Marine Bio Lab Practical
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:20 AM on 8/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
1
New cards
Atlantic croaker scientific name
Micropogonias undulatus
2
New cards
Ribbon Fish scientific name
Trachipterus jacksonensis.
3
New cards
Sand/sea trout scientific name
Cynoscion arenarius.
4
New cards
Scaled Sardine scientific name
Harengula jaguana.
5
New cards
Soles scientific name
Solea solea
6
New cards
Southern Flounder scientific name
Paralichthys lethostigma
7
New cards
Lizard fish scientific name
Synodus lucioceps
8
New cards
Bay anchovy scientific name
Anchoa mitchilli
9
New cards
Midshipman scientific name
Porichthys
10
New cards
Sea robin scientific name
Prionotus carolinus.
11
New cards
Spot scientific name
Leiostomus xanthurus
12
New cards
Hog choker scientific name
Trinectes maculatus
13
New cards
Red Fish scientific name
Sciaenops ocellatus
14
New cards
Hard head catfish scientific name
Ariopsis felis
15
New cards
Bay Squid scientific name
Uroteuthis noctiluca
16
New cards
Southern king fish scientific name
Menticirrhus americanus
17
New cards
Red snapper scientific name
Lutjanus campechanus
18
New cards
Porgy scientific name
Sparidae
19
New cards
Atlantic croaker

20
New cards
Ribbonfish

21
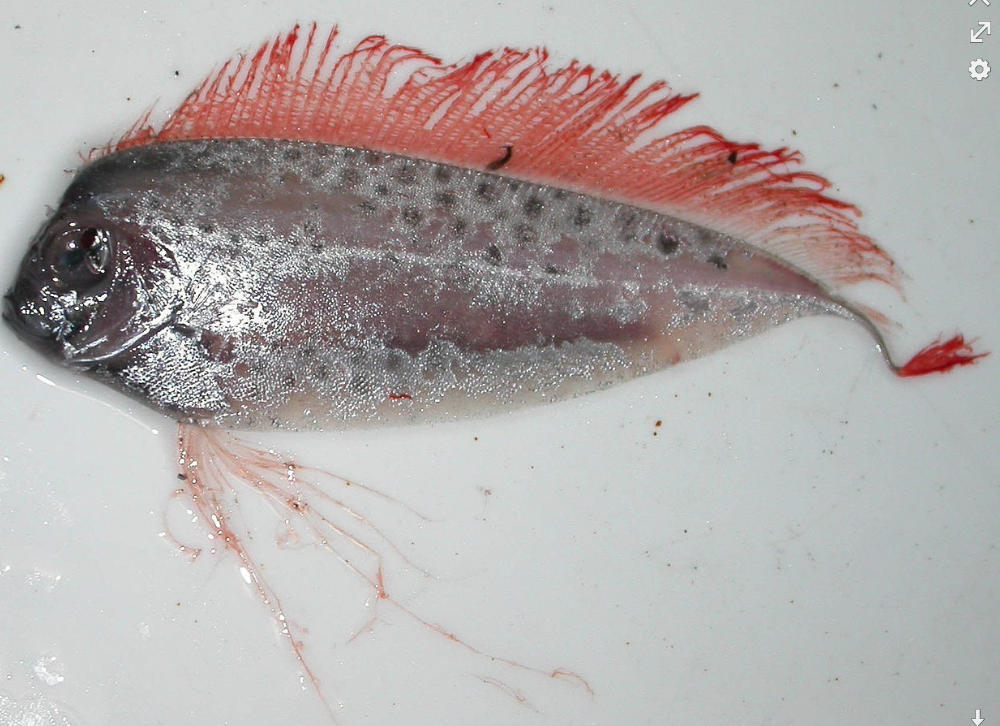
New cards
Sand/sea trout
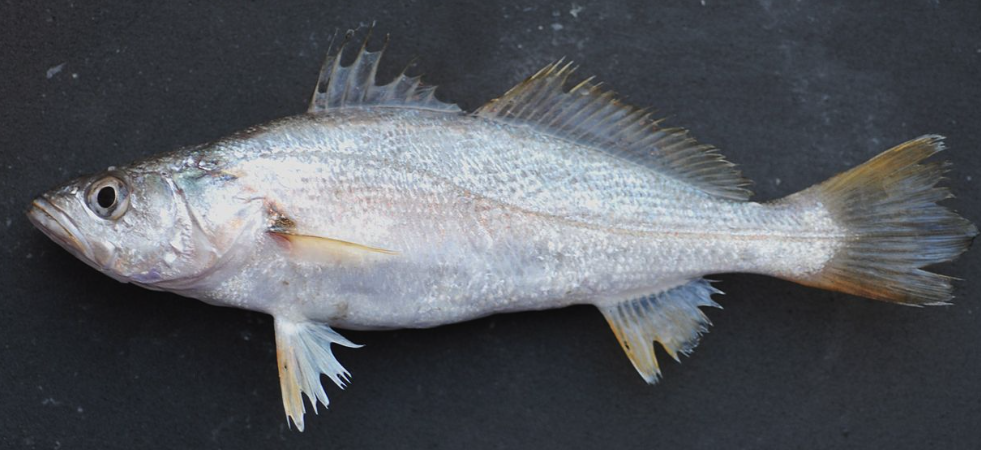

