M1: LEC 1: Speciation
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
define biodiversity.
the result of BOTH speciation (new species forming) and extinction (loss of species)
define speciation.
the process in which one species splits into two
Give an example of speciation.
1) one ancestor of Cichlids —> speciation —> more than 450 species of Cichlids in Lake Victoria
what is the morphological species concept?
the idea that “if the species look alike, then they are the same species” or species distinguished by physical traits (appearance)
what are the problems with the morphological species concept?
1) variation within species (ex: owls of different colors)
2) convergence evo.
covergence evo means different species may look similar due to similar adaptations
What are other ways to define species besides the morphological or biological species concept?
1) cryptic species: morphological similar, but genetically distinct
2) phenotypic plasticity: variations within species due to the environment
3) sexual dimorphism: male and female individuals of a species look different

Give an example of cryptic species.
The group of giraffes are morphologically similar, but are genetically different.
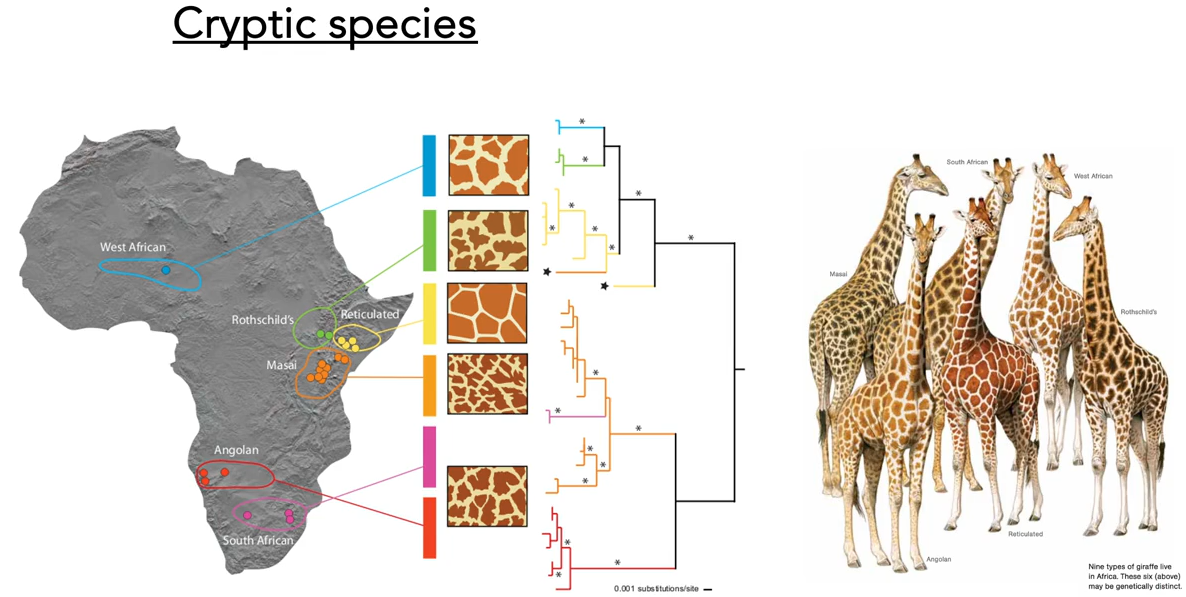
what is the biological species concept?
organisms can make offspring tgt, but cant make offspring with other types of groups or groups of interbreeding populations that are reproductively isolated
What are limitations to the biological species concepts?
does not apply easily to fossils, asexual organisms, or hybrids
define reproductive isolation.
biological diff. (physical or behavorial) reduces gene flow btwn groups of organisms
note: gene flow is possible by mating btwn groups
define reproductive isolating barriers.
biological characteristics reduces gene flow btwn groups of organism or a # of diff mechanisms that causes reproductive isolation
define prezygotic barriers.
barriers before fertilization —> prevents the formation of a hybrid offpspring
fertilization means the fusion of the sperm and egg
define postzygotic barriers.
barriers after fertilization —> the resulting zygote will face problems in the short-term or long-term
What are the types of prezygotic barriers?
geographic: pop. separated by a physical barrier
temporal: mate at diff times
ecological: mating occurs in diff eco. niches
behavioral: diff. mating behaviors
pollinators (a variation of eco. and behavorial): plants attract diff pollinators
mechanical: incompatible reproductive structures
gametic: egg and sperm do not fit tgt
Give an example of temporal isolation.
diff species of cicadas emerges once every # of years
Give an example of ecological isolation.
apple maggot flies mate on apples vs hawthorns
Give an example of behavioral isolation.
male frogs release diff pitches and female frogs prefer specific pitches
Give an example of pollinator isolation.
radial sym. monkey flowers attract bees while bilateral monkey flowers attract hummingbirds
Give an example of gametic isolation.
red sea urchin sperm does not fertilize purple sea urchin egg bc the egg has receptors alllowing successful fertilization of specific gametes
What are the types of postzygotic barriers?
extrinstic: hydrid offspring is unfit due to the environment
intrinstic: hydrid offspring is unfit due to genetic incompatibility
Give an example of extrinsic isolation.
orange/yellow blend butterflies + white/yellow blend butterflies = red/white butterflies are targeted more bc they do not contain the colors that indicate that they are poisonous
What are the two types of intrinsic barriers?
