Histology Quiz 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Last updated 4:27 PM on 1/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
Brightfield light microscope
which type of microscope was used to take the image?
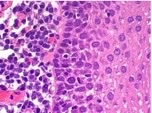
2
New cards
scanning em
which type of microscope was used to take the image?
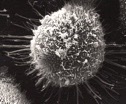
3
New cards
transmission em
which type of microscope was used to take the image?
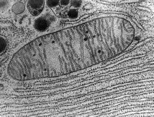
4
New cards
Fluorescence or confocal light microscope
which type of microscope was used to take the image?
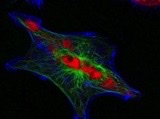
5
New cards
plasma membrane
* Semi-permeable -> fluid mosaic structure
* protection and structure
* controls what comes in and out of the cell
* Communication w/ environment
* protection and structure
* controls what comes in and out of the cell
* Communication w/ environment
6
New cards
nucleus
* Contains DNA/genetic material
* Site of DNA replication, transcription
* Can affect appearence of nucleus
* controls/regulates cell function
* Site of DNA replication, transcription
* Can affect appearence of nucleus
* controls/regulates cell function
7
New cards
ribosomes
function in protein synthesis
8
New cards
rough er
* Ribosomes attached
* Protein modification/packaging
* Folding, adding sugar groups
* Protein modification/packaging
* Folding, adding sugar groups
9
New cards
smooth er
* Lipid synthesis
* Calcium storage-> muscle cells
* Detoxification -> liver cells
* Calcium storage-> muscle cells
* Detoxification -> liver cells
10
New cards
golgi apparatus
Cellular product processing, sorting, shipping
11
New cards
secretory vesicles
Package product in golgi and travel to release product outside of cell
12
New cards
mitochondria
* Makes energy (ATP) through aerobic respiration
* Prevalent in active cells like muscle or kidney
* Prevalent in active cells like muscle or kidney
13
New cards
the cytoskeleton
* Network of protein filaments found throughout cell
* Provides internal structure, assist w/ specialized functions like intracellular transport, cell movement, cell division
* Provides internal structure, assist w/ specialized functions like intracellular transport, cell movement, cell division
14
New cards
microtubules
* “Steel beams”
* Made of protein tubulin
* Involved in intracellular transport
* Important in large cells like neurons
* Made of protein tubulin
* Involved in intracellular transport
* Important in large cells like neurons
15
New cards
intermediate filaments
* “Logs”
* Form shape and structure throughout cytoplasm
* Help w/ cell-cell attachment at junctions
* Important for epithelia especially skin
* Form shape and structure throughout cytoplasm
* Help w/ cell-cell attachment at junctions
* Important for epithelia especially skin
16
New cards
microfilaments
* Smallest filaments made of actin
* Important for cell movement
* Important for cell movement
17
New cards
cellular inclusions
Some cells have storage function and have abundant deposits within cytoplasm that aren’t membrane bound
18
New cards
functions
Different cell types are specialized for different ______
19
New cards
ribosomes and rough ER
cells have very basophilic cytoplasm, and also have very euchromatic nuclei, what structures might be enriched in the cytoplasm of these cells?
20
New cards
produces lots of proteins, very transcriptionally active
Cells have very basophilic cytoplasm, and also have very euchromatic nuclei what might these features suggest about the function of these cells?
21
New cards
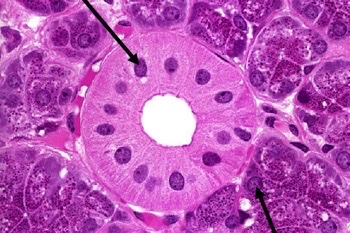
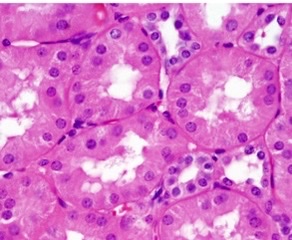
mitochondria, lysosomes, golgi apparatus,
The parietal cells in this image have very acidophilic cytoplasm what structures might be enriched in the \n cytoplasm of these cells?
22
New cards
mitochondria would need to produce lots of energy, lysosomes, golgi would have secretory functions
The parietal cells in this image have very acidophilic cytoplasm What does that tell you about the \n function of these cells?
