Chapter 6: Lipids, Membranes, and Cell Structure
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Exam 1 Mean
Average score before the curve is 65.
Exam 1 Median
Middle score before the curve is 67.
Curve
4 points added to final Exam 1 grade.
Plasma Membrane
Separates life from nonlife in cells.
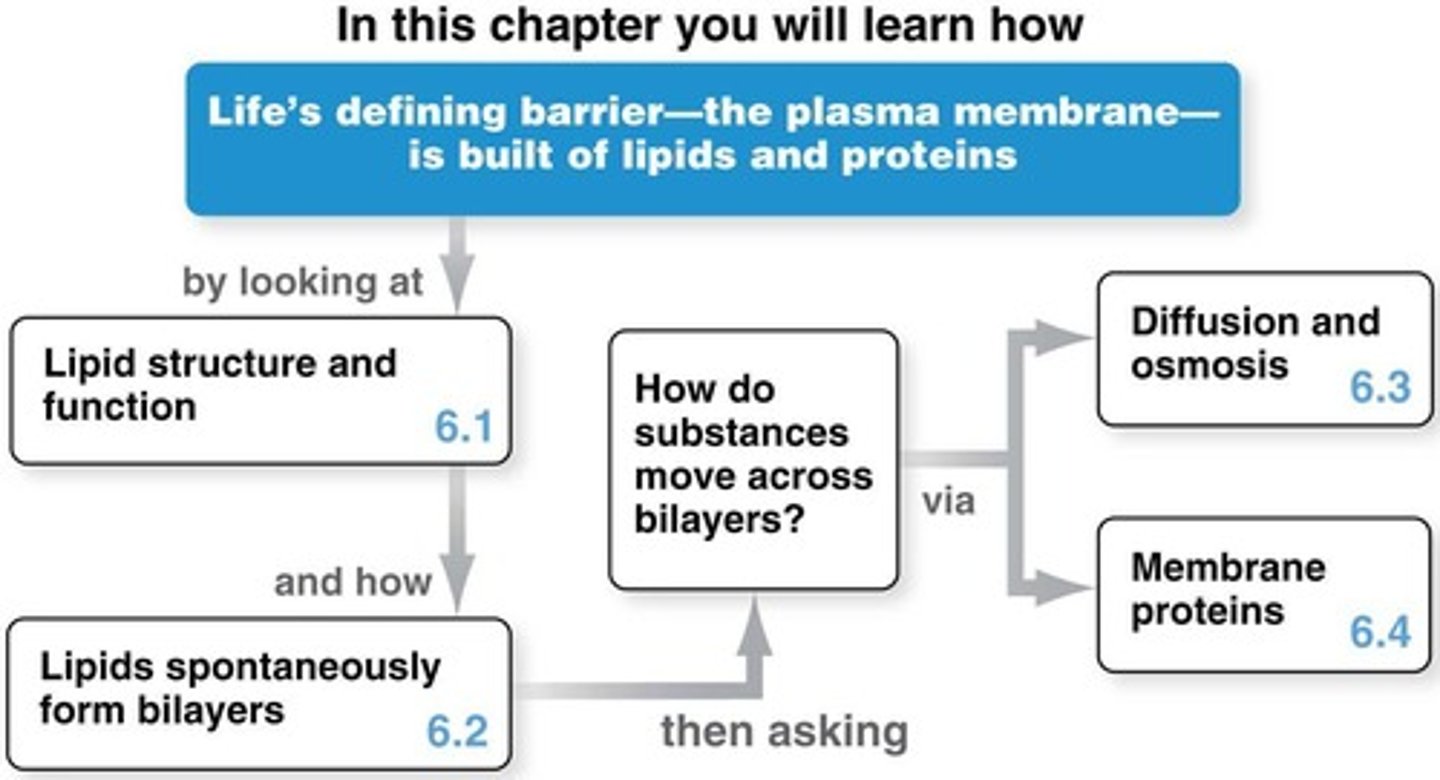
Membrane Functions
Protects, allows entry, facilitates reactions.
Phospholipids
Main components of cell membranes.
