Chapter 4 (Part 1. Development and Plasticity)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Four key takeaways regarding neurodevelopment
Ongoing, complex, experience plays a central role, and dire consequences if something goes wrong
Does the brain ever stop developing?
Not really – neurons are constantly changing shape and forming new connections. When you walk into PSYC 275 for one class and walk out, your brain changes slightly.
Do newborn babies have more brain neurons than adults?
Yes, newborn babies have roughly 100 billion brain neurons, compared to an adult’s 86 billion.
What does an ovum + sperm equal?
Zygote
What are the five stages of neural development
(Induction of the neural plate)
Neural proliferation
Migration
Differentiation
Mylenation
Synaptogensis
Induction of the neural plate
When the neural plate is created and installed, awaiting proliferation
Neural Proliferation
The production of new cells and neurons
What types of cells create the new cells in proliferation
Stem cells, which either divide into more stem cells, turn into glial neurons that migrate, or they stay where they are
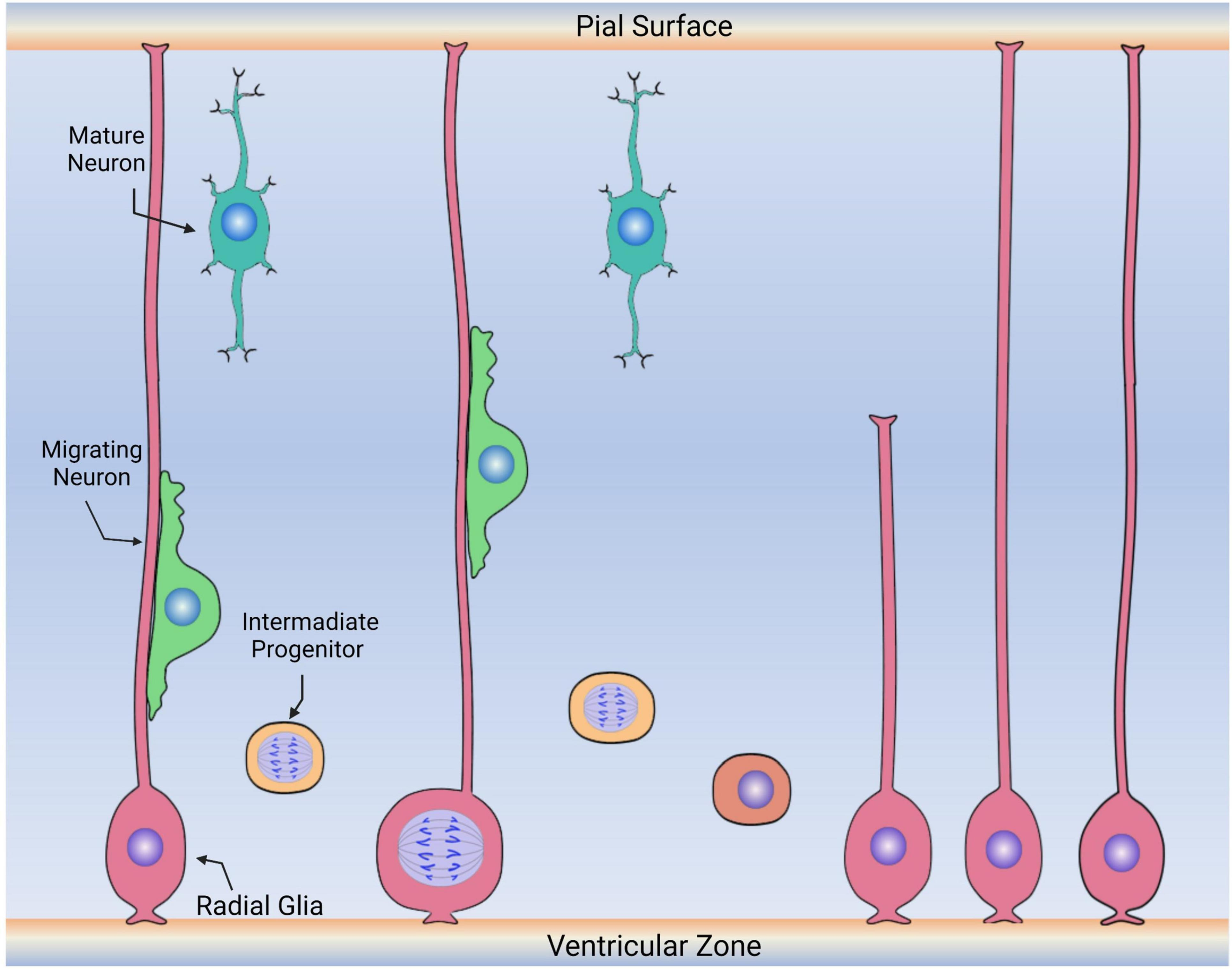
Migration and aggregation
Neurons and glial cells migrate when they are created through cell division
What chemicals guide migration neurons that are mere cell bodies?
