Meiosis: Stages, Chromosomes, and Genetic Variation in Biology
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Each body cell of a fruit fly (Drosophila) contains 8 chromosomes. How many chromatids would normally be present during Prophase I?
16
The illustration below represents which stage of meiosis?
Metaphase I
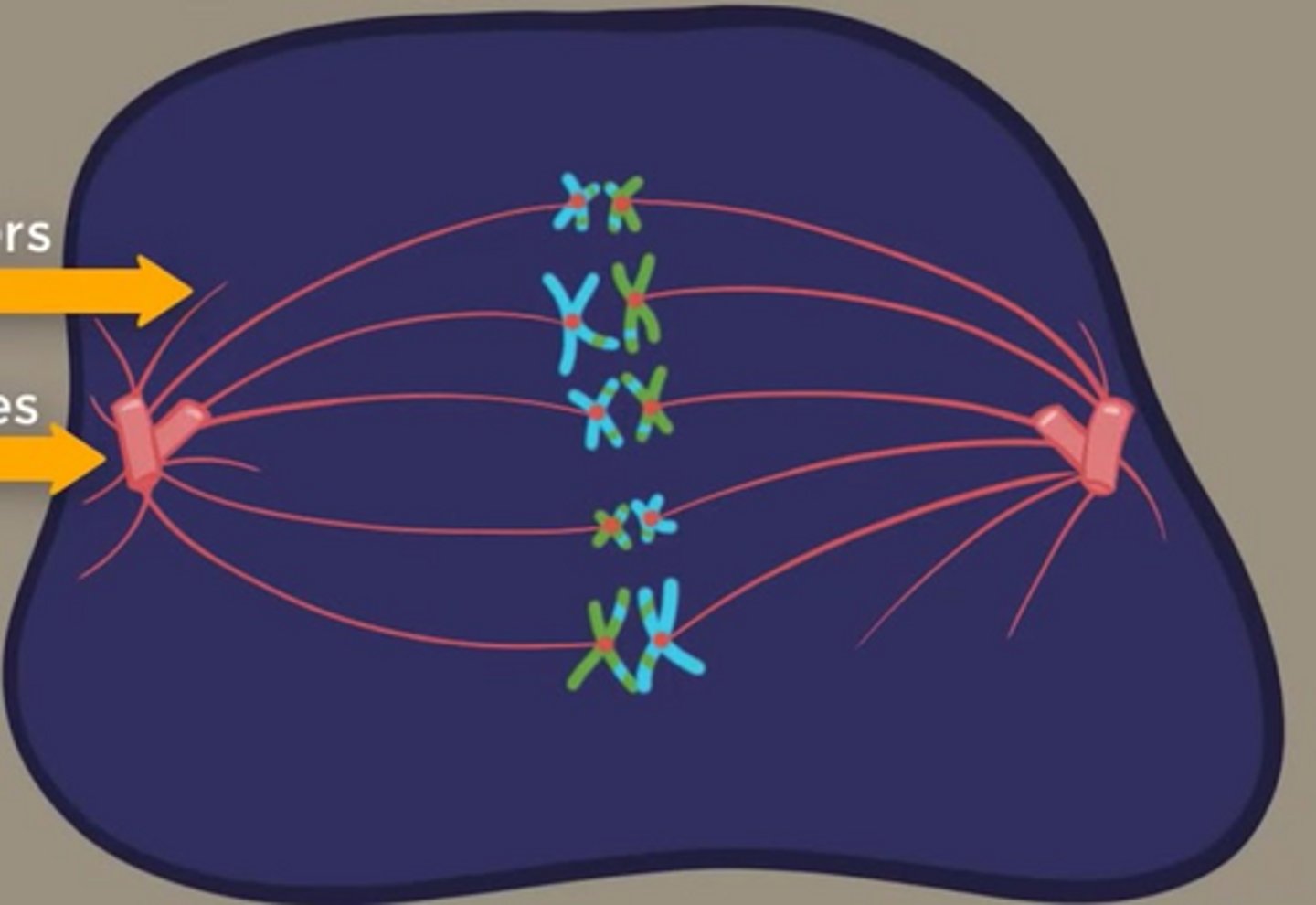
What is the number of chromatids of the illustration below?
