M6L2 - Phosphorylation in Signaling Pathways
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
RBC Production
2 million made per sec
Cells develop in bone marrow and circulate for 4 months
They’re digested and recycled by macrophages (WBC)
How are RBC Replaced
When progenitor cells stop dividing
They start to differentiate instead
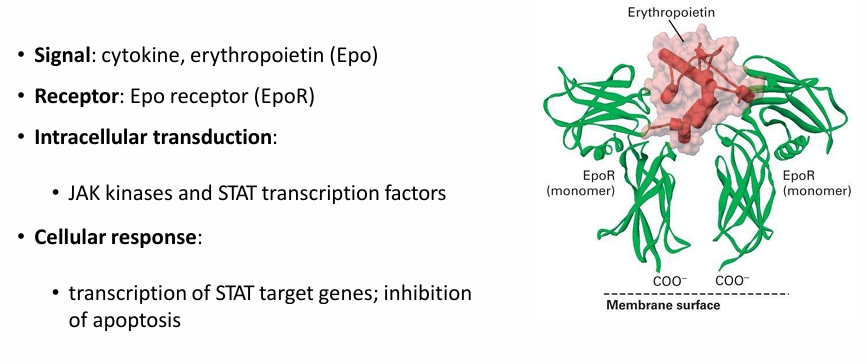
The signal for maturation is Epo
Signaling cytokine protein (erythropoietin)
How is erythropoietin expression regulated
by an O2 binding transcription factor in our kidney
It goes into circulatory systems where only the erythrocyte progenitor cells carry the right receptor
What’s the receptor for Epo
Erythropoietin receptor (EpoR)
It’s a cytokine receptor bc erythropoietin is a cytokine
It’s linked to the JAK-STAT STP
It’s activation inhibits cell death
Components of JAK-STAT Pathway
Signal: Epo
Receptor: EpoR
Intracellular STP: JAK-STAT
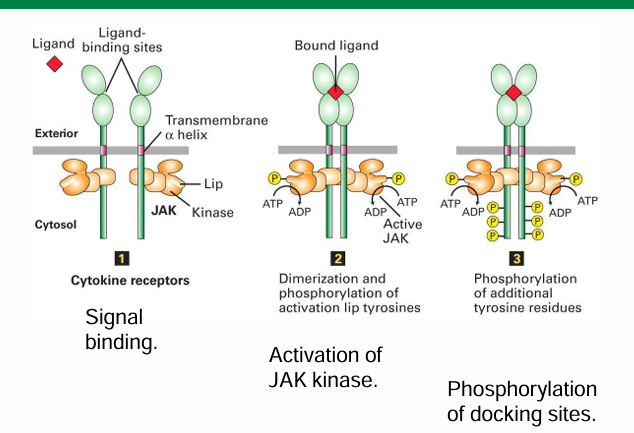
EpoR activation Mechanism
It’s inactive as a monomeric single-pass transmembrane protein
When Epo is available, its signal interacts with 2 EpoR receptors
This initiates dimerization
What are the 3 functional domains of the EpoR
Cytosolic domain
Transmembrane alpha-helix domain
extracellular domain
Autophosphorylation of JAK Kinases
Each EpoR has a JAK kinase in its cytosolic domain
It’s unphosphorylated state is inactive with weak kinase activity
When Epo binds, it leads to dimerization of EpoR
The 2 JAK kinases becoming closer allow the neighbour to be phosphorylated to activate it
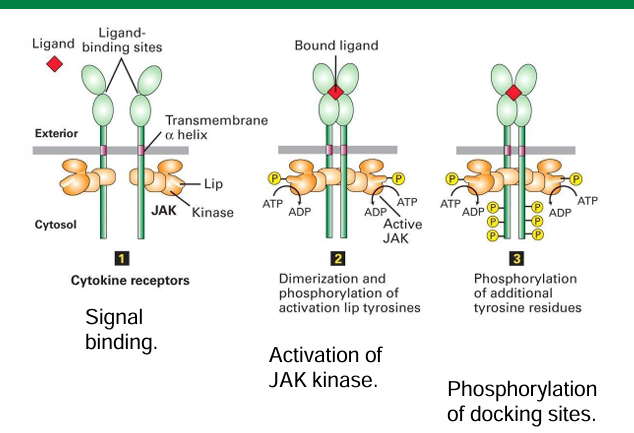
Phosphorylation Targets of JAK kinases
Many
Includes tyrosine residues on intracellular domain of EpoR
JAK kinase is a tyrosine kinase
Only tyrosine residues are phosphorylated
Intracellular Events Following EpoR activation
The phosphorylated docking sites can now bind with STAT transcription factors