22
New cards
scaled sardine

23
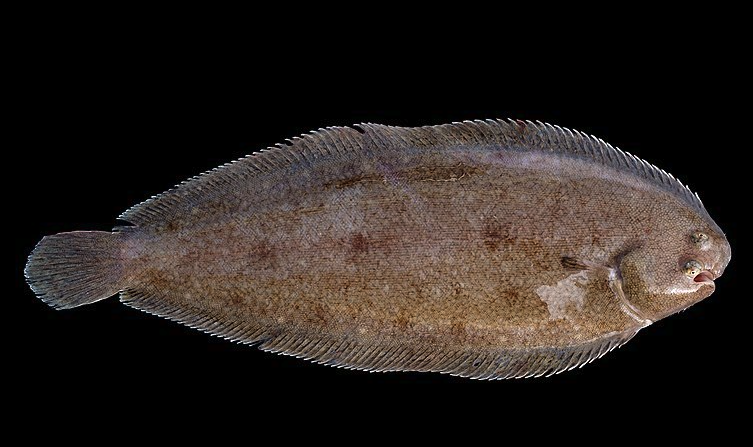
New cards
soles

24
New cards
Southern Flounder

25
New cards
Lizard fish

26
New cards
Bay anchovy

27
New cards
Midshipman

28
New cards
Sea robin

29
New cards
Spot

30
New cards
Hog choker

31
New cards
Red fish

32
New cards
Hard head catfish
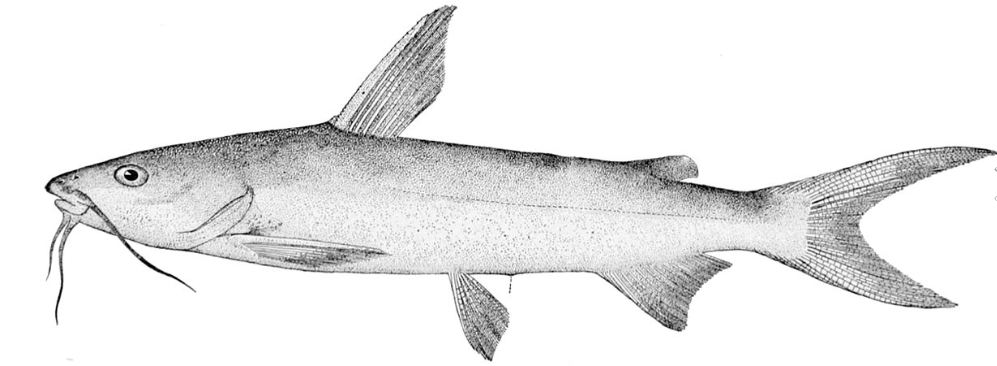
33
New cards
Bay Squid

34
New cards
Southern King fish

35
New cards
Red Snapper

36
New cards
Porgy
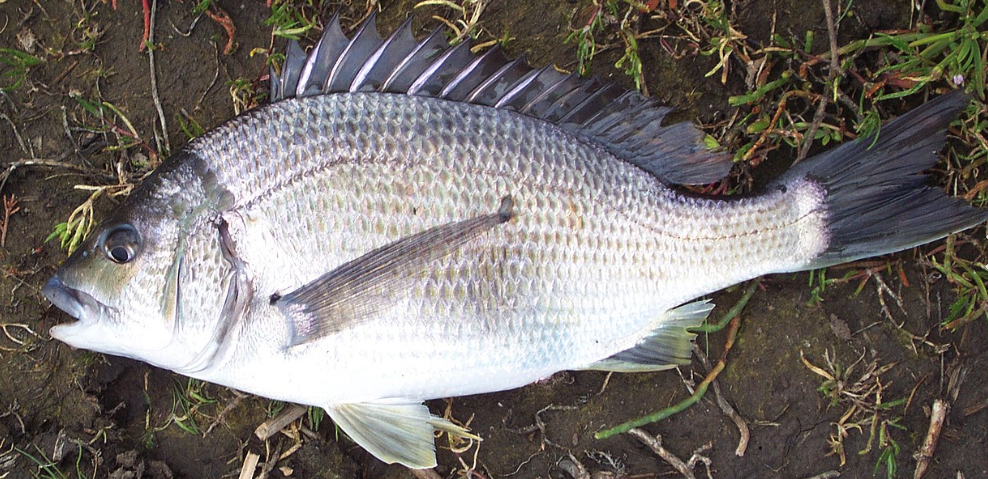

37
New cards
head of Mobile bay
Rivers entering the bay
38
New cards
mouth of Mobile bay
Bay exiting into GOM between Dauphin Island and Fort Morgan
39
New cards
Depositional environment
Sediment deposited on bay bottom by river flow
40
New cards
CTD and YSI
Conductivity-Temperature-Depth
Measures salinity, temperature, depth, and dissolved oxygen of water at each of the sampling locations
Measures salinity, temperature, depth, and dissolved oxygen of water at each of the sampling locations
41
New cards
water profile
The changes in salinity, temperature, dissolved oxygen, or other parameters as functions of depth
42
New cards
hydrocast
the act of lowering, then raising a meter through the water column each time
43
New cards
thermocline
