plant disease exam q corrections
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Explain why a high level of TMV infection reduces growth in a plant.
less chlorophyll
allow fewer chloroplasts
allow less light absorbed
ignore less photosynthesis
(so) less glucose / starch / protein made
A scientist noticed that in one area the gorse plants had yellow leaves and
had stunted growth.
One reason for yellow leaves and stunted growth is a deficiency of nitrate
ions in the soil.
Explain two other possible reasons for the yellow leaves and stunted
growth.
Do not refer to nitrate ions in your answer.
any two from :
• lack of magnesium (ions) (1)
(so) not enough chlorophyll for (efficient) photosynthesis (1)
(so) not enough glucose to make proteins for growth
or not enough glucose to release energy for growth (1)
allow (so) lack of chlorophyll produced
causes yellow leaves (1), (so) not
enough
photosynthesis to produce glucose
which is used to make proteins for
growth (1)
• infection by pathogen / bacteria / virus / fungus (1)
allow correctly named pathogen
allow has rose black spot / TMV
(so) leaves become discoloured / yellow so less photosynthesis
(1)
allow other symptoms of named
pathogens / disease
(so) not enough glucose to make proteins for growth or not
enough glucose to release energy for growth (1)
award once only
• infected by aphids (1) (which) remove sugars from phloem (1)
(so) not enough glucose to make proteins for growth or not
enough glucose to release energy for growth (1)
award once only
• lack of (available) light (1)
(so) chlorophyll breaks down (1)
(so) not enough glucose to make proteins for growth or not
enough glucose to release
The gorse plant has nodules on its roots.
The nodules are part of the living root tissue.
Bacteria which convert nitrogen gas into soluble nitrate ions live in the nodule
tissue.
Suggest how the nodules benefit the bacteria.
(bacteria) obtain glucose / sugar (from the plant)
(glucose used) for respiration or (glucose used) for making other
named substances
allow (glucose used) to release energy
The gorse plant has nodules on its roots.
The nodules are part of the living root tissue.
Bacteria which convert nitrogen gas into soluble nitrate ions live in the nodule tissue.
Explain how the nodules benefit the gorse plant.
(gorse plant) obtains nitrate (ions)
needed for amino acids / proteins
allow needed to make chlorophyll / DNA
Plants infected with aphids have stunted growth.
Explain one way the removal of dissolved sugars from the stem of the plant causes stunted growth.
either:
less (sugars for) respiration
(so) less energy released
or
less amino acids made (1)
(so) less protein produced or less protein synthesis (1)
or
less cellulose made (1)
(so) weaker cell walls (1)
Most aphids do not have wings when they hatch. After several generations,
some aphids hatch which have wings and can fly.
Explain the advantage to the aphid of being able to fly.
(aphids) can fly to another plant or part of the plant
ignore to fly unqualified
to get (more) food
allow to find a mate
allow idea of less competition for food
allow to escape predators
do not accept escape prey
The leaves of some plants release oils onto their surface.
Suggest how the production of oil on the surface of a leaf may protect the
plant from aphids.
(oil) prevents aphids from attaching to leaf or causes aphids to slide
off leaf
ignore ‘the leaf is slippery’
or
idea that oil may harm / kill the aphid
allow oil may be unpleasant to the aphid
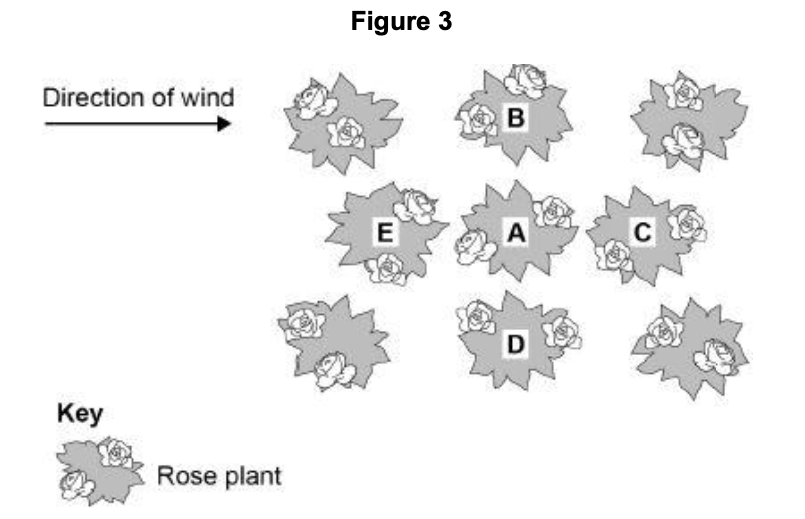
Figure 3 shows a plan of a garden containing rose plants.
