12. Reactive Lesions
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
tumor of gingiva or alveolar mucosa is called…?
epulis
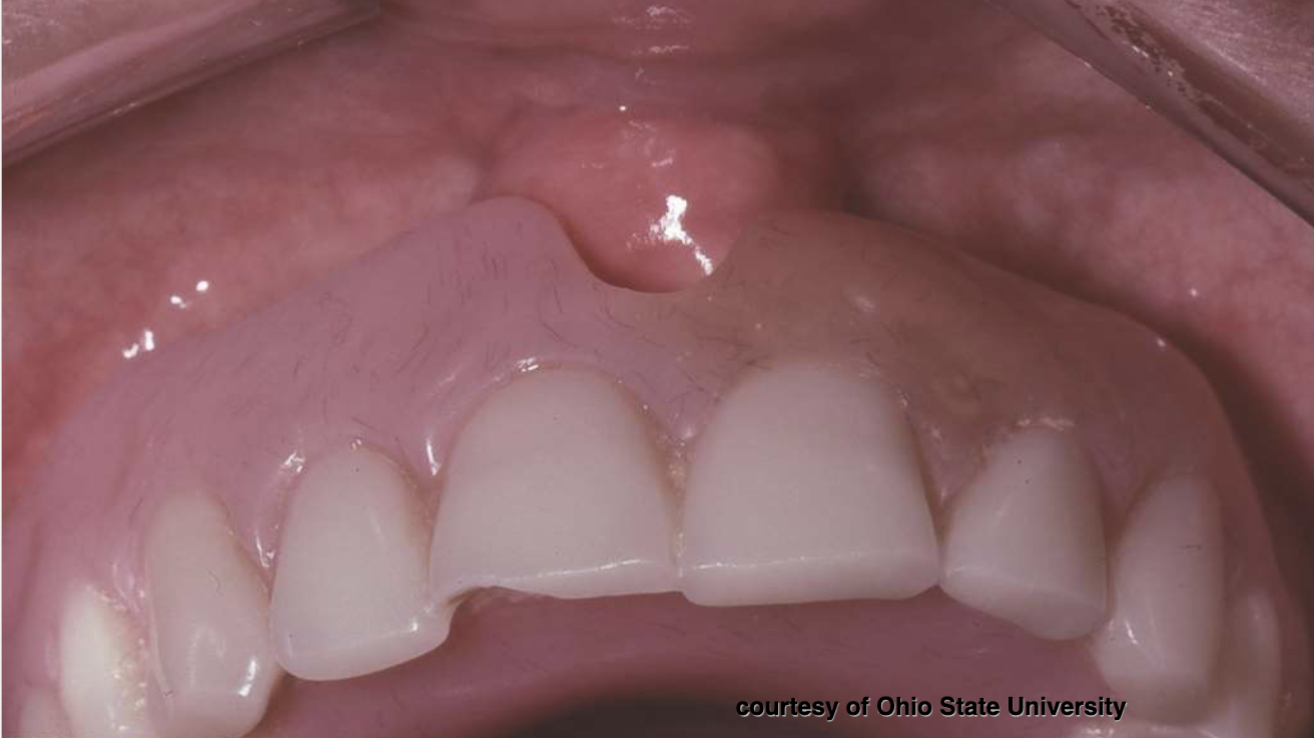
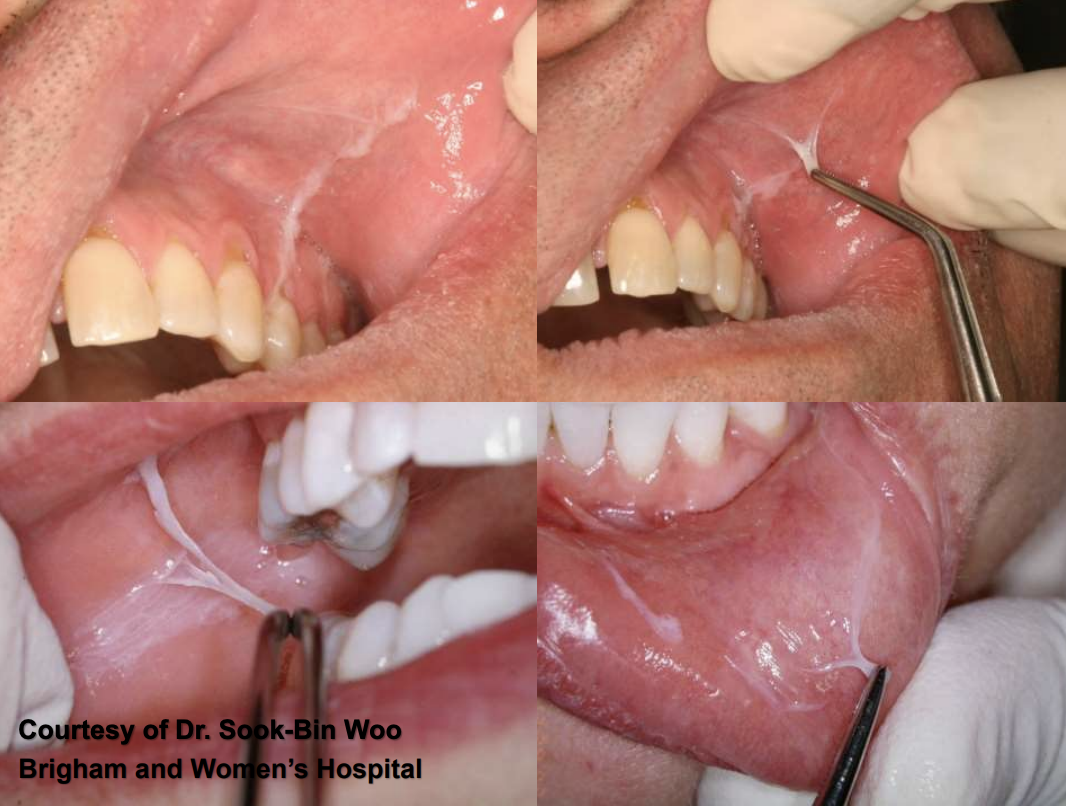
what condition is a tumor-like hyperplasia associated with flange of poorly-fitting denture?
epulis fissuratum
slide 4
Inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia, denture epulis
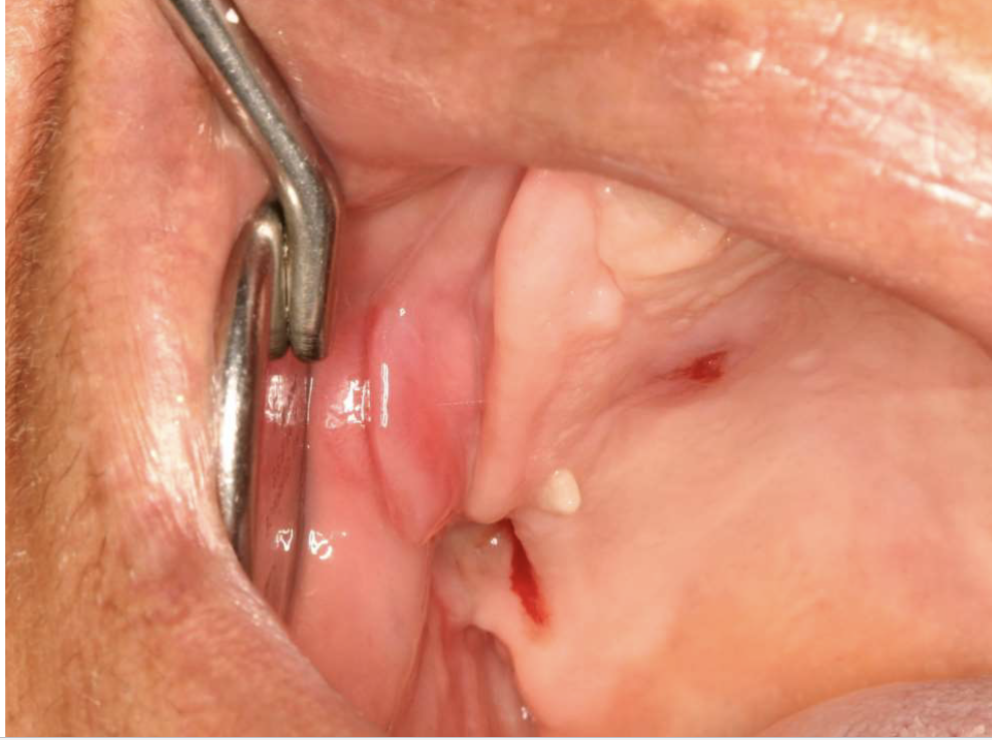
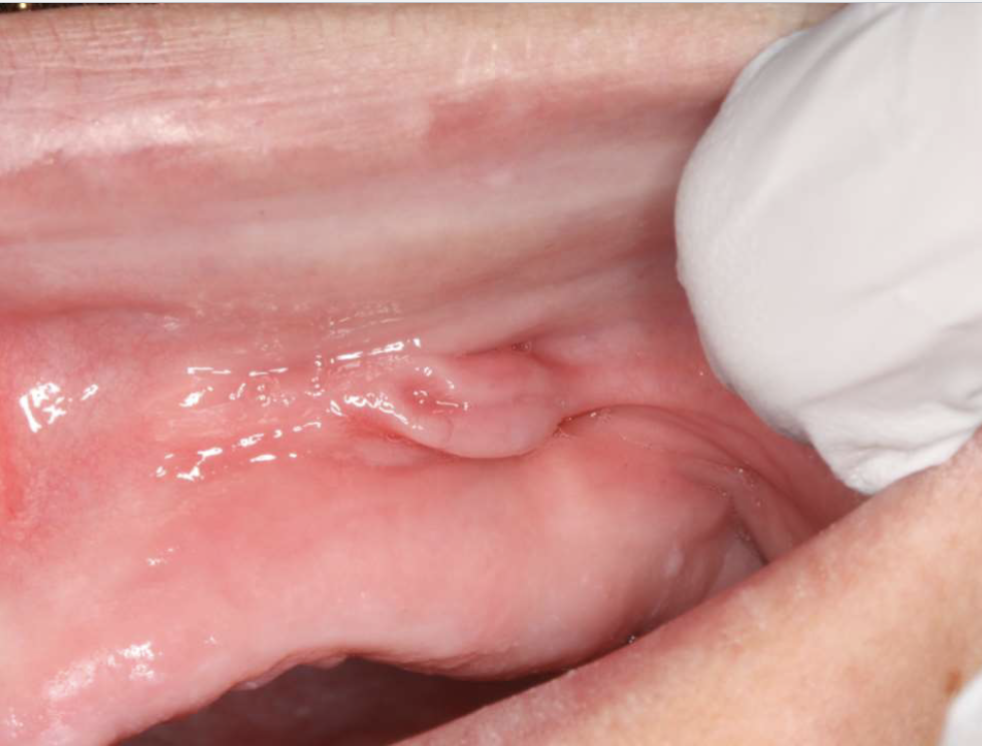
what are clinical features of epulis fissuratum?
single or multiple folds of hyperplastic tissue in alveolar vestibule
fibroepithelial polyp/leaf-like denture fibroma along palatal mucosa
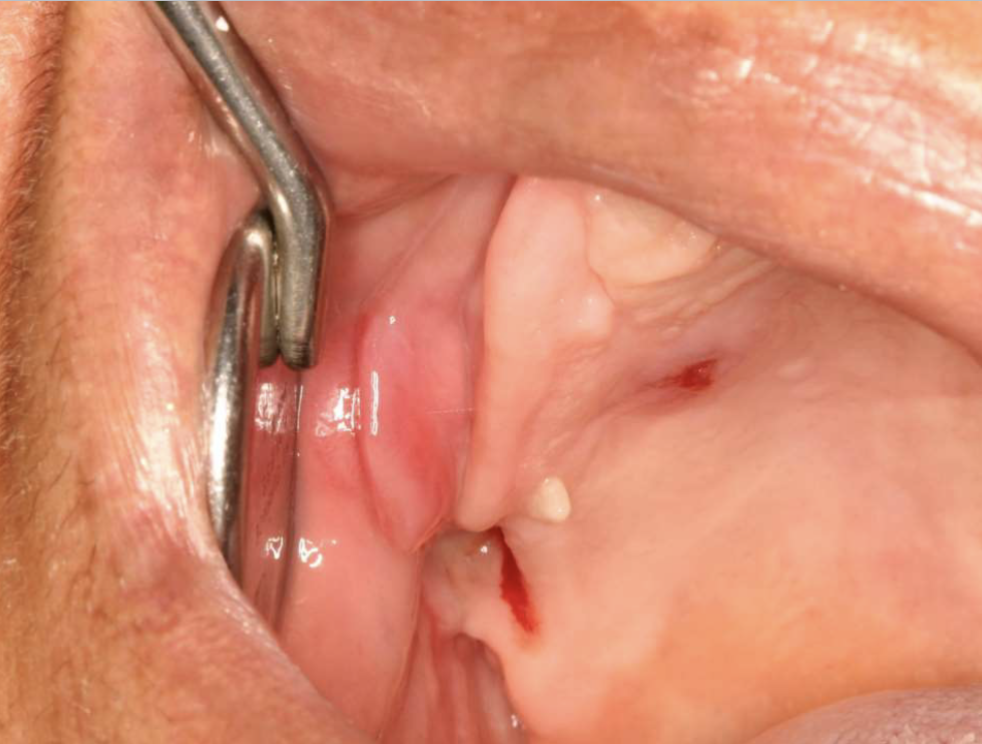
epulis fissuratum

epulis fissuratum
epulis fissuratum

epulis fissuratum
epulis fissuratum
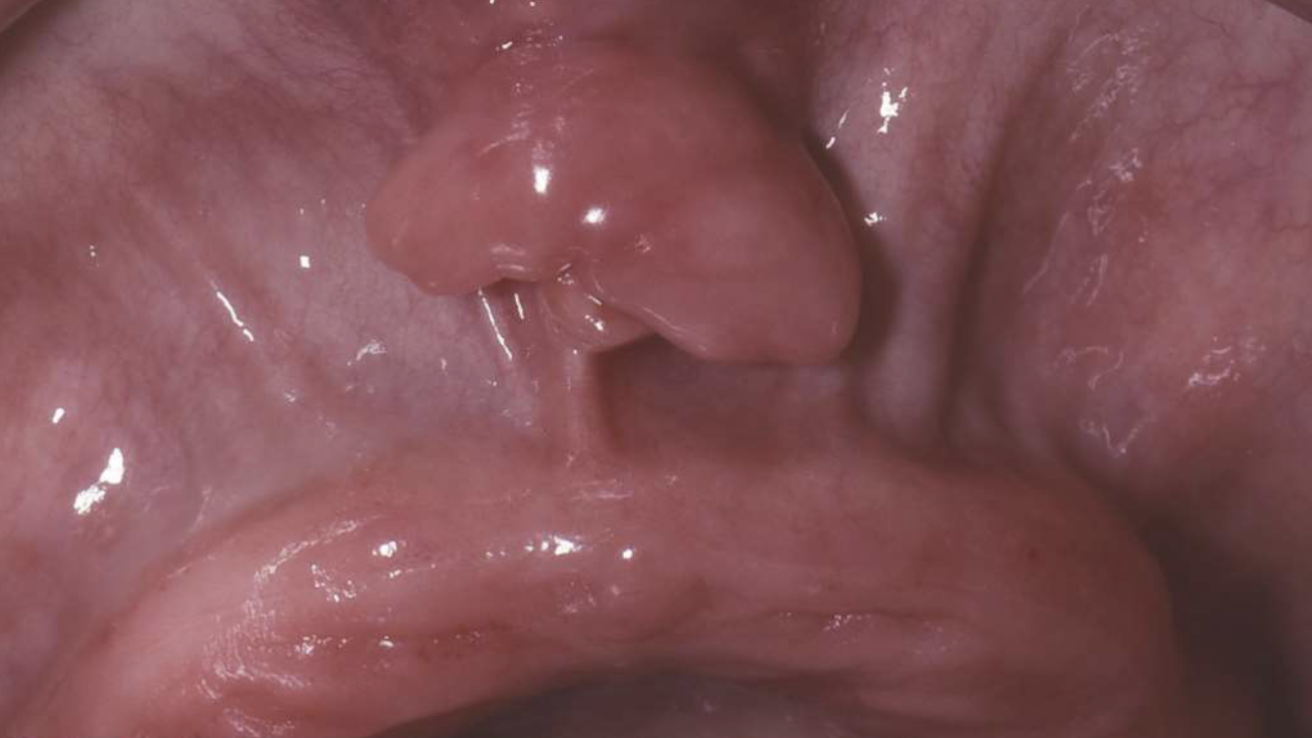
epulis fissuratum
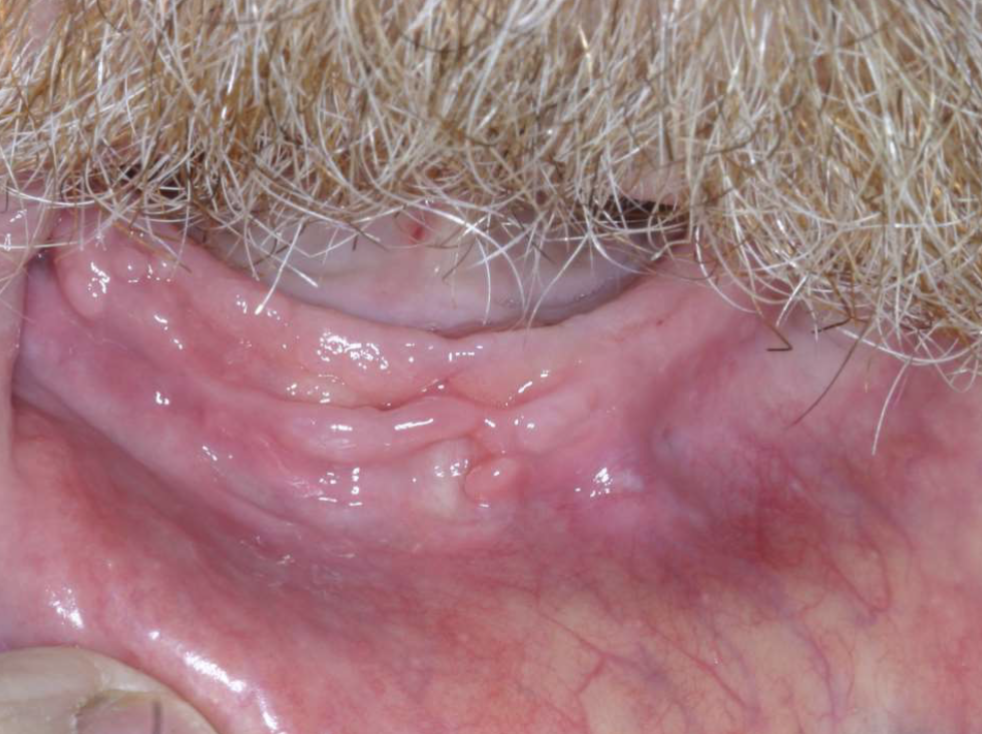
epulis fissuratum
what are histopatholgic features of epulis fissuratum?
