Rutgers Animal Reproduction Exam 1
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
theriogeneology
the branch of veterinary medicine concerned with reproduction, physiology, and pathology of both male and female systems
How does a rabbit test detect human pregnancy?
hCG is detectable in human blood and urine during early pregnancy, hCG induces rabbit ovulation, inject serum, in 2-3 days check ovaries, if ovulation = pregnant
obestrics
branch of veterinary medicine concerned with pregnancy, parturition, and postpartum
The lactocrine hypothesis states that bioactive factors are transported by what means?
delivery of bioactive milk-borne factors into the neonatal circulation through nursing
Barker Hypothesis
the origins of chronic diseases of adult life lie in fetal responses to the intrauterine environment
Name 4 features that make rats great models of reproductive efficiency.
ovulate frequently, relatively short gestation period, high number of pups per litter (10-12), birth triggers ovulation, reaches puberty early (30-35 days)
True or False: XY Inc, Fort Collins, CO have licensed the technology to detect abnormalities in sperm cells.
false, licensed the technology to separate sperm based on DNA content, sex selection
Which sperm has more fluorescence, X or Y?
X sperm
One purpose of MicroSort Inc, Fairfax VA is?
prevention of sex-linked diseases and family planning
True or False: Because rabbits are spontaneous ovulators, they are a perfect candidate to be used as bio-assays for pregnancy detection.
false, rabbits are induced ovulators
How do home pregnancy tests work?
monoclonal antibodies were developed to detect hCG in urine, the antibody complex generates a color reaction, color change shows positive test
Name at least 5 advances in modern reproductive physiology.
cloning, at-home-pregnancy tests, MicroSort to prevent sex-linked disease, artificial insemination, sex selection
Briefly describe asynchronous concurrent lactation and how this supports the lactocrine hypothesis.
Colostrum composition changes depending on the needs of the growing fetus. Supports the hypothesis by showing that milk composition can adapt and guide specific aspects of growth.
What in the mother's milk of rhesus monkeys predicts a more nervous, less confident temperament in both sons and daughters?
glucocorticoids
True or False: MicroRNAs are not found in human, cow, and pig milk.
False, microRNAs are found in human, cow, and pig milk
True or False: An immature gut, soon after birth, can be described as "closed"
True
What connective tissue forms the broad ligament in the female reproductive tract?
Peritoneum
What are the components of the peritoneum and their functions?
mesovarium, mesosalpinx, mesometrium
functions: support, houses blood supply, lymph drainage, nerves
Name the tubular portions of the female reproductive tract in order from the outermost to the innermost.
serosa
musularis
mucosa
submucosa
What are the two types of hormones produced in the ovaries and examples of each?
steroid: androgens, estrogens, progestins
protein: inhibin, relaxin
Name 3 differences between an equine ovary compared to a non-equine ovary.
1. medulla and cortex are reversed (medulla outer, cortex inner)
