BIO 3&4 NUCLEIC ACIDS
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapter 2B edrolo
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What are nucleic acids?
Nucleic acids are the genetic material of a cell and determine how both individual cells and entire organisms will develop and function
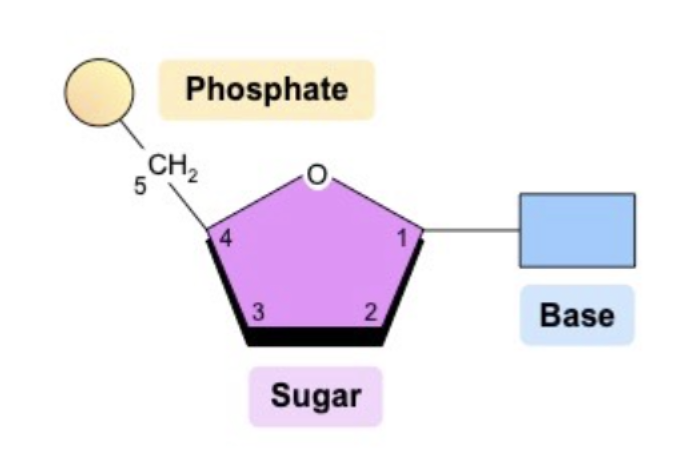
What is the structure of a nucleotide?
A central 5-carbon pentose sugar (pentagon), which is attached to a phosphate group (circle) and a nitrogenous base (rectangle)
How are nucleotides connected?
Nucleotides are joined by a condensation reaction forming a phosphodiester bond between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the 3′ position of the sugar of another nucleotide.
What are the nitrogenous bases of RNA?
adenine, uracil, guanine, cytosine
Term for double-ringed structure bases
PURINES
Adenine, guanine
Term for single-ringed structure bases
PYRIMIDINES
Cytosine, thymine (DNA), uracil (RNA)
Function of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
DNA is the genetic material and determines how cells function and which proteins are synthesised
Function of RNA (ribonucleic acid)
RNA is a nucleic acid that transfers genetic information and plays a key role in protein synthesis.
Differences between DNA and RNA
RNA is a single-stranded molecule, whereas DNA is a double-stranded molecule (promotes conservation of the base sequence)
RNA includes the base uracil, whereas DNA uses thymine instead (but the bases are almost identical and fulfil the same function)
RNA and DNA are composed of different pentose sugars (RNA contains ribose, whereas DNA contains deoxyribose)
Structure of DNA: How are the two chains of DNA held together?
Held together by hydrogen bonding between complementary bases.
Adenine and Thymine pair via two hydrogen bonds (A = T)
Guanine and Cytosine pair via three hydrogen bonds (G Ξ C)
What is the role of Messenger RNA (mRNA)?
mRNA carries a transient copy of a specific DNA sequence from the nucleus to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
What is the role of Transfer RNA (tRNA)?
tRNA carries amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome for protein synthesis.
What is the role of Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)?
rRNA forms the core of the ribosome and catalyses protein synthesis.