Plant A has the fungal disease rose black spot.
Which plant in Figure 3 is the fungus likely to spread to first?
Give a reason for your answer.
C
if any other letter given then no marks
for the question
(fungi / spores) blown by / in direction of the wind
allow black spot / disease is blown by /
in direction of the wind
or
it’s the closest plant (to A)
do not accept reference to bacteria /
viruses / pollen being blown
Suggest one way the gardener could reduce the spread of rose black spot
to the other plants in the garden.
any one from:
• spread rose bushes out more
allow isolate the infected plant
allow idea of barrier around infected plant
ignore separate unless qualified
• remove any infected parts of the plant
allow remove infected plant / A
• use a fungicide
ignore pesticide
do not accept insecticides / herbicide
Plants have adaptations to help defend themselves and to help them survive. Explain how the nettle is adapted for defence and protection.
stinging hairs / can sting
(so) this harms herbivores / stops animals eating them
(so) less of the plant is removed / damaged
Witch hazel is another plant adapted for defence.
Witch hazel produces oil with antiseptic properties. The oil prevents
bacteria from attacking the plant.
A student investigated how effective three different plant oils were at preventing the growth of bacteria.
The student tested tea tree oil using the same method.
The results showed tea tree oil was the most effective at preventing
bacterial growth.
The student concluded that tea tree oil could be used to treat bacterial
infections instead of antibiotics.
Give one reason why this is not a valid conclusion.
antibiotics were not tested
All tools should be washed in disinfectant after using them on plants infected with TMV.
Suggest why.
to kill virus
or
to prevent virus spreading
Scientists produced a single plant that contained a TMV-resistant gene.
Suggest how scientists can use this plant to produce many plants with the TMV-resistant gene.
take (stem) cells from meristem
or
tissue culture
allow take cuttings
Some plants produce fruits which contain glucose.
Describe how you would test for the presence of glucose in fruit.
use Benedict’s solution
glucoses turns solution blue to orange
TMV can cause plants to produce less chlorophyll.
This causes leaf discoloration.
Explain why plants with TMV have stunted growth. (6)
• less photosynthesis because of lack of chlorophyll
• therefore less glucose made
so
• less energy released for growth
• because glucose is needed for respiration
and / or
• therefore less amino acids / proteins / cellulose for growth
• because glucose is needed for making amino acids / proteins /
cellulose
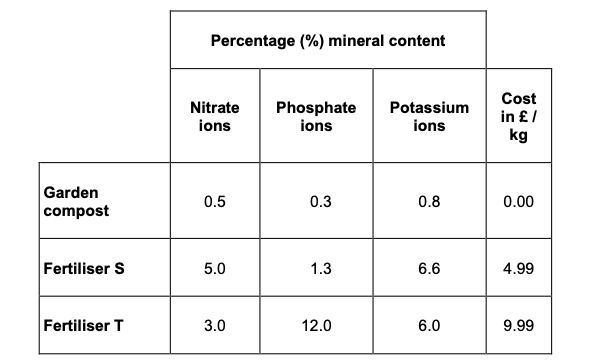
Plants need other mineral ions.
• Potassium ions are needed for healthy root growth.
• Phosphate ions are needed for healthy flowers and fruits.
The gardener makes his own garden compost.
The percentage (%) of minerals in his compost was compared with two
fertilisers he could buy.
The data are shown in the table below.
The gardener buys Fertiliser S.
Explain why he chose Fertiliser S.
(fertiliser S)
has most nitrogen for good growth
if no other marks awarded allow 1 mark for
(fertiliser s) has more minerals than compost
(and) has high(est) potassium content for stronger roots
(it is also) cheaper than fertiliser T
(however) has less phosphate than fertiliser T (although more than
compost) so flowers / fruit perhaps less important for the gardener