2. follicles and corpora lutea are located in the interior of the ovary
3. ovulation occurs at the ovulation fossa
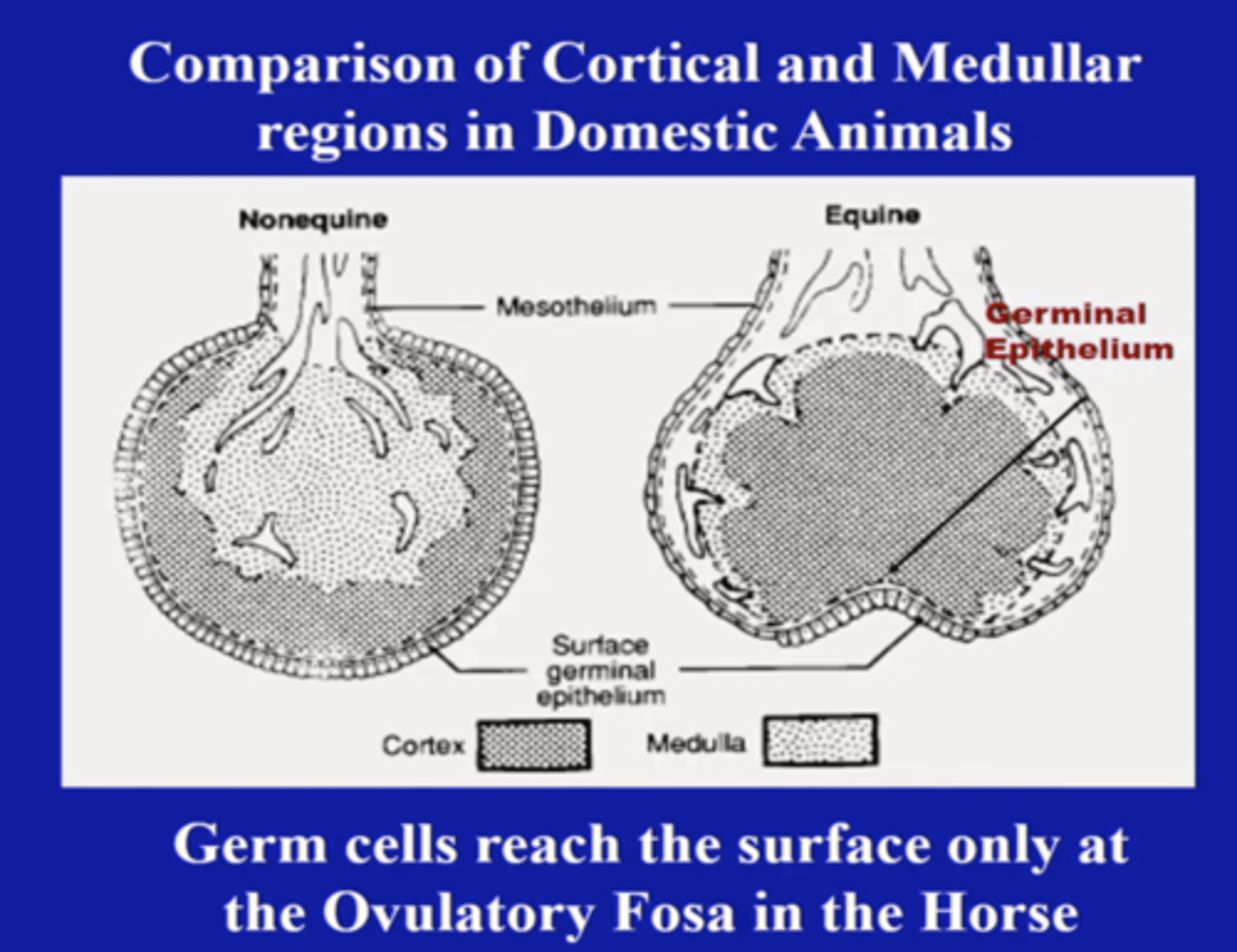
The follicle can ovulate anywhere in an equine ovary because surface germinal epithelium completely surrounds the ovary.
False, ovulation occurs at the ovulation fossa
primordial follicle
non-growing pool of follicles
oocyte with a single layer of squamous cells
primary follicle
growing pool of follicles
oocyte with cuboidal epithelium
secondary follicle
2 or more layers of granulosa cells
no antrum
tertiary/antral follicle
multiple avascular granulosa cell layers
fluid filled antrum
What FIRST forms at the site of follicle rupture on the ovary?
corpus hemorragicum
What type of cell does granulosa and theca cells differentiate into?
luteal cells
Name the primary hormone produced by the corpus luteum.
progesterone
Corpus Luteum formation
forms following rupture to prepare the uterus, if fermentation does not occur, the CL stops producing hormone and breaks down forming the corpus albicans
Corpus Albicans
scar-like structure composed of collagen
Atresia
programmed cell death, non-dominant follicles degenerate and die off during menstruation
theca externa
connective tissue of the follicle
theca interna
interior of follicle, source of androgens and blood supply
granulosa cells
majority of cells surrounding an oocyte, produce estrogens and progestins, avascular
polycystic ovarian syndrome
PCOS
multiple small cysts (unruptured follicles)
high androgens
infertility
insulin resistance
In one theory regarding the cause of ovarian cancer, the wound and repair of what cell type is thought to trigger mutation?
ovarian surface epithelium (OSE)
Which hormone(s) action(s) on the ovarian surface epithelium (OSE) is thought to induce tumor formation?
gonadotropin stimulation - release FSH and LH
Ovarian Reserve Index (ORI)
test determining the number of eggs a woman has left in her ovary
The blood levels of which three hormones are measured with the Ovarian Reserve Index (ORI)?
inhibin B, anti-mullerian hormone (AMH), and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Antral Follicle Count (AFC)
ideal # is 15-20 per two ovaries
AFC below 10 is considered low
Polycystic Ovary
high AFC and ovarian volume
35+ is considered high
What two cells "luteinize" or differentiate to form the corpus luteum?
theca interna and granulosa cells
What is 25-55% of early embryonic loss due to?
corpus luteum insufficiency
functions of the corpus luteum
secretes progesterone
maintains pregnancy
regulates the cycle
How is the avian reproductive system different from the mammalian reproductive system?
only left ovary and oviduct function, produce a shell membrane, have yolk (no antrum or follicular fluid), have a cloaca
Where is the site of fertilization by sperm in an avian ovum?
germinal disk (IN OVUM)
Where does fertilization occur in the avian tract?
infundibulum (IN TRACT)
From the site of fertilization in birds, trace the path of the egg in the avian reproductive tract.
infundibulum → magnum → isthmus → shell gland or uterus → vagina → cloaca
Ovum
mammalian oocyte equivalent
called the yolk
consists of a germinal disk and vitelline membrane
What is another name for the shell gland in the avian reproductive tract?
