Macroeconomics Unit 1: Basic Economics Concepts
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Scarcity
The economic problem of having unlimited human wants with limited recourses.
Consumer Goods
Products manufactured for direct consumption by consumers
Capital Goods
Goods used to produce other goods and services.
Trade-Offs
Sacrificing all of the other choices to gain another choice
Opportunity Cost
The next best alternative that isn’t chosen when making a decision.
Centrally Planned Economics
An economic system where the government makes all decisions regarding the production and distribution of goods and services.
Free Market Economics
An economic system where prices are determined by unrestricted competition between privately owned businesses.
Mixed Economies
Economic systems that combine elements of both free market and centrally planned economies, allowing for a blend of private and public sector involvement.
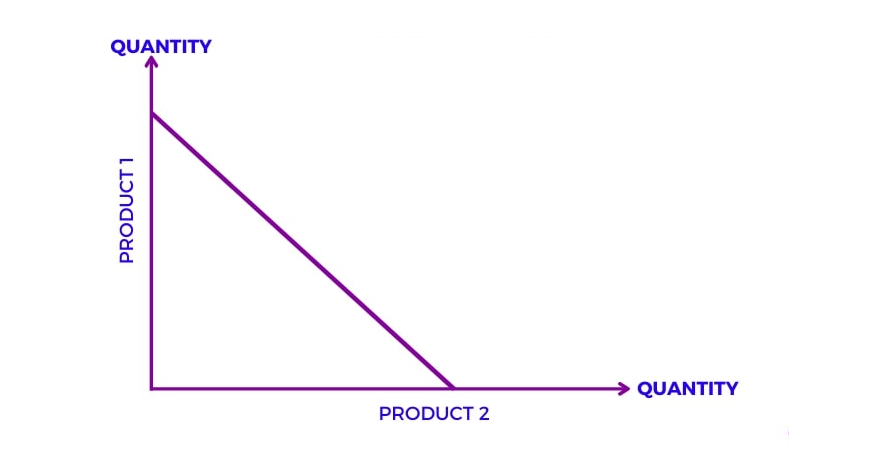
Constant Opportunity Cost
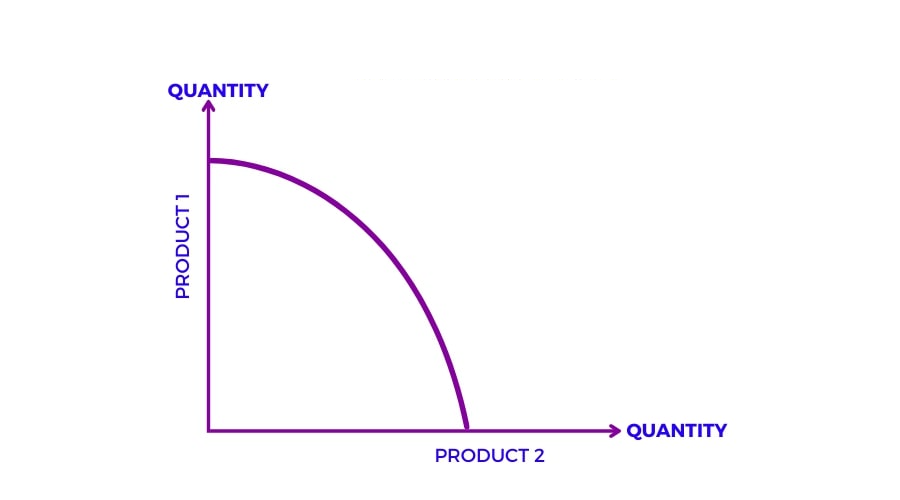
Increasing Opportunity Cost
The Law of Demand
As the price of a good decreases, the quantity demanded increases, and vice versa, all else being equal. Inverse relationship
The Law of Supply
As the price of a good increases, the quantity supplied increases, and vice versa, all else being equal. Direct relationship.
Change in quantity demanded
Movement along the demand curve due to a change in the price of the good
Change in demand
Shift of the entire demand curve due to factors other than price, such as consumer preferences or income changes.
The five shifters of supply
Prices of factors of production, technology, number of sellers, seller expectations, and government policies.
The five shifters of demand
Consumer income, consumer preferences, prices of related goods, expectations of future prices, and number of buyers.
Substitutes
Goods that can replace each other in consumption, where an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in demand for the other.
Compliments
Goods that are consumed together, where an increase in the price of one leads to a decrease in demand for the other.
Normal Goods
Goods for which demand increases as consumer income rises, and decreases as income falls.
Inferior Goods
Products that people buy less of when their income increases.
Surplus
When there’s more supply than demand
Shortage
A situation where demand exceeds supply, leading to insufficient goods available for consumers.
Price Ceiling
A government-imposed limit on how high a price can be charged for a product, intended to keep prices affordable for consumers.
Price Floor
A government-imposed minimum price that must be paid for a good or service, aimed at ensuring producers receive a fair price.
Subsidy
A financial assistance provided by the government to support a specific economic sector, lowering the cost of production and encouraging supply.
Double shift rule
might be indeterminate
Investment
Commitment of resources to achieve later benefits
Capital Stock
The value of physical assets a company uses in production, including machinery, buildings, and equipment.
Specialization
Allows for countries to reach higher productivity rates
Outputs acronym
Other goes Over, O.O.O.
Inputs acronym
Other goes under, I.O.U.
Opportunity Cost
calculate by using IOU or OOO
Recession
A period of temporary economic decline during which trade and industrial activity are reduced. We have the people, but not the ability.