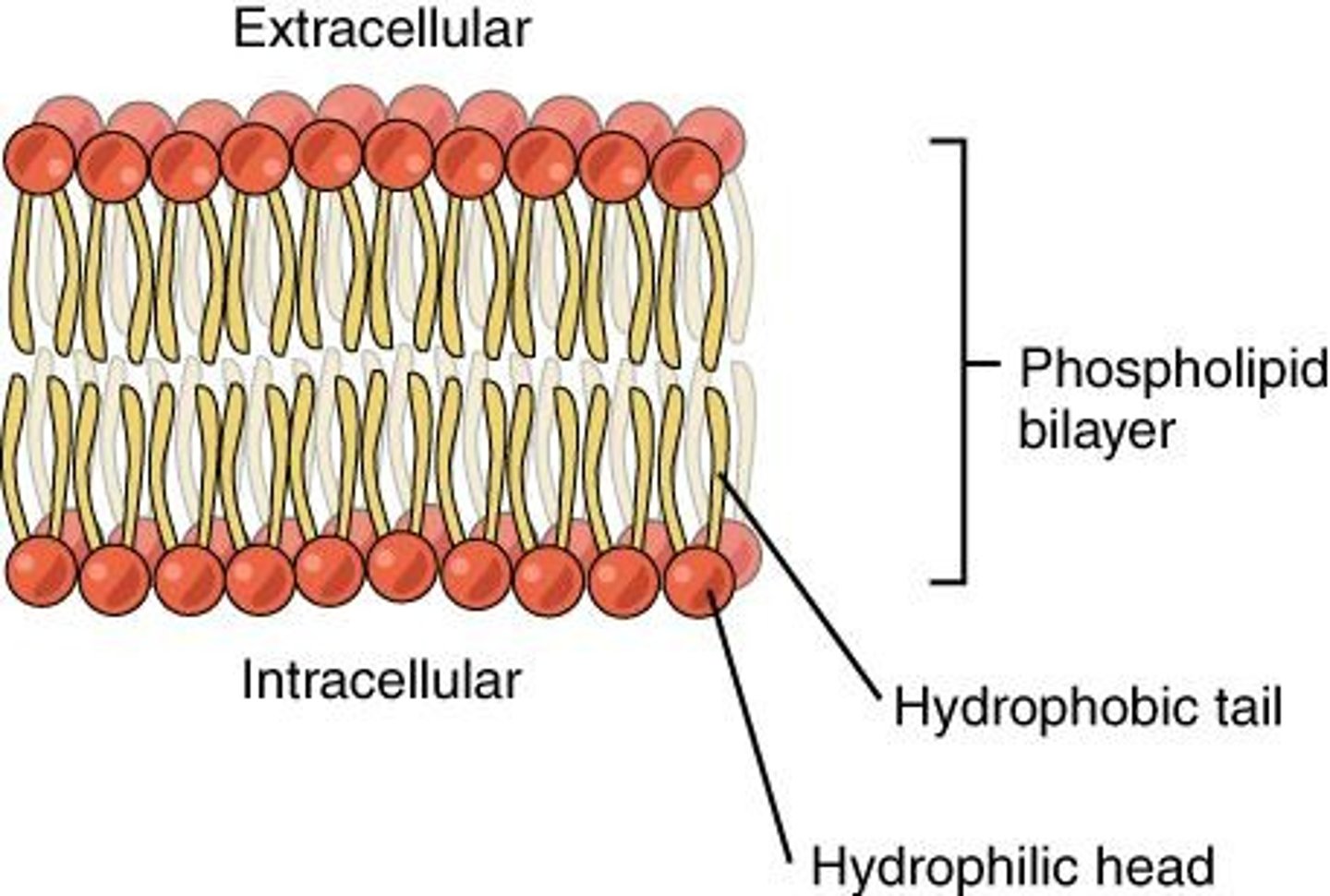
Hydrophobic
Repellent to water; nonpolar.
Hydrophilic
Attracted to water; polar.
Fatty Acid
Hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group.
Saturated Fatty Acids
Only single C-C bonds; maximum H.