a zone located beneath the surface in which a rapid decrease in temperature occurs relative to the change in depth
44
New cards
pycnocline
density gradient
45
New cards
how are pycnocline and thermocline related
water temperature is a critical factor in determining water density, so the thermocline and pycnocline are directly related
46
New cards
stratified water
A water column that has ‘layers’ because of the large density difference across the thermocline
47
New cards
salinity is measured in
parts per thousand (ppt) 0/00
48
New cards
Approximate ocean salinity
35 ppt
49
New cards
halocline
A sharp change in salinity with depth
50
New cards
Salinity stratified
Water that has different salinity layers and has a strong halocline
51
New cards
refractometer
hand-held device for measuring salinity
52
New cards
Density of open ocean water
1\.025 g/ml
53
New cards
Are phytoplankton or zooplankton larger
zooplankton
54
New cards
holoplankton
remain planktonic for their entire life cycle
55
New cards
meroplankton
Have both planktonic and benthic stages of life, and are usually larval stages of larger organism
56
New cards
Mobile Bay sediment
muddy/clay typically hypoxic or anoxic in summer
57
New cards
nekton vs. plankton
nekton are capable of swimming/fighting against a water current of at least 1 knot on their own. Plankton cannot swim against a current of 1 knot.
58
New cards
Phytoplankton
consists of representatives of seven plant divisions, all algae, plus a \n photosynthetic group of bacteria (the cyanobacteria).
59
New cards
dominant members of the phytoplankton caught in nets
diatoms and dinoflagellates
60
New cards
dinoflagellates
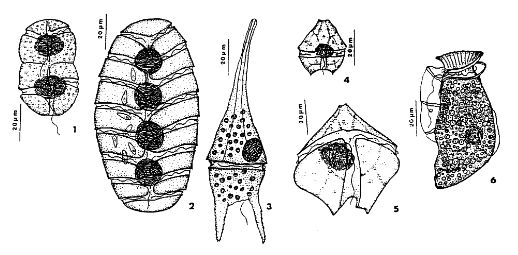
61
New cards
diatoms
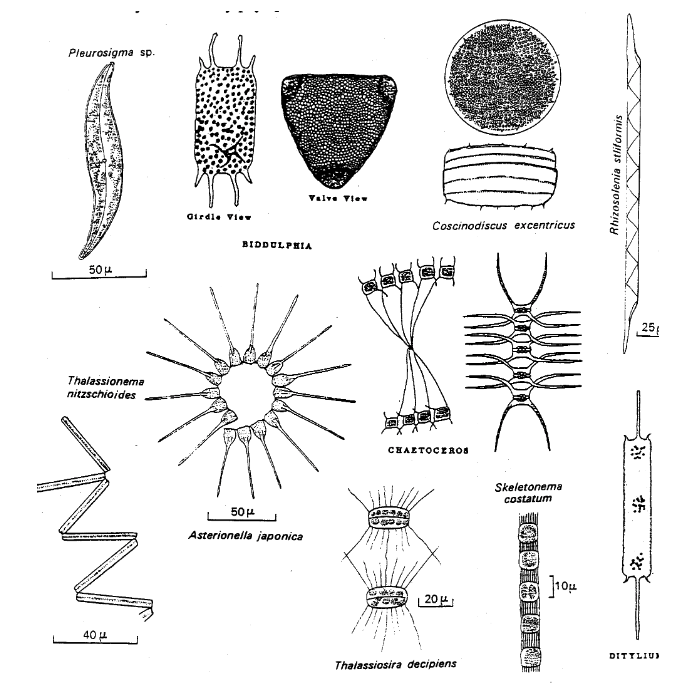
62
New cards
zooplankton
consists of members of almost all 35 animal phyla
63
New cards
copepod
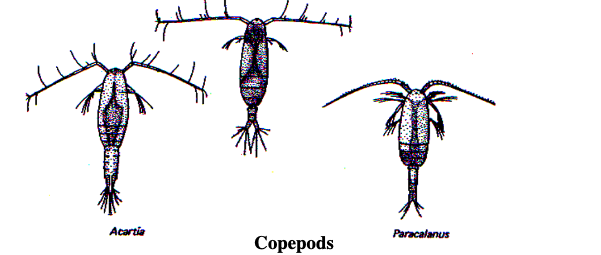
64
New cards
decapod
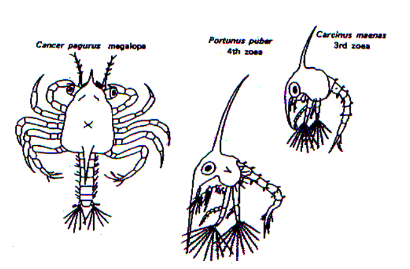
65
New cards
Polychaetes
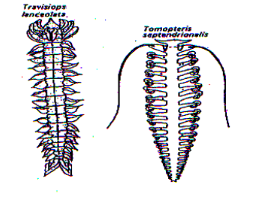
66
New cards
Mysids
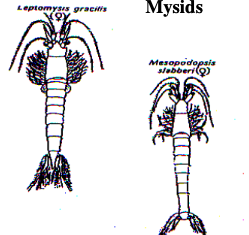
67
New cards
Anchovy larvae
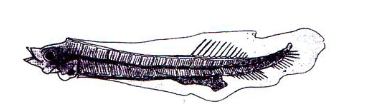
68
New cards
Chaetognath
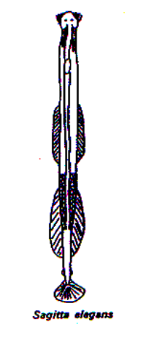
69
New cards
Larvacean
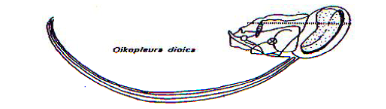
70
New cards
Echinoderm larvae
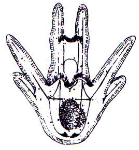
71
New cards
Species of plant in sandy beach habitat
Sea oats, seaside morning glory, American beach grass, seashore dropseed, pennywort, smooth cordgrass and others
72
New cards
Sea oats
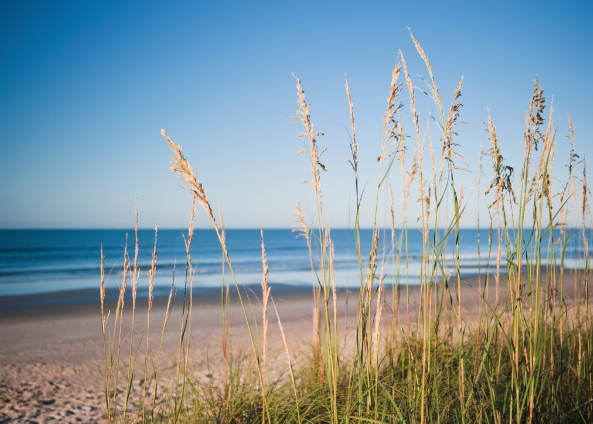

