ENDOCRINE - Overview & Assessment
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1. chemical communication
2. coordination system
3. reproduction
4. growth and development
5. regulation of energy
Structure and function of the endocrine system
An integrated (1) and (2) that enables (3), (4), (5)
Together with the nervous system, it maintains homeostasis and coordinates responses to both environmental changes and stress
Principal function of the endocrine system
maintains homeostasis and coordinates responses
Complete the sentence
Together with the nervous system, it (1) to both environmental changes and stress
Glands and glandular tissues
Endocrine system is composed of (1)
S - synthesize
S - store
s - release
CHEMICAL MESSENGERS known as hormones
The endocrine system is composed of glands and glandular tissues that perform the 3S.
The 3S refer to
They are chemical messengers that affect specific target organs and travel to the body tissues through the bloodstream
What are hormones? (General def)
A chemical substance synthesized and secreted by a specific organ or tissue carried by the blood to the other sites of the body where they exert their action
They are messengers to specific cells and organs
Do stimulating and inhibiting process
Hormones - Characteristics (WHAT IS A HORMONE)
Stimulating and inhibiting process
What kind of process do hormones do?
1. Local
2. General
Major categories of hormones (WHERE DO HORMONES COME FROM)
Local - specific effect in the area of secretion
General - distant sites for specific action
Differentiate local and general hormones
Local
Hormones with specific effect in the area of secretion
Cholecystokinin (CKK) - gall bladder
Pancreozynin (PZI) - pancreas
Samples of local hormones
General
Transported in the blood to distant sites where they exert their action/effect
:> nice
Draw the hypothalamus with the anterior pituitary hormones etc etc
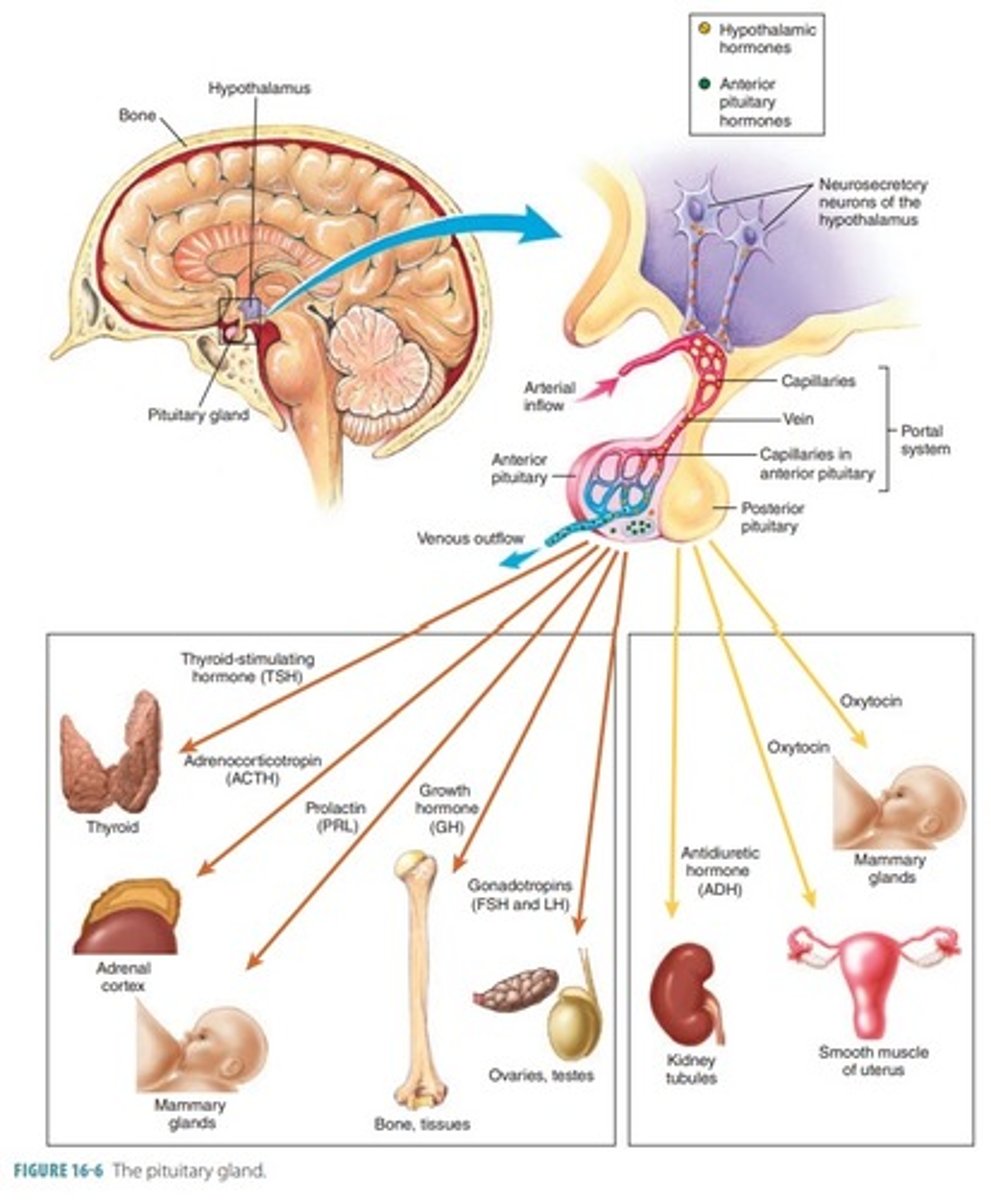
1. Growth hormone (GH)
2. Prolactin (PRL)
3. Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
4. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
5. Thyrotropic hormone (TSH)
6. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
Hormones of the anterior pituitary gland
Growth hormone
Bones and muscles
Prolactin (PRL)
Mammary glands
FSH & LH
Testes or ovaries
ACTH
Adrenal cortex
1. Amine
2. Peptides
3. Steroids
Structure (WHAT IS A HORMONE MADE OF?)
Amino acids
Amines were derived from
They bind to receptors in the cell nucleus
Where do amines bind to?
Fight or flight hormones
Amines are also known as
Catecholamines (epinephrine and norepinephrine)
Example of an amine
Large in size
Lipid insoluble