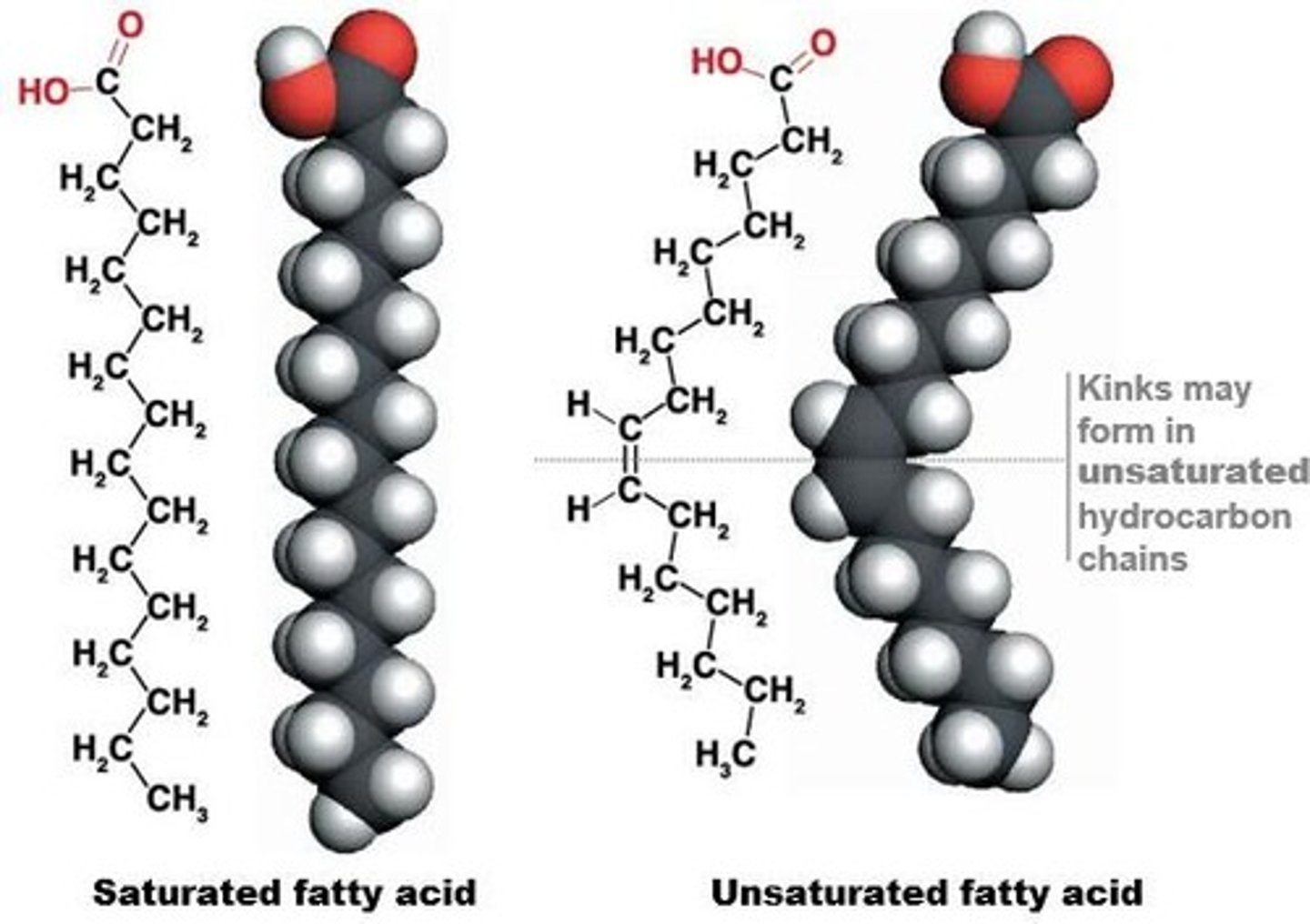
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
One or more double C=C bonds.
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
Multiple double bonds in hydrocarbon chain.
Lipid Types
Steroids, fats, phospholipids based on solubility.
Steroids
Lipids with bulky four-ring structure.
Cholesterol
Component of plasma membranes; steroid.
Fats (Triglycerides)
Three fatty acids linked to glycerol.
Ester Linkage
Bond between glycerol and fatty acid.
Phospholipid Structure
Two fatty acids, glycerol, phosphate group.