73
New cards
Seaside morning glory
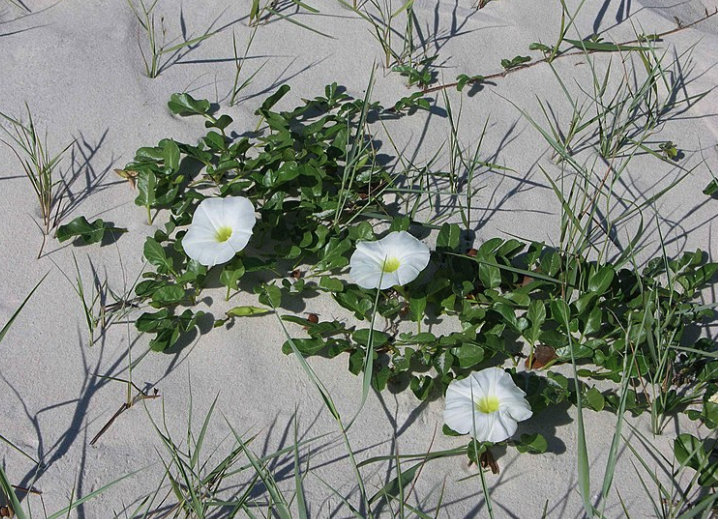

74
New cards
American beach grass

75
New cards
smooth cordgrass
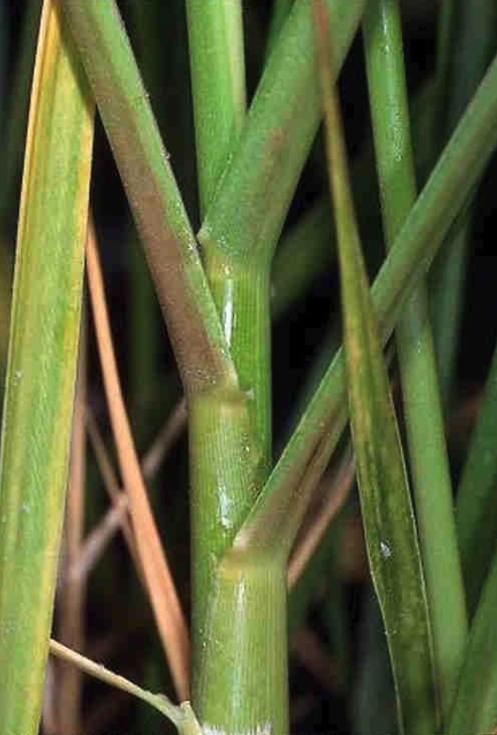

76
New cards
Seashore dropseed

77
New cards
pennywort
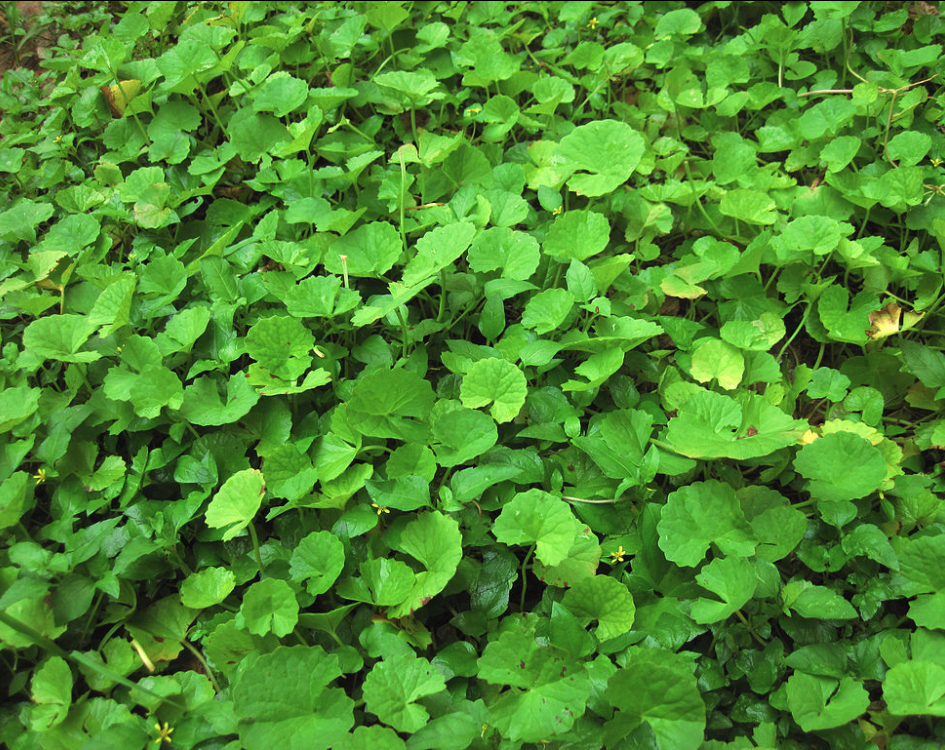

78
New cards
Birds observed in class
Brown pelican, laughing gull, great blue heron, red-winged blackbird, grackle, snowy egret, great egret, least tern, osprey, black skimmer, clapper rail
79
New cards
Common salt marsh plants
Spartina, juncus, saltwort and glasswort, seashore dropseed, seaside morning glory and others
