Clinical Medicine - Pulmonology
1/525
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
526 Terms
Honeycombing
clustered cystic air spaces that are usually subpleural, peripheral, and basal in distribution
Traction bronchiectasis
describes dilation of bronchioles
Ground glass opacities
area of increased attenuation in the lung with preserved bronchial and vascular markings
Nodular opacification
broad patterns of pulmonary opacification
pulmonary nodule, airspace nodule, or part of underlying reticulonodular pattern
Alveolar ventilation (V)
the amount of air that reaches the alveoli (liters/min)
Perfusion (Q)
pulmonary blood flow (liters/min)
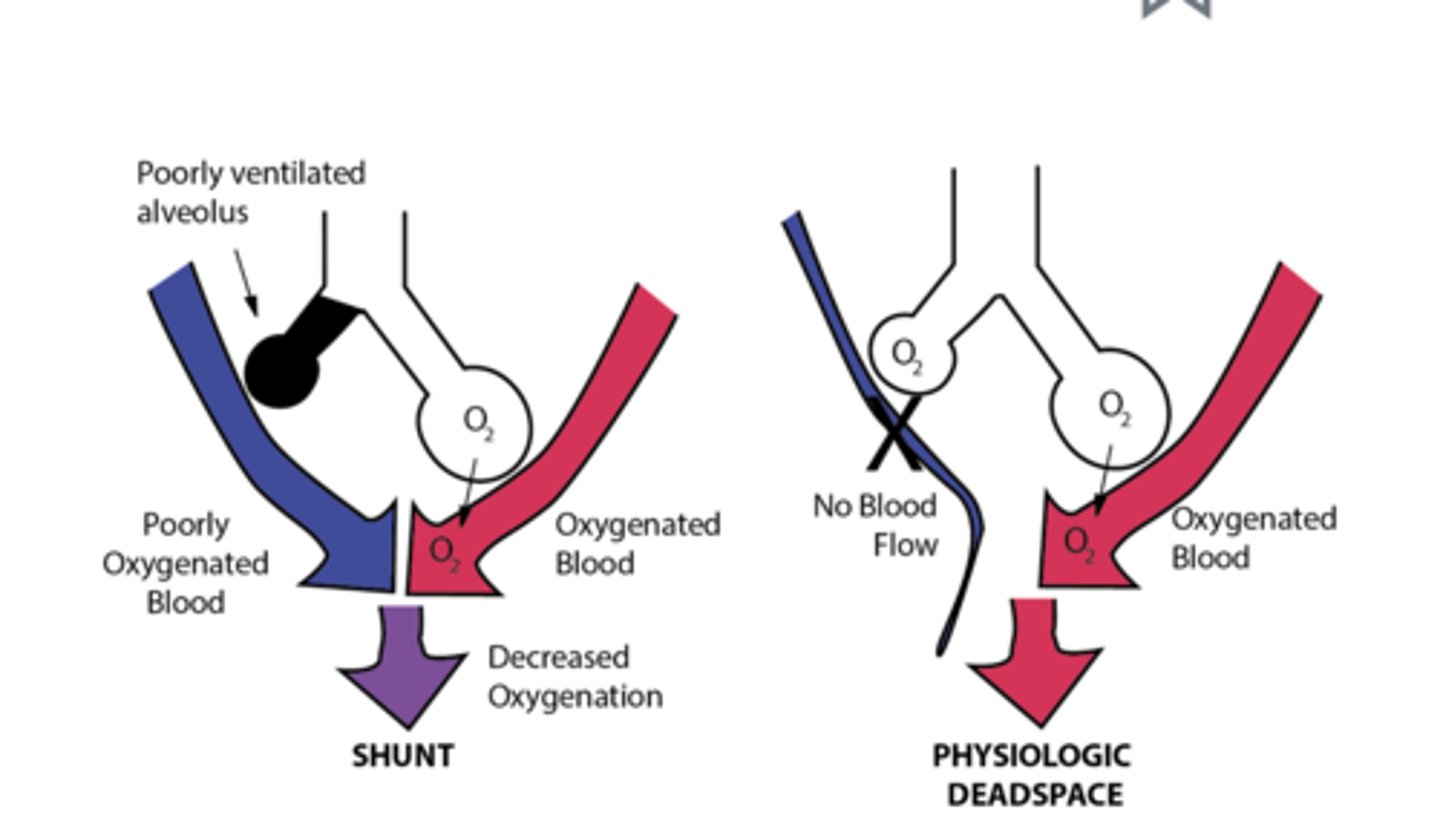
Physiologic shunt
poorly ventilated alveolus leads to poorly oxygenated blood returning from the lungs
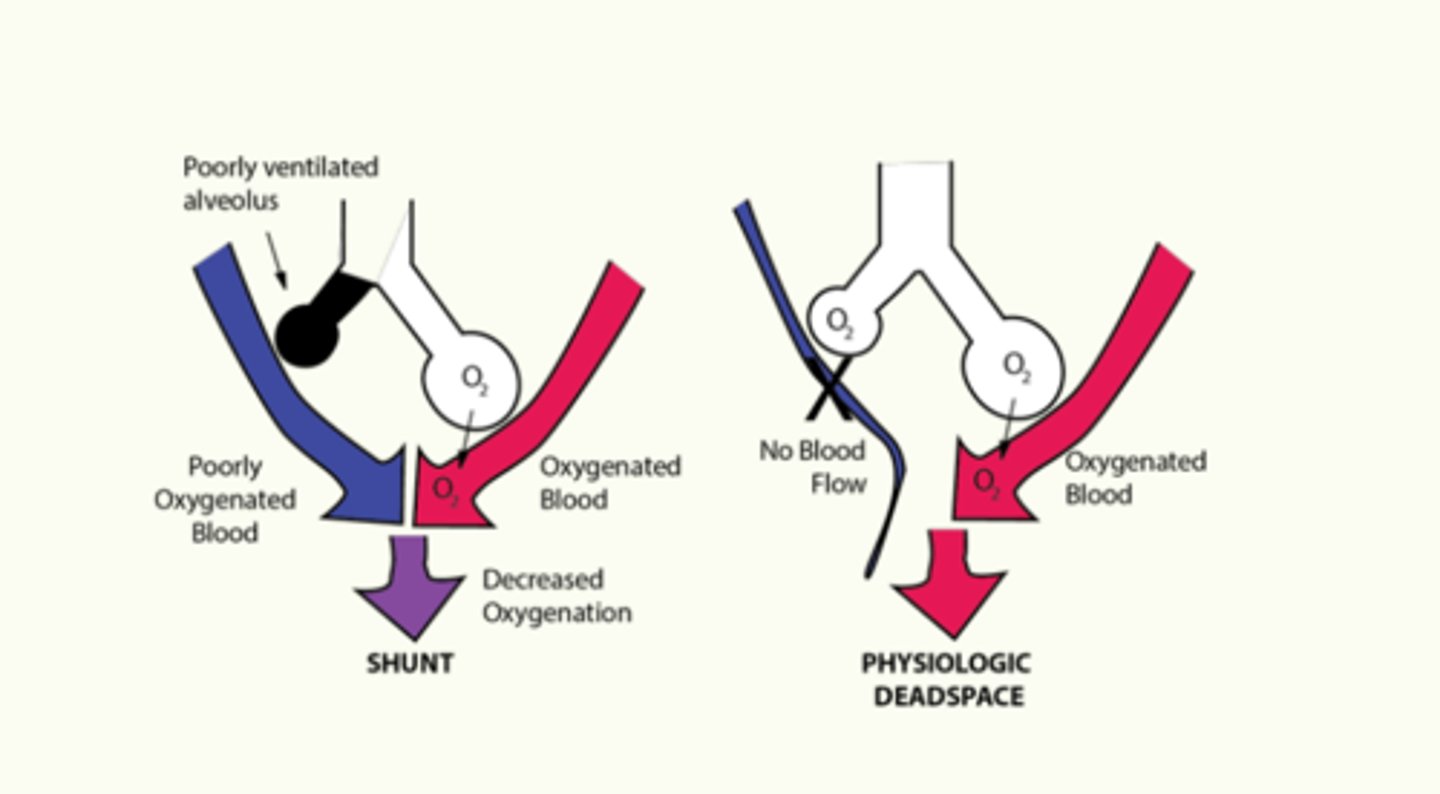
Physiologic deadspace
impaired blood flow to alveoli
VQ mismatch: shunt causes
pneumonia
pulmonary edema
tissue trauma
atelectasis
VQ mismatch: dead space types
anatomic - fixed
physiologic - shock, emphysema, pulmonary embolism
Respiratory dysfunction impact on MSK
respiratory alkalosis --> muscle weakness --> suppression of ventilations
Respiratory dysfunction impact on cardio
chronic lung disease --> pulmonary hypertension --> right sided heart failure
Respiratory dysfunction impact on neuro
hypercapnia --> somnolence/lethargy --> increased cerebral blood flow/CSF pressure/seizures/papilledema
Hypoxia in general will cause
ischemia/infarction of cells/tissues/organs
Obstructive pulmonary diseases
conditions that make it hard to exhale all the air in the lungs
increased RV
ex. COPD, asthma
Restrictive pulmonary diseases
conditions that make it hard to fully expand the lungs with air
