is this?
What kind of veins?
Flower parts?
Roots? Branches?
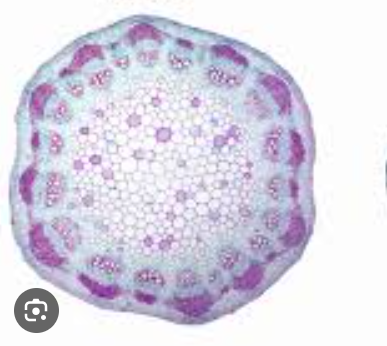
Dicot stem cross section
Net-veined leaves
Flower parts in multiple of four or five
Tap Roots & Lateral Branches
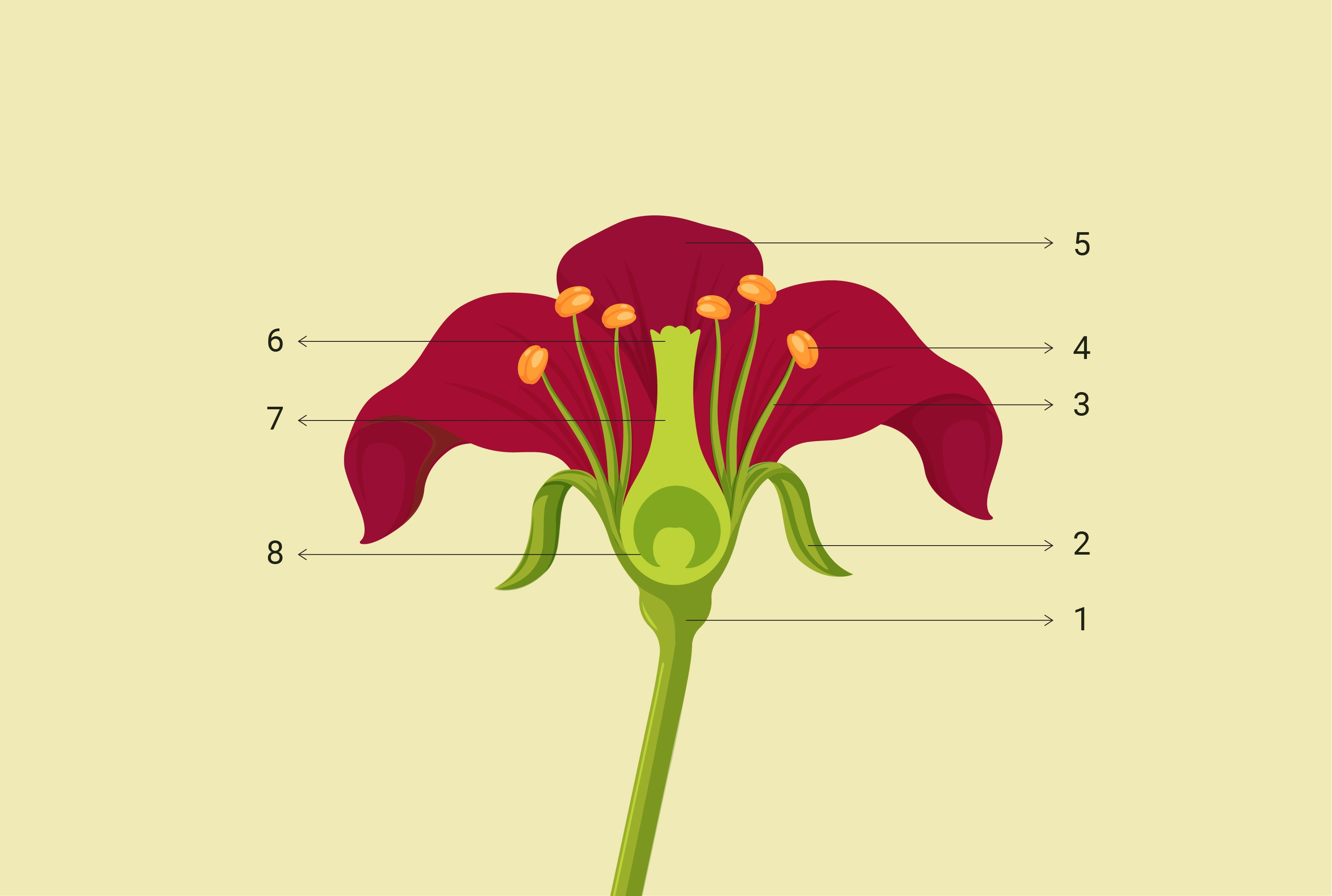

Parts of the flower?
