Sport psychology
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Sport and exercise psychology
study of people and their behaviors in sport and exercise
Objectives for the sport and exercise study
a)understand how psychological factors affect an individual’s physical performance
b) understand how participation in sport and exercise affects a person’s psychological development, health, and well-being.
Research Role
Study problems such as exercise adherence, the psychology of athletic injuries, and the role of exercise in the treatment of HIV
Teaching Role
Teach courses in the psychology department
Consulting Role
Consulting with athletes to develop psychological skills for enhancing competitive performance and training
What are the two distinctions of contemporary sport psychology
Clinical sport psychology and educational sport psychology
Clinical sport psychologists
Extensive training in psychology so they can detect and treat individuals with emotional disorders, mainly athletes.
Educational sport psychology
“Mental coaches” who educate athletes and exercisers about psychological skills and their development. not trained to work with people with severe emotional disorders nor are licensed psychologists
Period 1: Early years 1893-1920
Triplett found that children reeled in more line when they worked in the presence of another child
E.W. Scripture conducted data-based studies of athletes at Yale, examining reaction and movement times as well as transfer of physical training
He also describes personality traits that he believes could be fostered via sport participation
Patrick discusses the psychology of play
Cummins assesses motor reactions, attention, and abilities as they pertain to sport
Coleman Griffith conducts informal studies of football and basketball players at the University of Illinois
Period 2:Griffith Era (1921-1938)
Griffith publishes 25 research articles about sport psychology
University of Illinois research in an athletics laboratory is established, Griffith is appointed director
Giffith publishes the psychology of Coaching
Griffith publishes psychology of Athletics
Period 3 Preparation for the future (1939-19650
Franklin Henry assumes the position in the Department of Physical Education at the University of California at Berkeley and establishes the psychology of physical activity graduate program
Dorothy Yates works with college boxers and studies the effects of her relaxation training intervention
Warren Johnson assesses precompetitive emotions of athletes
John Lawther writes Psychology of Coaching
First World Congress of Sports Psychology is held in Rome
Period 4: Establishment of Academic Sport Psychology (1966-1977
Clinical psychologists Bruce Ogilvie and Thomas Tutko write Problem Athletes and How to Handle Them, and begin to consult with athletes and teams
Cratty of UCLA writes the Psychology of Physical Activity
The first annual NASPSA conference is held
Proceeding of NASPSPA conference are published for the first time
Period 5 Multidisciplinary Science and Practice in Sport and Exercise Psychology (1979-2000)
Journal of Sport Psychology establishes
Olympic committee develops sport psychology advisory board
American television coverage of the Olympic games emphasizes sports psychology
US Olympic Committee hires first full-time sport psychologist
AASP is established
APA Division 47 is developed
U.s Olympic team is accompanied by an officially recognized sport psychologist for the first time
Journal of Applied Sport Psychology begins
AASP establishes the “certified consultant” designation
Period 6:Contemporary Sport and Exercise Psychology (2001-present)
The journal Psychology of Sport and Exercise is developed and published in Europe.
The 2009 International Society of Sport Psychology Conference in Morocco had more than 7000 participants from 70 countries
Concerns emerge about the best ways of preparing and educating students. APA Division 47 focuses on sport psychology as a specialized competency area
Exercise psychology flourishes, especially in university environments driven by external funding possibilities and by its utility in facilitating wellness and holding down health care costs
Strong, diverse, and sustained research programs are evident around the world
Increased interest in applied sport psychology continues
Increased interest in applied sport psychology continues
Why is the Internation Society of Sport Psychology important
They promote and disseminate information about sport psychology throughout the world. Focuses on topics as human performance, personality, motor learning, wellness and exercise, and coaching psychology
Scientific method
How scientifically derived knowledge comes about and how it works:
Systematic approach
Standardizing the conditions, for example one might assess the children’s self esteem under identical conditions with carefully designed measure
Control
Key variables, or elements in the research, are the focus of the study, with other variables controlled so they do not influence the primary relationship
Empirical
Based on observation. Objective evidence must support beliefs, and this evidence must be open to outside evaluation and observation
Critical
involves rigorous evaluation by the researcher and other scientists. Critical analysis of ideas and work helps ensure that conclusions are reliable
Theory
set of interrelated facts that present a systematic view of some phenomenon in order to describe, explain, and predict its future occurrence. Theory turns into practice
Social facilitation theory
Some people performed better in front of an audience and other times they performed worse. When someone knew their stuff they performed better, the opposite happens when they were unfamiliar with the topic.
Study
involves an investigator’s observing or assessing factors without changing the environment in any way.
Experiment
Differs from a study in that the investigator manipulates the variables along with observing them, and then examines how changes in one variable affect changes in others
Experimental group
receive training in how to set goals and use imagery and positive self-talk
Control group
would not receive any psychological skills training
unbiased data
data or facts that speak for themselves and are not influenced by the scientist’s personal feelings
Reductionistic
It is too complex to study all the variables of a situation simultaneously; the researcher may select isolated variables that are of the most critical interest
Internal validity
Science favors the extent to which results of an investigation can be attributed to the treatment used, usually judging a study by how well scientists conform to the rules of scientific methodology and how systematic and controlled they were in conducting the study.
External validity
if the issue has true significance of utility in the real world
Professional practice knowledge
knowledge gained through experience.