23
New cards
lipids or high sugar areas
The cells in this image have multiple white \n structures in their cytoplasm what could they be?
24
New cards
not intensely, must use EM to see more detail
How does the plasma membrane stain with H&E?
25
New cards
plasma membrane w/ TEM
What structure is pointed at in the photo and what microscope was used?
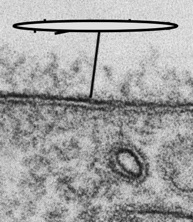
26
New cards
purple, basophilic
The nucleus stains ___ in H&E because it is _______
27
New cards
nucleus w/ H&E
What structure is pointed at in the photo and what microscope/technique was used?
28
New cards
nucleus w/ TEM
What structure is pointed at in the photo and what microscope/technique was used?
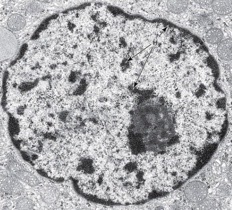
29
New cards
basophilic, purple
When ribosomes are concentrated in one part of the cell, the cytoplasm there will be ____ as a result and appear _____ in H&E staining.
30
New cards
function requires lots of proteins
What might you infer about the activities of a cell with an abundant supply of ribosomes in its cytoplasm?
31
New cards
ribosomes w/ TEM
What structure is pointed at in the photo and what microscope/technique was used?

32
New cards
doesn’t stain intensely bc of lipid abundance
how does smooth ER stain w/ H&E
33
New cards
same as ribosomes, basophilic and purple
how does rough ER stain w/ H&E
34
New cards
Cells with major secretory functions, pale pink stained region near nucleus
In what type of cells will the golgi apparatus be apparent in H&E? How does it appear in them?
35
New cards
secretory product inside
What does the appearance of secretory vesicles depend upon?
36
New cards
secretory vesicle
What is this?
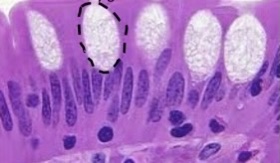
37
New cards
golgi apparatus
The arrows point to what pale staining cell structure?
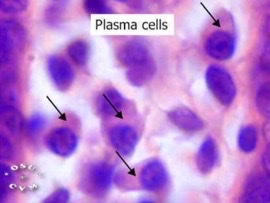
38
New cards
acidophilic, bright pink
How do mitochondria stain in H&E
39
New cards
pink, they need lots on energy and are active (like muscle/kidney)
What color is the cytoplasm of cells with abundant mitochondria? What could be inferred about these cells?
40
New cards
mitochondria
What cell structure is this?
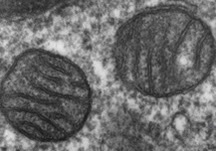
41
New cards
Mitochondria
What cell structure is this?
42
New cards
microtubules
green in image
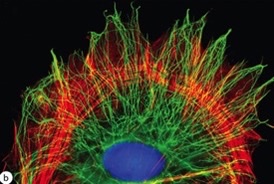
43
New cards
microfilaments
Red in image
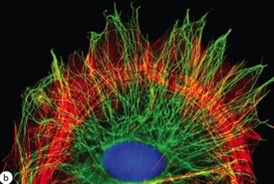
44
New cards
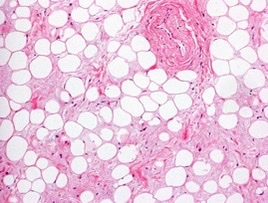
cellular inclusions
What cell structure is the photo and example of?
45
New cards
tissues
The cells of the body aggregate and organize \n into cooperative groups called ______
46
New cards
Organs
_______ are then assembled from multiple types of cells and tissues, working cooperatively
47
New cards
epithelial, connective, muscle, nervous
What are the 4 types of tissues in the human body?
48
New cards
lining internal and external surfaces
Where is epithelial tissue found?
49
New cards
primary barrier
Epithelia form _______ between us and the world
50
New cards
covering and protecting surfaces, mediating what enters the body, secretion, sensation
what are 4 main functions of epithelial tissue?