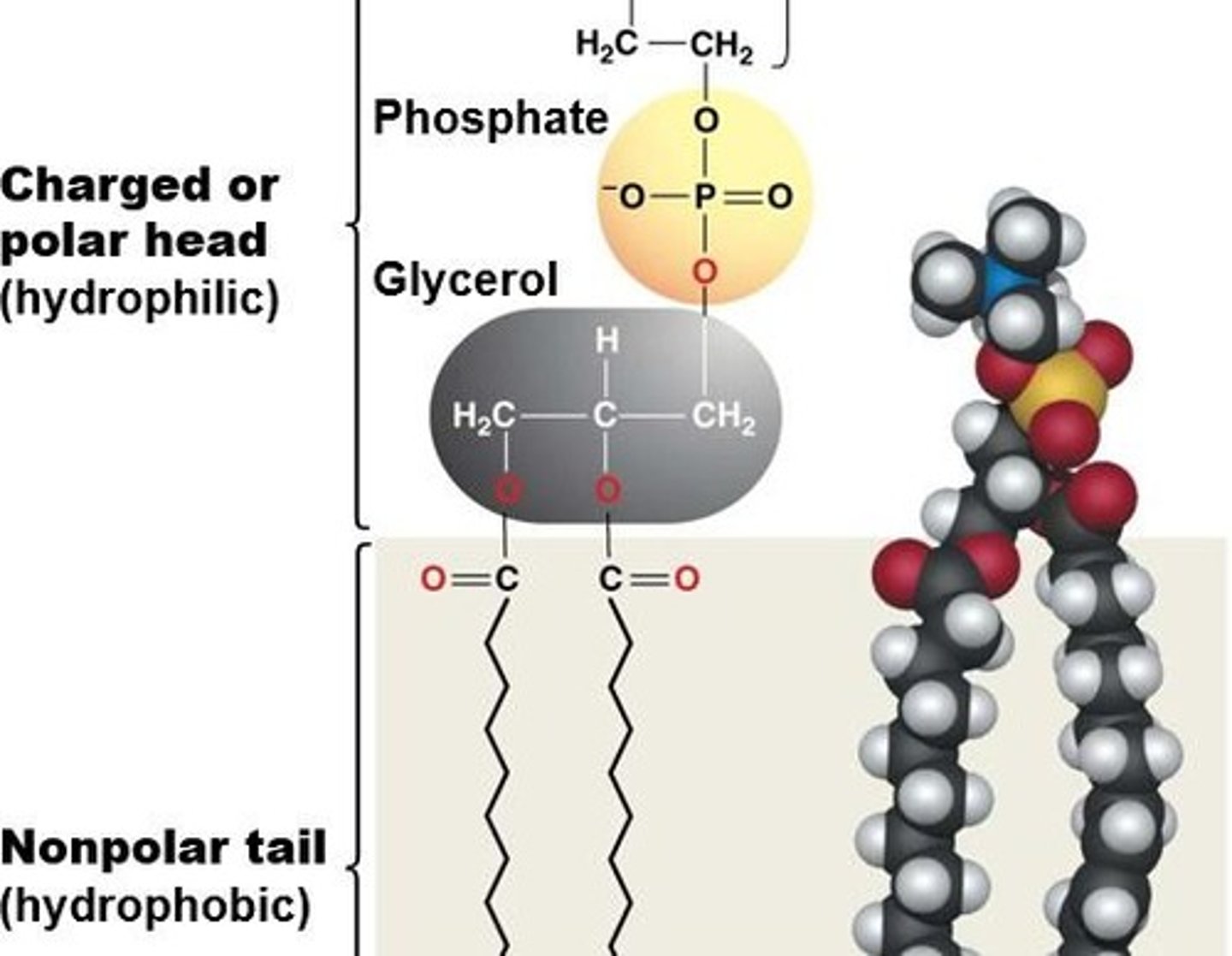
Amphipathic
Molecules with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts.