Unable to penetrate cell membrane & bind to receptors
Activate intracellular process that ultimately affects the activity of the genes
Describe peptides
Secreted by adrenal cortex and gonads
Synthesized from cholesterol
Lipid soluble, able to diffuse into cells and bind to specific receptors in the nucleus
Describe steroids
Adrenal cortex and glands
Steroids secreted by
Cholesterol
Steroids synthesized
1. Simple feedback
2. Complex feedback
3. Physiologic rhythm/diurnal rhythm/circadian rhythm
4 Chemical feedback mechanism
Regulation of hormones secretion (WHAT/WHO CONTROLS)
Basically (+)/(-) feedback
Simple feedback explain
Hormonal control of ionic calcium
Sample of simple feedback
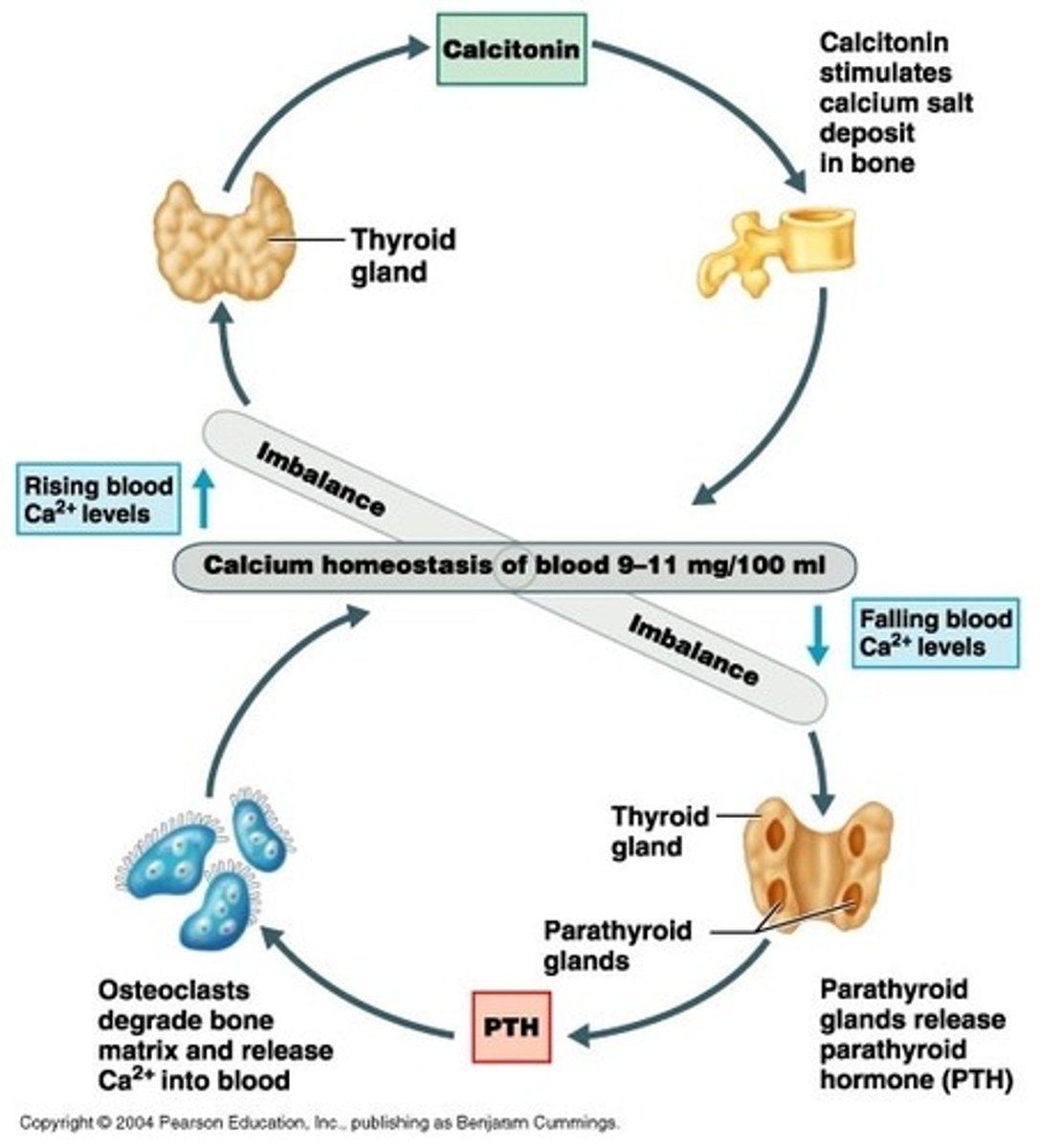
Involves 2 or more organs to regulate homeostasis
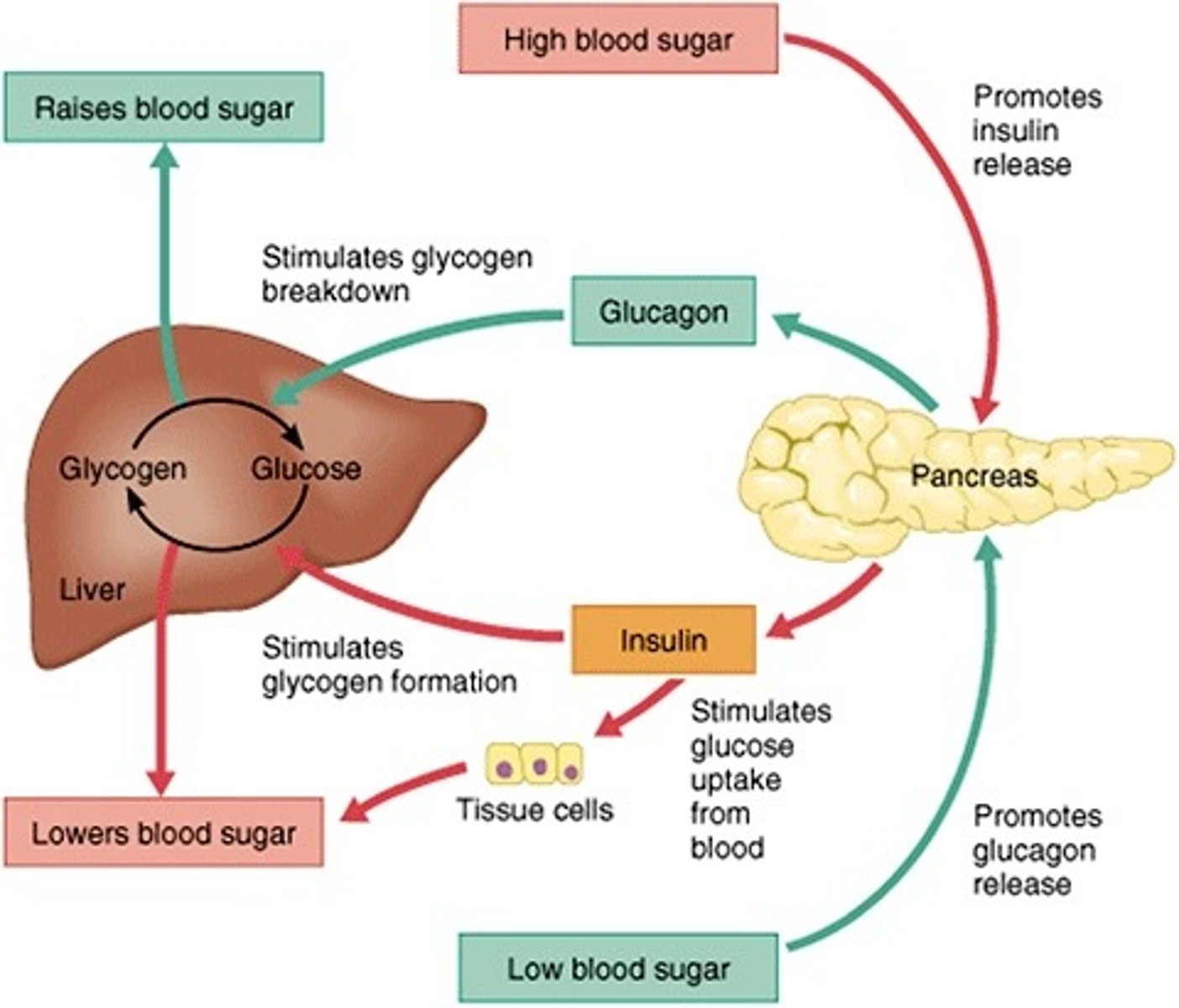
Explain complex feedback mechanism
Homeostasis of blood glucose
Sample of complex feedback mechanism
Some endocrine glands are directly affected by the activity of the nervous system
Chemical feedback mechanism explaint
Environmental changes/stressors
Cause of chemical feedback mechanism
SNS activity symptoms:
Manifestation of chemical feedback mechanism
Tremors
Heavy sweating
Stomach upset
Frequency of urination
Increased v/s
SNS activity include
Hormone level fluctuates predictably within an 24 hour period
Explain physiologic rhythm