20
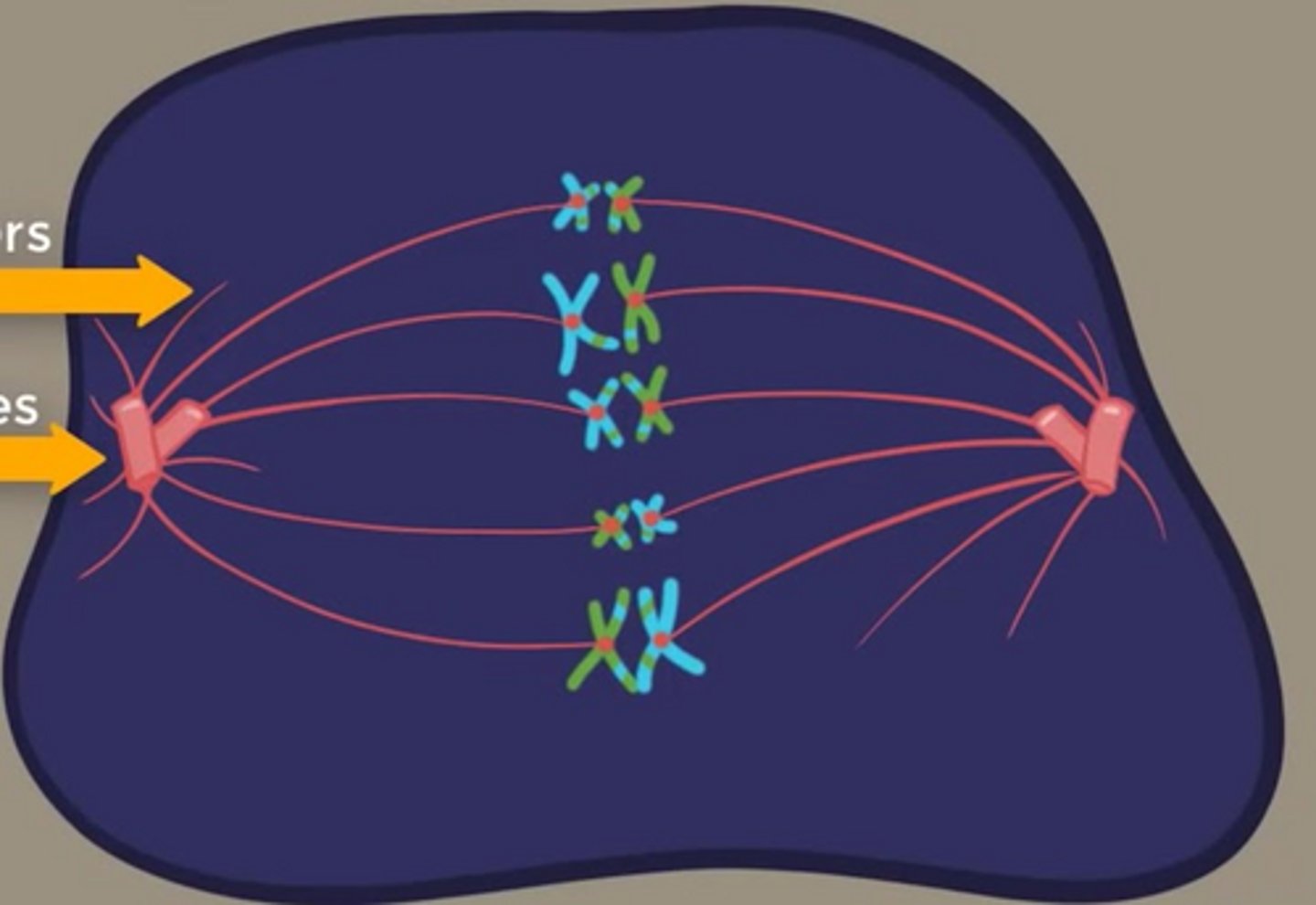
Which phase of meiosis does crossing-over occur?
Prophase I
What holds the sister chromatids together?
Centromeres
Which of the following are examples of haploid?
AB; aB
dog's sperm cell contains 39 chromosomes. What is the total number of chromosomes normally present in a stomach cell of this dog?
78
Which statements are true about meiosis?
1.) During meiosis I, the number of chromosomes are cut in half
2.) During meiosis II, the number of chromatids are cut in half
3.) During meiosis I, the number of chromatids are cut in half
A cell undergoes meiosis. How do the gametes it produces compare with the original cell and with one another?
The gametes have half the chromosomes of the parent cell, and are genetically different from one another
What is the number of chromatids of the illustration below?