Hyperparakeratosis or hyperorthokeratosis
Papillary hyperplasia and/or pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia
Hyperplasia of connective tissue
what is the treatment and prognosis of epulis fissuratum?
surgical removal
remake denture to prevent recurrence
Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia is associated with …?
poorly-fitting dentures
poor denture hygiene
continuous denture wear
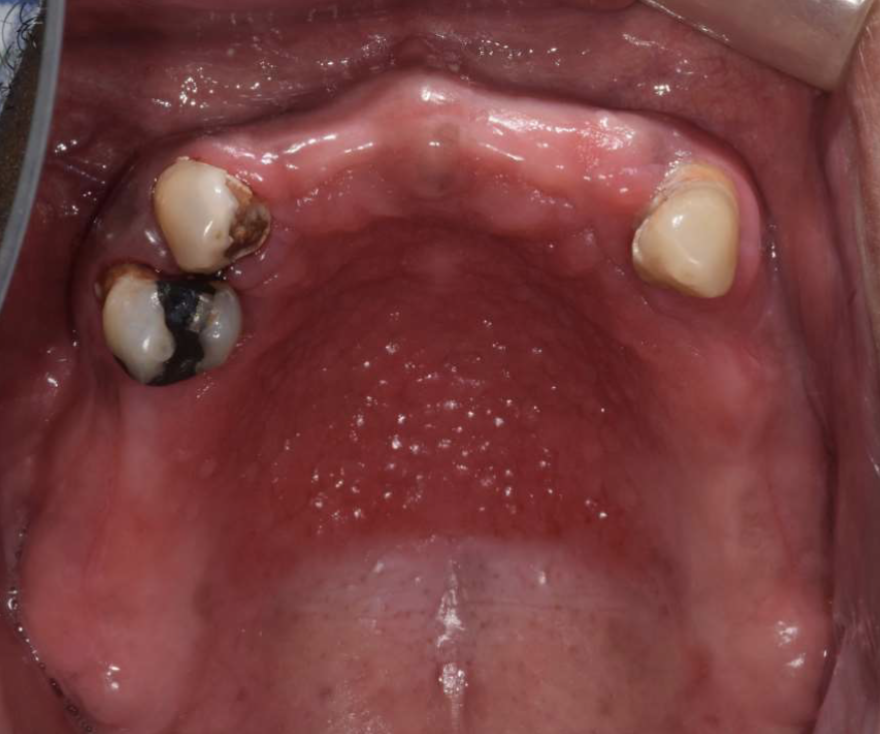
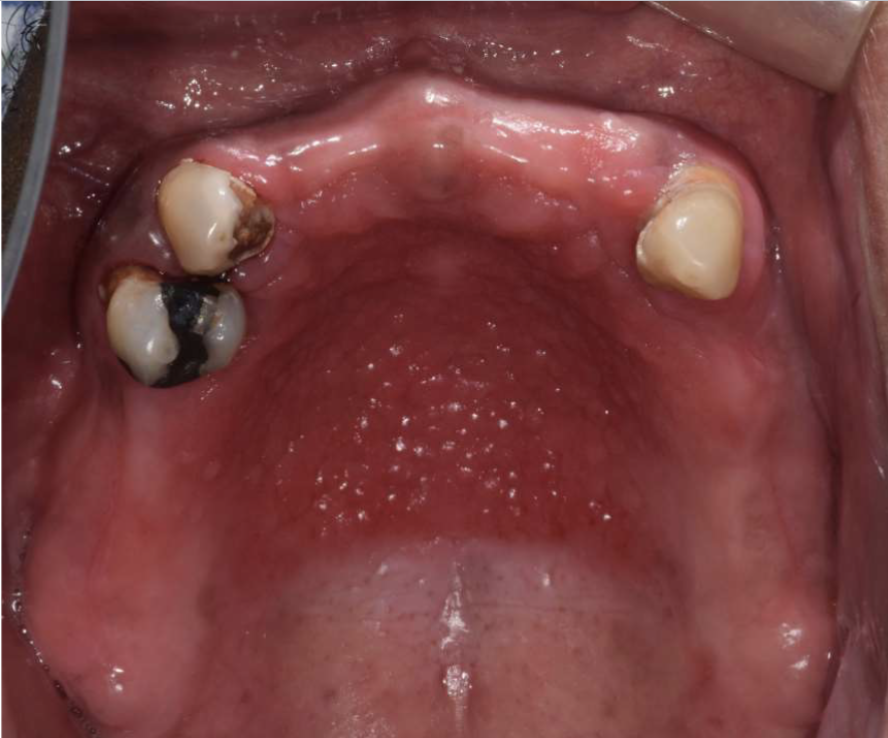
what condition is also known as denture papillomatosis and is a reactive tissue growth on the hard palate mucosa?
Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia
what are clinical features of Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia?
on hard palate beneath denture base
pink/red pebbly mucosa
erythema = secondary candidal infection
what is the difference between Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia and Epulis Fissuratum?
location
Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia → hard palate
Epulis Fissuratum → alveolar vestibule
Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia (with candidal infection)
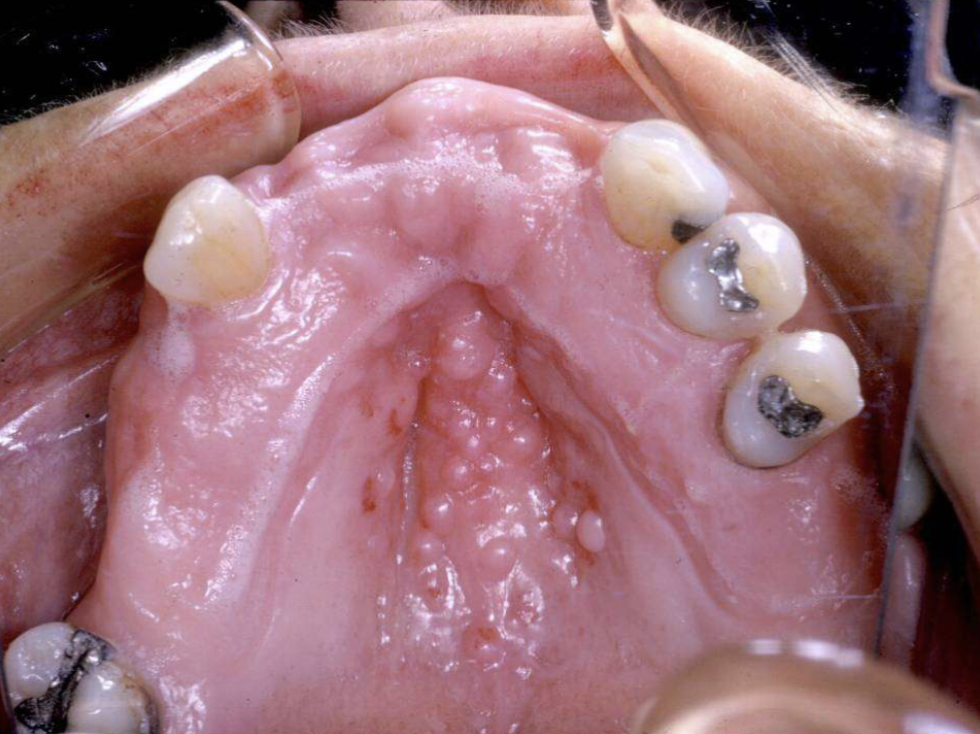
Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia (alone. WITHOUT candidiasis cuz there’s no erythema)
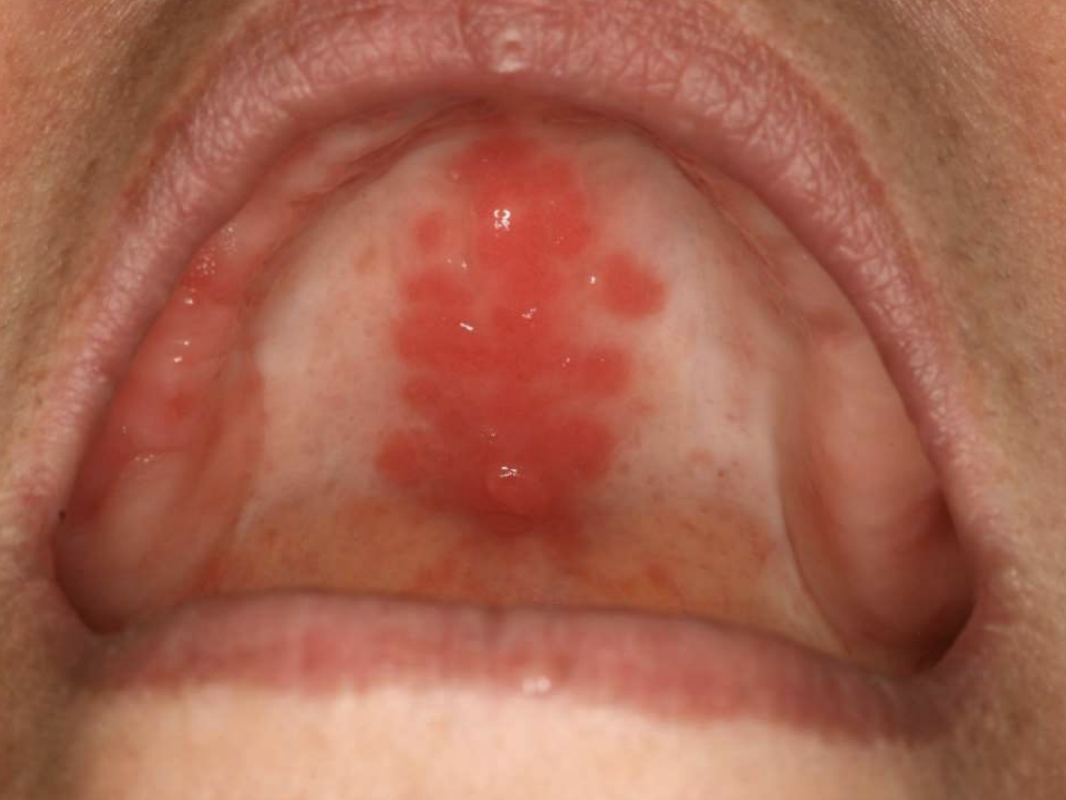
Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia (with candidal infection)
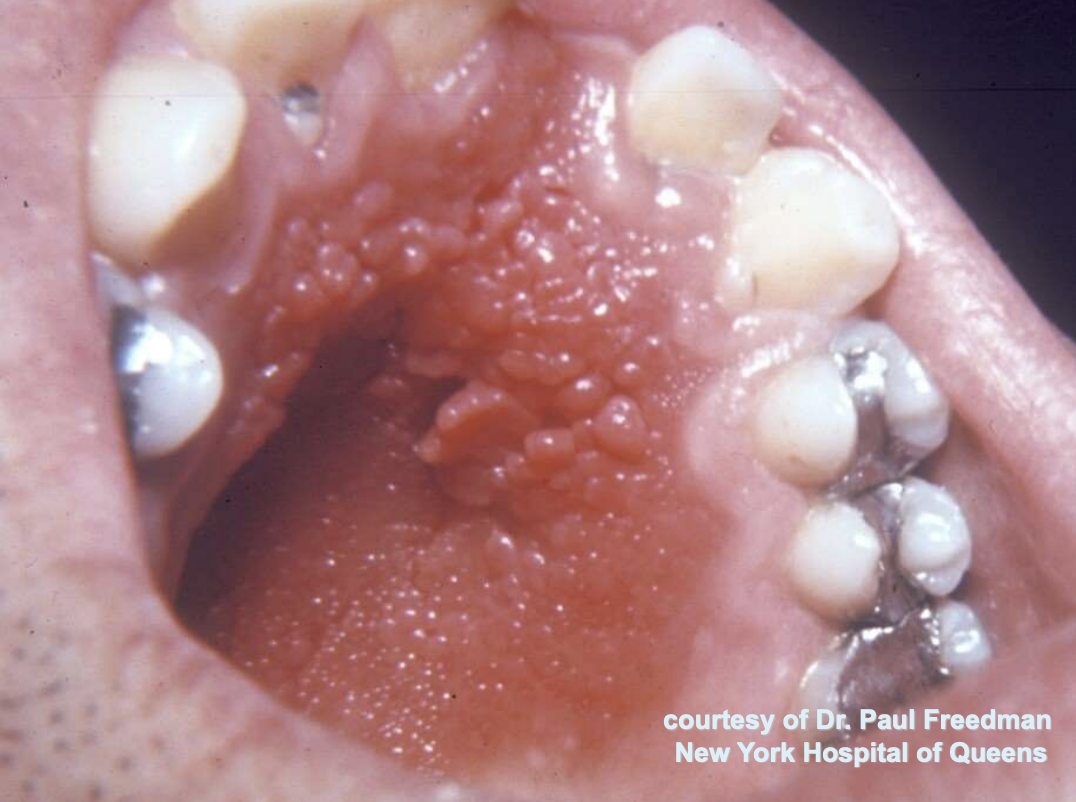
Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia (with candidal infection)
what are histopathologic features of Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia?
papillary growths on surface
pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia
Sialadenitis (inflammation of salivary glands)
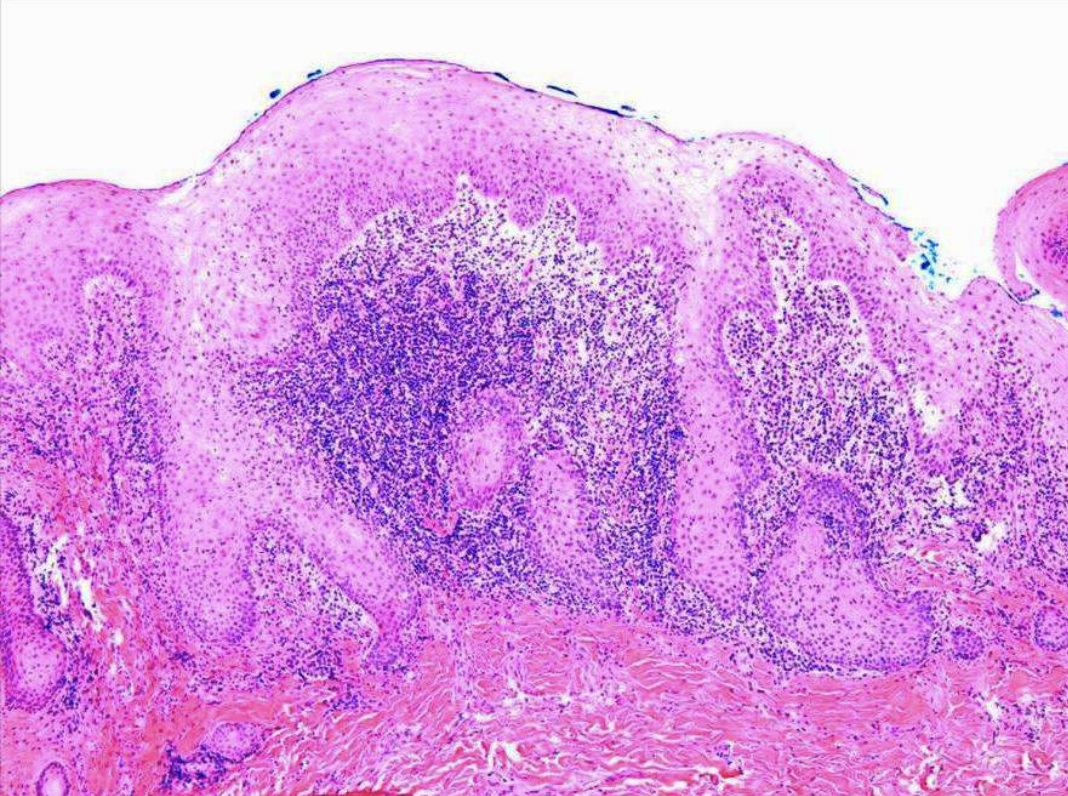
what is the treatment and prognosis of Inflammatory Papillary Hyperplasia?
