Biology- Chapter 4- Cells
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Robert Hooke
Discovered cells in a slice of cork with a microscope
Named them cells after the rooms in his monastery
Thought they were only in plants and fungi at the time
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Discovered protists and bacteria cells
Called them “animalcules“
Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann
Declared the basic unit in living things is cells
Discovered all plants and animals have cells
Rudolf Virchow
Declared all cells come from other living cells
All living things are composed of one or more cells
Cells are an organism’s most basic unit of structure and function
Cells can only be created from pre-existing cells
The cell theory states…
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
Two types of cell
do not store their genetic information in a nucleus
Genetic information is stored in the cytoplasm
very basic cells (unicellular)
Bacteria cells
Prokaryotic cells
Contain a nucleus
Genetic information stored in Nucleus
Other organelles are bound by membranes
Can be unicellular or multicellular
Plant and Animal cells
Eukaryotic cells
Organized or specialized structures in a cell; like mini organs
Organelle-
group of organs that work together to perform a specific function
Organ System-
Protective barrier that is semi permeable, controls what goes in and out of the cell
Cell membrane-
Control center of the cell and controls the functions within the cell, contains the genetic information
Nucleus-
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain and display genetic information
Chromosomes-
Only in plants, give structure and support to the cell, not a gate, its a wall
Cell Wall
only plants, uses light energy to make food
Chloroplast-
Stores food, water, and waste products (allows plants to support heavy objects)
Vacuole
Converts food energy into usable energy for the cell
Mitochondria-
Makes proteins
Ribosomes
Gel-like substance that fills the cell, helps move nutrients in a cell and helps shape the cell
Cytoplasm-
Disposes of waste products, invading molecules, etc.
Lysosome-
Receives, processes, and packages molecules around and out of the cell
Golgi Bodies-
Rough ER- assists in making proteins
Smooth ER- makes lipids
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Pulls apart chromosomes and assists in cell movement
Microtubules-
Tough flexible framework that makes up the cell, assists in cell movement
Microfiliaments-
Make up the majority of the membrane (Phospholipid Bilayer)
The lipids in the cell membrane…
hydrophilic, water loving
The head of a lipid is
hydrophobic, water hating
The tail of a lipid is
are large masses that act as a channel and control what goes in/out
Proteins in the cell membrane…
Little chains on the surface of the cell membrane that help with cell communication
Carbohydrates in the cell membrane…
membranes that allow some substances through but not others
Semi Permeable-
Concentration of specific molecules inside and outside of a cell
Concentration Gradient-
High to low- with the gradient
Low to high- against the gradient
What is the flow of the concentration gradient?
1 type, requires energy, goes against the gradient (low to high)
Active Transport-
diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
Passive Transport types
3 types, does not require energy, moves with the gradient (high to low)
Passive transport
Diffusion
Movement of SMALL molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration that results in an equilibrium
Facilitated Diffusion
Movement of LARGE molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration, uses protein channels, results in equilibrium
Osmosis
movement of water across the cell membrane, solvents not solutes crossing the membrane, aims to even the ratio of solvents to solutes out
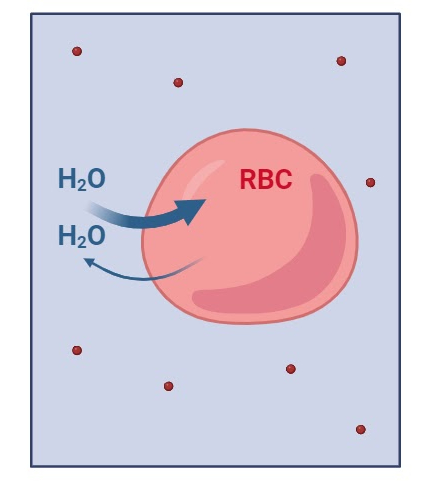
Hypotonic solution
More solvents than solutes (ex: more water than salt), the cell swells and might burst
Hypertonic
Is this a Hypotonic, Hypertonic, or Isotonic solution
Hypotonic
Is this a Hypotonic, Hypertonic, or Isotonic solution
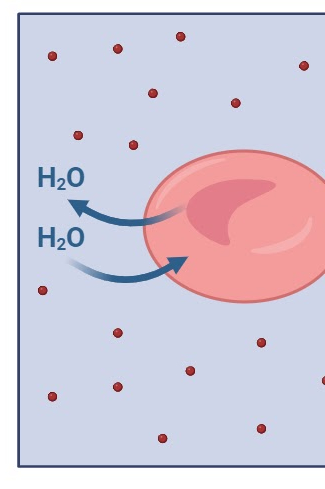
Isotonic
Is this a Hypotonic, Hypertonic, or Isotonic solution
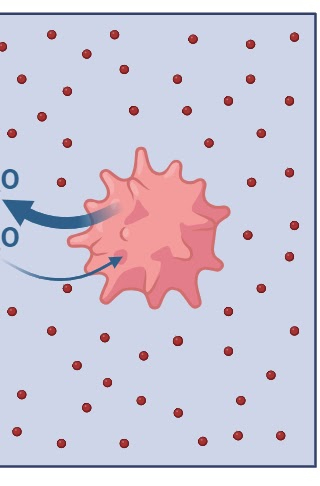
Hypertonic Solution
More solutes than solvents (ex: more salt than water), the cell shrivels
Isotonic solution
Equal solutes and solvents, cell remains the same
Solution concentration equation
mass of solute (thing being dissolved) divided by mass of solvent (thing doing the dissolving)
the faster the diffusion
The more surface area in a cell…
the slower the diffusion
The more volume in a cell…
Small cells
What size cell is more effecient?
Size, growth, and to replace other cells
Why does a cell divide?
The process of cell division and growth that cells undergo
Define cell cycle
cyclin
What protein regulates the cell cycle?
replicate (duplicate) its DNA
In order for a cell to fully divide and function it must
chromosomes
Where is DNA located
Carry the DNA and transfer genetic information
What is the main function of chromosomes
interphase, mitosis, cytokinesis
Stages of the Cell Cycle
G1, Synthesis, G2
Stages of Interphase
Interphase
Most of a cell's life is spent in which stage?
G1
Most cell growth occurs during this stage
Synthesis
Cell duplicates DNA
G2
Cell finishes growth and prepares to divide
Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase
Stages of Mitosis
Spindle fibers form, nuclear envelope disappears, Prepares to divide.
Prophase-
Duplicated chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell, spindle fibers connect in the middle of the chromosome pair by a centromre
Metaphase-
Chromosomes are pulled apart by spindle fibers, separated into two identical chromatids
Anaphase-
2 new nuclei are formed, spindle fibers disappear
Telophase-
Full division of one cell into two
Cytokinesis
Energy, space, and pre-existing DNA
What must a cell have in order to divide?
Cancer occurs when cells divide uncontrollably and become cancer cells
What is Cancer?
Unorganized, unusual looking large or multiple nuclei
What do cancer cells look like?
UV exposure, Genetics, diet, radiation, viruses, etc.
What are risk factors for cancer?
It can spread to the rest of the body and potentially kill an organism
What happens when cancer is left untreated
What are the treatment options for cancer
Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, various therapies