Female parts?
Male Parts?
Function of parts?
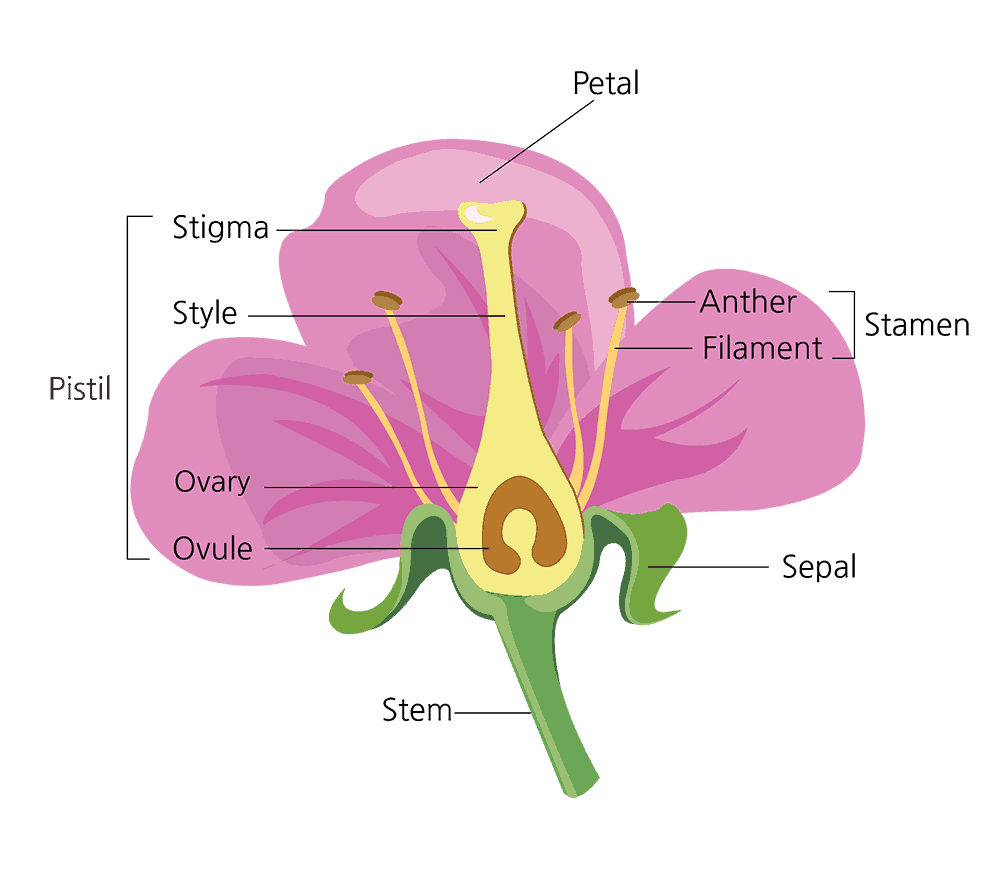
Female Parts (Carpel):
Stigma
Style
Ovary
Ovule
Male Parts (Stamen):
Anther
Filament
Function of Flower parts:
Anther: creates pollen
Stigma catches pollen
Ovaries does seed germination
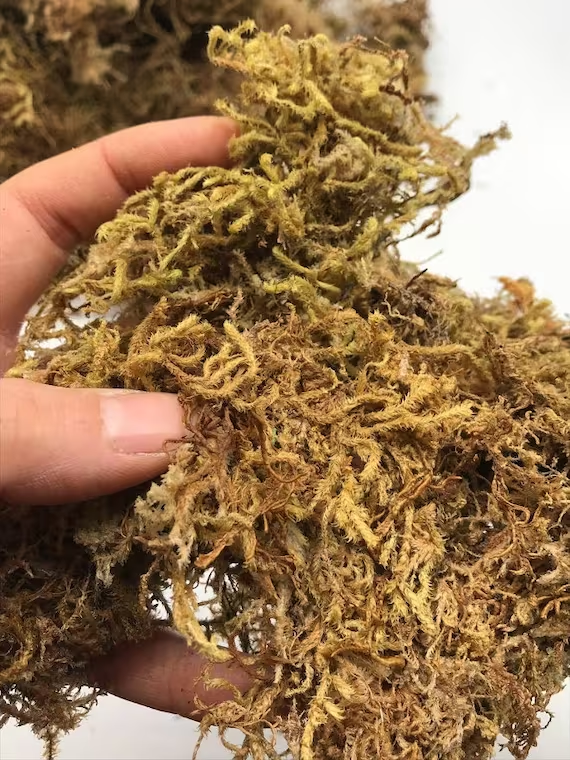

What is this?