mild cases → resolve with removal of denture
established cases → relining/refabricating denture following excision of hyperplastic tissue
antifungal therapy (as neeeded)
t/f: traumatic ulcers are a common oral pathology
true
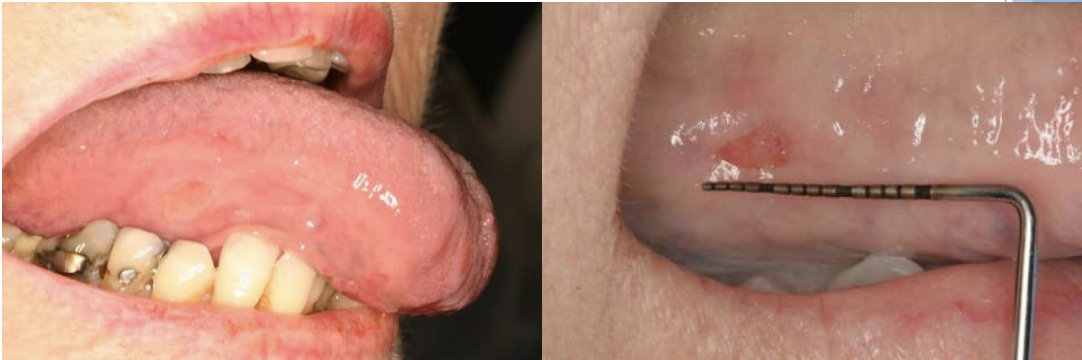
describe the histopathology of traumatic ulcers
ulcerated surface with fibrin membrane
granulation tissue
variable amounts of inflammation
traumatic ulcers
anesthetic-associated lip bite is a type of traumatic ulcer that is often secondary to what type of nerve block?
inferior alveolar nerve block (history of recent dental treatment)
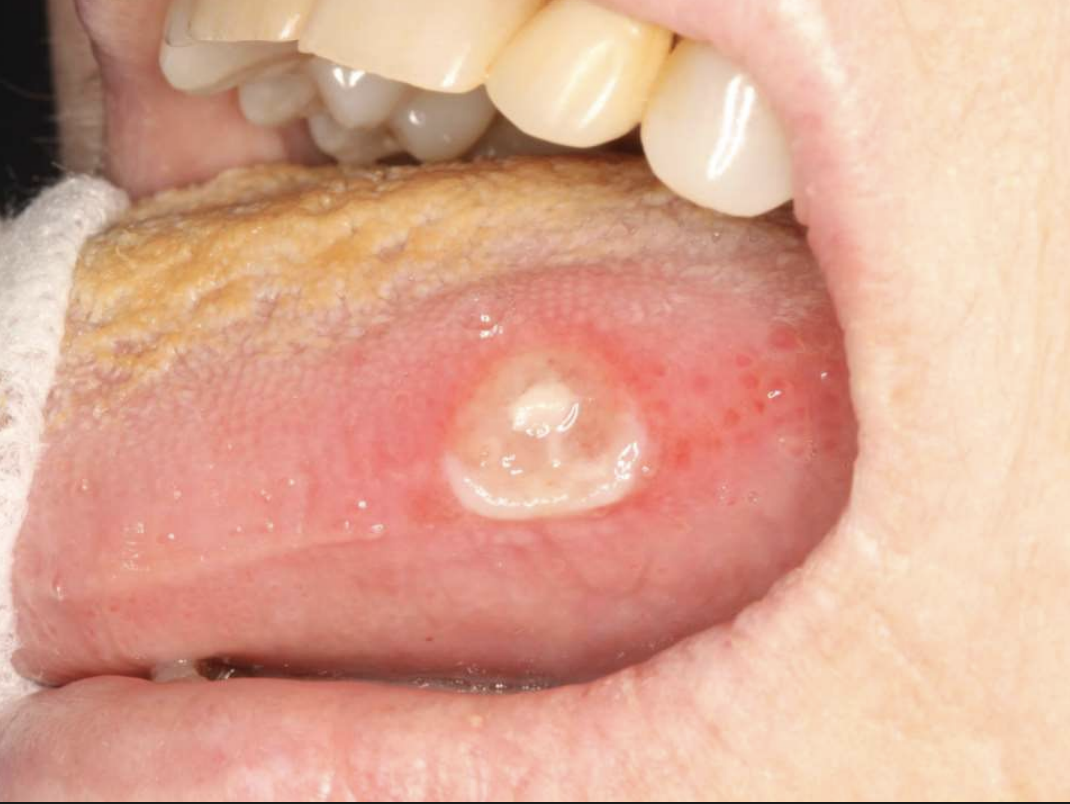
what is a slow-healing, penetrating ulcer takes weeks to months to resolve?
Traumatic Ulcerative Granuloma
t/f: Traumatic Ulcerative Granuloma is a true granuloma
false. not a true granuloma (but can be mistaken for malignancy)
Traumatic Ulcerative Granulomas are most common where?
tongue
t/f: Traumatic Ulcerative Granuloma have a male predilection
true
