ch16 - plant responses to abiotic stress
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what is an abiotic stress
factors in the environment that can negatively affect an organisms growth, productivity and survival
name abiotic stresses which affect plants
changes in daylight hours due to seasonal changes
excessive heat/ cold
lack/ excess of water
what is photoperiodism
a plants’ sensitivity to the levels of light in the environment
what type of plant is highly sensitive and is affected by levels of light
deciduous trees
what occurs to deciduous trees as a result of photoperiodism
during summer - daylight hours are at maximum = full of leaves to maximise photosynthesis
during autumn - daylight hours start to decrease = causes leaf fall
during winter - daylight hours are at minimum = enters period of dormancy
during spring - daylight hours start to increase = exits period of dormancy
what are phytochromes
light sensitive pigments which detect the duration/ length of light and darkness
where are phytochromes found
in the cytoplasm of plant cells
name the 2 forms of phytochromes
Pr
Pfr
what occurs when there is a change in daylight hours
decrease in daylight hours = leaf fall - abscission
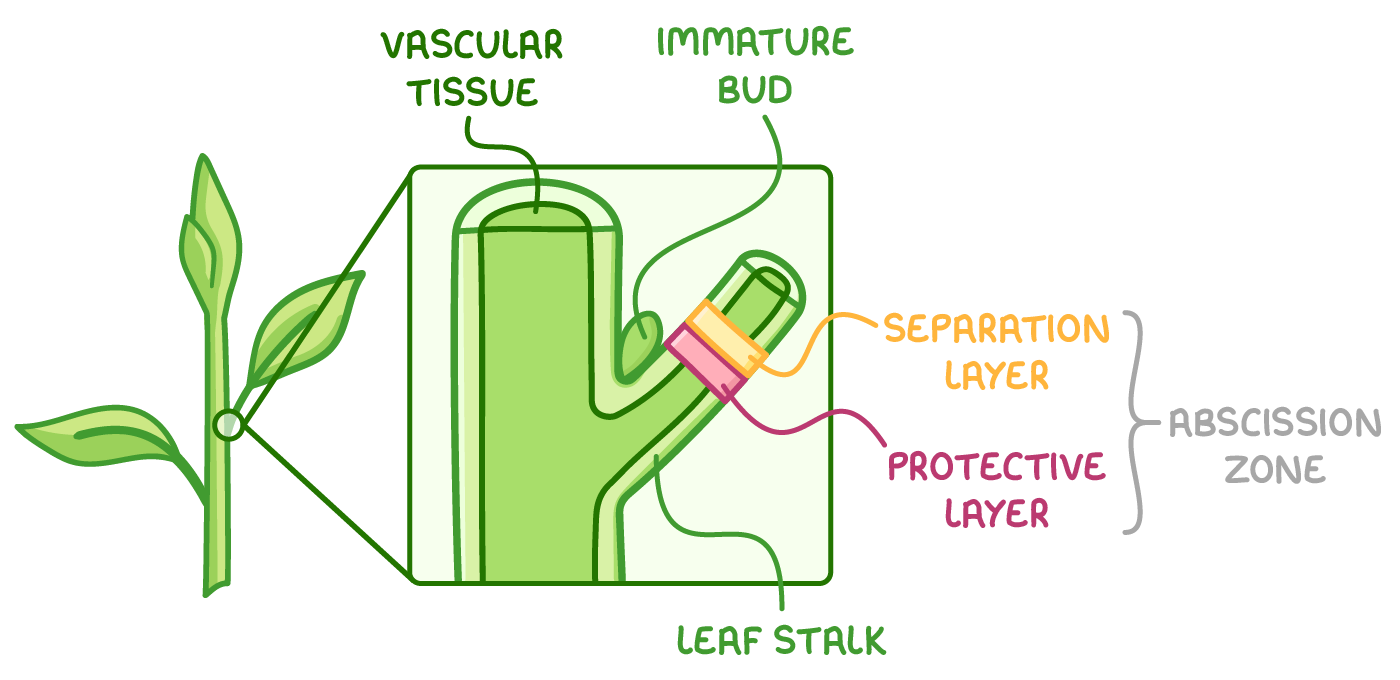
outline the process of leaf abscission
phytochromes detect decrease in daylight hours/ light levels leading to decrease auxin levels & increase ethene levels
ethene activates genes in cells of the abscission zone to produce digestive enzymes e.g. cellulase
cellulase digests the cellulose cell wall in the separation layer
vascular bundles are sealed off
wind and other environmental factors cause leaf to fall
fat is deposited which forms a scar at the protective layer to prevent entry of pathogens
2 why is abscission so useful during winter
many leaves fall > reduced SA as there is less total leaves on plant > reduced respiration and metabolism > less energy required to maintain them plant tissues
fallen leaves act as leaf litter which reduces heat loss by insulating the root
what can excessive cold cause in a plant
cellular freezing
what can a plant do to prevent cellular freezing and describe the mode of action
synthesize sugars, amino acids, and proteins
> sugars and amino acids = increase solute concentration in the cytoplasm, lowers temperature of freezing - prevents cytoplasm from freezing
> proteins = act as antifreeze by binding to small ice crystals which may have formed to prevent them growing larger reducing damage to cell
explain how sugars and amino acids lower the temperature of freezing
To become ice, water molecules lose kinetic energy to slow down so hydrogen bonds can form
Solutes like sugars and amino acids disrupt hydrogen bonds forming, which means water molecules must lose even more kinetic energy - for this to happen temperatures of freezing will be lower
what do plants do when there is lack or excess of water
cause stomatal opening or closing
outline what occurs in plants when there is a lack of water
root hair cells detect there is very small amount of water present in the soil and produce ABA
ABA is transported from the roots (up the stem) to the leaves
ABA binds to the complementary receptors on the surface of guard cells causing conformational shape change = enabling K+ ion channels to open and diffuse out
As K+ ions leave cell = water potential increases so water leaves guard cells via osmosis
guard cell becomes flaccid = stomata close = minimises water loss as there is less transpiration (water is retained)
outline what 2 things can occur in plants when there is high temperatures
stomata open
more water evaporates from leaves via transpiration removing heat and cooling down the plant
VERY HIGH TEMPS
stomata may also close since higher temperatures will mean much more evaporation so much more water loss