80
New cards
Plant adaptations to avoid desiccation in salt marsh
Root mats, rhizomes, less surface area above ground to support, skinny body to handle wind, no leaves/small leaves to deal with salt content, larger roots or taproot for water retention, etc.
81
New cards
Common salt marsh animals and adaptations
Periwinkle snails (suction to spartina to avoid washing away), fiddler crabs (burrow), hermit crabs, bird species, ragworm, capitellid worm, and others
82
New cards
Shark external anatomy
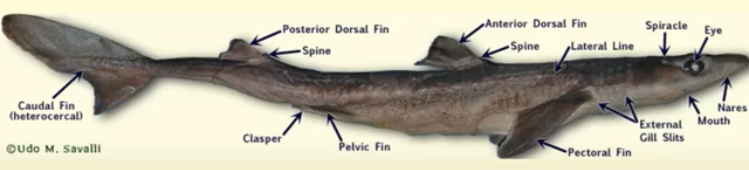
83
New cards
Shark internal anatomy
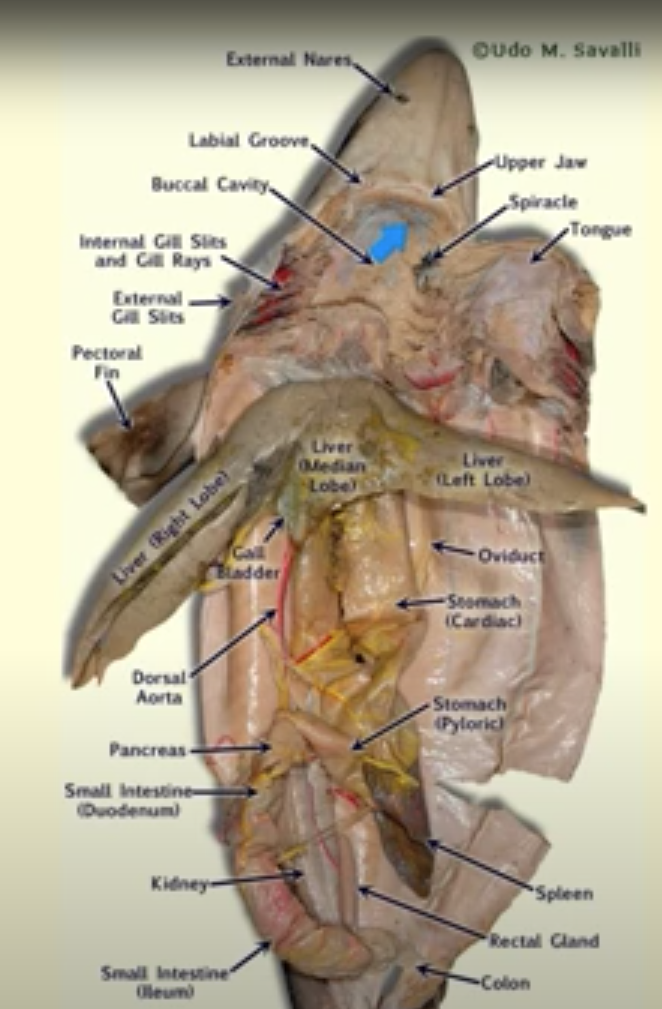
84
New cards
Bony fish external anatomy
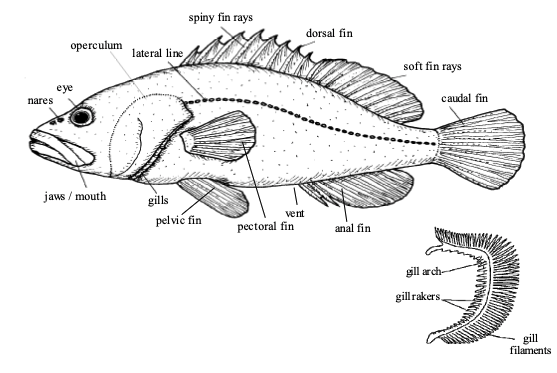
85
New cards
Bony fish internal anatomy
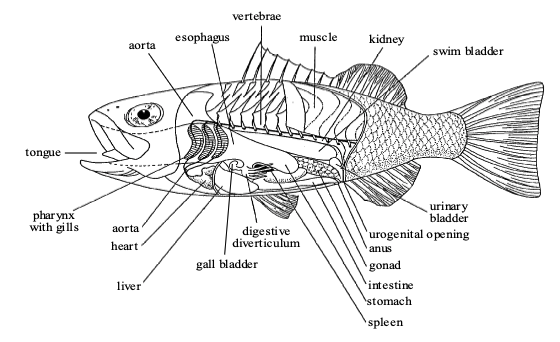
86
New cards
Blue crab external anatomy (how to determine male or female)
Males are larger. Females have a darker abdomen on ventral side and more pairs of pleopods
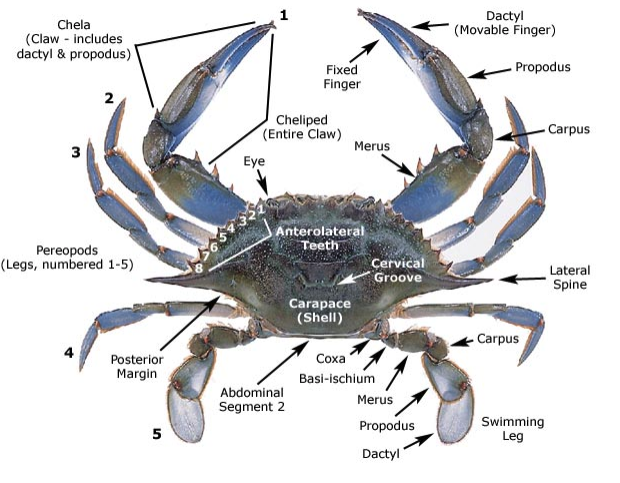
87
New cards
Female blue crab internal
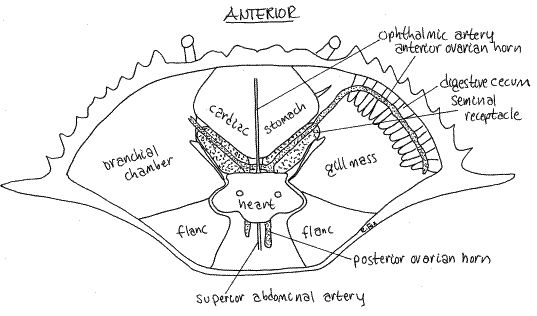
88
New cards
Male blue crab internal