Traumatic Ulcerative Granulomas are often surrounded by…?
white hyperkeratotic rim (may help distinguish from aphthous ulcers or SCCA)
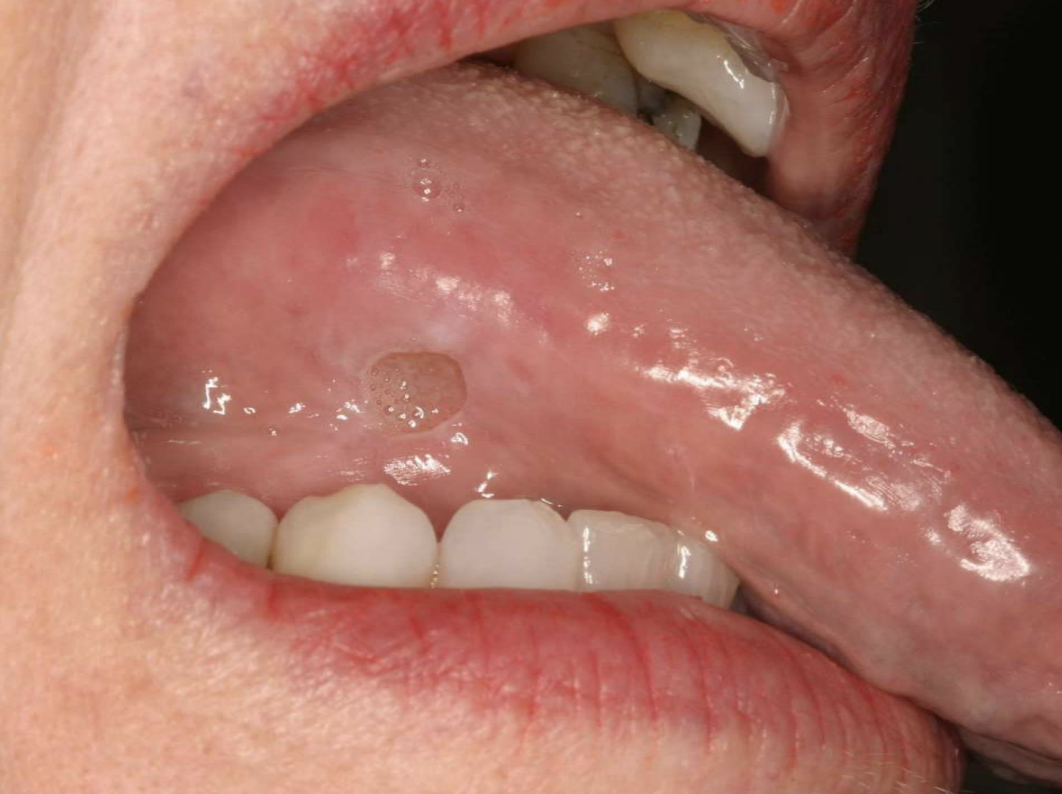
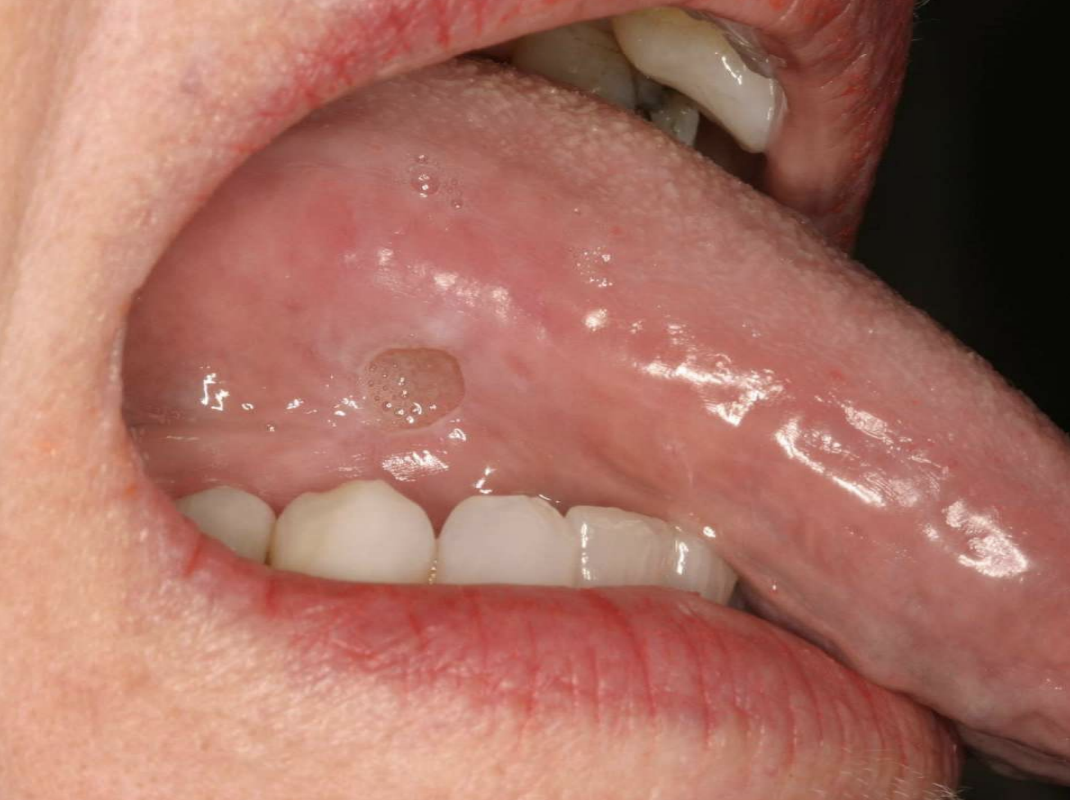
Traumatic Ulcerative Granulomas
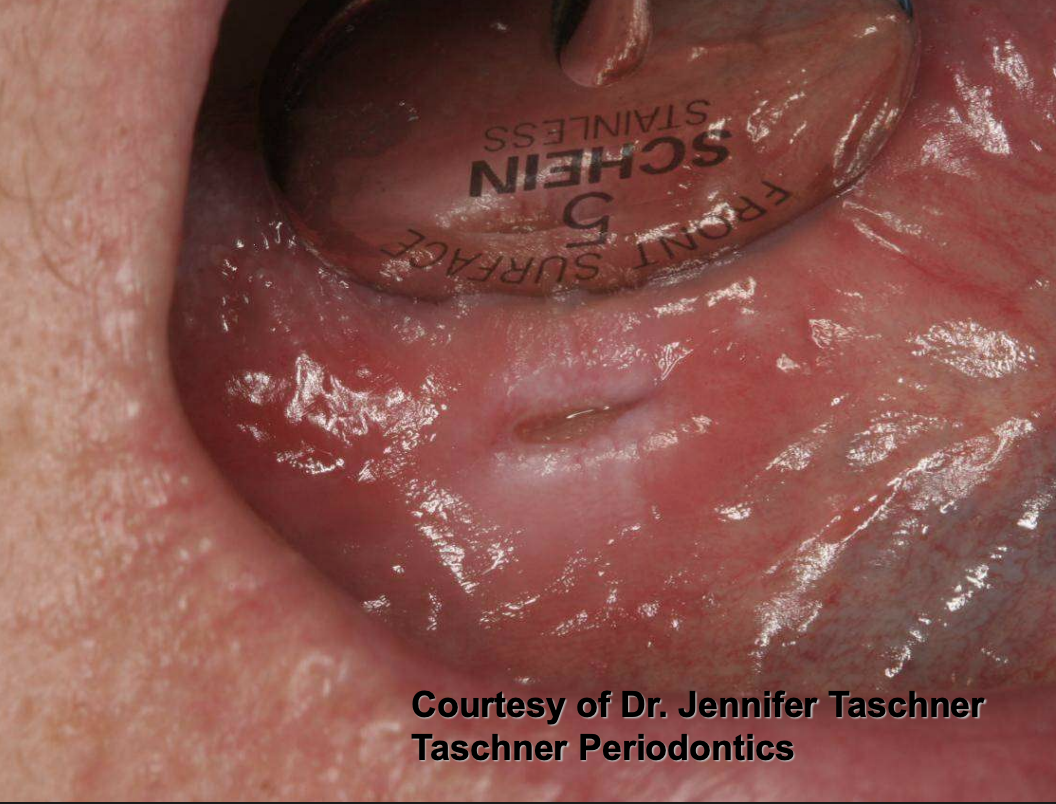
Traumatic Ulcerative Granulomas
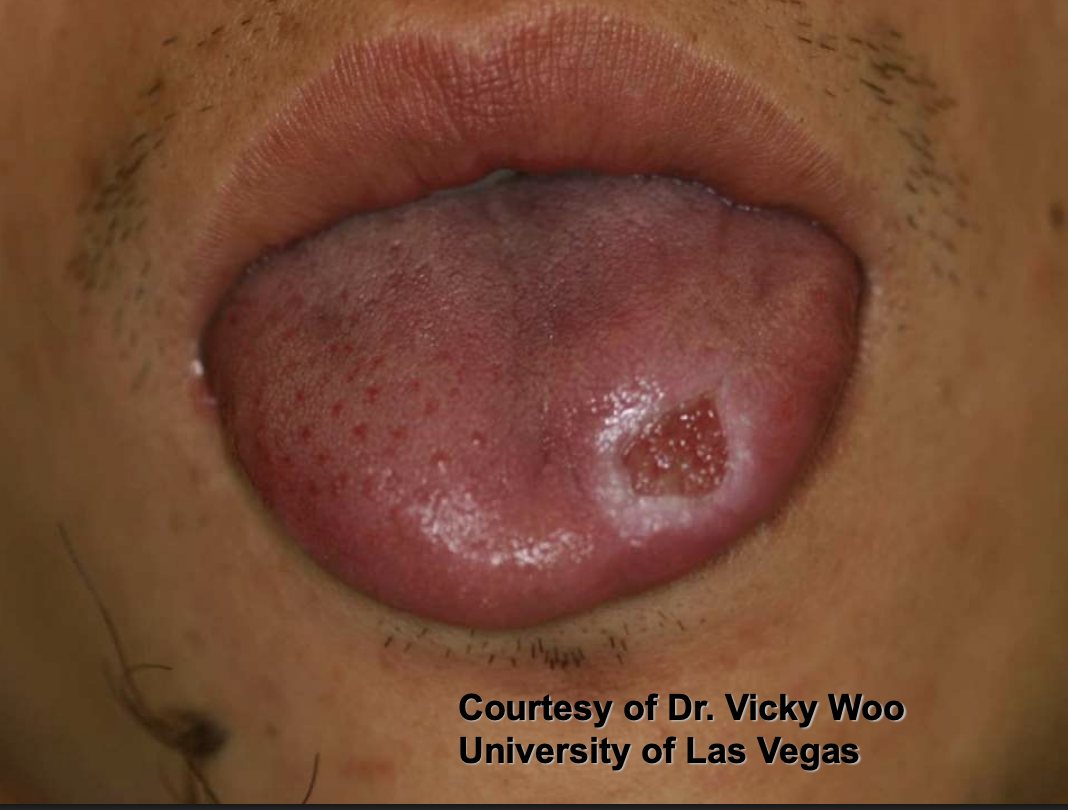
Traumatic Ulcerative Granulomas
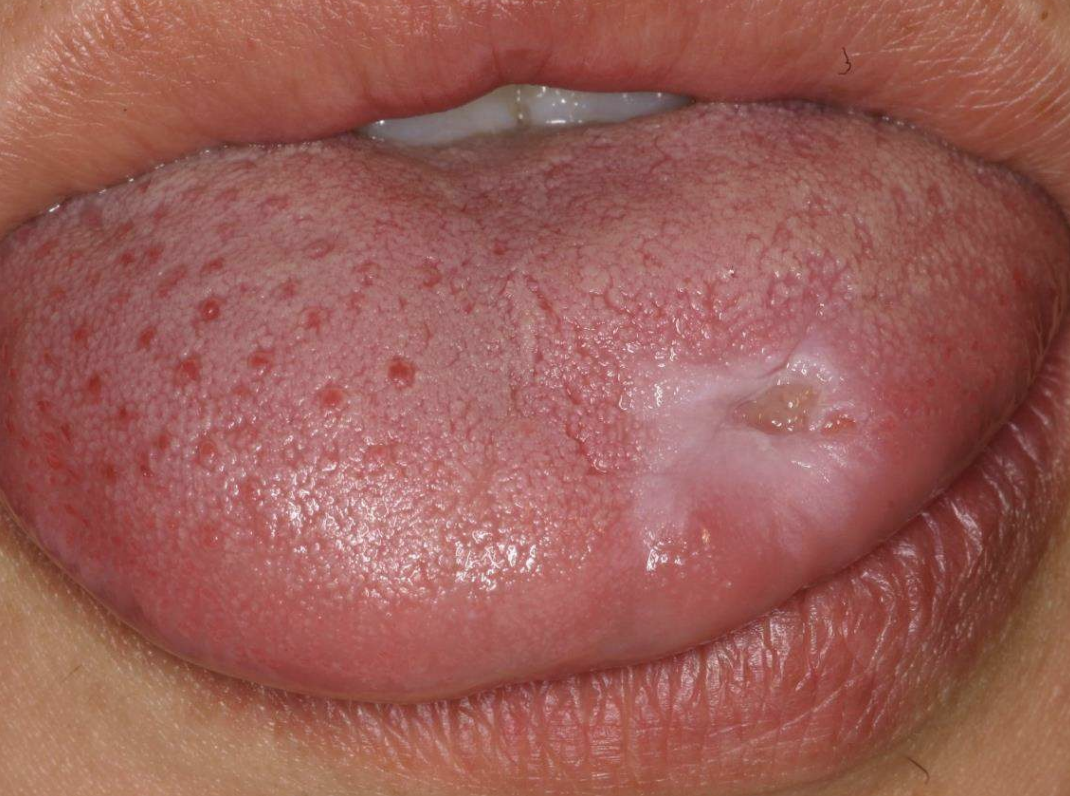
Traumatic Ulcerative Granulomas
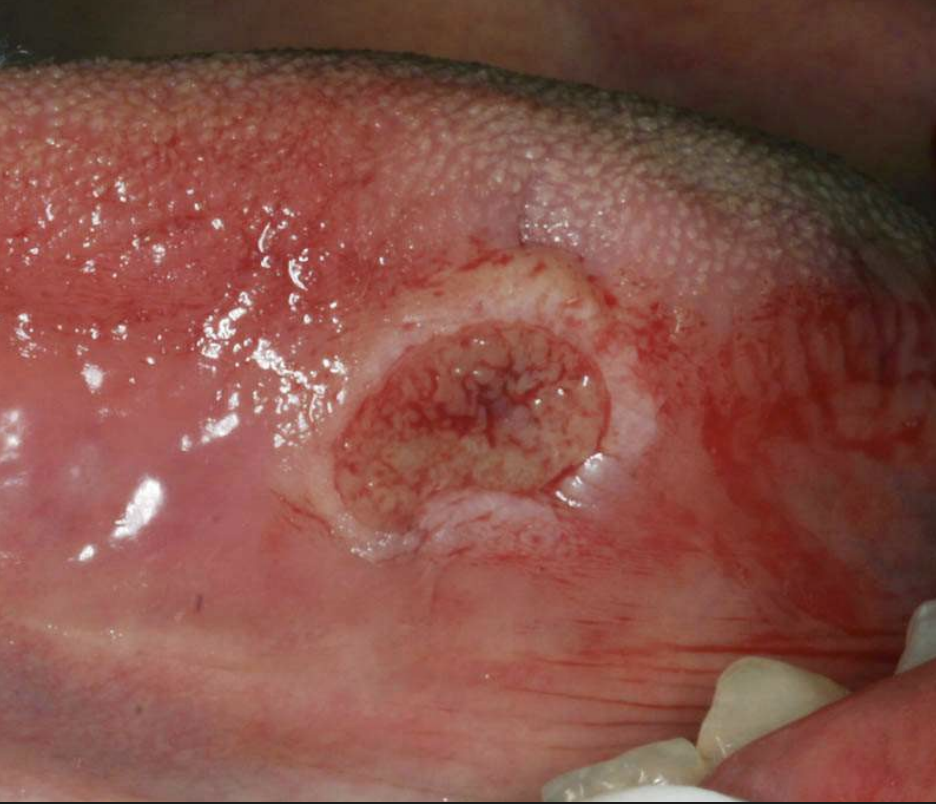
Traumatic Ulcerative Granuloma
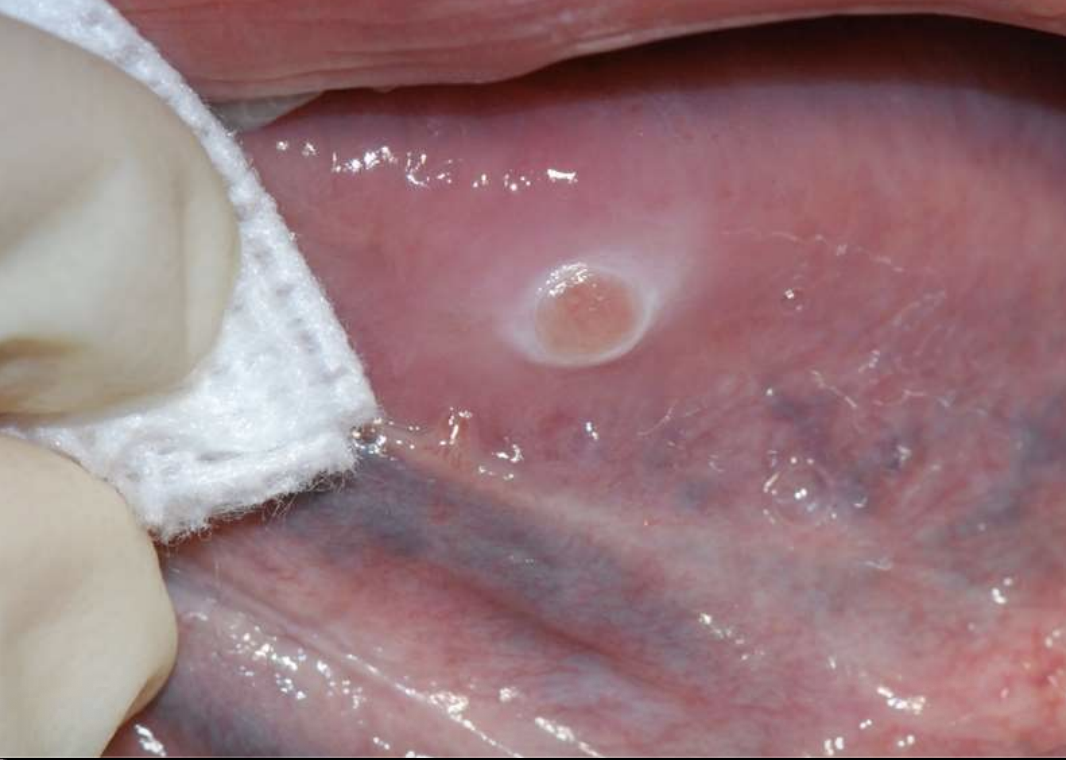
Traumatic Ulcerative Granuloma
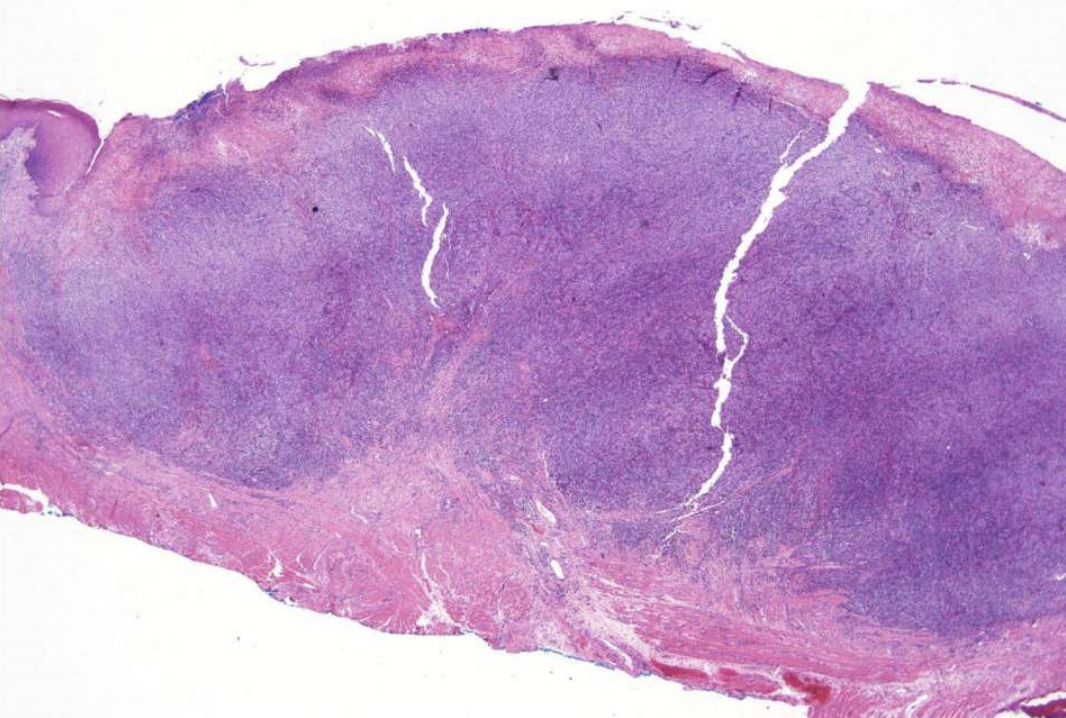
what are histopathologic features of Traumatic Ulcerative Granuloma?
numerous eosinophils
may be called Traumatic Ulcerative Granuloma with stroma eosinophilia (TUGSE)
inflammation of skeletal muscle
granulation tissue
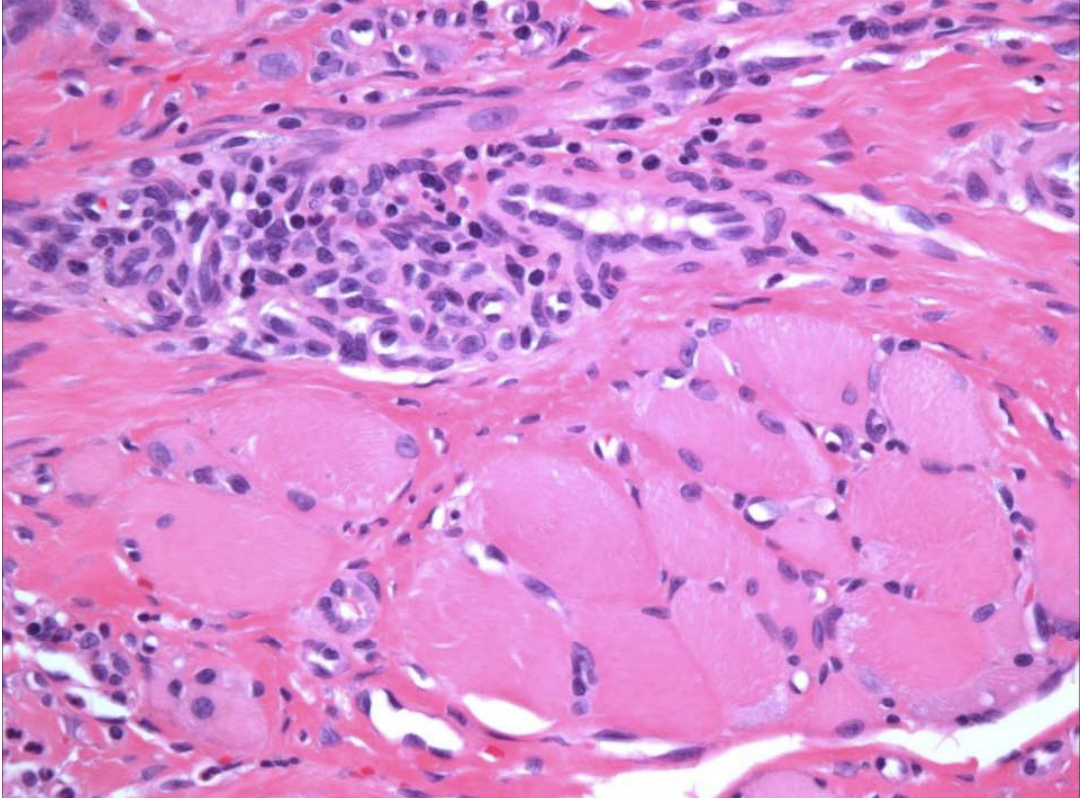
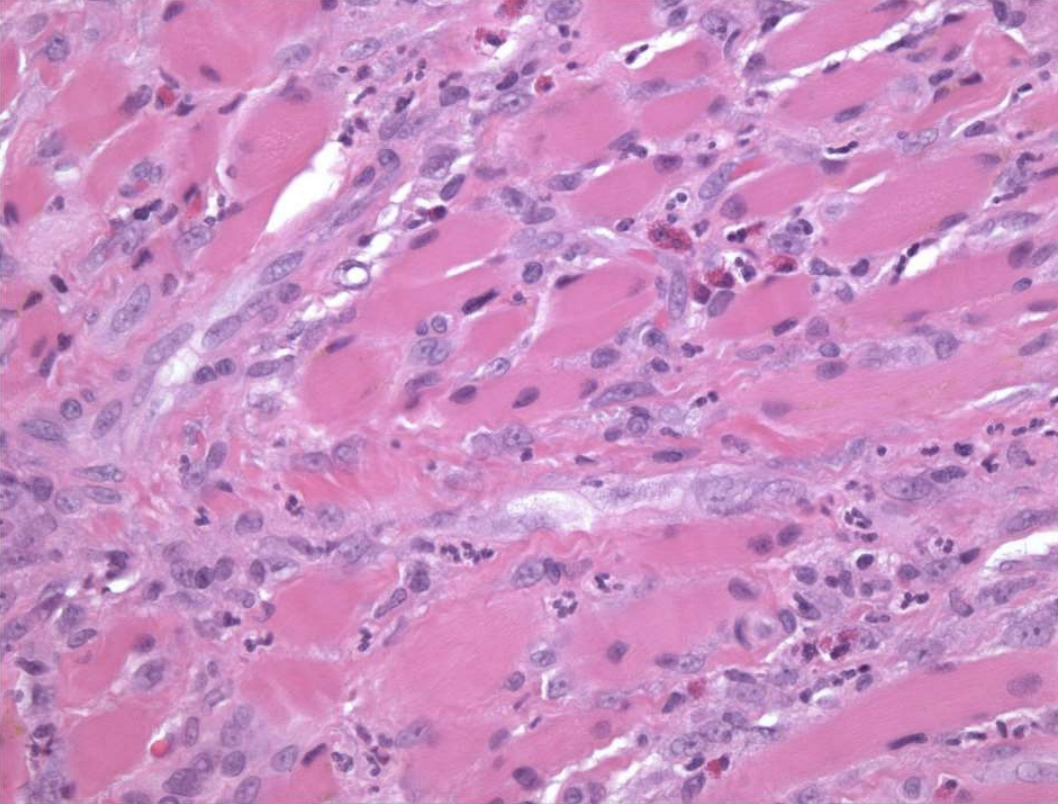
what is the treatment and prognosis of Traumatic Ulcerative Granuloma?
