bus 272 - ch. 11 (leadership)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
leadership
the ability to influence a group towards the achievement of a vision or set of goals
charisma
a quality or gift that sets someone apart from others
charismatic leadership
followers attribute heroic or extraordinary leadership abilities to a person when they observe certain behaviours
has vision, take pesonal risks, sensitive to follower's needs
transactional leadership
leaders who need primarily by using social exchanges
clarifying goals and task requirements
method used: contigent reward, management by exception
transformational leadership
leadership that, enabled by a leader's vision and inspiration, exerts significant influence
method used: idealized influence, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation, individualized consideration
authentic leadership
leaders who know who they are, what they believe in, and act on those values and beliefs openly and candidly
ethical leadership
leaders who reinforce ethics through organizational mechanisms such a communication and the reward system
servant leadership
leaders who go beyond one's self interest and instead focus on opportunities to help followers grow and develop
three general types of leadership theories
trait theories
behaviour theories
contingency theories
trait theories
considers personal qualities and characteristics that differentiate leaders from non-leaders
says that leaders are born, not created
behavioural theories
proposes that specific behaviours differentiate leaders from others
leaders can be trained
Ohio State Studies
initiating structure behavior and consideration behavior
innitiating structure behaviour
the extent to which leaders are likely to define and structure their role and the roles of employees to attain goals
cosideration behaviour
the extent to which a leader is likely to have job relationships characterized by mutual trust, respect for employees' ideas, and regard for their feelings
University of Michigan Studies
employee oriented and production oriented
found that leaders who are employee oriented are strongly associated with high group productivity and high job satisfaction
employee oriented
emphasizing personal relationships between leaders and employees
production oriented
emphasizing task/technical accomplishment
contingency theories
looks at the context/situation to which the leadership is being presented to