decreased TLC
ex. interstitial lung disease, neuromuscular disease, scoliosis, marked obesity
Interstitial lung disease
group of disorders with common characteristics
Interstitial lung disease S&S
progressive gradual onset dyspnea
nonproductive chronic cough with or without hemoptysis
bibasilar late inspiratory crackles
tachypnea
digital clubbing
Interstitial lung disease diagnostics
CXR or CT: reticulonodular ("net like) changes, septal thickening, honeycombing, could also be normal
Lung biopsy (VATS)
PFT
Interstitial lung disease causes
environmental or occupational exposure: pneumoconiosis
autoimmune like Sjogren's, systemic sclerosis, RA
medications: amiodarone, nitrofurantoin, methotrexate
idiopathic: most common
FEV1/FVC < 70%
obstructive lung disease
FEV1/FEV > 70%
restrictive lung disease
Idiopathic fibrosing interstitial pneumonia
most common type of interstitial lung disease
combination of inflammation and fibrosis - NOT infectious
sporadic or genetic
Idiopathic fibrosing interstitial pneumonia treatment
pulm referral
corticosteroids trial
Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) treatment
NO steroids
immunosuppressants - nintedanib and pirfenidone to reduce rate of decline
definitive treatment - lung transplant with 5 year survival
Pneumoconiosis etiology
chronic fibrotic lung disease due to inhalation of inorganic dust particles: silica, asbestos, coal dust, beryllium, talc, fiberglass, cement, metals
can occur years after initial exposure
Pneumoconiosis diagnosis
diffuse nodular opacities on imaging
based on history/exposure
no biopsy needed
Pneumoconiosis treatment
supportive and supplemental O2
pulmonary rehab
Coal worker's pneumoconiosis etiology