Classification?
Reproduction?
Habitat?
Other?
Sphagnum Moss
Classification:
K- Plantae
P- Bryophyta
C-Spagnoesida
O- Sphagnales
F- Spagnacece
G- Sphagnum
Reproduction: relies on water to carry male gametes to female gametes, has distinct sexes, grows from spores
Habitat: grows on surface of soil or swamp, wet climates, stagnant, nutrient poor areas
Other: 15,000 extant species, nonvascular, most diverse of non-vascular plants.
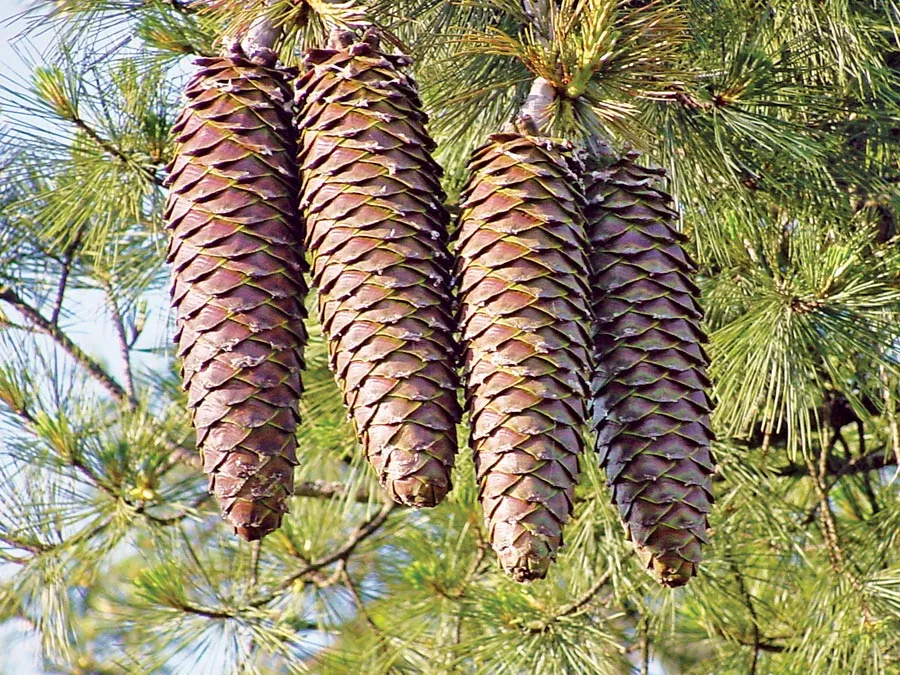

What is this?
Female v.s. Male?
Classification?
Habitat?
Gymnosperm or Angiosperm?
Other?
Pinecone
Male pine cones are slimmer/taller, female pinecones are fatter.