Immunoglobulins and chemokines
Radial glial cells
They also help neurons migrate. They are like a long strand that neurons transport down, somewhat like a power line
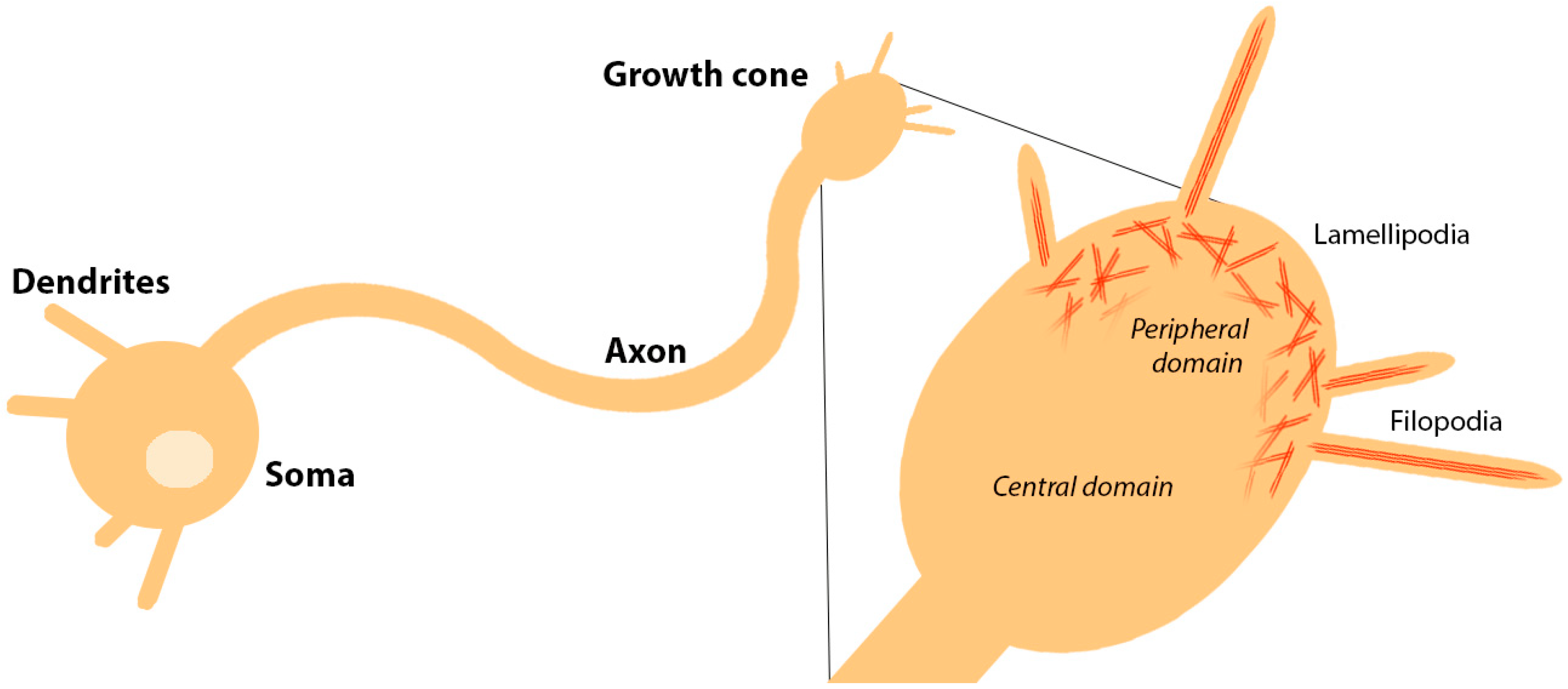
Differentiation
The formation of the axon and dendrites that give the neuron its distinctive shape
Growth cones and filopodia
A growth cone is located at the end of each axon, and it extends and retracts filopodia to help the neuron find its way
Mylenation
When glial cells (Schwann cells, to be specific) produce the fatty sheath (myelin) that covers the axons of some neurons
How do babies begin to move?
Babies begin to move as a result of the development of myelin in the spinal cord
Synaptogenesis
The formation of synapses between neurons. A fully developed neuron is pretty much useless if it doesn’t interact with others neurons via synapse
What two parts of the brain of new neurons forming daily?
The basal ganglia and hippocampus.
Do the axons in nerves grow straight, or do they rotate accordingly to reach their target?
They rotate and grow accordingly
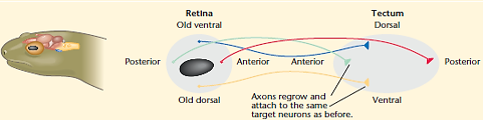
The chemo affinity hypothesis
Proposed by Roger Sperry, suggests that neurons connect to their correct targets by recognising and interacting with specific molecular markers on their surfaces.
Essentially, growing axons reach their target area by following a gradient of chemicals, in which they are attracted by some chemicals and repelled by others