ingestion of inhaled coal dust by alveolar macrophages --> forms coal macules
Coal worker's pneumoconiosis S&S
often asymptomatic with PFTs unremarkable
more complicated: productive cough with black pigment, wheezing, end inspiratory crackles
mimics COPD
Coal worker's pneumoconiosis imaging
diffuse small fibrotic opacities from coal macules
Coal worker's pneumoconiosis treatment
supportive
Pneumoconiosis: silicosis etiology
silica particle inhalation --> alveolar macrophage dysfunction --> inflammation and fibrosis --> silicotic (small rounded opacities) nodule formation throughout the lung
Pneumoconiosis: silicosis epidemiology
sandblasters
exposure to rocks and sand
Pneumoconiosis: silicosis S&S
asymptomatic with PFTs without change
complicated: dyspnea on exertion, dry cough
Pneumoconiosis: silicosis diagnostics
CXR: multiple nodules in the middle and upper lungs bilaterally, enlargement of hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes
PFTs: later stages show restrictive physiology
Pneumoconiosis: silicosis treatment
supportive - oxygen, vaccines, treat infections, pulm rehab
lung transplant with 6-7 year survival
prevention education
Pneumoconiosis: asbestosis
nodular interstitial fibrosis in workers exposed to asbestos fibers
Pneumoconiosis: asbestosis epidemiology
workers in shipyard, construction, pipe fitters, insulators
10-20 years of exposure
smoking increases risk
Pneumoconiosis: asbestosis S&S
progressive dyspnea
inspiratory crackles
clubbing
cyanosis
Pneumoconiosis: asbestosis diagnostics
CXR: pleural plaques
CT: parenchymal fibrosis and pleural plaques
PFTs: restrictive dysfunction, reduced diffusion capacity
Pneumoconiosis: asbestosis treatment
supportive
smoking cessation!