Domain: Eukaryote
Kingdom: Plantae
Phylum: Coniferiphyta
Temperate & subarctic regions,
Gymnosperm
Pinecones are open when ripe, close when not ripe
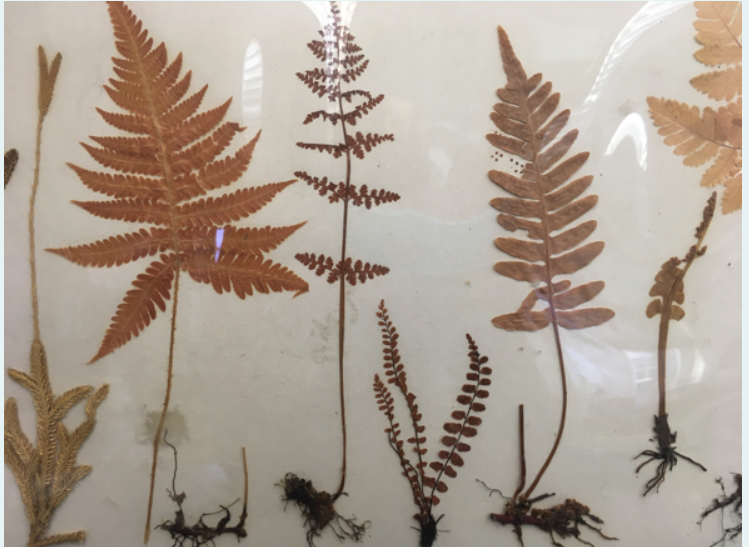

1.)Kingdom?
2.)Phylum?
3.) Seeded or non-seeded
4.) Flowering or non-flowering
5.)Vascular or nonvascular?
6.)Reproduction?
1.)Plantae
2.)Pyterophyta
3.) non-seeded
4.)Non-flowering
5.)Vascular
6.)Reproduction through spores
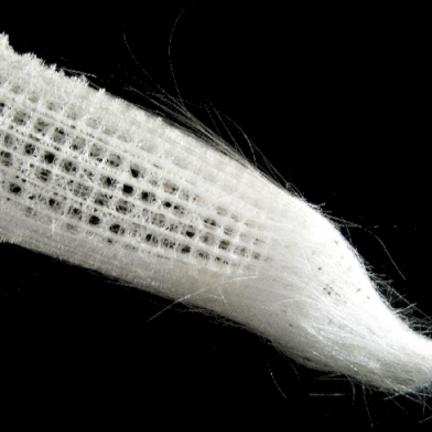

1.)Phylum?
2.)Class?
3.)Kingdom?
4.)Spicules? Made of?
5.)Found where?
6.) Filtration System?
1.) Porifera
2.) Hexactinellida
3.) Animalia
4.) Hexatine Spicules, made of Sicilia
5.) Found in Marine deep Sea (200-1,000m)
6.) syconoid & Leuconid
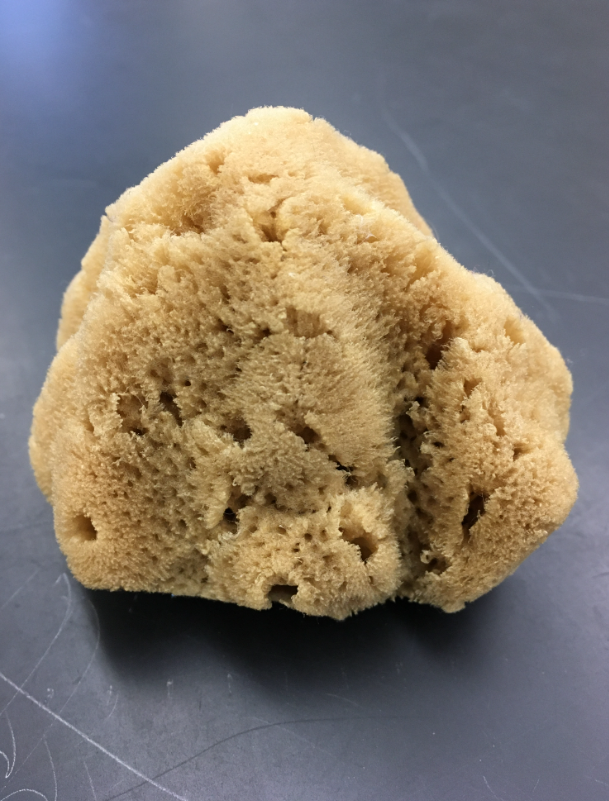

1.) Phylum?
2.) Class?
3.) Type of filtration system?
4.) Posses no spicules (True or False)
5.) Marine or Freshwater?
6.) Spicules? What kind?
7.) Filtration System?