remove irritant
excise excess tissue (if necessary)
topical and/or intra-llesional steroids
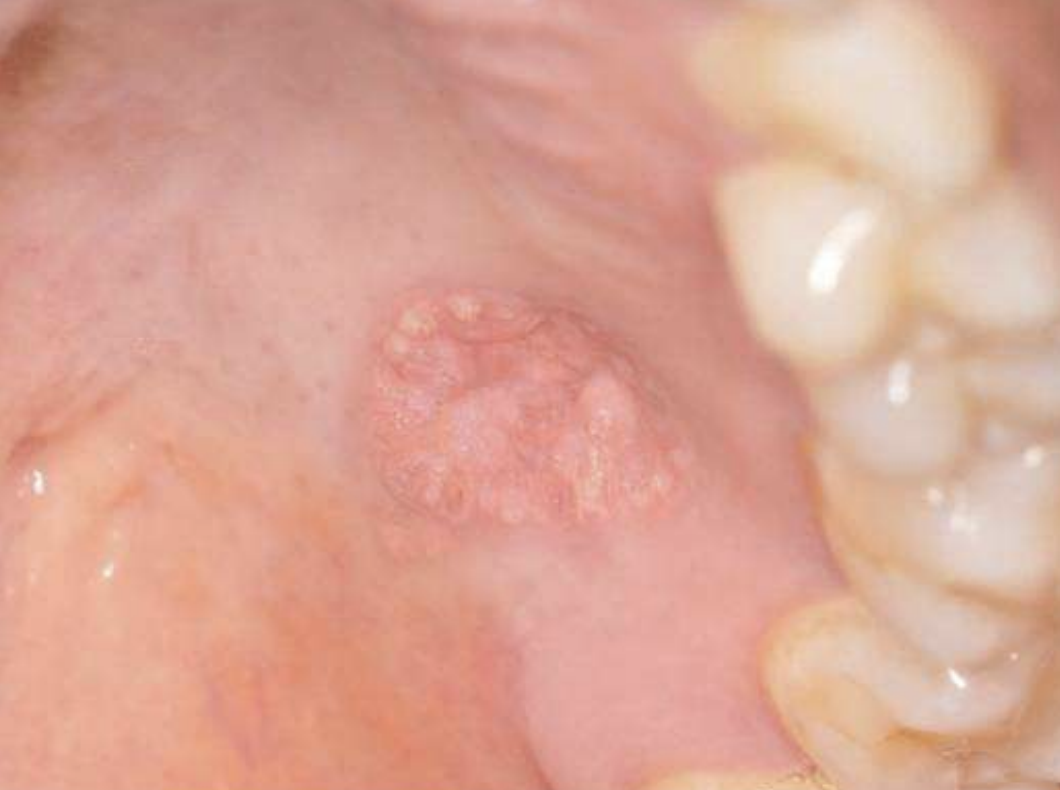
hyperplastic epithelium of mouth, skin, and genitalia
lipid-laden macrophages beneath epithelium
well-demarcated verrucous mass
may resemble squamous papillomas or early carcinomas
What condition?
Verruciform Xanthoma
is Verruciform Xanthoma associated with HPV?
no. it is papillary but not associated with HPV
50% of oral lesions due to Verruciform Xanthoma are on what surfaces?
gingiva or alveolar mucosa
what colors can Verruciform Xanthoma lesions present as?
pink, white, red, yellow, orange
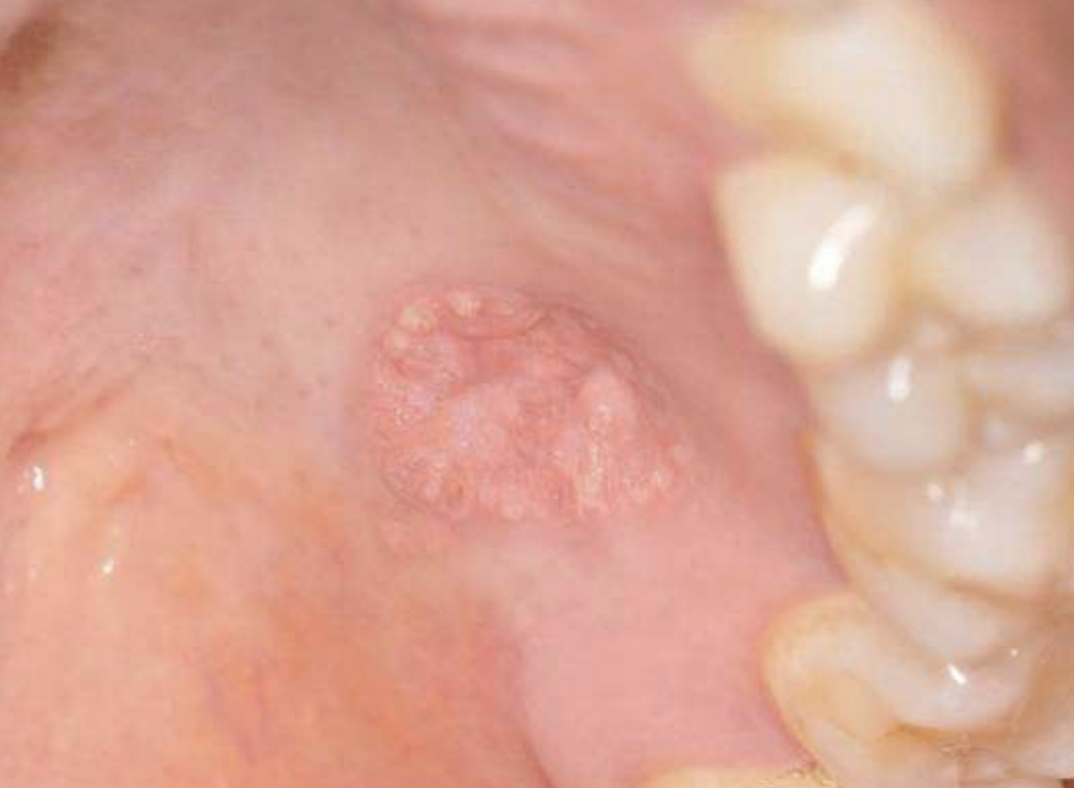
Verruciform Xanthoma
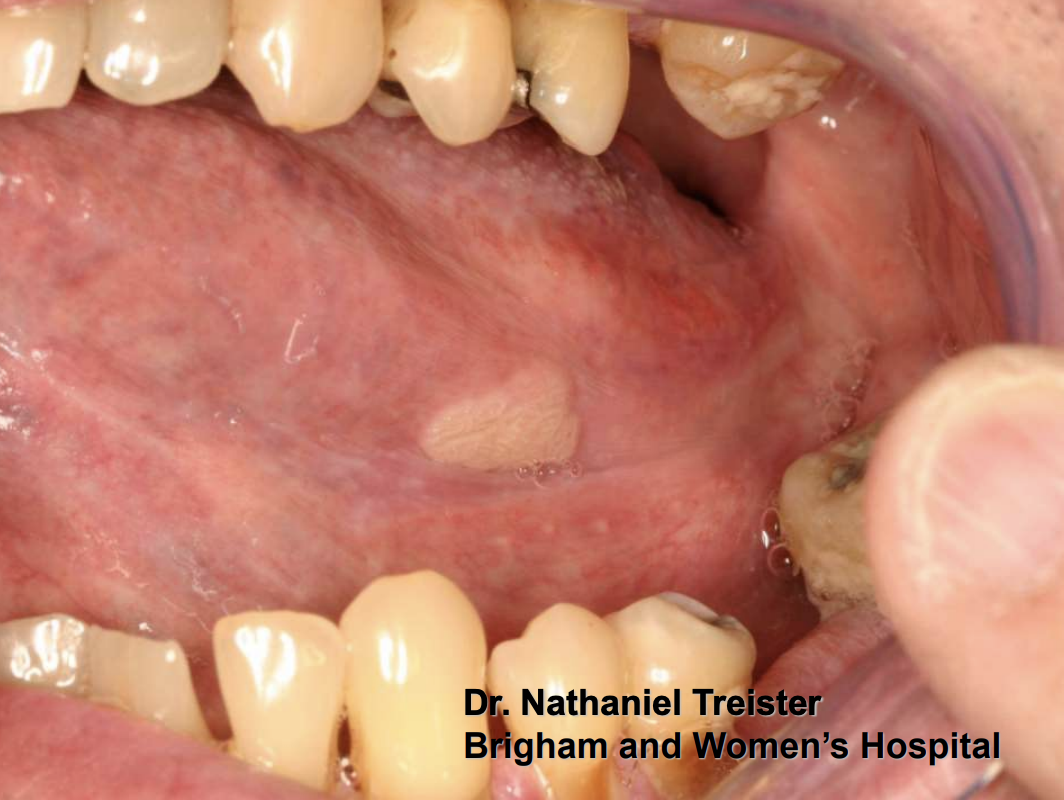
Verruciform Xanthoma
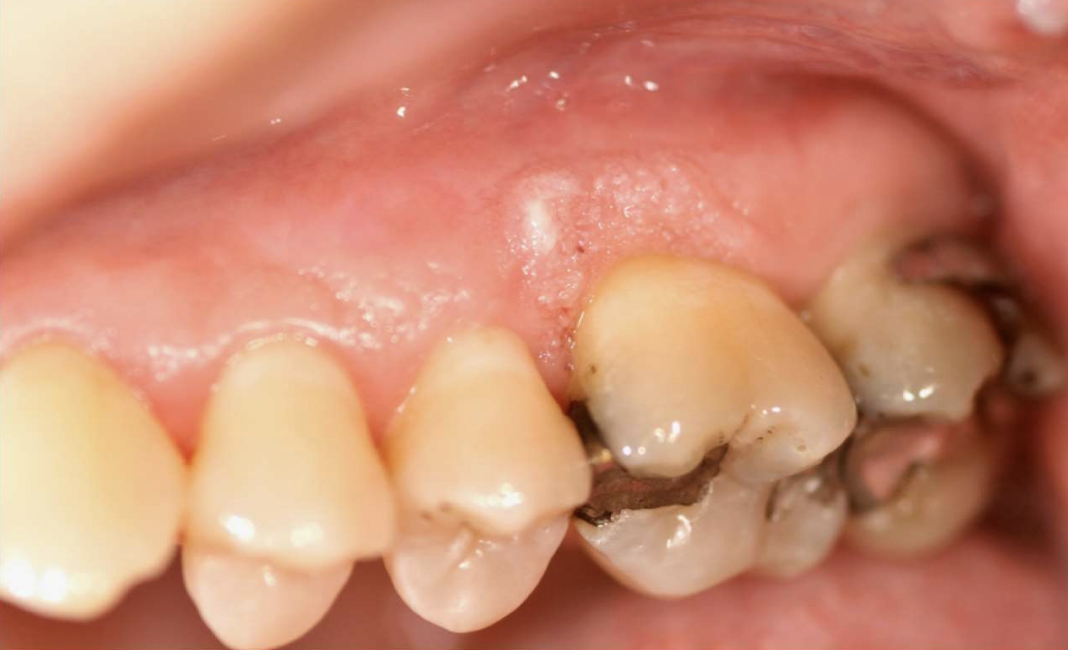
Verruciform Xanthoma
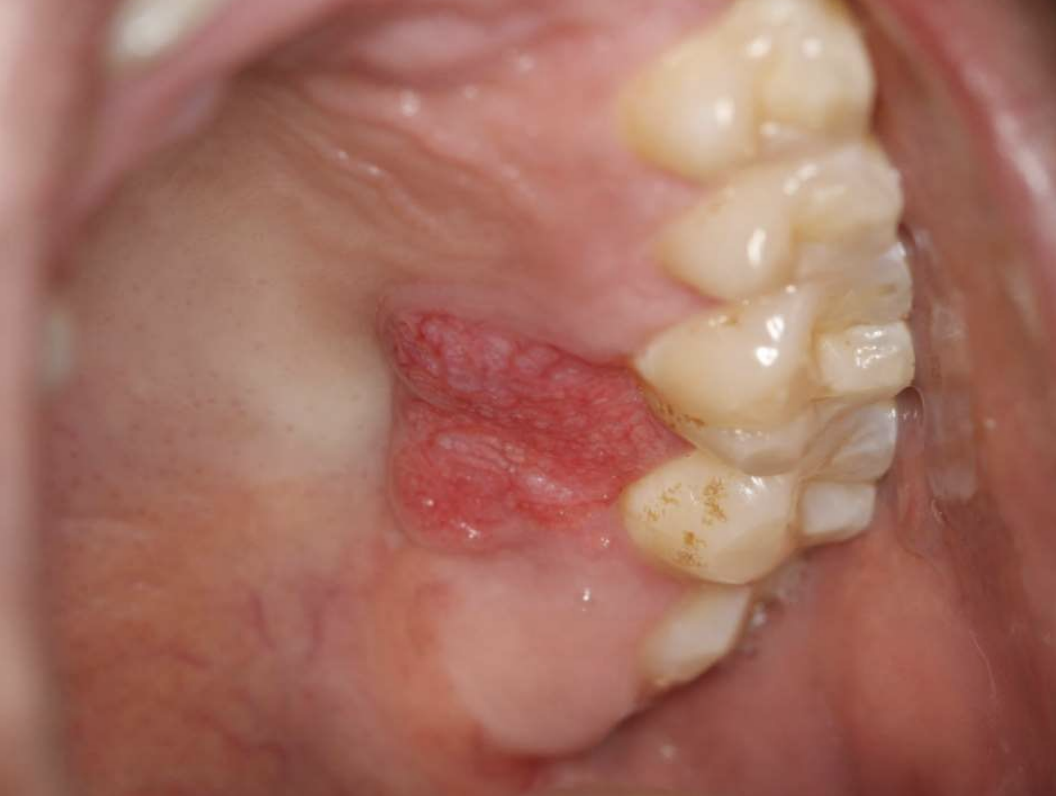
Verruciform Xanthoma
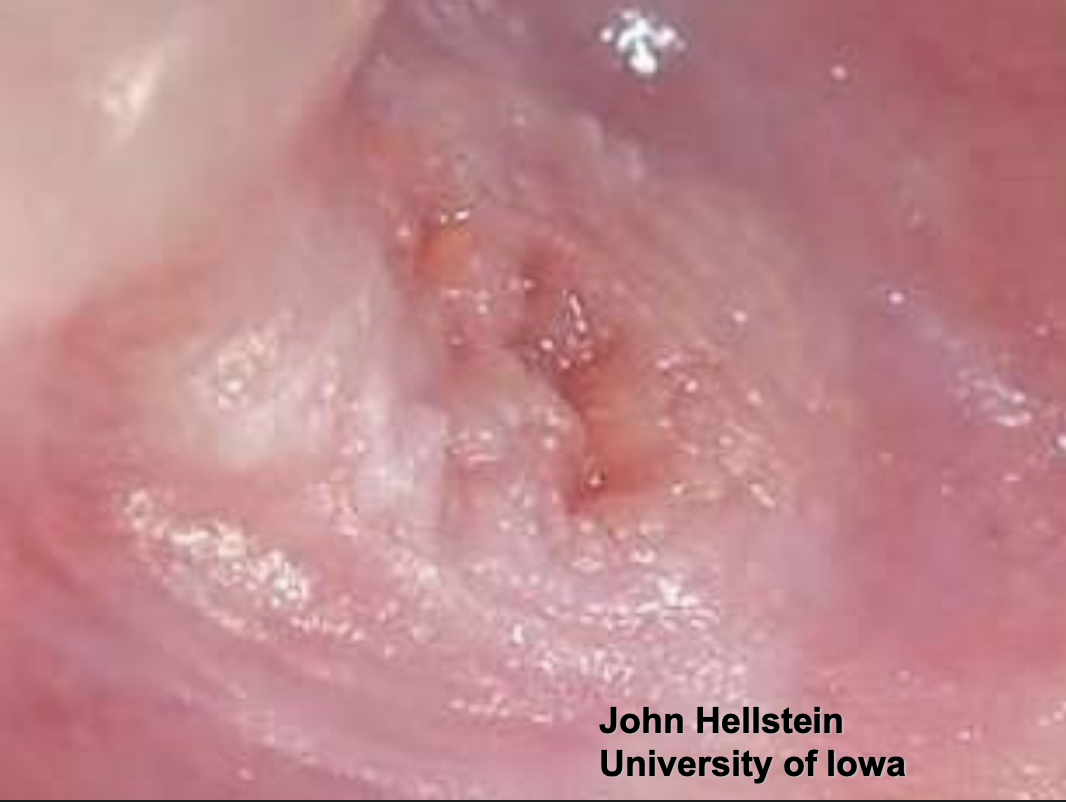
Verruciform Xanthoma
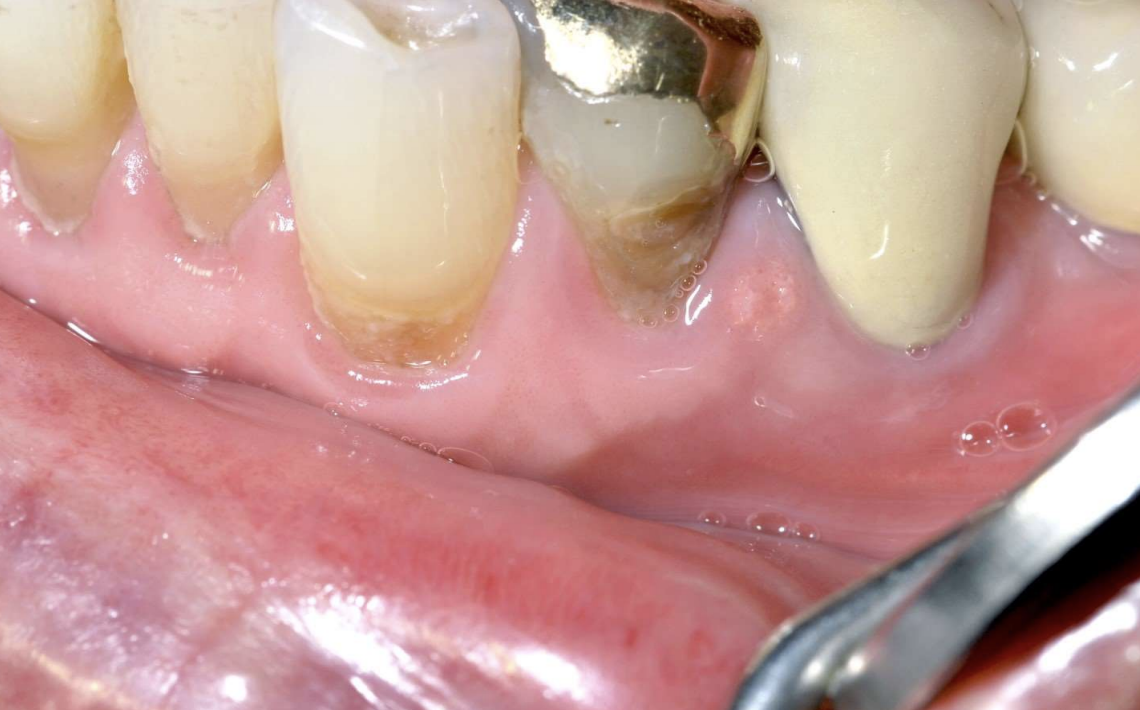
Verruciform Xanthoma
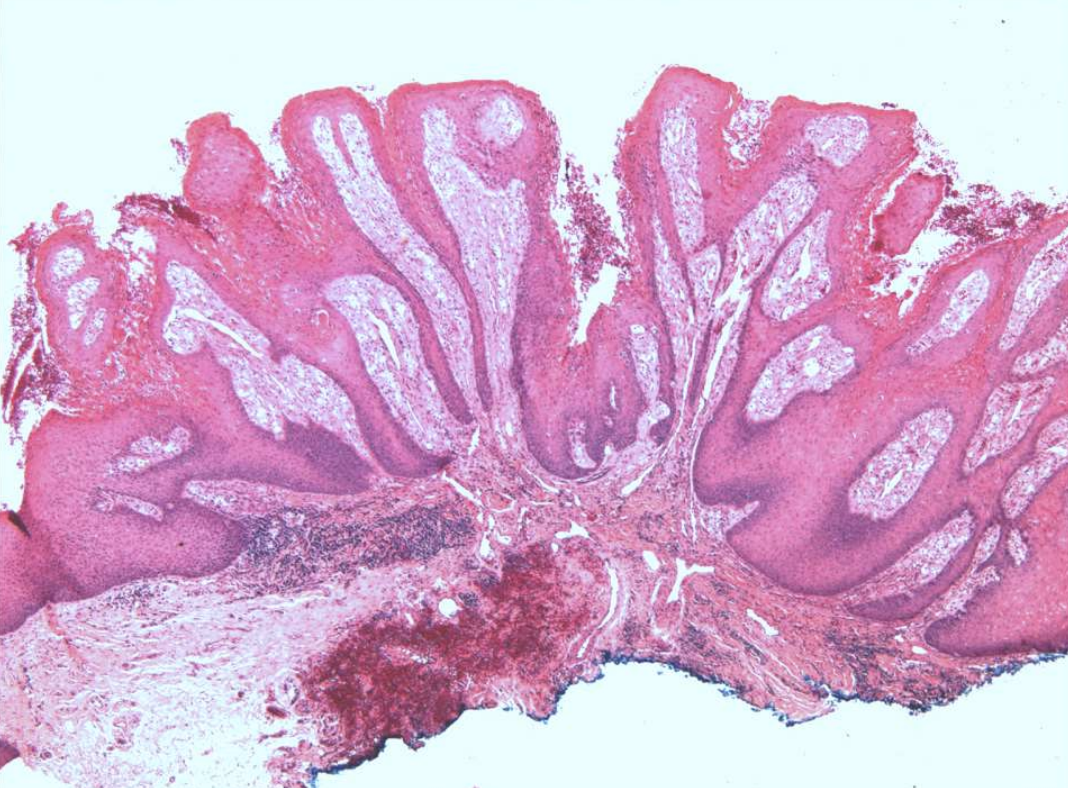
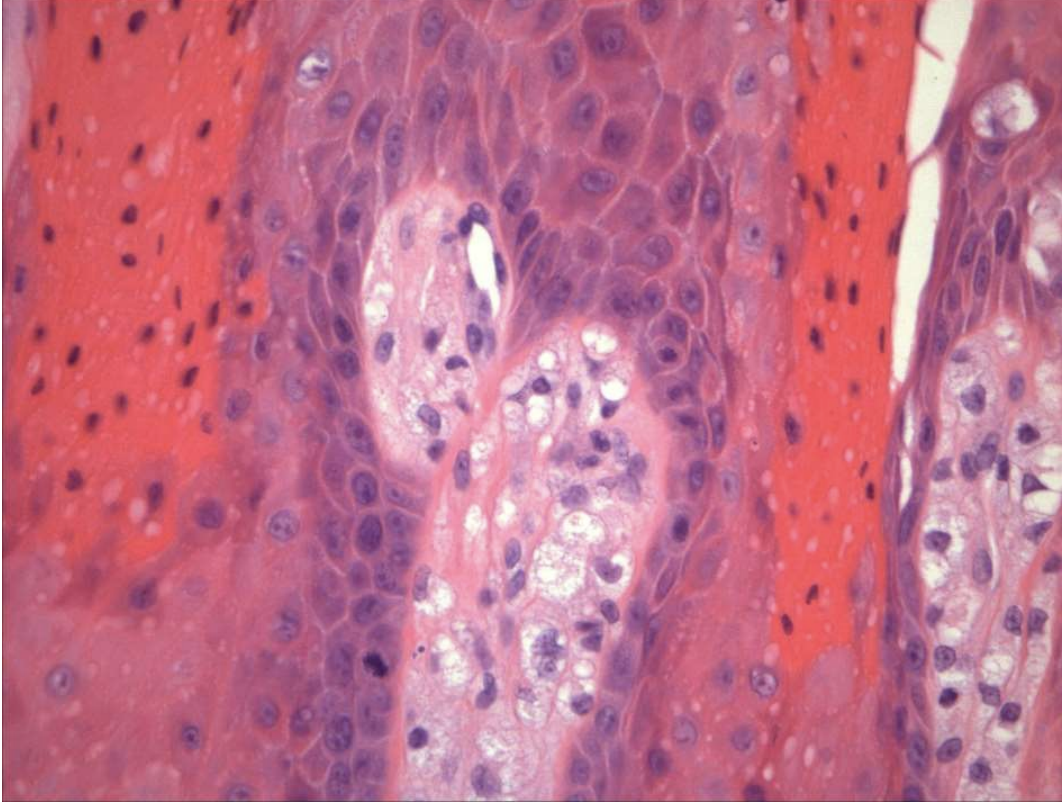
