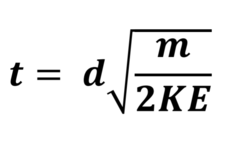AQA Chemistry A Level - Atomic Structure
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/63
Last updated 11:22 AM on 11/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
1
New cards
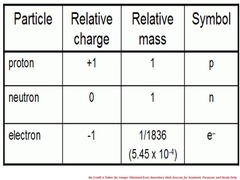
Relative charge and relative mass of proton, neutron, electron
2
New cards
What does an atom consist of?
A nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons
3
New cards
Mass number
The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus (A)
4
New cards
Atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom (Z)
5
New cards
Mass spectrometer gives accurate information about...
...relative isotopic mass and the relative abundance of isotopes
6
New cards
mass spectrometry can be used to...
...identify elements and determine relative molecular mass
7
New cards
Isotope
Atoms with the same proton number but a different neutron number, caused by instability in an atom
8
New cards
Electron impact ionisation/electron gun ionisation
The sample is bombarded by high energy electrons. Sample molecule loses an electron forming M+
High energy electrons from an electron gun are fired at the sample
This knocks off one electron from each particle forming a 1+ ion
High energy electrons from an electron gun are fired at the sample
This knocks off one electron from each particle forming a 1+ ion
9
New cards
Electrospray ionisation
Sample is dissolved in a polar volatile solvent and injected through a fine hypodermic needed as a fine spray. The tip of the needle has a high voltage.
Particles are ionised by gaining a proton from the solvent
Particles are ionised by gaining a proton from the solvent
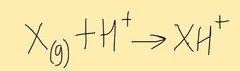
10
New cards
Acceleration area:
Negative plate used to give ions the same kinetic energy
11
New cards
Ion drift:
Ions are separated in a flight tube (region with no electric field) depending on their mass and charge
12
New cards
Ion detector
Records flight times, only positive ions are recorded - they pick up an electron, causing a current and a peak
13
New cards
Data analysis
Flight times are analysed and recorded as a mass spectrum
14
New cards
A sample of 65Cu+ was accelerated to have 1 x 10-19 kJ of kinetic energy. How long would it take to drift along a 80cm long tube?
Mass of 1 mole = 65g = 0.0065kg
0.065/6.022 x 1023 = 1.08 x 10-25kg = mass of one ion
t = 0.8√(1.08 x 10-25)/(2 x 1 x 10-19)
= 5.87 x 10-4 seconds
0.065/6.022 x 1023 = 1.08 x 10-25kg = mass of one ion
t = 0.8√(1.08 x 10-25)/(2 x 1 x 10-19)
= 5.87 x 10-4 seconds
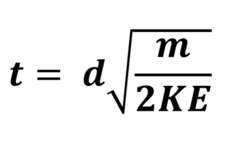
15
New cards
First ionisation energy
The energy required to remove one electron from a gaseous atom
e.g. Na(g) ---> Na+(g) + e-
e.g. Na(g) ---> Na+(g) + e-
16
New cards
Second ionisation equation
Na+(g) ---> Na2+(g) + e-
17
New cards
What happens to the ionisation energy down group one?
Value decreases due to increased shielding and greater distance from the nucleus - outer electron is easier to remove
18
New cards
What happens to the ionisation energy down group two?
Values are greater than group one, more nuclear charge = stronger pull on electron = more energy to remove it
Deceases down the group due to more energy shells, weaker attraction of ion to lost electron
Deceases down the group due to more energy shells, weaker attraction of ion to lost electron
19
New cards
How many electrons does group s hold?
2
20
New cards
How many electrons does group p hold?
6
21
New cards
How many electrons does group d hold?
10
22
New cards
What are the 2 exceptions?
Chromium and copper
23
New cards
What is the rule when ions are formed?