5
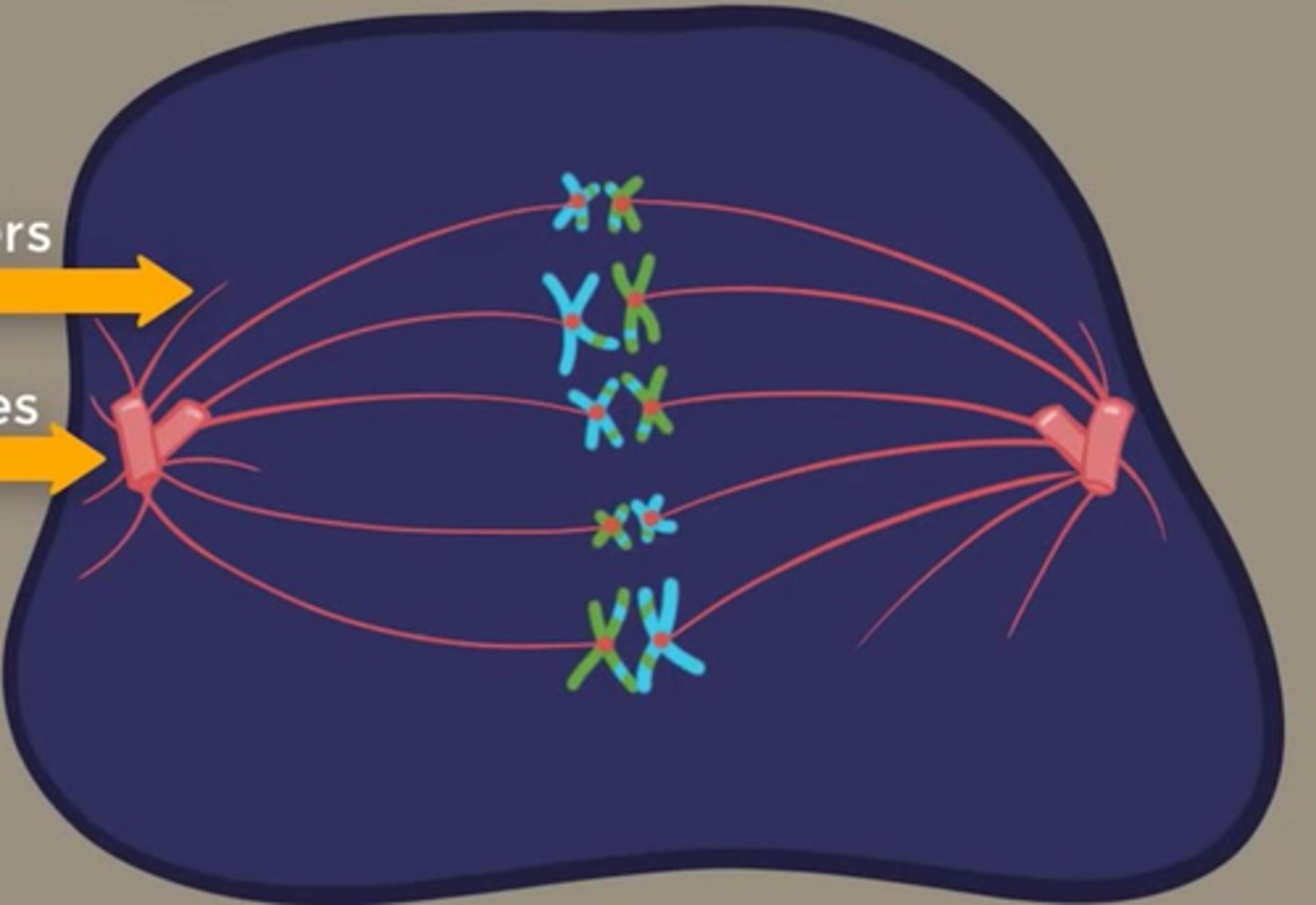
What is the correct sequence of meiosis?
2N --> N
During meiosis, the process of cell division results in:
Four haploid daughter cells
What is the number of homologous chromosomes of the illustration below?