They then dimerize to become activated
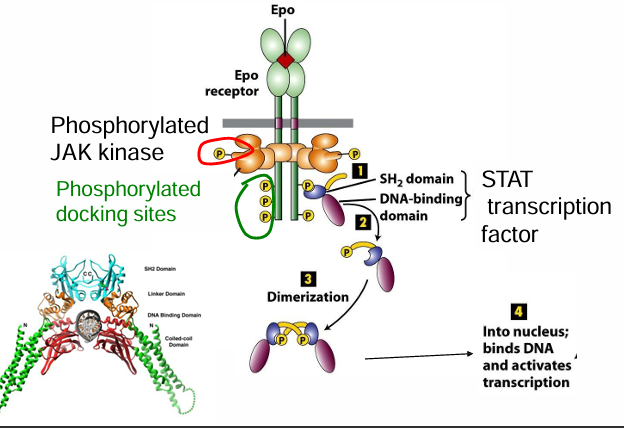
How does STAT become phosphorylized
STAT has a domain (SH2) that specifically recognizes phosphorylated tyrosine residues
They accumulate on the EpoR docking sites to be proximal to JAK kinase
STAT becomes the target of phosphorylation by JAK kinase
It’s phosphorylization allows STAT dimerization
This changes the conformation to unmask a nuclear localization sequence
It goes through nuclear pores to activate transcription of target genes
How does STAT recognize phosphorylated tyrosine residues on EpoR
SH2 domain can re-localize proteins (like sending it to the nuclear pore when active)
It’s a domain ONLY for protein-protein interaction
SH2 can link together proteins in a pathway
SH2 binding pocket fits perfectly with target peptide
Target Sequence: Pro-Asn-pTyr- Glu-Glu-Ile
Pro
It binds with high affinity to this
Binds with low affinity when tyrosine is unphosphorylated
The binding is reversible
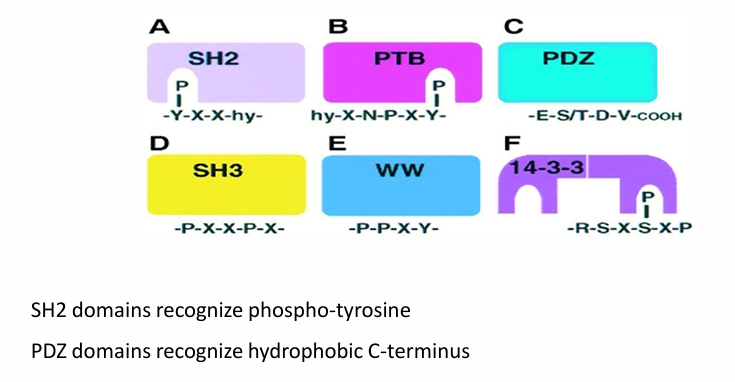
Different Domains with Different protein-protein interactions
They all link together 2 proteins
SH2 / PTB / 14-3-3: Bind with phosphorylated tyrosine but not unphosphorylated
Allows reversibility
PDZ: Bind hydrophobic residues at C-terminus
Not reversible
SH3 / WW: Bind proline-rich domains
Not reversible
What STAT protein is erythrogenesis (RBC Production) associated with and what gene is coded for by its activation
The activation of the STAT5 transcription factor
Many genes are regulated by this activated STAT5 needed for differentiation of progenitor cells
Ex. of a gene is Bcl-XL protein
It inhibits apoptosis
Allows progenitor cells to persist and differentiate
What happens when you produce too many RBC (when signal wont turn off bc mutation or smth)
Results in elevated hematocrit
Increases blood viscosity which can block narrow capillaries
This can result in stroke / heart-attack