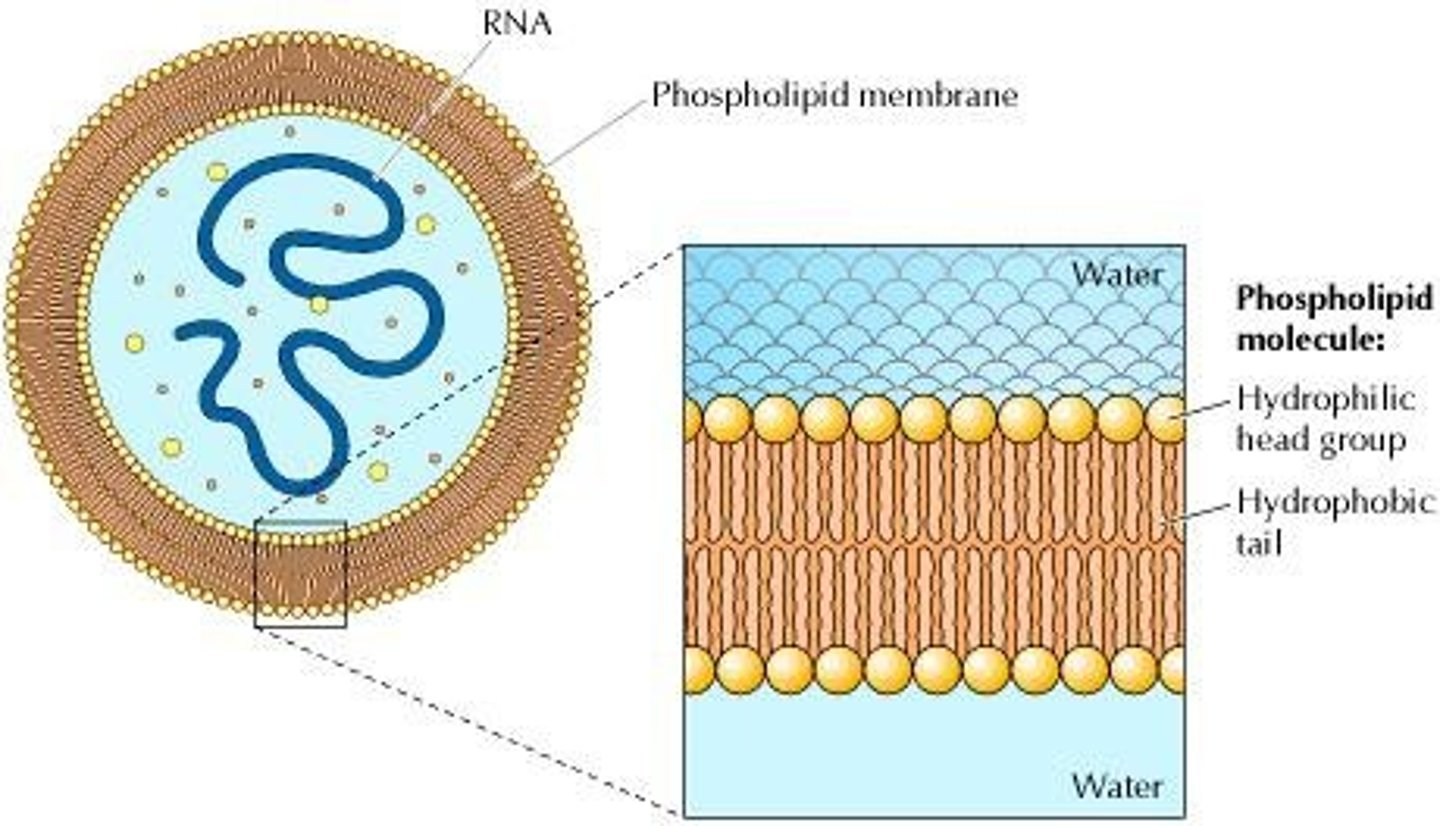
Lipid Bilayer
Two sheets of phospholipids forming membranes.
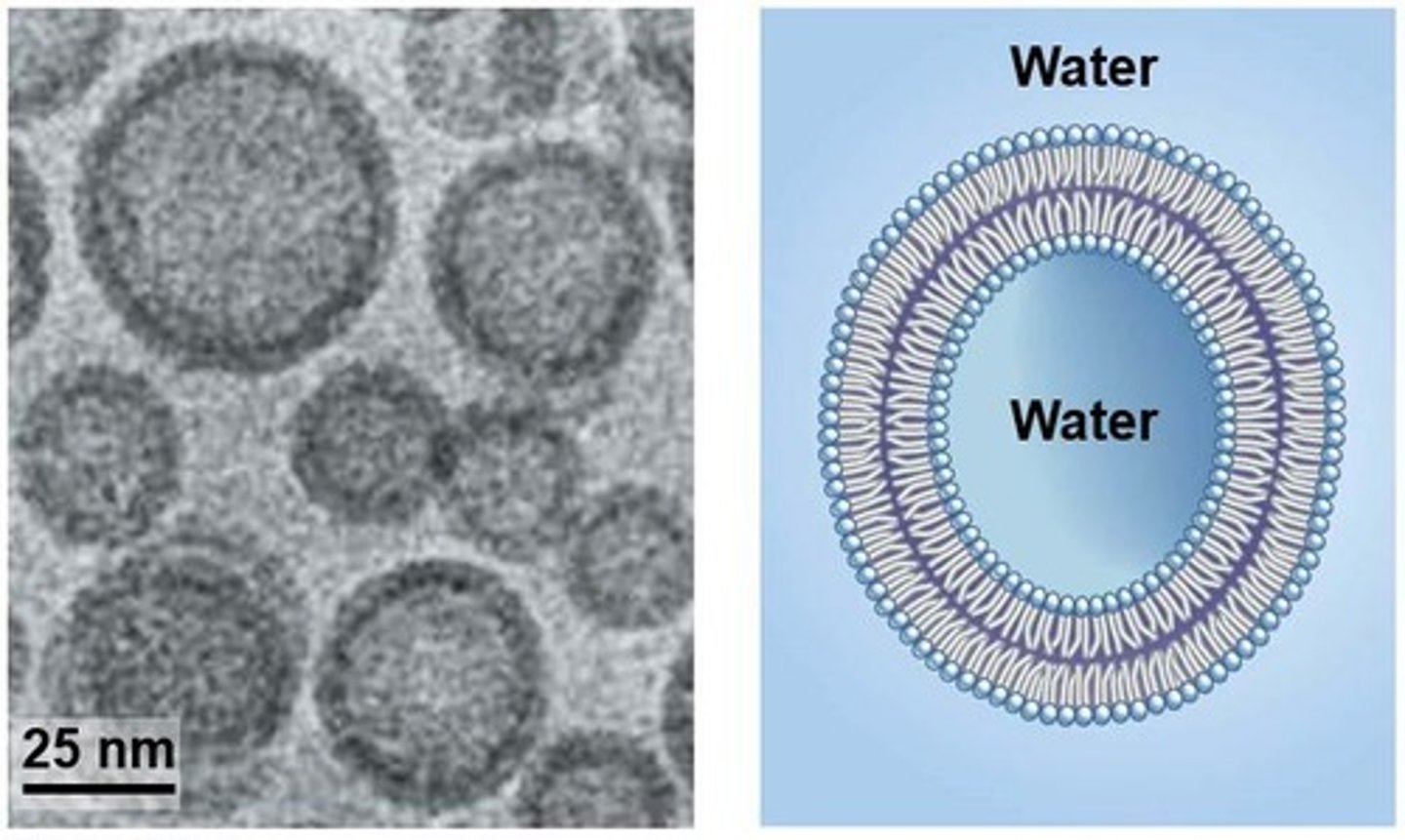
Liposomes
Artificial vesicles made of phospholipids.
Selective Permeability
Ability of membranes to control substance passage.
Diffusion
Movement of substances from high to low concentration.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a membrane.
Fluid-Mosaic Model
Describes membrane structure with proteins and lipids.
Transmembrane Proteins
Proteins spanning the membrane; involved in transport.
Channel Proteins
Facilitate passive transport of specific ions/molecules.
Gated Channels
Open/close in response to signals.
Aquaporins
Channel proteins allowing water passage.
Carrier Proteins
Change shape to transport larger molecules.
GLUT-1
Carrier protein increasing glucose permeability.
Active Transport
Moves substances against their gradient; requires energy.
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Transports Na+ out and K+ in using ATP.
Electrochemical Gradient
Concentration and charge difference across a membrane.
Membrane Fluidity
Influenced by saturation and temperature.
Low Temperature Effect
Decreases membrane fluidity and permeability.
Cholesterol Role
Increases hydrophobic density, reducing permeability.
Hydrophobic Interactions
Stronger with longer saturated tails; less permeable.
Vesicles
Small bubble-like structures surrounded by membranes.
Chemical Evolution Evidence
Lipids synthesized under early Earth conditions.
Hydrocarbon Structure
Only C and H; nonpolar and hydrophobic.
Functional Groups
Specific groups determining molecule properties.
Hydrocarbon Chain
Chain of carbon atoms in lipids.
Kink in Chain
Caused by double bonds in unsaturated fats.
Building Blocks
Complex lipids formed from fatty acids.
Membrane Proteins
Proteins that alter membrane structure and function.
Passive Transport
Movement without energy; includes diffusion.
Facilitated Diffusion
Passive transport via channel or carrier proteins.
Primary Active Transport
Directly uses ATP to move substances.
Secondary Active Transport
Uses electrochemical gradients to move substances.