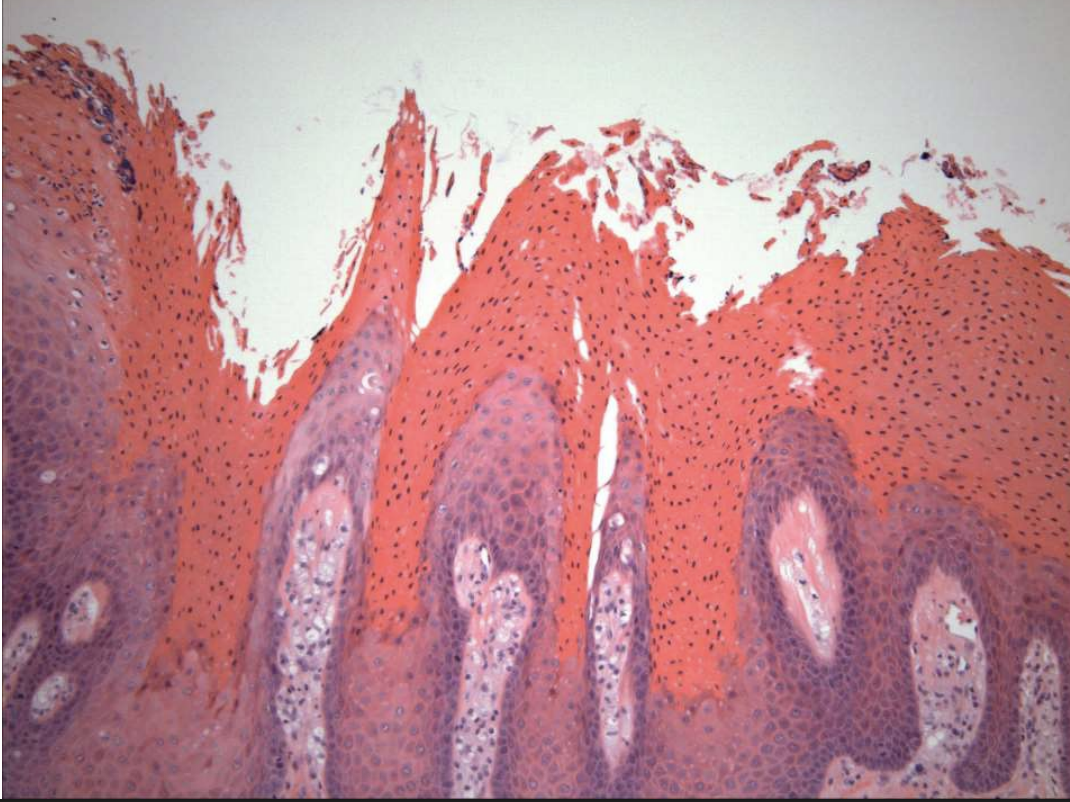
what are histopathologic features of Verruciform Xanthoma?
Papillary, acanthotic surface covered by parakeratin
Large macrophages with foamy cytoplasma
what is the treatment and prognosis of Verruciform Xanthoma?
conservative excision
recurrences are rare
what are some different types of chemical injuries?
medicaments
iatrogenic
what are some things that can cause factitial medicament chemical injuries?
aspirin
mouthwashes/hydrogen peroxide
tooth-whitening products
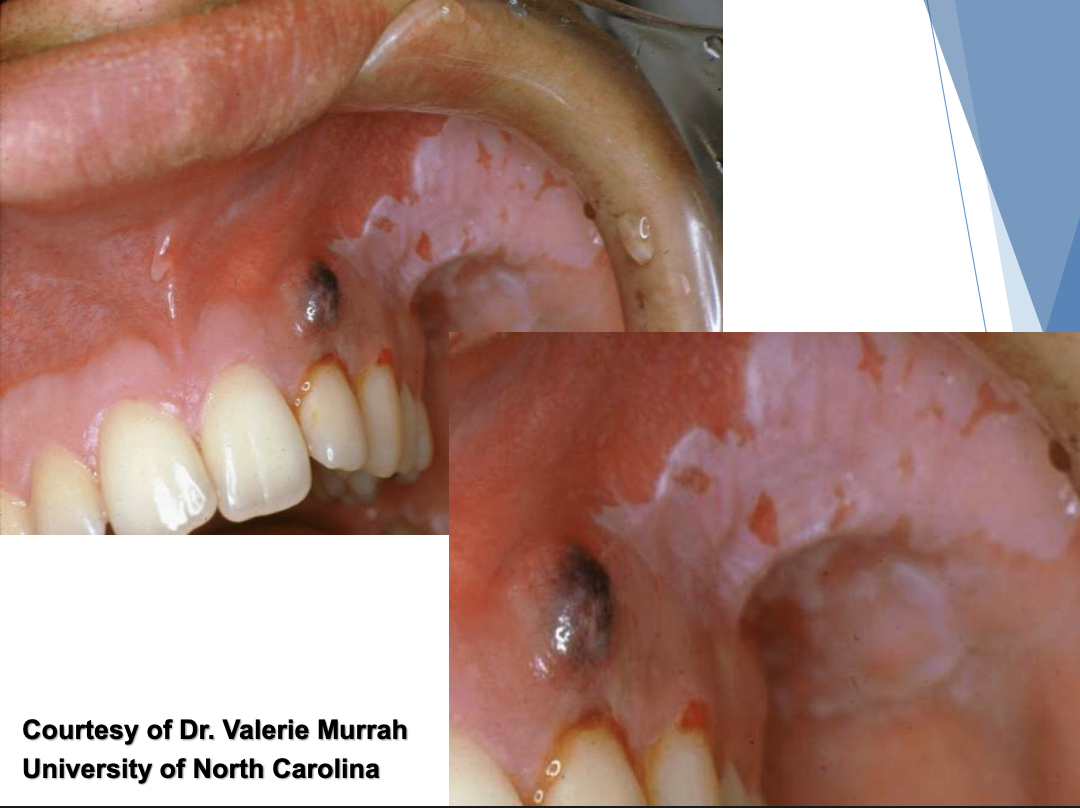
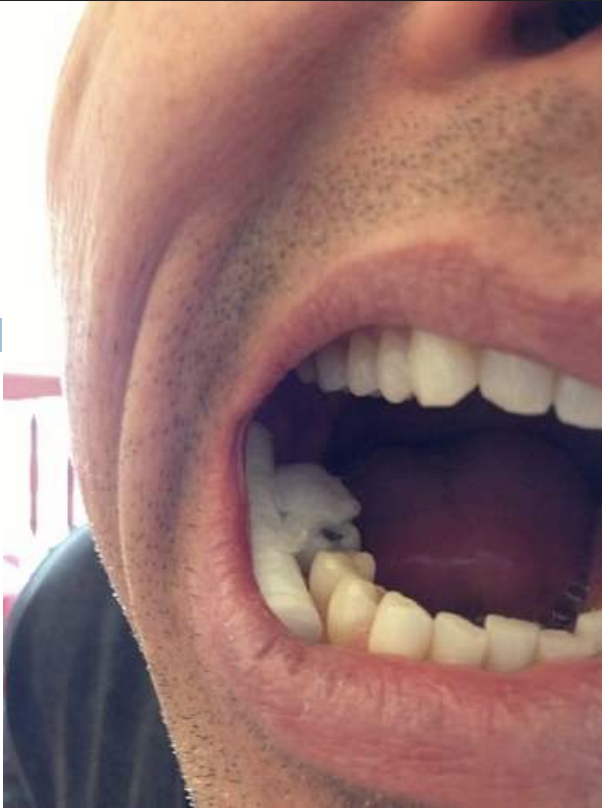
factitial medicament chemical injury from aspirin tablet burn
factitial medicament chemical injury (aspirin burn)

factitial medicament chemical injury (aspirin burn)
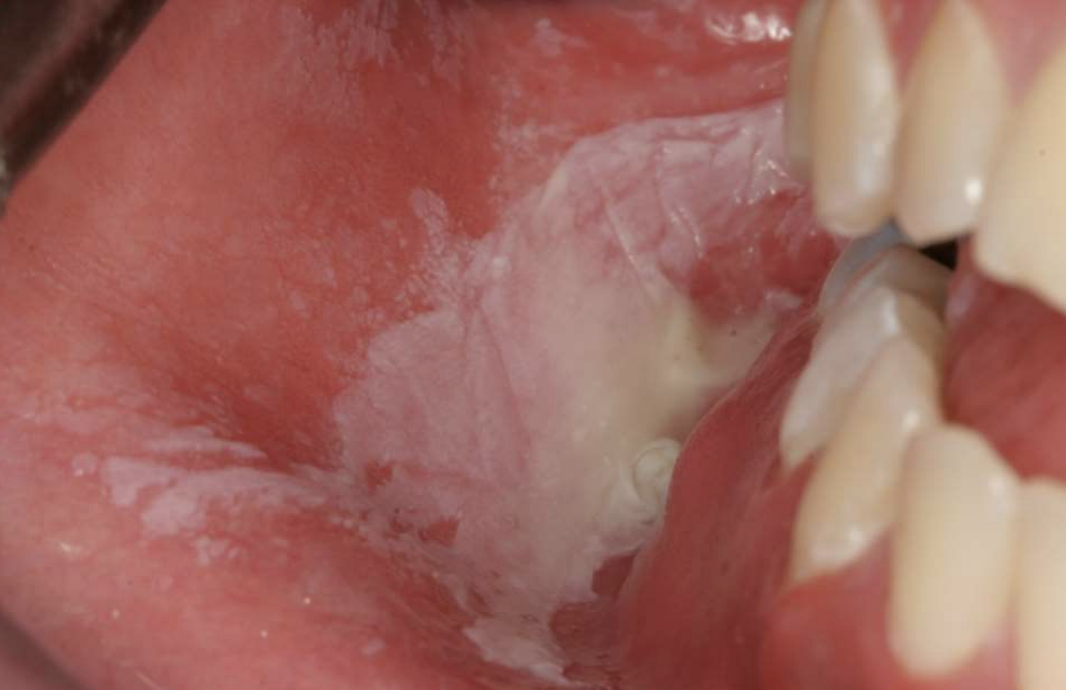
factitial medicament chemical injury (listerine)
what are some things that can cause iatrogenic chemical injuries?
silver nitrate
phenol
endodontic materials
cotton roll “burn”
what can reduce incidence of iatrogenic chemical injuries?
rubber dam application
what is a cotton roll “burn”?