1) hybrid sterility (can’t make offspring)
2) hybrid inviability (can’t live too long)
Give an example of intrinsic isolation, specifically hybrid sterility.
horse + donkey = sterile mule (bc they have a mismatch of the # of their chromosomes)
What are the (3) geographic modes of speciation?
allopatric, parapatric, and sympatric
What are the two types of allopatric speciation?
1) vicariance - barrier splits the ancestral population into two
2) dispersal - few individuals colonizes a new region (called the founder’s effect)
define allopatric speciation.
pop.s are geographically separated, little to no gene flow
define parapatric speciation.
pop.s with some gene flow, experiencing diff selection pressures
give an example of parapatric speciation.
1) anthoxanthum on normal soil vs mine tailings (waste)
2) lizards living in white sand vs dark soil, but they can still mate with e/o
define sympatric speciation.
pop.s are in the same geographic area, lots of gene flow
Give an example of sympatric speciation.
two types of palm trees due to diff soil types leading to divergence in their pop.s
Why does sympatric speciation occurs rarely?
it has high gene flow
Rank the 3 geographic mode of speciation from highest gene flow to lowest gene flow.
sympatric, parapatric, and allopatric
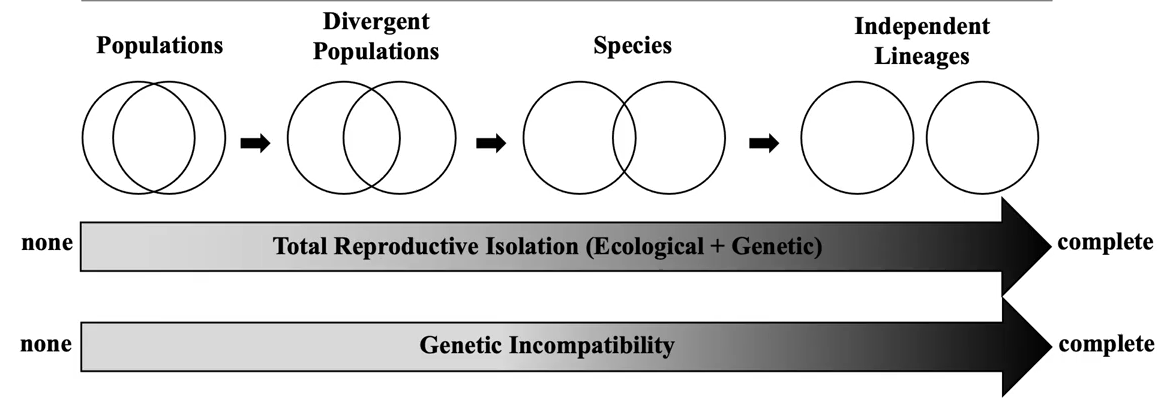
What does the process of speciation look like?
co-exist + gene flow —> physical or ecological barriers —> over time, species start to differ —> total RI and genetic incompatibility is complete
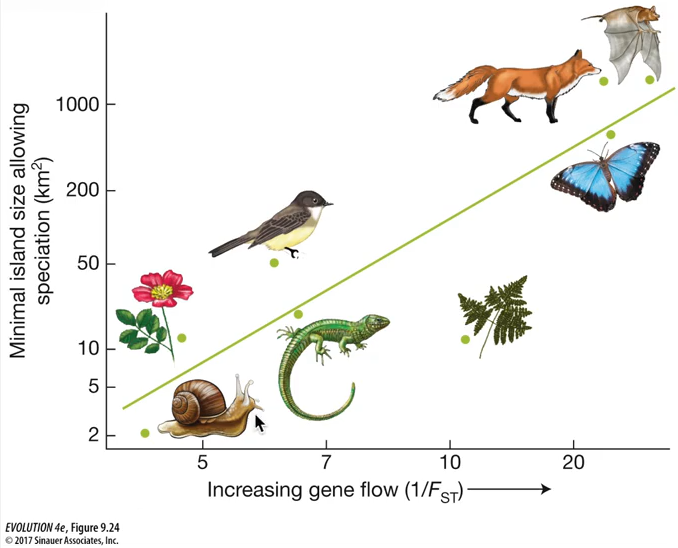
Why is allopatric speciation the most common to occur?
1) It is easier to see how it occur. It can occur w/o gene flow, so differences can easily arise within pop.s
2) The evidence (from the image) shows that immobile species tend to speciate while living on a small island.
What are other factors that causes speciation?
1) strong sexual selection
2) single event speciation:
a) polyploidy: hybrids w extra set of chromosomes than its parental species
b) hybrid: hybrids survives in a diff habitats than its parental species
Why does reproduction isolation arise from polypoidy speciation?
the difference in chromosome # leading to the gametes not being able to match w/ e/o