uterus
What are the parts of the mammalian oviduct?
infundibulum, ampulla, isthmus
What structural aspect of the infundibulum assists in the transport of the oocyte?
fimbriae
oviduct functions
transport of gametes and the embryo
secretions to maintain oocyte, sperm, and fertilized egg
Where is the site of fertilization in the mammalian oviduct?
ampulla
duplex uterus type 1
2 cervices
2 separate uterine horns
2 vaginas
no uterine body
ex. marsupials
duplex uterus type 2
2 cervices
2 uterine horns
1 vagina
ex. rabbits
biocornuate uterus
2 uterine horns
small uterine body
1 cervix
ex. mare and cow
simple uterus
no uterine horns
large uterine body
exp. humans
uterine functions
sperm transport
regulation of CL function
implantation/placentation
parturition
Uterine signal that causes CL regression
prostaglandin
cow, ewe cervix
annular rings of cartilage
sow cervix
interdigitated rings
boar cervix
penile adaptation called corkscrew
mare cervix
longitudinal folds
cervix in early pregnancy
thick cervical mucous
barrier to sperm transport
prevents uterine infection
cervix at time of birth
cervical mucous thins
cervical plug liquifies
cervical canal opens
What controls the viscosity of the cervical mucous?
hormones
high serum estradiol = watery mucous
high progesterone = thick mucous
vagina structure - cranial
near cervix
columnar epithelium
highly secretory
vagina structure - caudal
vestibule
stratified squamous epithelium
vagina functions
copulatory organ
excretory duct
birth canal
vulva
external part of the tract
labia major and minor
outer and inner folds of skin, contains fat and smooth muscle
clitoris
homolog of the penis
erectile tissue, sensory nerves, epithelium
erect during estrus
sensory function
Describe the equine placenta.
diffuse
epitheliochordial
microtyledons
Epitheliochorial
3 fetal layers
3 maternal layers
Microtyledons
thousands of microscopic structures on the placental surface
site of maternal-fetal interaction
increase placental surface area
equine gestation length
331-350, 11 months
What is the source of progesterone in the first half of mare gestation?
corpus luteum
What is the source of progesterone in the second half of mare gestation?
feto-placental unit
Endometrial Cups
diffusion
transitory day 35-60
produce eCG
Equine Chorionic Pregnancies (eCG)
unique to equine pregnancies
form from trophoblast tissue and are embedded in the endometrium
eCG function
like LH, luteinizes follicular waves to create secondary CL during pregnancy
What is Premarin?
hormone replacement therapy to relieve symptoms of menopause
Premarin use
source of equine estrone, equilin, and equilenin
found to have associations with coronary heart disease and breast cancer when used with progestin
placental insufficiency consequences
stillborn births, premature delivery
premature birth conditions
respiratory hypoxia, neurological issues, postpartum foal death
Mare reproductive loss syndrome (MRLS)
issue in KY and OH
over 5000 cases of early and late-term abortion
caused massive financial loss
Three functions of relaxin
relaxes reproductive smooth muscle
remodels connective tissue
promotes growth
What is the primary source of relaxin in horses?
placenta
What is Oligohydrallantois?
reduced fetal fluid production
What is the disorder in horses characterized by an excess of fetal fluid production?
hydrops
True or false: A mare with a pituitary tumor was seen to have a prolonged gestation.
true, other issues too like placental separation
True or false: A study showed a decreased amount of circulating relaxin during gestation in mares with twins
false, decreased relaxin
What fungus, which infects fescue pastures, and toxin it produces is linked to reproductive problems in horses?
fungus - ergovaline
endophyte infected fescue
What health problems are associated with fescue toxicosis?
prolonged gestation, dystocia, placental operation, placental thickening, decreased blood flow, agalactia
How does ergovaline exposure lead to fescue toxicosis?
Ergovaline is an ergot alkaloid that acts as an agonist at dopamine receptors, particularly D2 dopamine receptors. When these receptors are stimulated by ergovaline, it inhibits the release of prolactin, a hormone critical for several reproductive functions, especially in late pregnancy.
Inhibition of prolactin affects the development of the mammary glands, leading to agalactia.
Explain how an enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELISA) works to detect a protein hormone, like relaxin.
1. 2 antibodies needed, one that recognizes the hormone of interest and one linked to an enzyme detection system
2. hormone AB is bound to a solid support
3. hormone of interest in blood binds to AB and forms a complex
4. the enzyme AB binds to the hormone complex
5. a substrate is added and a color reaction occurs
What does the spermatic cord suspend
suspend the testes in the scrotum
Explain how the pampiniform plexus regulates the testes temperature.
warm arterial blood is cooled when it enters the PPP, the heat is transferred to the spermatic vein which returns cool blood to the body