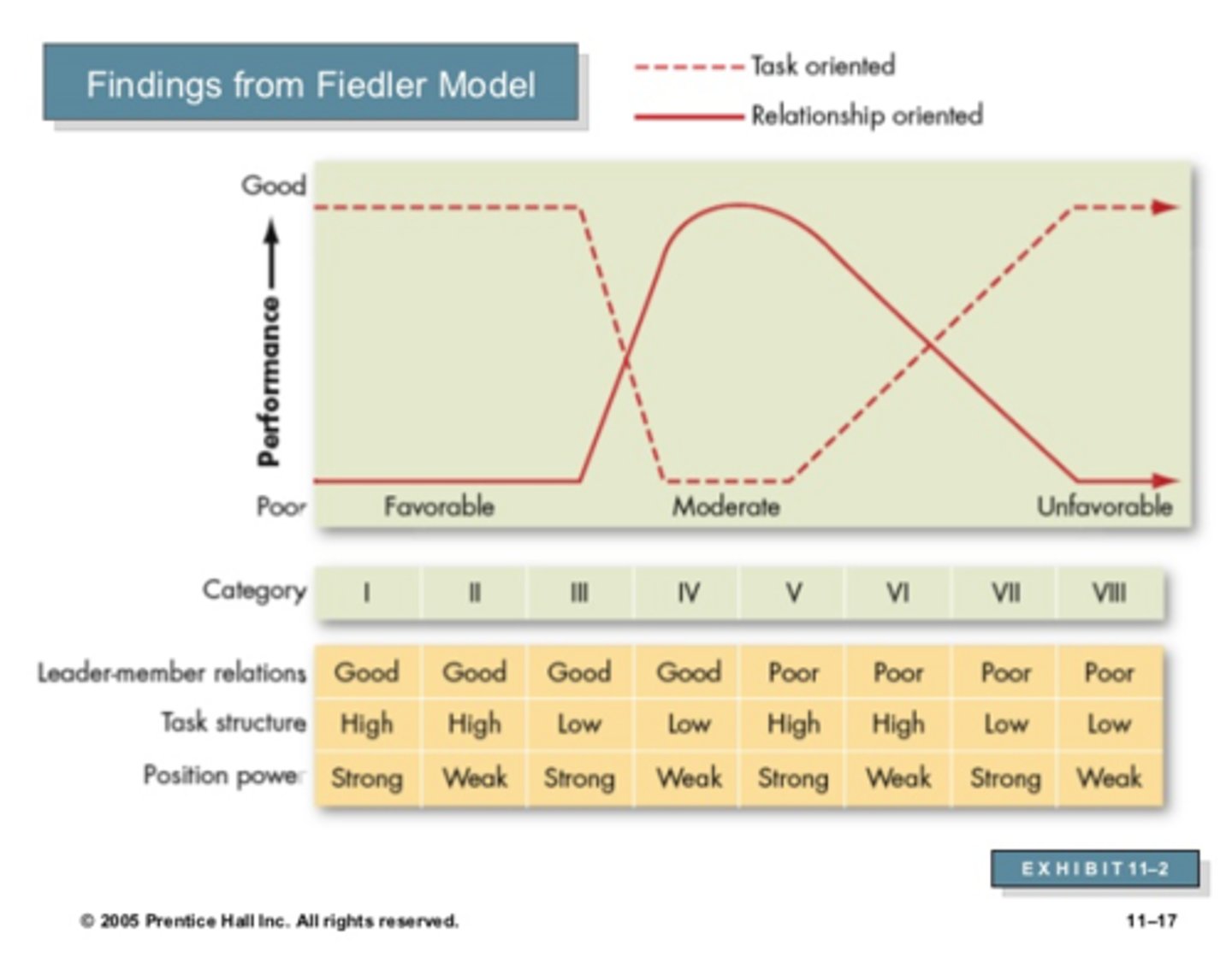
Fiedler Contingency Model
effective leadership depends on matching leadership styles with the situation
Least-preferred co-worker (LPC): determines leadership style by measuring responses to 18 pairs of contracting adjectives
high score - a relationship-oriented style
low score - a task-oriented style
3 categories: leader-member relation, task structure, position power
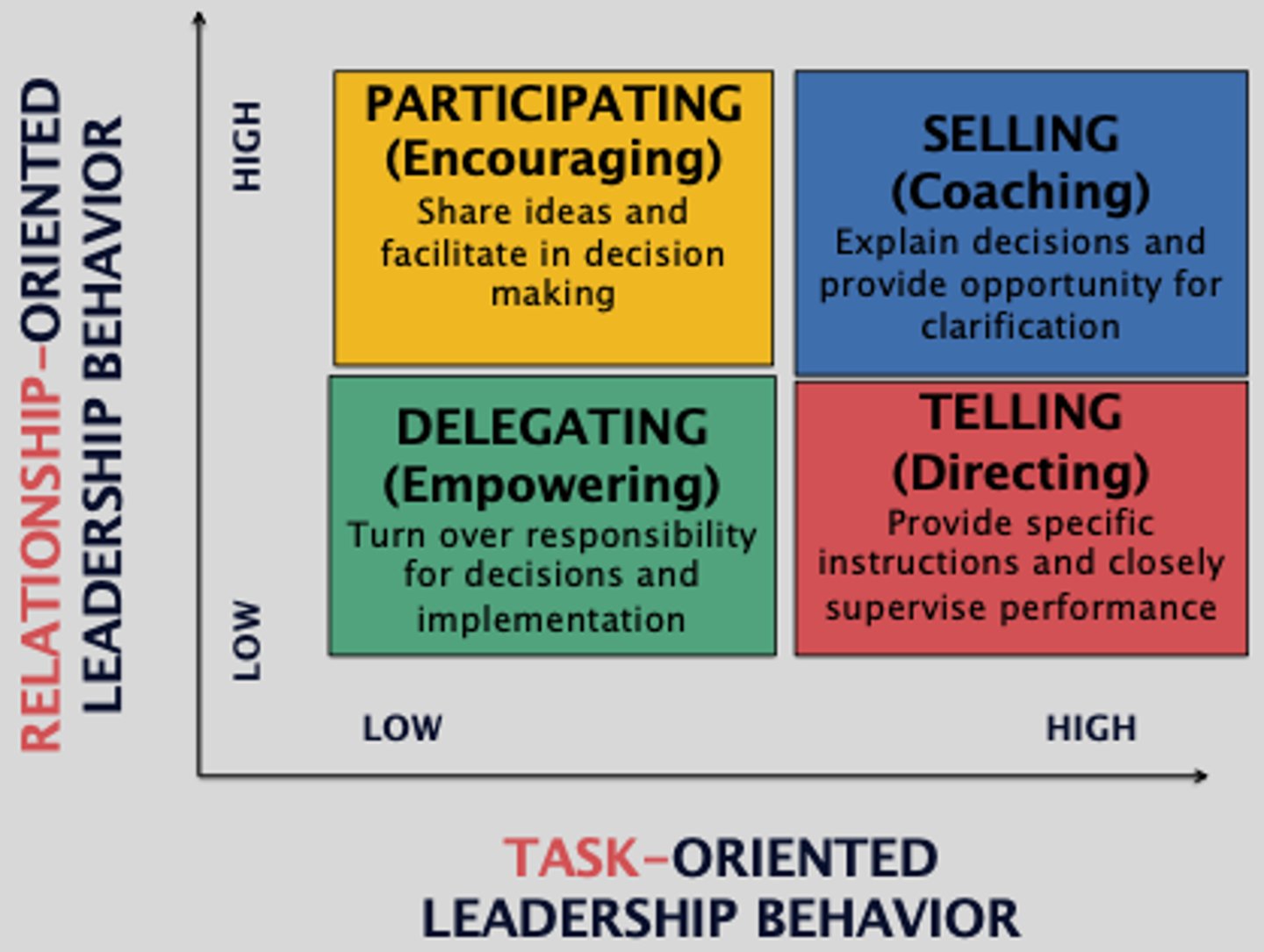
situational leadership theory
focuses on the readiness of followers (willingness and competence)
Delegating (able and willing)
participating (able and unwilling)
selling (unable and willing)
telling (unable and unwilling)
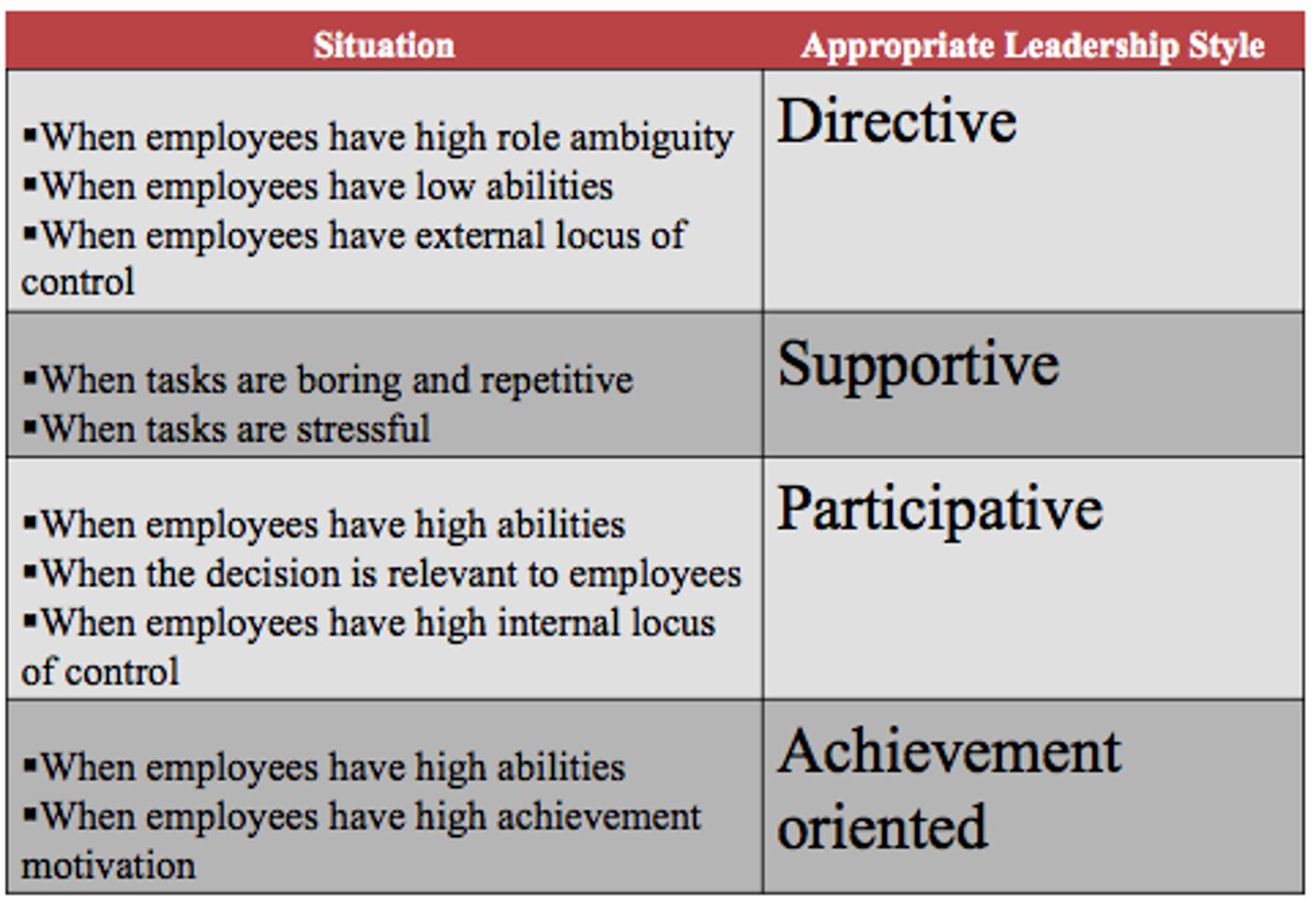
path goal theory
the leader's job is to assist followers in attaining their goals and to provide direction or support needed to ensure that their goals are compatible with those of the group/organization
path goal theory situations
developed by Robert house
Directive: give info and guildance on what to do
supportive: addresses the needs of followers
particapative: consultative leaders who uses suggestions before making decisions
achievement-oriented: strict and have high expectation from employees