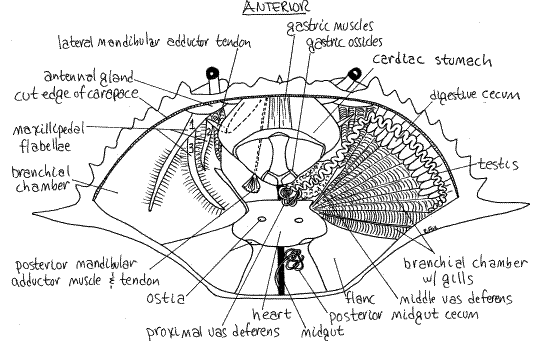
89
New cards
How are oysters beneficial
American oysters are commercially beneficial, they filter pollutants and sediment out of the water, and create oyster reefs which are important habitats
90
New cards
American oyster
91
New cards
Common sea grasses in Big Lagoon
Thalassia testudinum (turtle grass), Halodula wrightii (manatee grass)
92
New cards
Thalassia testudinum (turtle grass)
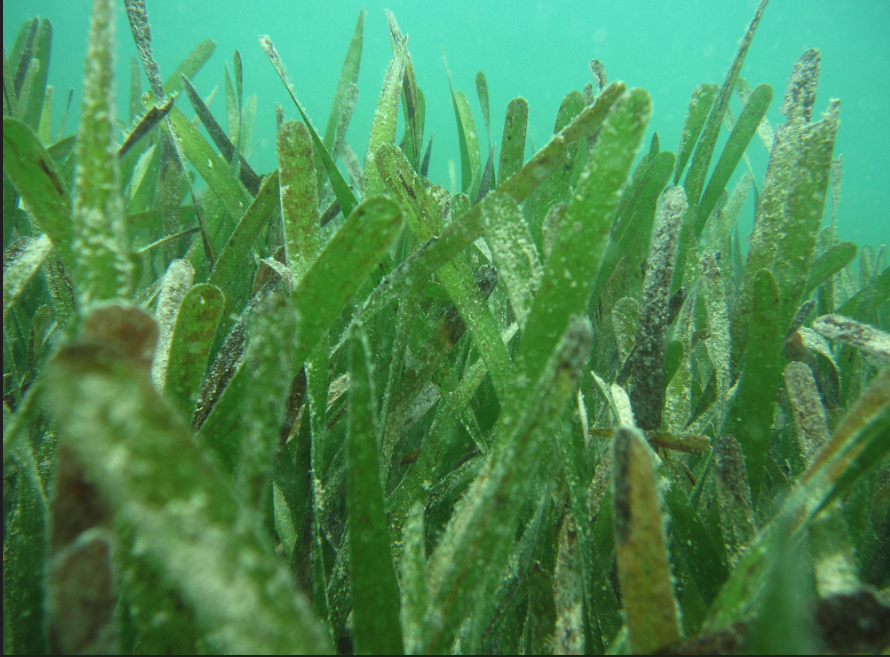

93
New cards
Halodula wrightii (shoal grass)

94
New cards
Syringodium filiforme
manatee grass