1.) Porifera
2.) Demospongiae
3.) Leuconid
4.)False
5.) Mostly Marine, 1 species is freshwater
6.)Monoaxon spicules and Tetraxon Spicules
7.) All Leuconid

1.) Phylum?
2.) Class?
3.)Spicules? Made of?
4.) Found where?
1.) Porifera
2.) Calcarea
3.) Spicules made of Calcium Carbonate
4.)Found in Shallow marine waters

1.) Phylum?
2.) Class?
3.)Reproduction?
4.) Found where?
5.) Body morphology?
1.) Cnidaria
2.) Anthozoa
3.) Asexual reproduction
4.)All marine waters
5.) Polyps whole life cycle

1.) Phylum?
2.) Class?
3.) Body morphology?
1.) Cnidaria
2.) Hydrozoa
3.) Juvenile stage is polyp, adult stage is medusa
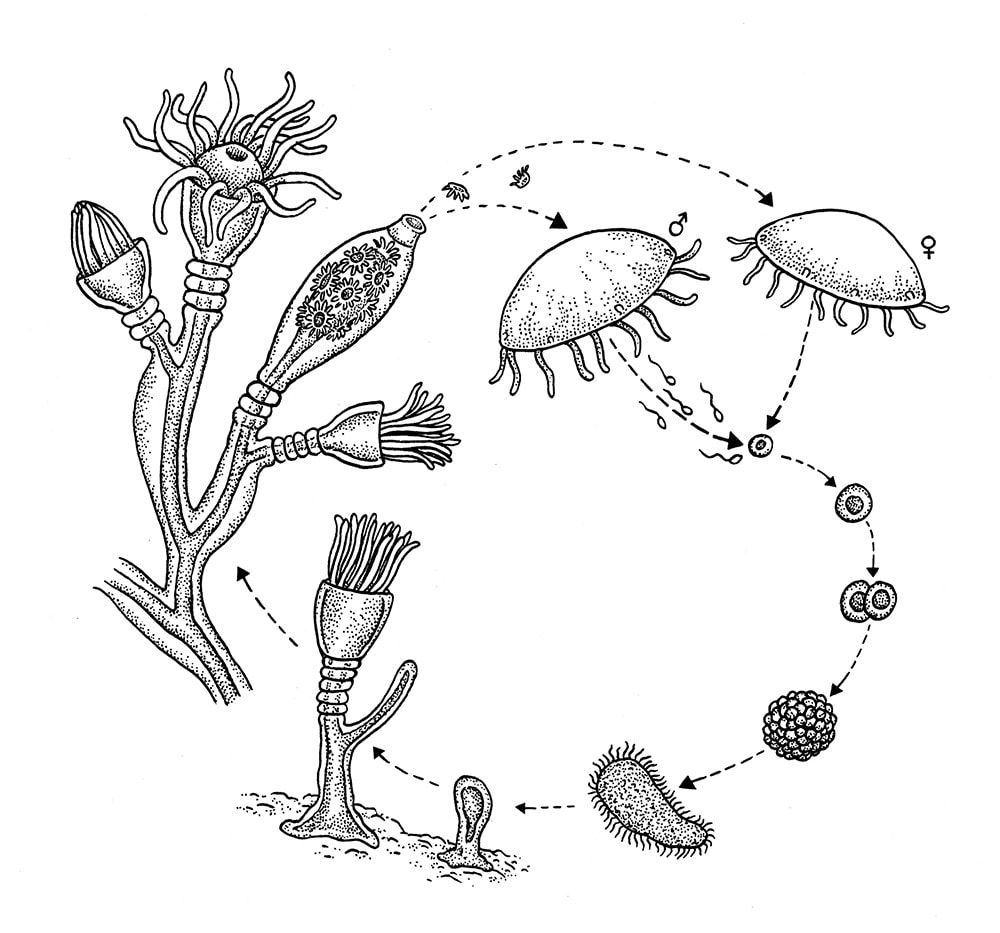

1.) Phylum?
2.) Class?
3.)Body morphology?
4.) Other?
