Biology Final Study Guide
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:18 AM on 5/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
183 Terms
1
New cards
five characteristics of living things
made of cells, reproduce, grow and develop, respond to environment, and use energy
2
New cards
five needs of living things
food, water, energy, gasses, space
3
New cards
covalent bond
consists of mutual sharing of one or more pairs of electrons between two atoms
4
New cards
ionic bond
formed by the complete transfer of some electrons from one atom to another
5
New cards
hydrogen bond
an attraction between two atoms that already participate in other chemical bonds
6
New cards
solute
substance that is being dissolved
7
New cards
solvent
dissolving medium
8
New cards
hypertonic solution
higher solute concentration
9
New cards
hypotonic solution
lower solute concentration
10
New cards
isotonic solution
solutions that contain the same concentration of water and solutes as the cell cytoplasm
11
New cards
aqueous solution
solution where water is the solute
12
New cards
four basic macromolecules
carbs, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
13
New cards
monomer
atoms/small molecules that bond together to form polymers
14
New cards
polymer
large molecules made of monomers
15
New cards
elements of carbs
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
16
New cards
elements of lipids
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
17
New cards
elements of proteins
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
18
New cards
elements of nucleic acids
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorous
19
New cards
monomers of carbs
monosaccharides
20
New cards
monomers of lipids
glycerol, fatty acids
21
New cards
monomers of proteins
amino acids
22
New cards
monomers of nucleic acids
nucleotides
23
New cards
function of carbs
provide material to build cell membrane
24
New cards
function of lipids
store energy, insulate organs, direct growth
25
New cards
function of proteins
provide structure, aid in molecule movement, provide immunity
26
New cards
function of nucleic acids
contains genetic info, directs growth
27
New cards
examples of carbs
glucose, fructose, lactose, cellulose
28
New cards
examples of lipids
fats, oils, waxes
29
New cards
examples of proteins
insulin, hemoglobin, antibodies, enzymes
30
New cards
examples of nucleic acids
DNA, RNA
31
New cards
five properties of water
cohesion, adhesion, high surface tension, expands when freezes, universal solvent
32
New cards
cohesion
water sticks to other water molecules
33
New cards
adhesion
water can also be attracted to other surfaces/molecules
34
New cards
high surface tension
water has a tension at its surface
35
New cards
expands when freezes
solid water is less dense than liquid water
36
New cards
universal solvent
dissolves ionic and polar substances
37
New cards
in a water molecule, which atom gives water the partially positive charge?
hydrogen
38
New cards
in a water molecule, which atom gives water the partially negative charge?
oxygen
39
New cards
diffusion
molecule movement from high to low concentration
40
New cards
osmosis
movement of water across semipermeable membrane
41
New cards
intracellular fluid
inside the cell
42
New cards
extracellular fluid
outside the cell
43
New cards
does the solute move inside or outside the cell: intracellular fluid=5% salt, extracellular fluid=10% salt
outside; the water wants to go where there is more salt
44
New cards
nucleus
organelle of eukaryotic cells that acts as a control center controlling the actions of the cell and containing the genetic material
45
New cards
mitochondria
cell organelle that transforms energy from sugars into usable energy for the cell
46
New cards
golgi apparatus
organelle that receives substances from the ER and packages them into membrane sacs called vesicles to be delivered inside or outside of the cell
47
New cards
cytoplasm
consists of everything within the cell membrane except for the nucleus and also contains the gel-like fluid of the cell called cytosol which all the cell organelles are suspended in
48
New cards
ribosomes
rough endoplasmic reticulum is studded with these, though smooth ER lacks these; they are involves in making proteins
49
New cards
hydrophylic
cell membrane is structured as a phospholipid bilayer where the _____ heads of the phospholipid are making contact with the watery environments inside and outside the cell
50
New cards
hydrophobic
tails the phospholipid are facing each other to escape the watery environments inside and outside the cell
51
New cards
reactants (imputs) of cellular respiration
sunlight, water, CO2
52
New cards
products (outputs) of cellular respiration
oxygen, glucose
53
New cards
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
high-energy molecule used by cells (energy for all living things)
54
New cards
three stages of cellular respiration (and where each stage occurs)
glycolysis (cytoplasm) citric acid cycle (mitochondria) electron transport chain (mitochondria)
55
New cards
process by which DNA makes an exact copy of itself
DNA replication
56
New cards
three parts of a nucleotide
deoxyribose sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base
57
New cards
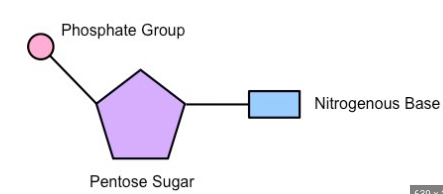
here’s a diagram of a nucleotide
wow ok thanks
58
New cards
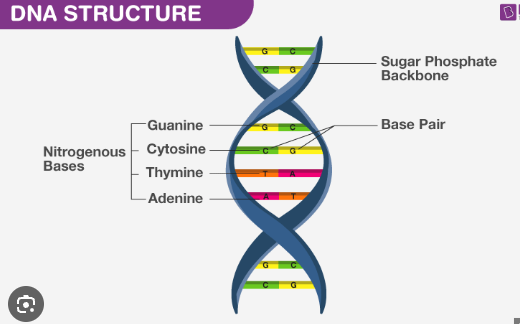
here’s a diagram of DNA
woah that’s so cool
59
New cards
what makes up the sides of the DNA “ladder?”