Medicament concentrated against the tissue
e.g., Acid etch solution
Removal without first moistening strips mucosa
what are some cancer treatments (antineoplastic therapies) that can cause Noninfectious Complications?
chemotherapy
radiotherapy
what are 2 acute changes that arise as Noninfectious Complications of Antineoplastic Therapy?
mucositis
hemorrhage
what are some oral complications that arise due to chemotherapy?
mucositis (within days)
bone marrow suppression
thrombocytopenia
agranulocytosis
opportunistic infections
herpes simplex
candidiasis
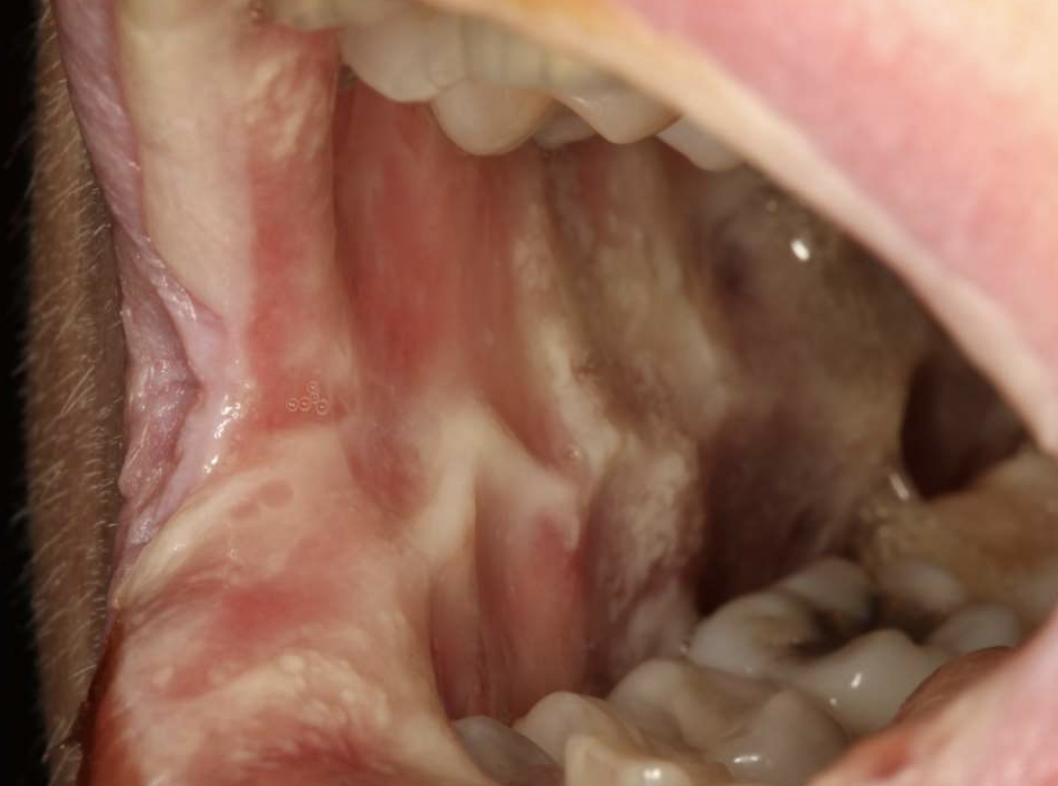
chemotherapy-related oral mucositis
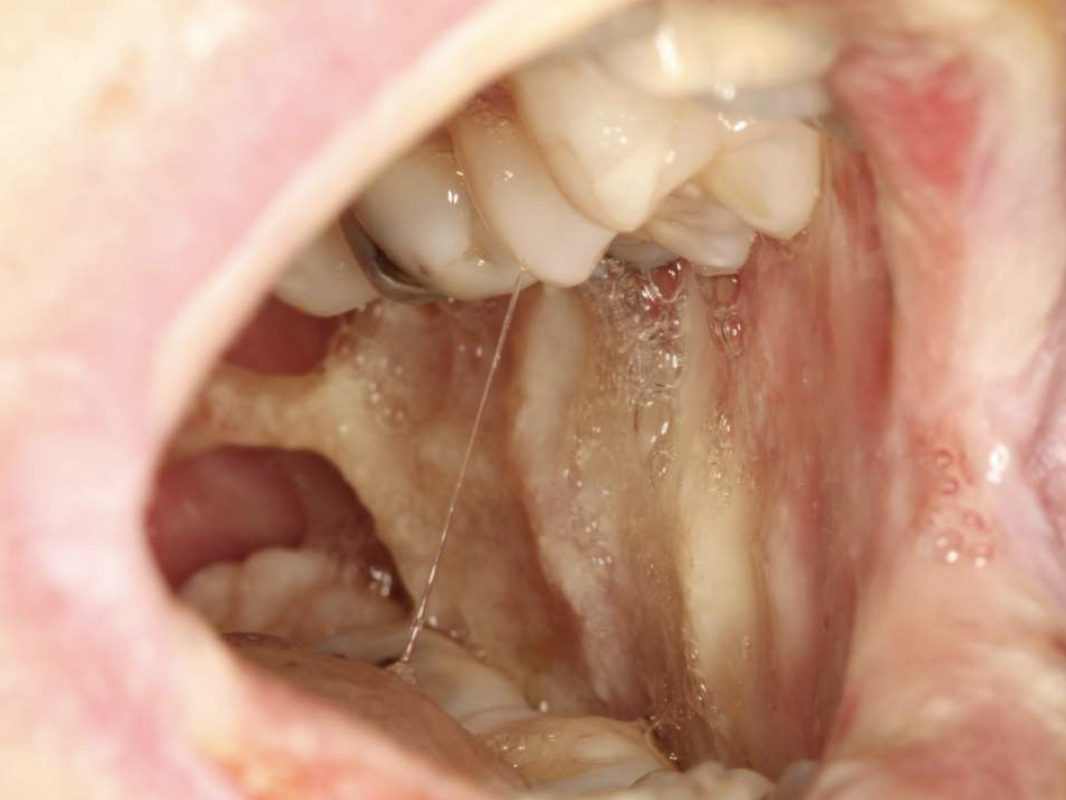
chemotherapy-related oral mucositis (ropey saliva due to affected salivary glands)
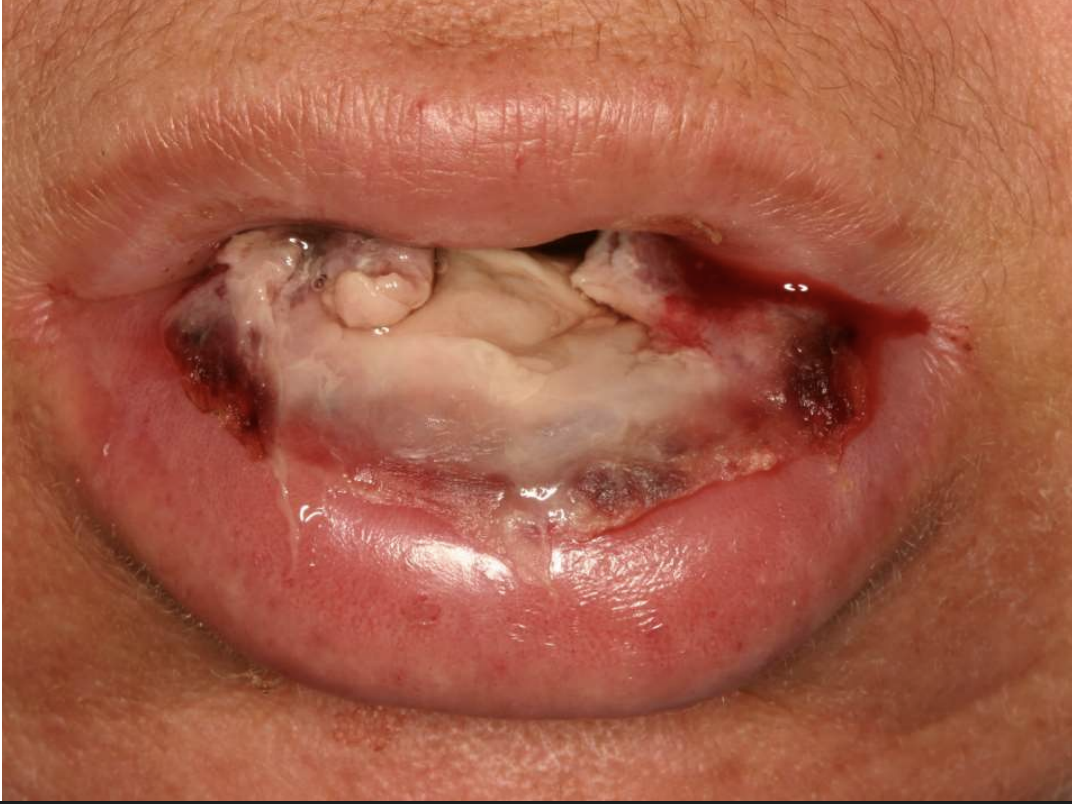
chemotherapy-related oral mucositis
what are causes of osteonecrosis of the jaws?
• Medication
• Radiation
• Infections
• Chemicals
• Trauma
• Idiopathic
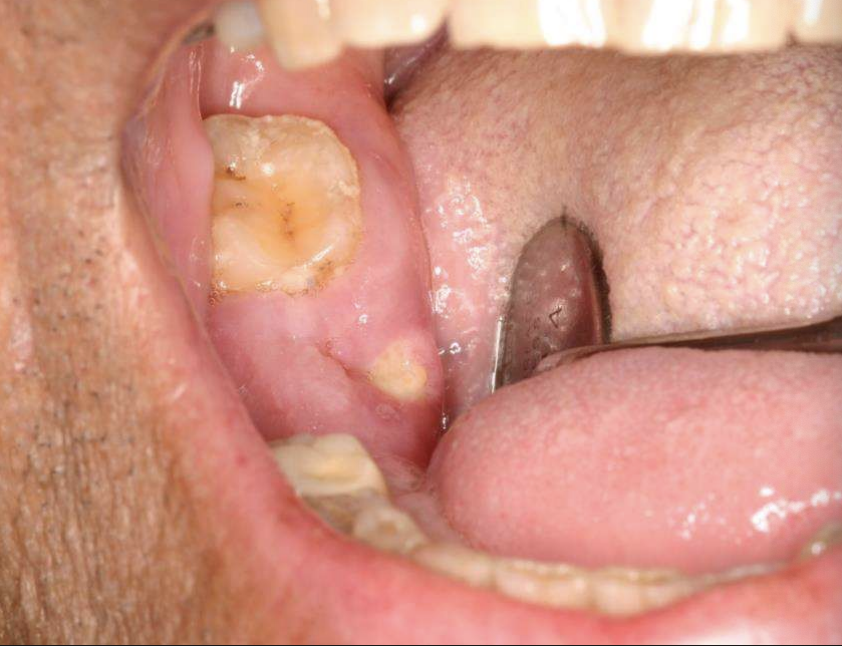
osteonecrosis of the jaws
what are some anti-resorptive agents that can cause osteonecrosis of the jaws?
Bisphosphonates
Denosumab
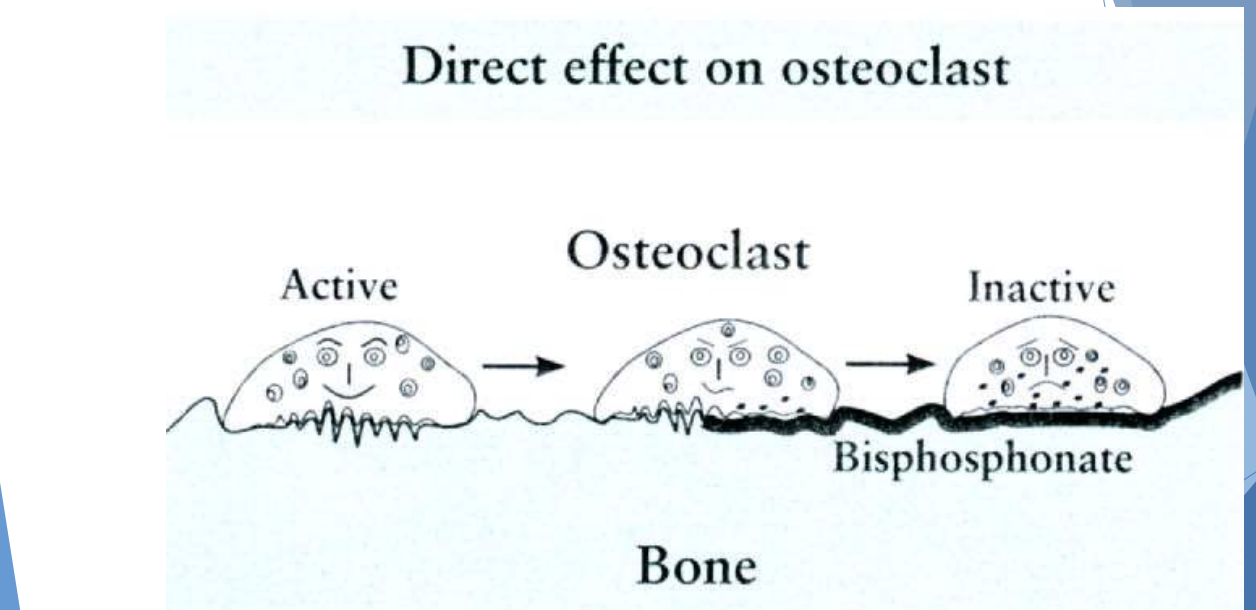
what are some anti-angiogenic agents that can cause osteonecrosis of the jaws?
monoclonal antibodies
tyorsine kinase inhibitors
what classification of medications can cause osteonecrosis of the jaws?
anti-resorptive agents
anti-angiogenic agents
what are prereqs to diagnosing a pt with Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ)?
Current/previous treatment with anti-resorptive OR antiangiogenic agents
Exposed bone OR bone that can be probed through a sinus tract persisting > 8 weeks
No h/o radiation or obvious metastasis to the jaws
when evaluating Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ), what are some other conditions to consider and rule out?