5
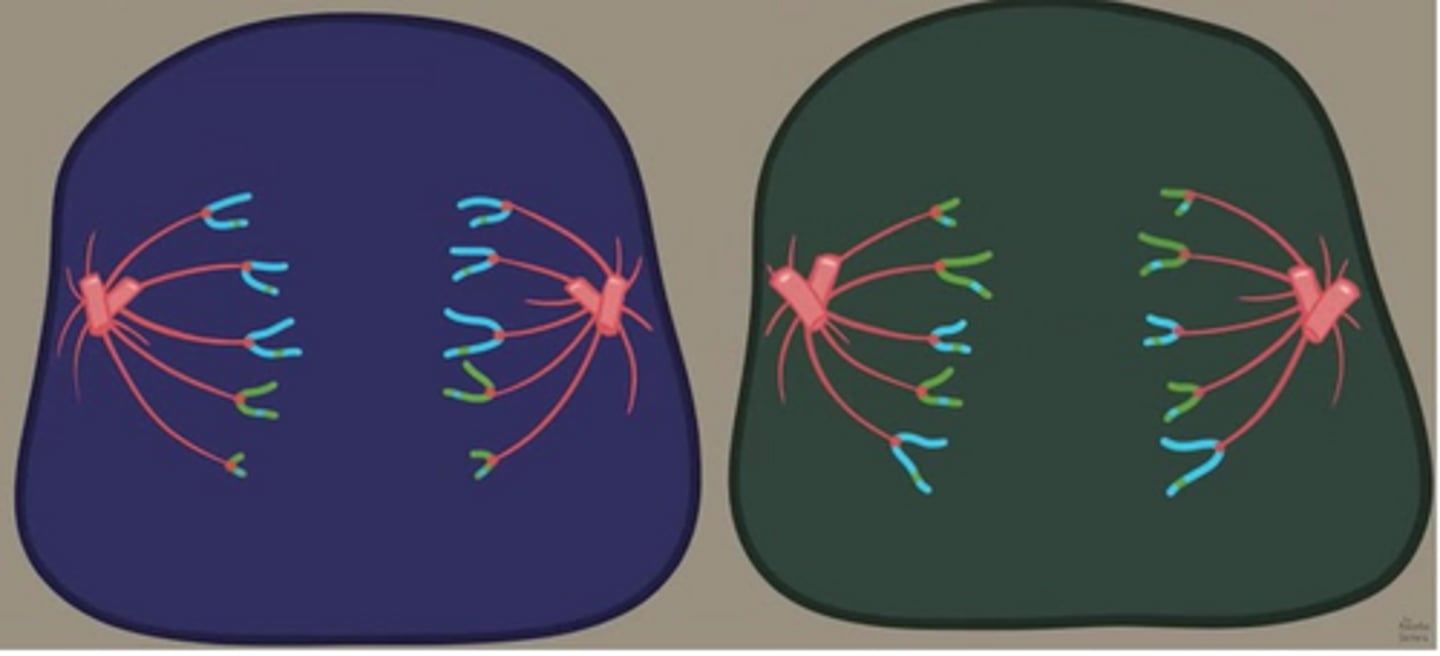
The illustration below represents which stage of meiosis?
Anaphase II
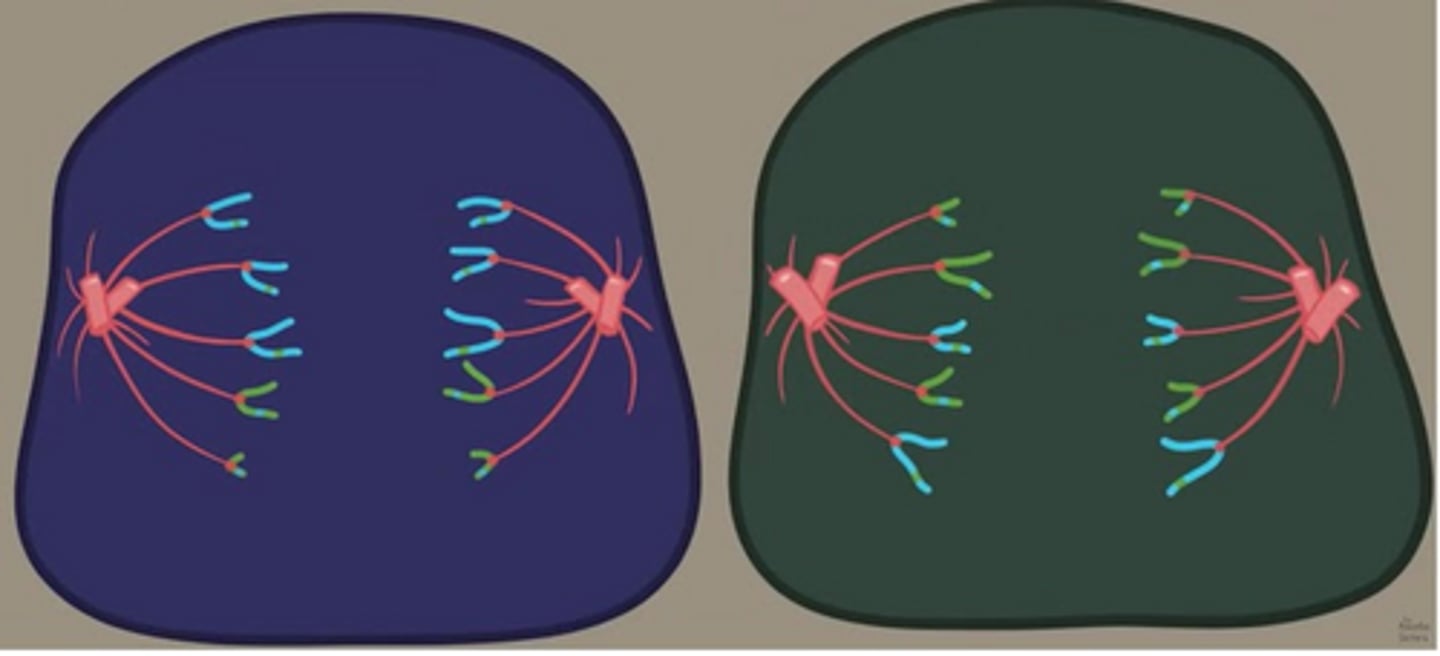
Each body cell of a fruit fly (Drosophila) contains 8 chromosomes. How many chromosomes would normally be present in a gamete produced by this fruit fly?
4
Which statements are true about meiosis?
1.) During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes separate
2.) During anaphase II, the paired chromatids separate
Which of the following sequences represents chromosome number during fertilization?
N + N --> 2N
Which of the following are ways to describe a diploid cell?
1.) 2N
2.) Contains two sets of homologous chromosomes
Cells undergo a round of DNA replication, forming duplicate chromosomes during:
Interphase
Which of the following are examples of a gamete?
1.) Sperm cells
2.) Egg cells
Individual chromosomes gather at each of the two poles. In most organisms, the cytoplasm divides, forming two new cells.
Telophase I
The homologous chromosomes separate. The chromosomes of each pair are pulled to opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers. The chromatids do not separate at their centromeres.
Anaphase I
The chromosomes condense, and the nuclear envelope breaks down. Homologous chromosomes pair all along their length and then cross over.
Prophase I
After one division of the nucleus, a new spindle forms around each group of chromosomes.
Prophase II
The pairs of homologous chromosomes are moved by the spindle to the equator of the cell. The homologous chromosomes, each made up of two chromatids, remain together.
Metaphase I
The centromeres divide, and the chromatids move to opposite poles of the cell.
Anaphase II
Individual chromosomes line up along the equator, attached at their centromeres to spindle fibers.
Metaphase II
A nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes. Two cells undergo cytokinesis, forming 4 haploid offspring cells.
Telophase II
What are chromosomes made of?
DNA molecules that contain genes.
Where are chromosomes located in eukaryotic cells?
In the nucleus.
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46 chromosomes.
What is the function of the centromere?
It holds sister chromatids together.
What are homologous chromosomes?
Paired chromosomes.
What are the two types of chromosomes?
Autosomes and sex chromosomes.
What do autosomes control?
Somatic/body chromosomes.
How many pairs of autosomes do humans have?
22 pairs or 44 non-sex chromosomes.
What determines gender in humans?
Sex chromosomes: XY for males and XX for females.
What is a gamete?
A sex cell that is haploid (1n).
What is a zygote?
A diploid cell (2n) formed from the fusion of an egg and sperm.
What is the process of meiosis?
Cell division that produces sex cells and results in genetic diversity.
What happens to the number of chromosomes during meiosis?
The number of chromosomes is cut in half (2N → N).
What occurs during Prophase I of meiosis?
Nuclear membrane breaks down, chromosomes condense, and homologous chromosomes pair up.
What is crossing over?
The exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes during Prophase I.
What happens during Metaphase I?
Homologous chromosomes line up at the center of the cell.
What occurs during Anaphase I?
Homologous chromosomes separate.
What happens during Telophase I?
Nuclear membrane reforms and cytokinesis generates two daughter cells.
What is the outcome of Meiosis II?
Four daughter cells are produced, each with a unique genetic makeup.
What is the significance of meiosis in reproduction?
It produces gametes that contribute to genetic diversity in offspring.