Pneumoconiosis: berylliosis
chronic beryllium disease (CBD)
granulomatous (clusters of WBCs) disease caused by exposure to beryllium - inhaled or skin
Pneumoconiosis: berylliosis etiology
beryllium exposure --> T-cell sensitization --> immune response with further exposure --> aggregation of immune cells (macrophages and CD4 cells) --> noncaseating granulomas and fibrosis
Pneumoconiosis: berylliosis epidemiology
working history in metal shops, defense industries, jewelry making, electronics industry
Pneumoconiosis: berylliosis S&S
infectious appearance:
fever
weight loss/night sweats
dry cough
LA and hepatosplenomegaly
crackles
rash
Pneumoconiosis: berylliosis differential
similar presentation to TB, but TB has caseating granulomas and necrosis
Pneumoconiosis: berylliosis diagnostic criteria
must meet 3 criteria:
exposure history
positive beryllium lymphocyte proliferation test (BeLPT test) via blood or bronchoalveolar lavage
compatible histology with granulomatous inflammation on biopsy
Pneumoconiosis: berylliosis imaging
XR: nonspecific - normal, can show hilar LA, ground-glass opacities, or interstitial fibrosis
CT: nonspecific, can show parenchymal nodules, ground-glass, opacities, pleural thickening, hilar LA
Pneumoconiosis: berylliosis treatment
vaccines
smoking cessation
corticosteroids if symptoms
if steroids fail: methotrexate and folic acid
supplemental O2
monitor PFTs
trend imaging
Sarcoidosis
systemic disease with granulomatous inflammation of lung but can also affect skin, eyes, heart, and liver
Sarcoidosis epidemiology
North American Black or northern European White people
onset in 3rd-4th decade
Sarcoidosis S&S
fever, malaise
insidious onset of dyspnea
skin with erythema nodosum or Lupus pernio
iritis
peripheral neuropathy
cardiomyopathy
asymptomatic
LA, hepatosplenomegaly, parotid enlargement
Lupus pernio
rare cutaneous manifestation of sarcoidosis on nose, ears, or face
Erythema nodosum
tender nodules on the extensor surfaces of legs
sign of sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis labs and diagnostics
labs: leukopenia, elevated ESR, hypercalcemia, elevated ACE
PFTs: restrictive
ECG: heart block, dysrhythmia (A fib)
Sarcoidosis radiographs with staging
stage 1: b/l hilar adenopathy
stage 2: hilar adenopathy, parenchymal involvement
stage 3: parenchymal involvement only
stage 4: advanced fibrotic changes in upper lungs
Sarcoidosis diagnostic criteria
clinical/radiographic changes + exclusion of similar dx + histologic changes of noncaseating granulomas on biopsy
Sarcoidosis treatment
asymptomatic - none
symptomatic - prednisone for months-years
immunosuppressive meds if steroid intolerance: methotrexate, azathioprine, infliximab
long term follow up to monitor liver/renal function and PFTs
ophth referral and cardio referral
Sarcoidosis prognosis
hilar adenopathy - best outlook
erythema nodosum - good outcome
lung parenchymal involvement - worse prognosis
Pulmonary nodule aka
coin lesion
Pulmonary nodule
rounded opacity outlined by normal lung
not associated with infiltrate or atelectasis
<3cm
What could pulmonary nodule be?
risk of malignancy
benign lesion
infectious granuloma
inflammatory
Hamartoma
most common benign neoplasm
Solitary pulmonary nodule found on imaging. What's next?