Systematic observation
Collecting data through careful and consistent monitoring of behavior or events
Case study
a process or record of research in which detailed consideration is given to the development of a particular person, group, or situation over a period of time
shared public experience
practical contact with and observation of facts or events:
intuition
he ability to understand something immediately, without the need for conscious reasoning
psychophysiological orientation
relationship between mental activities and physiological processes
social-psychological orientation
the scientific study of how people’s thoughts, feelings, beliefs, intentions, and goals are constructed within a social context by the actual or imagined interactions with others.
cognitive-behavioral orientation
assumes that behavior is determined by both the environment and cognition, with thoughts and interpretation
Certified Mental Performance Consultants (CMPC)®
Certification through the Association for Applied Sport Psychology (AASP)
Can come from psychology OR sport science backgrounds
Focus on performance enhancement + well-being through mental skills training
Not automatically licensed to treat clinical disorders (unless also a psychologist)
The Ethical Basis of Experimentation
Provides the ethical foundation for experimentation
If the answer is already known = no need (and not ethical) to run the study
Experiments should only be done when results are unknown, but possible to learn
Equipoise
genuine uncertainty about which outcome will occur
Core Principles of Good Science
steps for the scientific method
Step 1: Ask a Question / Identify Problem
What do we want to know about behavior?
Step 2: Develop Hypotheses & Predictions
Testable, measurable, falsifiable statements
Step 3: Research Design & Data Collection
Experimental, correlational, qualitative, mixed methods
Step 4: Analyze & Interpret Results
Statistical tests, thematic analysis, comparison to hypotheses
Step 5: Replication & Theory Development
Findings must be repeatable
Strong evidence builds theories
Forms of Scientific Research
Experimental Research Tests cause-and-effect using controlled designs
Qualitative Research Explores experiences and meanings through words, not numbers
Analytical Research Uses existing data, theory, or literature (historical, philosophical, review)
Descriptive / Observational Research Describes what exists without manipulating variables (e.g., surveys, interviews, case studies, epidemiological studies)
Physical Activity Defined
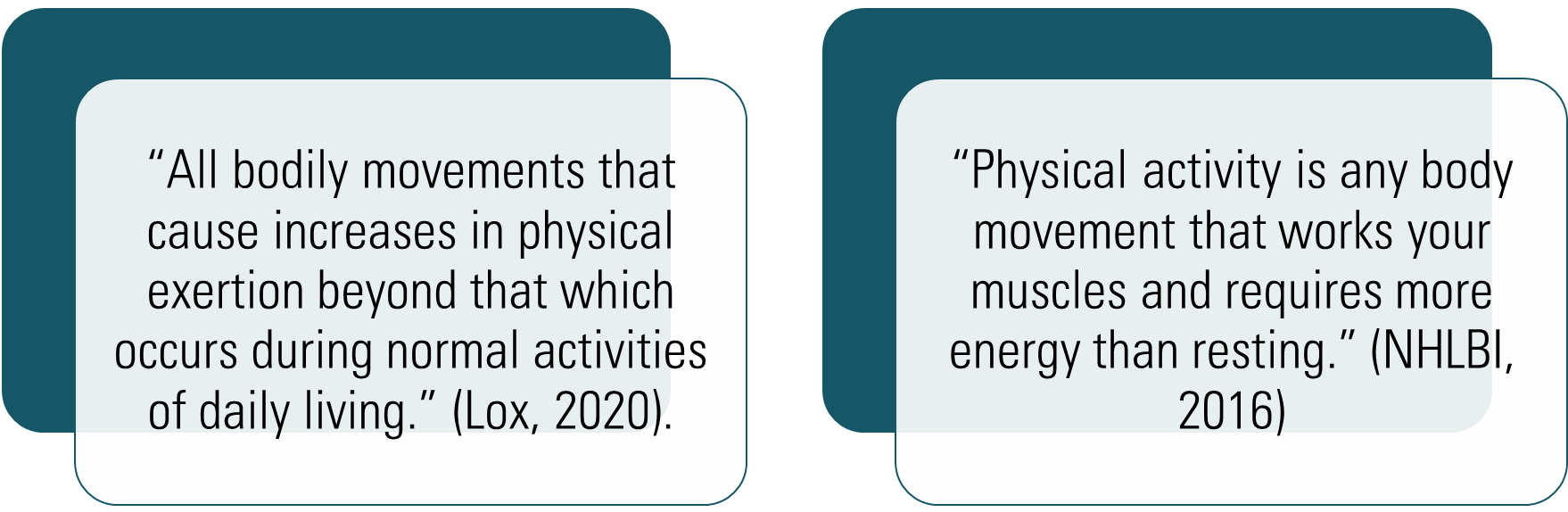
Exercise Defined
A form of leisure physical activity that is undertaken in order to achieve a particular objective (e.g., improved appearance, improved cardiovascular fitness, reduced stress, fun). – Lox (2020)
Physical Fitness
Health-Related Fitness
Influenced by physical activity and heavily concerned with improving health status
Performance-Related Fitness
Optimal fitness required for occupation or sport performance (e.g., agility, speed, balance, coordination, power)
The parent discipline
Psychology: The scientific study of mind and behavior, including how people think, feel, and act.
Exercise Science: The study of how the body responds, adapts, and performs during physical activity and exercise.
A Biopsychosocial perspective
The belief approach that the body, mind, and social environment influence one another and, ultimately, behavior