51
New cards
cell junctions, basement membrane
Epithelia adhere tightly through _____ and attachment to a ________ to create a strong protective surface
52
New cards
polarized
epithelia are ______ because they have 2 different sides
53
New cards
apical side
faces external environment/lumen not attatched to tissue
54
New cards
basal side
attached to basement membrane+underlying tissue
55
New cards
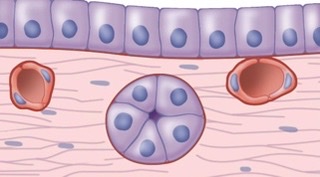
basement membranes
what do the pink lines in the figure represent
56
New cards
Attachment to underlying connective tissue, support and organizes epithelium, regulate what materials cross epithelium
What are the basement membrane’s key functions?
57
New cards
Hemidesmosomes
special junctions that attach epithelial cells to basement membrane
58
New cards
laminin and collagen
basement membranes are a dense, self-assembling, mesh-like network of ____ and _____
59
New cards
sticky glycoproteins and reticular collagens
What attaches basement membranes to underlying tissue?
60
New cards
tight, adherens, desmosomes, gap
order where the junction types are found from apical to basal
61
New cards
cell-cell junctions
\n Help epithelial cells adhere to their neighbors and communicate with one another to form a tough, continuous, selectively permeable surface
62
New cards
tight junctions
Prevent molecules and pathogens from passing in between cells, creates an apical membrane domain
63
New cards
adherens junctions
Reinforces strong cell-cell connections by connecting actin networks of adjacent cells
64
New cards
desmosomes
Connects intermediate filament cytoskeletons of adjacent cells for strong cell-cell adhesion
65
New cards
gap junctions
Creates pores that connect cells for cell-cell communication
66
New cards
tight and adherens
What junction type(s) form a continuous belt around cell
67
New cards
tight
What junction type(s) prevent pathogens and toxins from crossing epithelium via extracellular space
68
New cards
gap junctions
What junction type(s) connect the cytoplasm of adjacent cells to promote cell-cell communication
69
New cards
adherens and desmosomes
What junction type(s) connect cytoskeletons of adjacent epithelial cells
70
New cards
desmosomes
What junction type(s) form extremely strong “spot-weld” connections to allow epithelial cells to adhere to one another
71
New cards
claudins and occludins
What are tight junctions made of?
72
New cards
cadherins and catenins
What are adherens junctions made of?
73
New cards
cadherins
What are desmosomes made of?
74
New cards
connexins, circular patches between cells
What are gap junctions made of and what structure do they form?
75
New cards
apical
Which surface can microvilli and cilia be found on
76
New cards
Microvilli
* Increase apical surface area to increase absorption capabilities
* Actin based internal structure
* Not mobile
* Actin based internal structure
* Not mobile
77
New cards
cilia
* Larger than microvilli
* Microtubule based
* May be mobile
* Often move same direction to create current
* To move fluids over cell surface or function in intercellular signing
* More likely to be visible w/ light microscopy
* Microtubule based
* May be mobile
* Often move same direction to create current
* To move fluids over cell surface or function in intercellular signing
* More likely to be visible w/ light microscopy
78
New cards
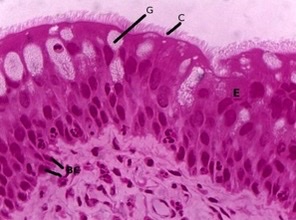
cilia
What is shown in the image?
79
New cards
microvilli
What is shown in the image?
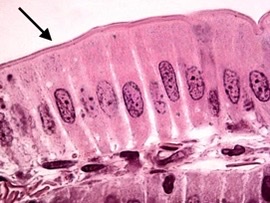
80
New cards
\# of cell layers and cell shape
What 2 criteria determine epithelia classification?