Cortisol
Rises in the morning causing wake, declines in the evening causing sleep
Growth hormone
Has a peak secretion during sleep up to 15 y/o
1. Change in personal appearance, hair, nails, skin, texture & pigmentation
2. Change in 3S - size, shape, symmetry of face, neck, eyes, and tongue
3. Change in energy level
4. Temperature intolerance
5. Abnormal secondary sex characteristics (ex. Facial hair in woman, changes in amount and distribution of axillary, pubic hair)
HEALTH HISTORY (FIRST 5) INCLUDES
6. Changes in emotional state, thought pattern, intellectual functioning
7. Signs of increased SNS activity symptoms
8. Changes in bowel habits, appetite, weight, hunger or thirst
9. Changes in urinary pattern, frequency, and amount of urine
10. Changes in sleep pattern/disturbances
HEALTH HISTORY (LAST 5)
Background information including:
1. Stresses of all kind
2. Place of employment
3. Kind of work
4. Marital status
5. Usual coping patterns
6. Lifestyle (alcoholic, gambling, smoking, multiple sexual partners)
Social and Personal History
1. Hereditary and constitutional factors
2. Growth and development pattern
Family History
I. PHYSICAL DATA
1.Mental-emotional status
2. Inspection
3. Palpation
II. VITAL SIGNS
III. SERIAL MONITORING - weight, height, appearance
Objective data include
Blood hormone test
Laboratory tests include