alternating deoxyribose sugars and phosphate groups
60
New cards
what makes up the rungs of the DNA “ladder?”
base pairs (ATCG)
61
New cards
what type of bonds hold the DNA ladder rungs together?
hydrogen bonds
62
New cards
three scientists who contributed to the discoveries of DNA
James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Francis Crick
63
New cards
what did those three scientists discover about DNA?
its double-helix, twisted ladder structure
64
New cards
what is helicase? what function does it perform?
enzyme; unzips DNA
65
New cards
what is DNA polymerase? what does it do?
enzyme; helps to match nucleotides and build new DNA
66
New cards
what sugar is found in DNA
deoxyribose
67
New cards
what sugar is found in RNA?
ribose
68
New cards
in what part of the cell does DNA replication, transcription, and translation occur
replication: either nucleus or cytoplasm
transcription: nucleus
translation: cytoplasm
transcription: nucleus
translation: cytoplasm
69
New cards
nitrogen base pairing rules
AT, CG
70
New cards
homozygous
having two identical alleles of a particular gene/genes
71
New cards
heterozygous
having two different alleles of a particular gene/genes
72
New cards
purebred
two parents who are the same (think dog breeds)
73
New cards
hybrid
having two parents who are different
74
New cards
artificial selection
human intervention within nature
75
New cards
natural selection
survival of the fittest
76
New cards
gene
basic unit of heredity; occupies a specific location on a chromosome
77
New cards
allele
specific variation of a gene
78
New cards
dominant
winner gene; overcomes recessive trait and is expressed
79
New cards
recessive
loser gene; is overcome by dominant gene
80
New cards
geneotype
not concerned with expression, only pairs
81
New cards
phenotype
the expression of a trait
82
New cards
locus
position of a gen/mutation on a chromosome
83
New cards
sex chromosome
XX female, XY male
84
New cards
autosome
chromosome that is not a sex chromosome
85
New cards
simple dominance
one allele masks another
86
New cards
incomplete dominance
both alleles are partially expressed; resulting in a different phenotype
87
New cards
codominance
two versions of the same gene expressed seperately (spots)
88
New cards
polygenic inheritance
one characteristic controlled by 2 or more genes
89
New cards
mutation
changing of structure of a gene
90
New cards
genetic engineering
human interference of genes
91
New cards
punnett square
diagram used for genotypic prediction
92
New cards
monohybrid
hybrid that is heterozygous with respect to a specified gene
93
New cards
dihybrid
hybrid that is heterozygous for alleles of two different genes
94
New cards
diploid
containing two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent
95
New cards
haploid
having a single set of unpaired chromosomes
96
New cards
gametes
sex cells
97
New cards
zygotes
fertilized ovum
98
New cards
pedigree
family history; charts a hereditary trait thru past generations and aids in tracing phenotypes and predicting genotypes
99
New cards
humans have how many chromosomes
46, or 23 pairs
100
New cards
interphase
cell grows, replicates its chromosomes, and preps for cell division