Processes involved in generation of ATP
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Mitochondria
the ATP factory
the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate releases energy
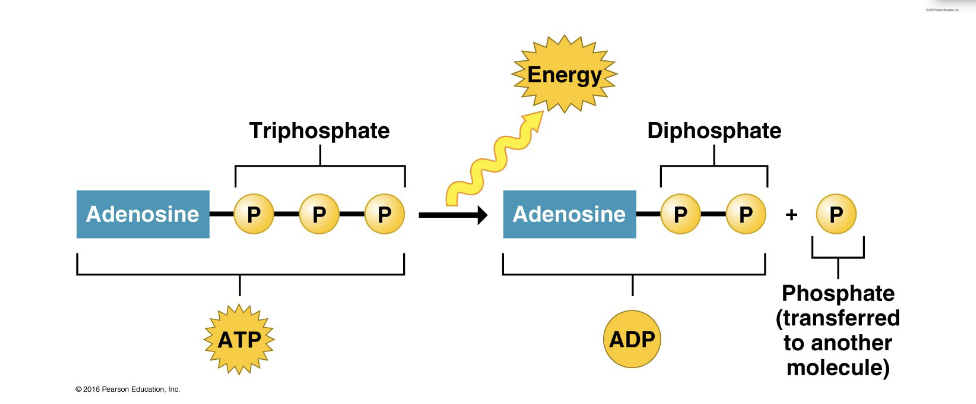
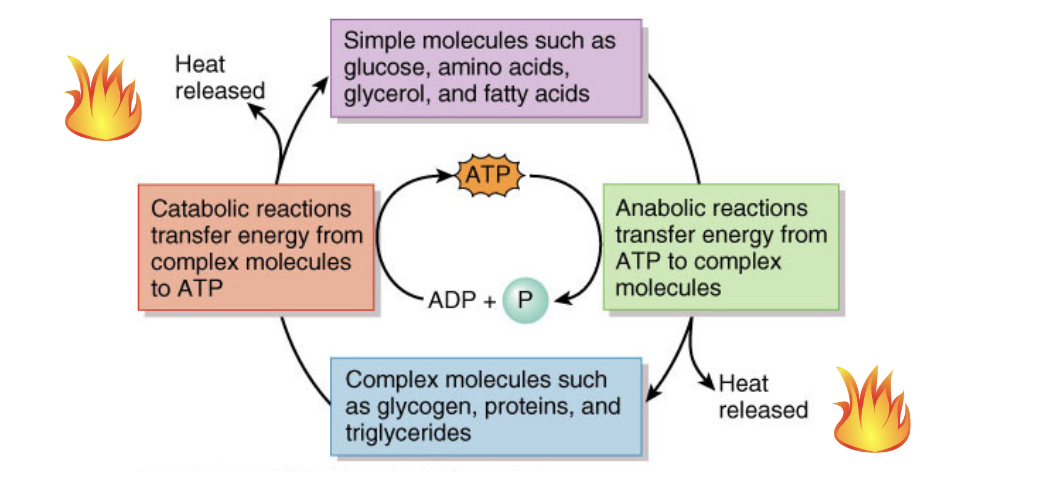
The ATP cycle
not spontaneous
the transfer of energy between complex and simple molecules in the body, with ATP as the mediator
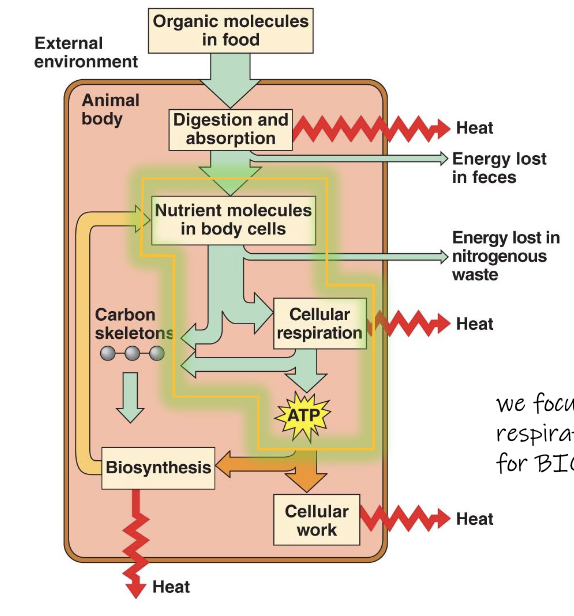
Fuel is needed to generate ATP
carbohydrates - broken down into simple sugars
proteins - broken down to amino acids
fats - broken down to simple fats
Glucoregulation
glucose in food → glucose in blood stream → (facilliated by insulin) into cell →
cellular resp → cellular work
OR
storage for harder times → glucose in bloodstream
Cellular Respiration
the controlled release of energy from organic compounds to produce ATP
Conversion of glucose to ATP
glycolysis
pyruvate oxidation
citric acid cycle
oxidative phosphorylation
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY
Glycolysis
occurs in cytosol
reactant is glucose
2 ATP, 2 Pyruvates, 2 NADH is produced
Anaerobic - does not need O2
invest 2 ATP → Produce 4 ATP
Pyruvate Oxidation
occurs in mitochondrial matrix
reactant is 2 pyruvates
2 Acetyl CoA, 2 NADH, 2 CO2 is produced
Aerobic - O2 is required
remove CO2 → reduce NAD+ → add coenzyme A
Citric Acid Cycle
occurs in mitochondrial matrix
reactant is 2 Acetyl CoA
2 ATP, 2FADH2, 4CO2, 6 NADH is produced
Aerobic - O2 is required
the CAC is a series of reactions - the product of one reaction is the substrate for the next reaction
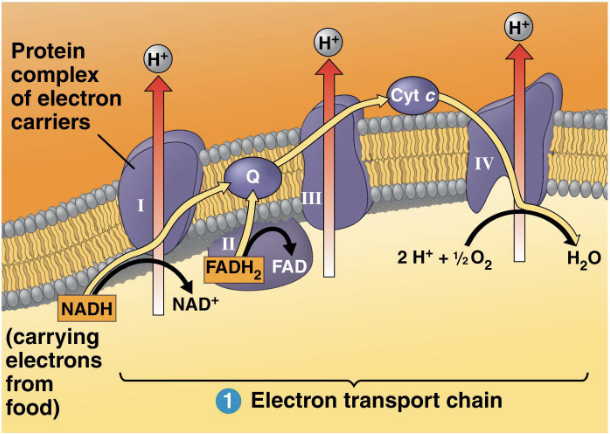
ETC & Chemiosmosis
occurs in inner membrane
reactant is ~ 10 NADH, ~2 FADH2
26 - 28 ATP is produced
Aerobic - O2 is required
Electron carries (NADH & FADH2) donate e’s to complex 1 and 2. Complex 1,3,4 pump H+ ions into the intermembrane space. H+ ions run down conc gradient through ATP synthase to spin turbine and produce ATP