• Alveolar osteitis
• Gingivitis/periodontitis
• Sinusitis
• Caries
• Periapical pathology
• Fibro-osseous diseases
• Cancer
• Condensing osteitis
• Temporomandibular disorders
describe the pathogeneisis of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ)
• Anti-osteoclastic
• Anti-angiogenic
• Inflammatory/infectious
• Immune dysfunction
• Soft tissue toxicity
what are the 2 major classes of bisphosphonates?
non-nitrogen containing
nitrogen containing (more)
potency is related to likelihood of developing Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ)

why might pts be taking bisphosphonates? (aka what are indications for bisphosphonates)
• Osteoporosis/osteopenia
• Multiple myeloma
• Metastatic carcinomas to bone
• Paget disease
• Osteogenesis imperfecta
anything to prevent bone or bone lesion
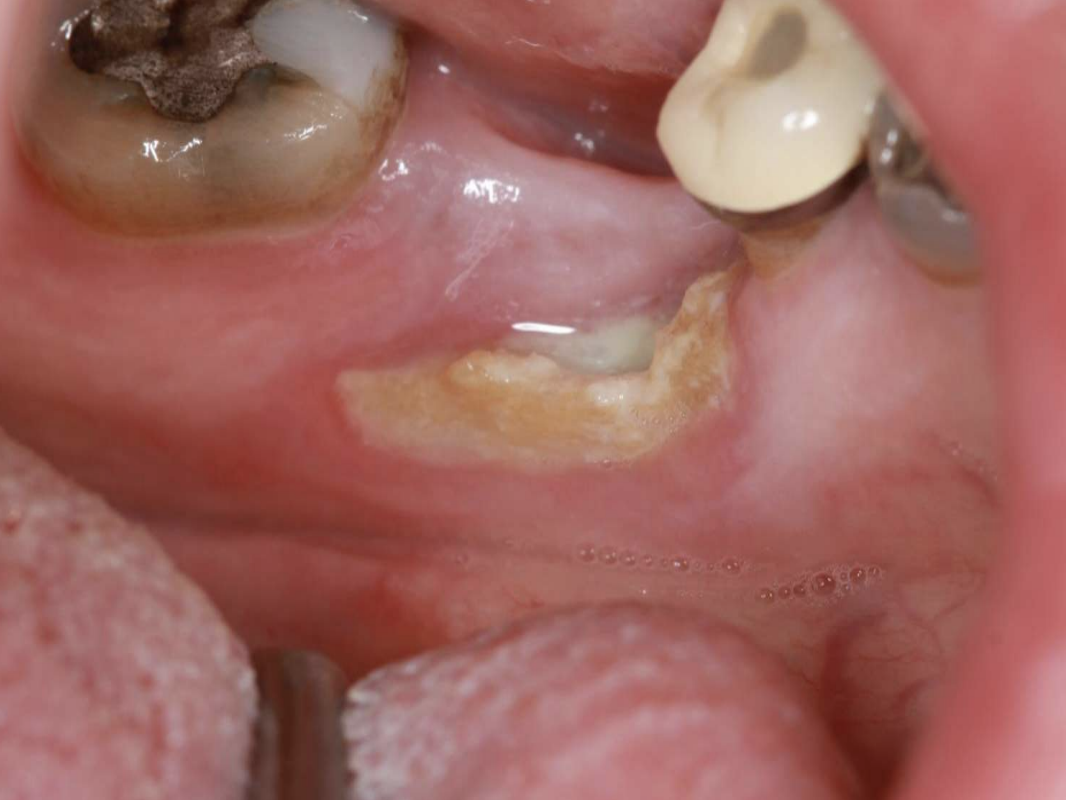
Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ)
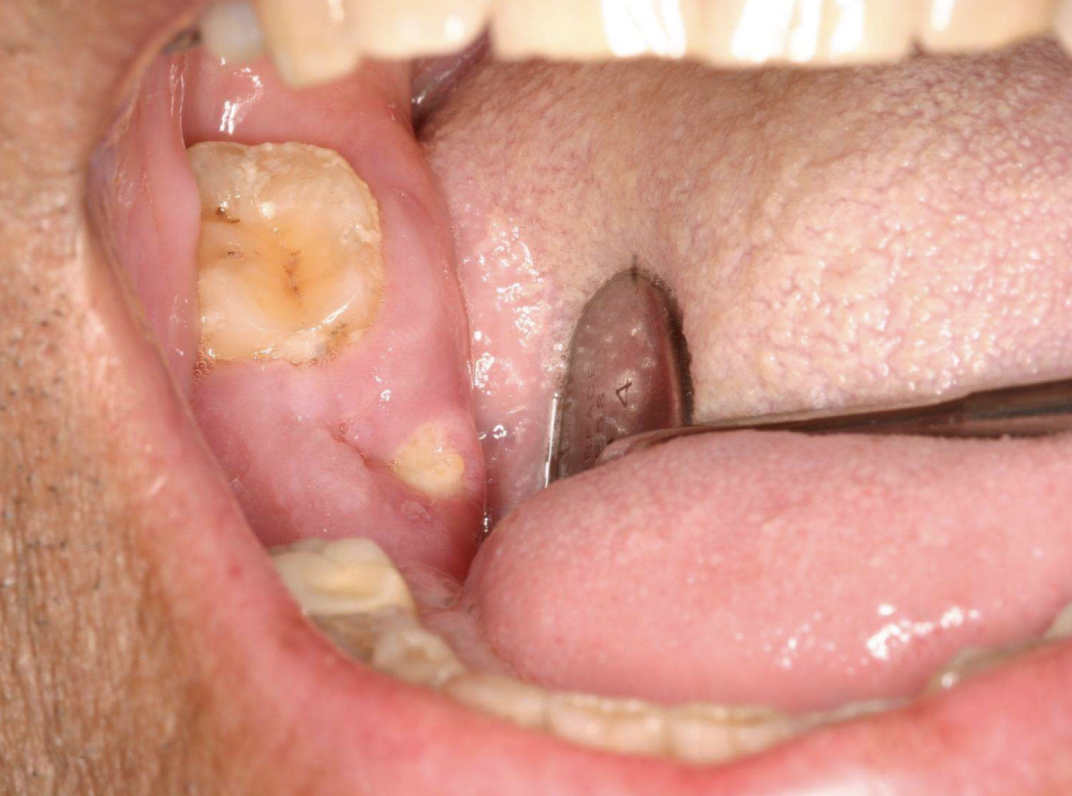
Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ)
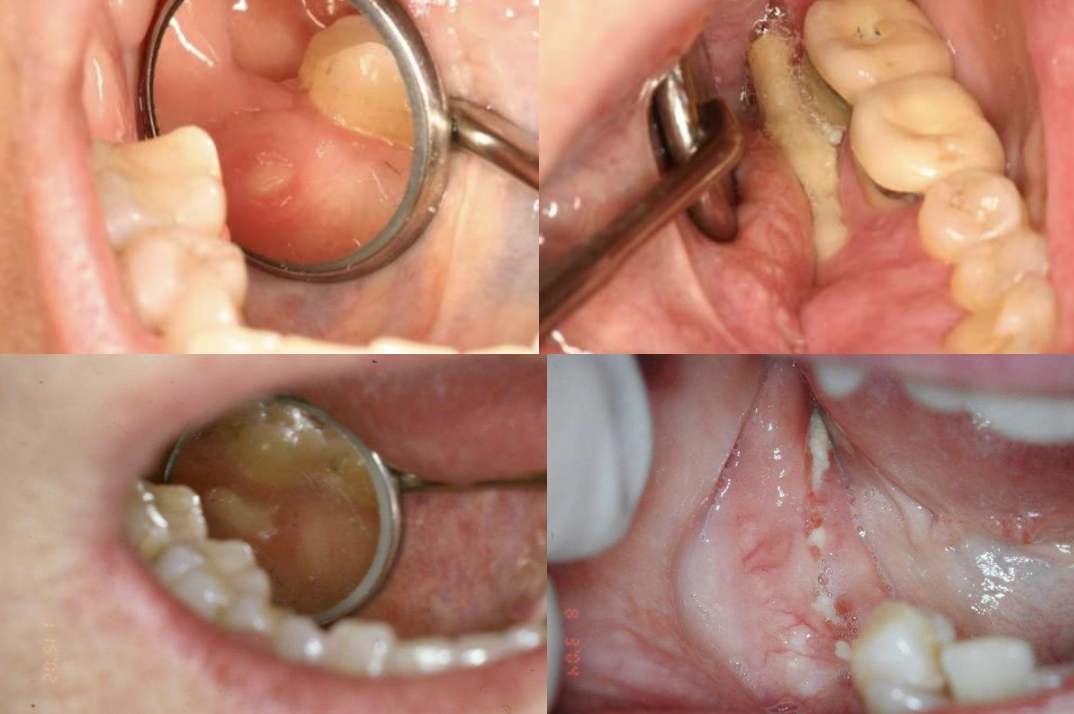
Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ)
what is the AAOMS Staging of Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ)?
• Stage 0: non-exposed
• Stage 1: exposed asymptomatic
• Stage 2: exposed symptomatic
• Stage 3: extensive disease
in Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ), what may be noted before clinical evidence of necrosis?
increased radiopacity
which jaw is affected more by Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ)?
Mandible affected more than maxilla, but discrepancy not as great as in osteoradionecrosis
what treatment is indicated for Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ)?
best treatment = prevention
asymptomatic
chlorhexidine rinse
smooth rough edges of exposed bone
soft splint
symptomatic
systemic antibiotic therapy and chlorhexidine
hyperbaric oxygen NOT beneficial

Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ)
what dental considerations can be applied for Medication-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaws (MRONJ)?
prophylactic dental care
less invasive procedures
multiple extraction performed by quadrant
what oral complications occur with radiotherapy?
saliva thickens (1 week)
salivary gland hypofunction
mucositis (1-2 weeks)
osteoradionecrosis
hypofunction (xerostomia)
cervical caries
hypogeusia
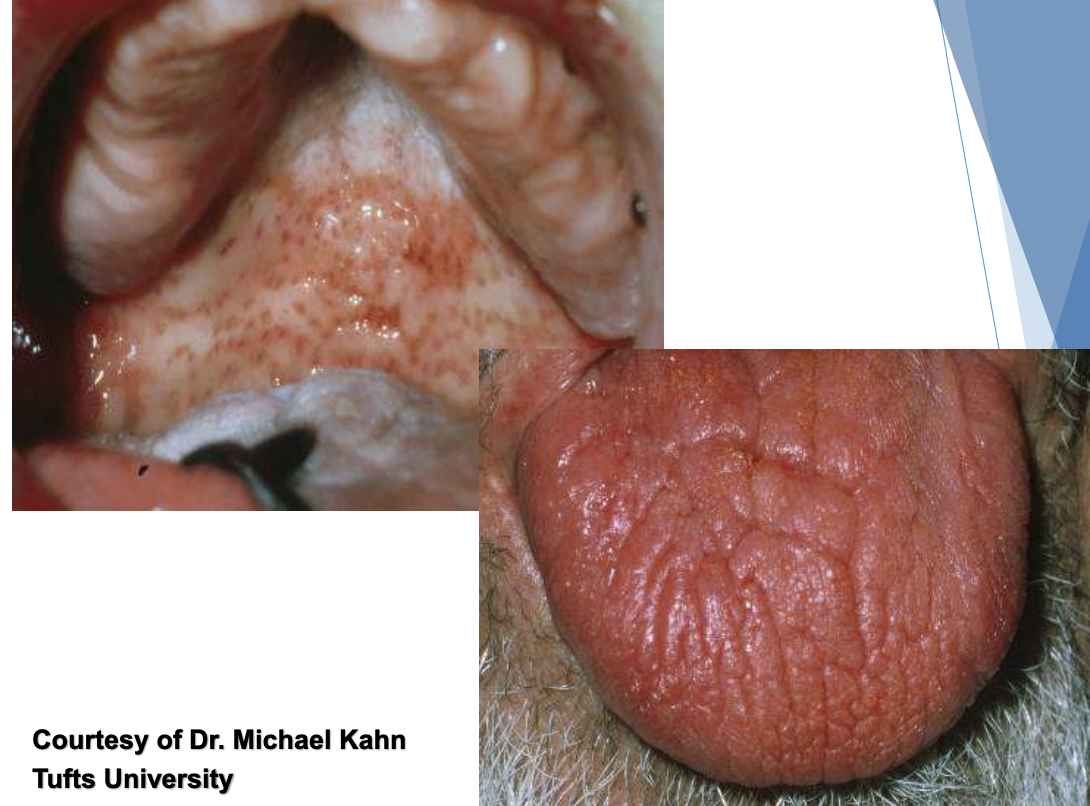
radiation related mucositis
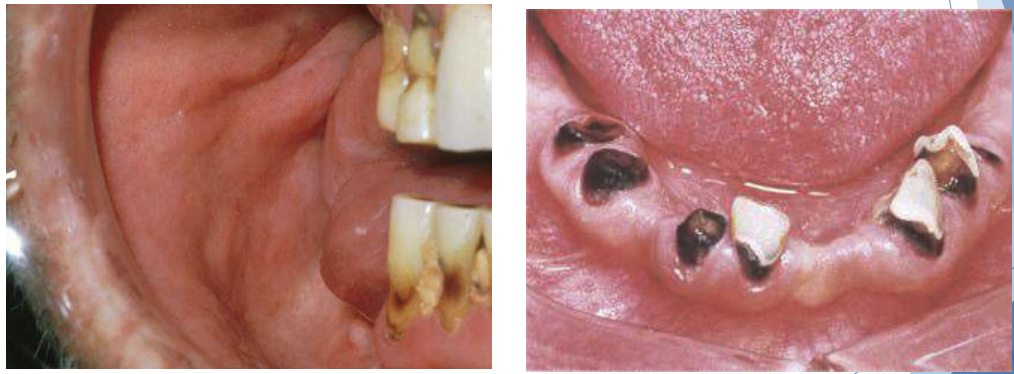
cervical caries (radiotherapy complication)
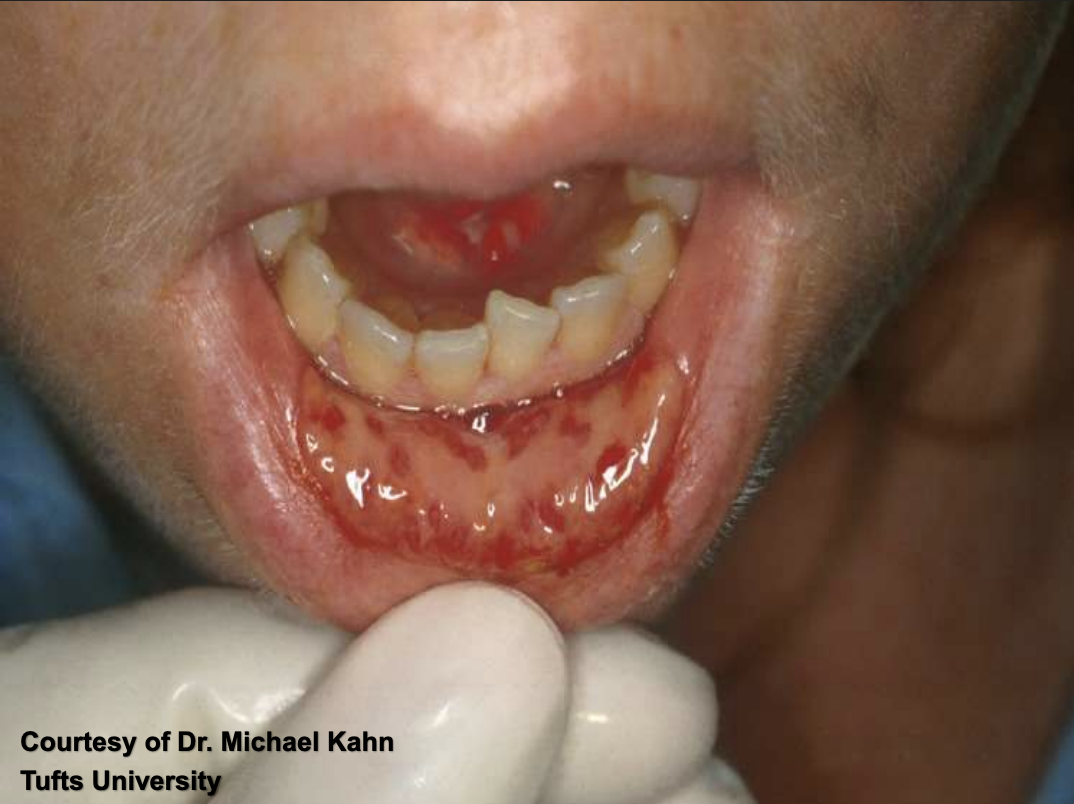
radiotherapy related mucositis
osteoradionecrosis is a type of _____ necrosis.
ischemic
is there infection present in osteoradionecrosis?
not necessarily
which jaw is more often affected in osteoradionecrosis?
mandible
osteoradionecrosis can lead to what symptoms…?
pain, fracture
what levels of radiation place pts at low risk for osteoradionecrosis? greater risk?
• Low risk < 45 Gy
• Greater risk > 60 Gy
(after 1 year, incidence decreases)
why might osteoradionecrosis create a complication for dental prosthesis wearers?
Dental prosthesis intolerance due to xerostomia
what treatements are indicated for osteoradionecrosis?
• Debridement
• Antibiotics
• Hyperbaric oxygen?
• Prophylactic extractions
what treatments are indicated for hyposalivation caused by radiotherapy?
• Pilocarpine or cevimeline
• Topical fluoride
• Caphosol
what treatments (management therapies) are indicated for mucositis caused by radiotherapy?
• Viscous lidocaine
• Chlorhexidine
• Milk of magnesia
• Kaopectate rinse
• Palifermin
• Systemic morphine
persistent scaling of vermilion
excess production and desquamation of keratin
various etiologies
perioral skin may become involved
What condition?
Exfoliative Cheilitis