1.) Cnidaria
2.) Scyphozoa
3.) Juvenile stage is poly, adult stage is medusa
4.) “true jellies”, “cup” shaped animals
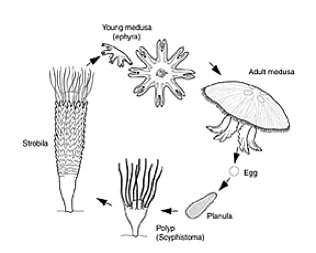
1.) What is Phylum Ctenophoria?
2.)Lives where?
1.) Comb Jellies
2.) Marine waters, lives on surface of water/near shores, most species prefer warmer waters.
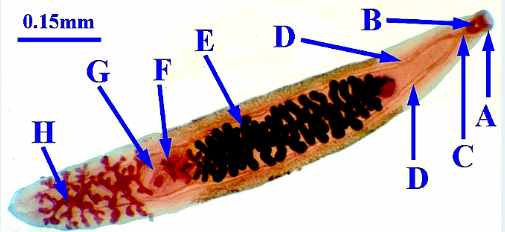
1.) Phylum
2.)Class?
3.)Species?
4.) Endoparasitic/Ectoparasitic/free-living?
5.)Identify some organs
6.) Intermediate host
7.) Monoecious or Diecious
1.)Platyhelminthes
2.)Trematoda
3.)Clonorchis sinesis
4.)Endoparastic
5.) picture
6.) Snails
7.) Monoecious
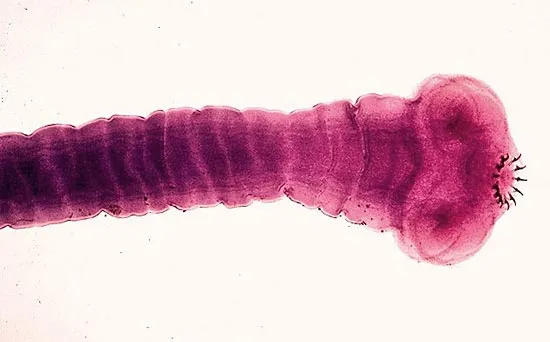
1.) Phylum?
2.) Class?
3.) Describe life stages
4.)Monoecious or Diecious?
5.)Pig tape worm?
6.) Intermediate host?
7.) Endoparasitic/Exoparasitc/Freeliving?