4s shell is lost before 3d
24
New cards
Why are only a small proportion of the alpha particles deflected through a large angle
The nucleus is very small
25
New cards
Why do some alpha particles get deflected
The nucleus is positive so repels the alpha particles
26
New cards
Why don't some alpha particles get deflected
The nucleus is empty space
27
New cards
Finding the molecular ion peak
The one with the largest m/z value
28
New cards
The full electron configuration of Fe
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d6 4s2
29
New cards
The full electron configuration of Ni
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d8 4s2
30
New cards
Write the formula of the compound formed when an atom with 17 electrons reacts with a group 2 metal in period 4
CaCl2
31
New cards
Write the formula of the compound that contains a 2+ ion and a 3- ion that have the same electron configuration as neon
Mg3N2
32
New cards
The first 5 successive ionisation energies of an element Z are 799, 2420, 4000, 25000 and 328000. Which group does this element belong to
Group 3
33
New cards
State and explain the general trend in ionisation energy across the period
Increases as decreased shielding and shorter distance from the nucleus, outer electron harder to remove as greater nuclear charge
More protons=more nuclear charge=smaller atomic radius
More protons=more nuclear charge=smaller atomic radius
34
New cards
Explain why the first ionisation energy for oxygen deviates from the general trend
Oxygen has a pair of electrons in a 2p orbital that repel each other
35
New cards
Equation for first ionisation energy of calcium
Ca(g) --> Ca+(g) + e-
36
New cards
What element in period 3 has the highest melting point and why
Silicon - lots of energy needed to break covalent bonds
37
New cards
Blocks in periodic table
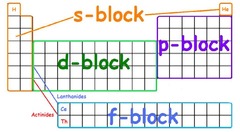
38
New cards
What element in period 3 has highest first ionisation energy and why
Argon - most nuclear charge, same number of shells
39
New cards
Why do isotopes have similar chemical reactions
They have the same number of electrons
40
New cards
Why is the second ionisation energy of boron higher than the first ionisation energy of boron
The electron being removed is closer to the nucleus so a stronger attraction
41
New cards
What might cause relative atomic mass of a sample to be different from in the periodic table
There may be other isotopes present/absent
42
New cards
Write an equation for the reaction when a tellurium ion hits the detector
Te+ + e- --> Te
43
New cards
How are ions formed in a time of flight mass spectrometer
Sample bombarded by high energy electrons, sample molecule loses and electron forming M+
44
New cards
Why is it necessary to ionise molecules when measuring their mass in TOF
Only ions can be accelerated and cause a current to flow when they hit the detector
45
New cards
What 2 measurements are recorded for each isotope in the mass spectrometer
m/z
abundance
abundance
46
New cards
Relative atomic mass
The weighted mean mass of an atom of an element relative to 1/12th of the mass of an atom of carbon-12
47
New cards
How is a current generated in a mass spectrometer
Electrons flow from detector to positive ion
48
New cards
Relative mass of an electron
1/1840
49
New cards
Equation for second ionisation energy of boron
B+(g) --> e- + B2+(g)
50
New cards
Give 2 reasons a sample must be ionised
- to deflect the beam
- to be accelerated to have the same KE
- to be accelerated to have the same KE
51
New cards
What can be adjusted in the mass spectrometer to enable ions formed by the different isotopes to be directed onto the detector
Electric field
52
New cards
Explain why atoms may have different mass numbers
Different number of neutrons
53
New cards
Why is the first ionisation energy is krypton greater than bromine
More protons as higher atomic number, but similar shielding
54
New cards
How are ions formed in TOF mass spectrometer
- Sample bombarded with high energy electrons
- Sample molecule loses and electron forming M+
- High energy electrons from the gun get fired at the sample which knocks off an electron from the particle to form an ion
- Sample molecule loses and electron forming M+
- High energy electrons from the gun get fired at the sample which knocks off an electron from the particle to form an ion
55
New cards
Suggest why krypton has lower first ionisation energy than argon
More electrons so more orbitals = increased shielding so less attraction to nucleus and easier to remove
56
New cards
Name the 3 processes that occur in a mass spectrometer before the vaporised isotopes can be detected
Ionisation - high energy electrons fired at sample
Acceleration - electric field and negative plate gives ions same kinetic energy
Deflection - with magnetic field
Acceleration - electric field and negative plate gives ions same kinetic energy
Deflection - with magnetic field
57
New cards
How is ionisation achieved in a mass spectrometer
- electron gun fired high speed electrons
- knocks off e- from particle
- knocks off e- from particle
58
New cards
Why is ionisation necessary
So ions can be accelerated by electric field, deflected by magnetic field and detected
59
New cards
Relative isotopic abundance
The relative abundance of each isotope present in a sample of an element
60
New cards
Give the symbol for the isotope which has the mass number of 34 and has 18 neutrons
Sulphur 34, 16
61
New cards
What is adjusted in a mass spectrometer to direct the ions with different mz values onto the detector
Magnetic field on the negative accelerator
62
New cards
What happens to particles immediately after they are ionised
Accelerated
63
New cards
What factors determine how much a particle is deflected in a magnetic field
- mass
- charge
- speed
- charge
- speed
64
New cards
Time of flight equation
KE = Joules
D = Metres
D = Metres