determine biopsy vs resect vs observe
imaging to determine comparison to old imaging studies, estimated growth, size, and appearance
Risk factors for malignancy of solitary pulmonary nodule
increases with age
smoking
prior malignancy
Growth rate of solitary pulmonary nodule
rapid growth (2x size over 30 days) - infection suggested
long-term stability - benign
Size and likelihood of malignancy of solitary pulmonary nodule
<5mm 1%
6-10mm 25%
11-20mm 33%
21-45mm 80%
Benign appearance of solitary pulmonary nodule
smooth, well defined edge
Malignant appearance of solitary pulmonary nodule
ill-defined margins or lobular appearance
spiculated margins and peripheral halo
cavitary lesions with thick walls
Probability of Malignancy and Treatment Guidelines - prediction models
Brock model
VA cooperative model
Low probability of malignancy of solitary pulmonary nodule (less than 5%) approach
observation
serial CT imaging studies
High probability of malignancy of solitary pulmonary nodule (more than 60%) approach
resection following staging if surgical risk is acceptable
biopsies rarely yield a specific benign diagnosis
Intermediate probability of malignancy of solitary pulmonary nodule (5-60%) approach
PET scan
biopsy with transthoracic needle aspiration (TTNA), bronchoscopy with biopsy, sputum cytology, or surgical biopsy
PET/CT scan
positron emission tomography with high sensitivity and specificity but false positives can occur with infection/inflammation
uses fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) uptake
____ activity on PET scan increases the likelihood of malignancy
Hypermetabolic (positive)
PET scans are not reliable for
brain
Sputum cytology
highly specific but lasts sensitivity
used for central lesions and in patients who are poor candidates for invasive diagnostic procedures
Surgical biopsy of solitary pulmonary nodule is done via
video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS)
nodulectomy via wedge resection
send to pathology for frozen section to determine if lobectomy
Lung cancer screening recommendations
annual low dose CT (LDCT) in patients age 50-80 with 20 pack year smoking history and currently smoke or quit within the past 15 years
screening discontinued once a person has not smoked for 15 years or develops health problem that limits life expectancy or willingness to complete curative surgery
Lung cancer screening patient education
discuss benefits, limitations, and harms of screening
refer to center with expertise for screening
smoking cessation
Bronchogenic carcinoma
malignant neoplasm arising from respiratory epithelium - cells most exposed to air
Bronchogenic carcinoma etiology
repeated exposure to carcinogens that induces gene mutations in respiratory epithelial cells
mutated cells divide at increased, uncontrolled rate and tumor (nodule/mass) forms
Lung cancer epidemiology
most common cancer death among men and women
cigarette smoking causes 85-90%
Other risk factors for bronchogenic carcinoma
second hand smoke
asbestos
radon gas
metals
radiation exposure
genetics
pulmonary fibrosis, COPD, sarcoidosis
previous lung cancer
Median age of diagnosis of bronchogenic carcinoma
71
Histologic categories of lung cancer
small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) - adenocarcinoma, SCC, large cell carcinoma
tissue also tested for driver mutations: EGFR, ALK, BRAF, ROS1 to determine targeted systemic therapy
Bronchogenic carcinoma - Small cell carcinomas
arises from neuroendocrine cells
begin centrally causing narrowing of the bronchus w/o discrete luminal mass - extrinsic masses
regional or distant metastasis with early hematogenous spread
aggressive course with median survival of 6-18 weeks w/o treatment
associated with paraneoplastic syndromes
Bronchogenic carcinoma - Adenocarcinoma
arises from alveolar type 2 cells within distal or terminal bronchioles
peripheral nodules or masses
"puckering" of overlying pleura
Bronchogenic carcinoma - adenocarcinoma in situ
spread along pre-existing alveolar structures
characterized by lepidic growth pattern w/o evidence of invasion
Bronchogenic carcinoma - Squamous cell carcinoma
arises from bronchial epithelium
presents with intraluminal mass
centrally located
more likely to present with hemoptysis
large tumors can undergo central necrosis and cavitary lesions
Bronchogenic carcinoma - large cell carcinoma
heterogenous group of undifferentiated cancers that share large cells
aggressive!
Bronchogenic carcinoma symptoms
decreased appetite and weight loss
cough and hemoptysis
SOB
pain
hoarseness
neuro sx if brain mets
Bronchogenic carcinoma signs
LA
clubbing
abnormal breath sounds or pleural effusion
dullness to percussion
bony tenderness
palpable soft tissue mass if metastasis
focal neuro signs
Bronchogenic carcinoma on imaging
post obstructive pneumonia/pleural effusion - endobronchial lesion or extrinsic compression
Why might hoarseness occur in bronchogenic carcinoma?
vocal cord dysfunction from recurrent laryngeal neve paralysis from tumor or lymph nodes
Superior vena cava syndrome
tumor pressing on SVC - oncologic emergency
Pancoast syndrome
malignant neoplasm of superior sulcus invades thoracic inlet brachial plexus and cervical sympathetic nerves (stellate ganglion)
Pancoast syndrome S&S
severe shoulder pain with radiation
atrophy of hand/arm muscles
Horner syndrome
facial/neck edema
Paraneoplastic syndromes
disorders that accompany benign or malignant tumors
NOT directly related to mass effects or invasion
patterns of organ dysfunction related to immune-mediated or secretory effects of neoplasms
small cell lung cancer