1.) Platyhelminthes
2.) Cestoda
3.) Mature proglottid segments infect cow/pig from contaminated vegetation. Humans eat contaminated muscle(larvae in muscle). Tapeworm grows to full maturity in human. Shedding of mature proglottid segments causes spread
4.) Monoecious
5.) Taemia solium (intermediate host: pig)
6.) Pig or cow
7.) Endoparasitic
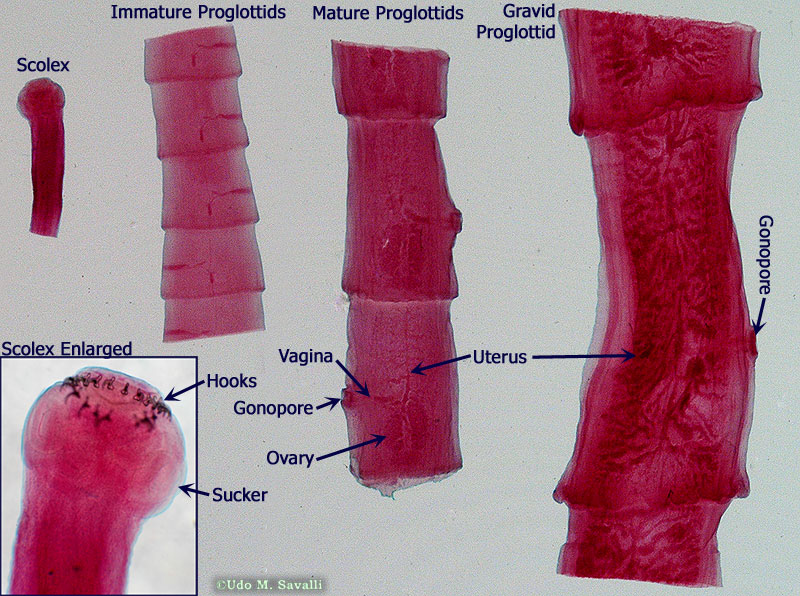
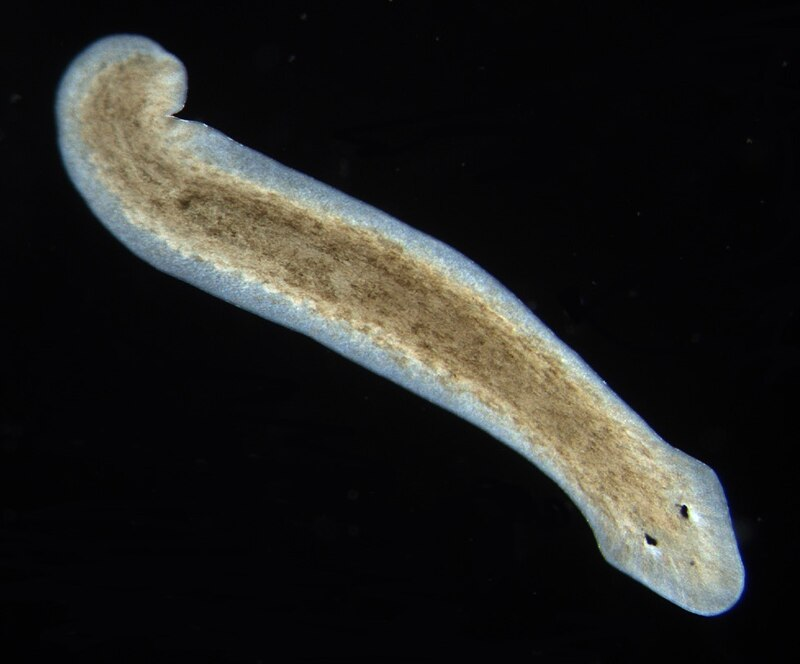
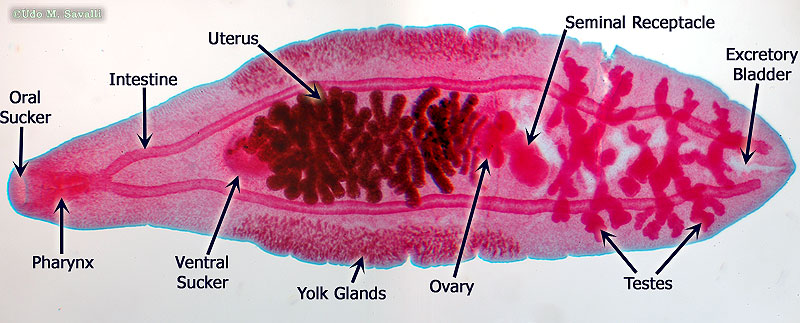
1.) Phylum?
2.) Class?
3.) Free living/Endoparasitic/Exoparasitic?
4.) Genus?
5.)Host?
6.)Found where?
7.) Monoecious or diecious
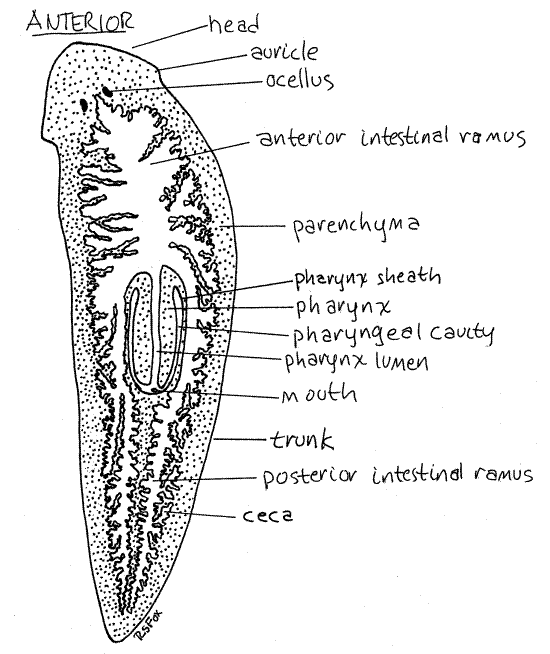
1.) Platyhelminthes
2.)Tubellria
3.) Free living
4.) Planaria
5.) No Host
6.) Found in freshwater, rivers streams, n ponds, under rocks/objects in shallow water (some are marine)
7.) Monoecious