81
New cards
Psedostratified epithelia
* Single layer of cells w/ varying shape
* Nuclei at different heights but all still tough basement membrane
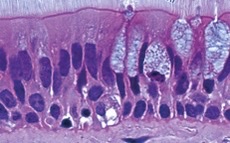
* Relatively uncommon-> found primarily in respiratory system
* Nuclei at different heights but all still tough basement membrane
* Relatively uncommon-> found primarily in respiratory system
82
New cards
simple columnar
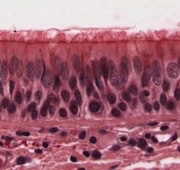
* Often notably internally polarized
* Cytoplasm can hold multiple structures for protein production secretion ect
* Can carry out absorption w/ microvilli
* Present where absorption or secretion occur
* Ie digestive system
* Cytoplasm can hold multiple structures for protein production secretion ect
* Can carry out absorption w/ microvilli
* Present where absorption or secretion occur
* Ie digestive system
83
New cards
simple cuboidal
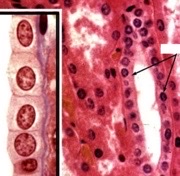
* Thin enough for efficient absorption but enough cytoplasm to hold organelles for functions like energy production
* Common in places like the kidney where active transport is required (can generate the ATP required)
* Common in places like the kidney where active transport is required (can generate the ATP required)
84
New cards
simple squamous
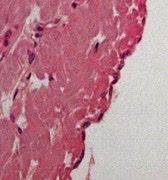
* Can often only see nucleus w/ minimal cytoplasm
* Great at rapid exchange of materials, can diffuse easily across
* Often found in places where rapid diffusion important
* Line blood vessels, alveoli of lung
* Great at rapid exchange of materials, can diffuse easily across
* Often found in places where rapid diffusion important
* Line blood vessels, alveoli of lung
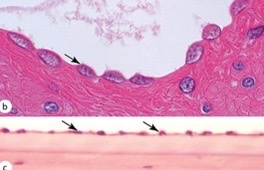
85
New cards
simple squamous
What type of epithelia?
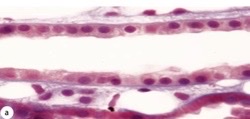
86
New cards
simple cuboidal
What type of epithelia?
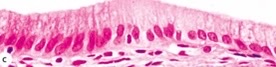
87
New cards
simple columnar
What type of epithelia?
88
New cards
Psedostratified
What type of epithelia?
89
New cards
simple cuboidal, kidney
What type of epithelia? Where could it be located?
90
New cards
simple squamous, alveoli, blood vessel lining
What type of epithelia? Where could it be located?
91
New cards
Psedostratified, respiratory system
What type of epithelia?
92
New cards
simple columnar, digestive system
What type of epithelia?
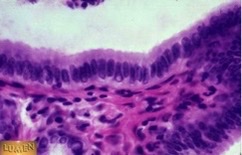
93
New cards
Non-keratinized stratified squaemous, mouth
What type of epithelia? Where could it be located?
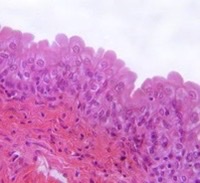
94
New cards
transitional, urinary system
What type of epithelia? Where could it be located?
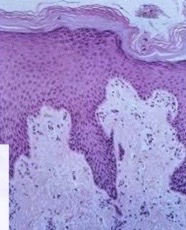
95
New cards
keratinized stratified squamous, skin
What type of epithelia? Where could it be located?
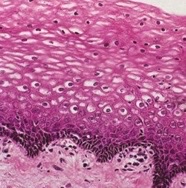
96
New cards
endocrine
Is the gland endocrine or exocrine?
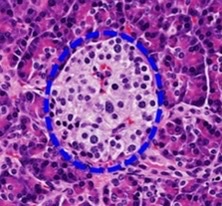
97
New cards
exocrine
Is the gland endocrine or exocrine?
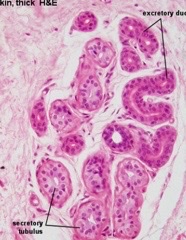
98
New cards
Serous
Is the gland producing a serous or mucous product?
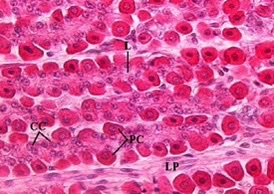
99
New cards
mucous
Is the gland producing a serous or mucous product
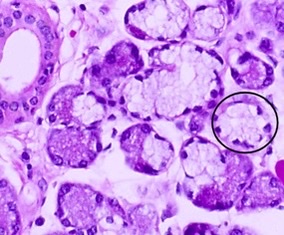
100
New cards
stratified epithelia
* At least 2 distinct layers
* Only 1 basal most layer contacts basement membrane
* Only 1 basal most layer contacts basement membrane