Microbio Lab Quiz (5.1)
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Smear
1) Specimen is spread on a slide
2) Allow specimens to air dry
3) fixing
heat fixing
chemical fixing (alcohol)
fixing
prevents material from washing off the slide during the staining process
differential staining
uses two different-colored dyes
cell components react differently tot he dyes
used to distinguish cell types or parts
ex: gram stain, acid-fast stain, and endospore stain
differential stain steps
1) Primary dye
2) decolorizer
3) Counterstain
primary dye
stains all the cells
decolorizer
removed dye form some types of cells
counterstain
stains the cells that had their dye removed
no effect on cells that retained the primary dye
gram stain
separates bacteria based on differences in their cell wall compostion
gram positive
thick layer of peptidoglycan
gram negative
thin layer of peptidoglycan with an outer membrane
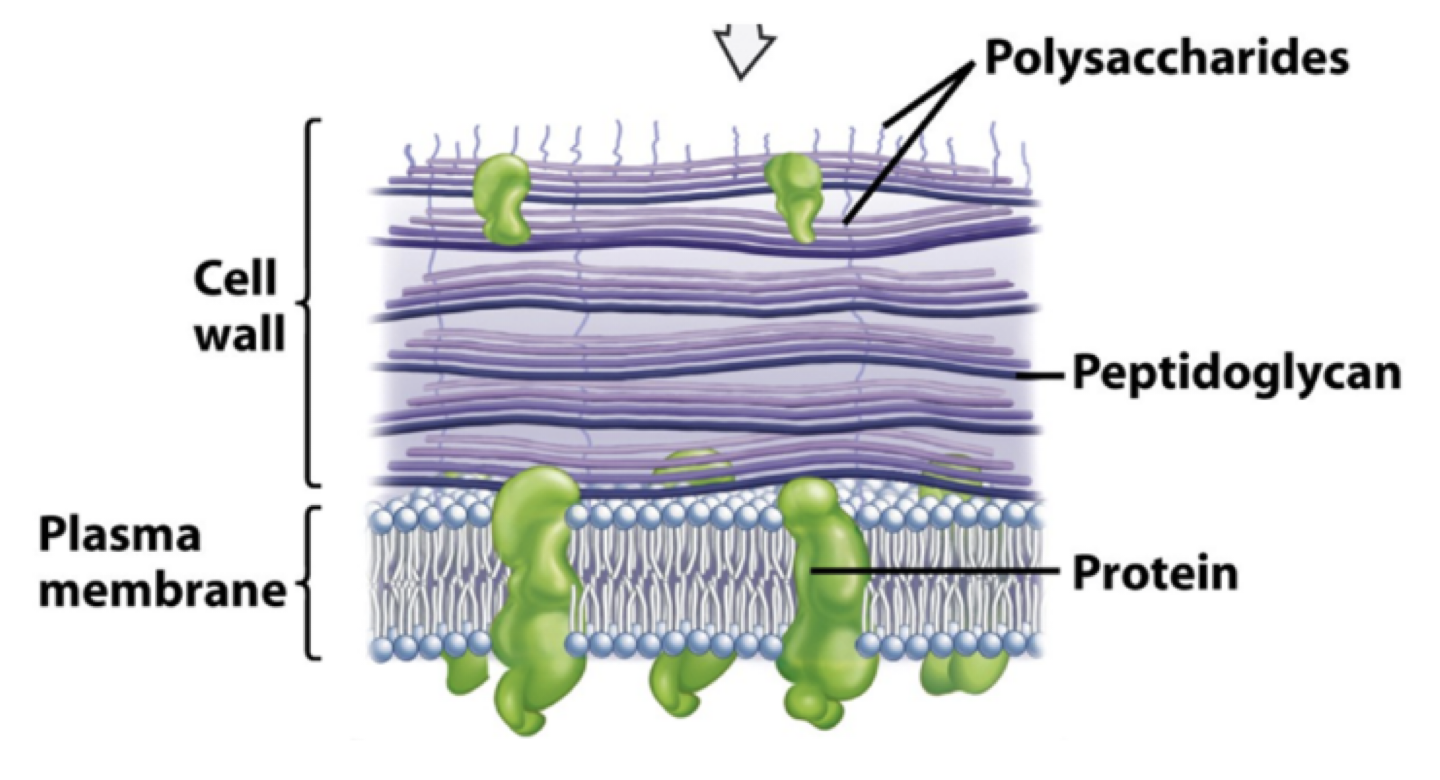
gram positive bacteria
call walls that contain multiple layers of peptidoglycan (60%-90%)
molecules of teichoic acid within the layers of peptidoglycan
teichoic acid may strengthen the cell wall
retain the primary dye
gram positive cell wall
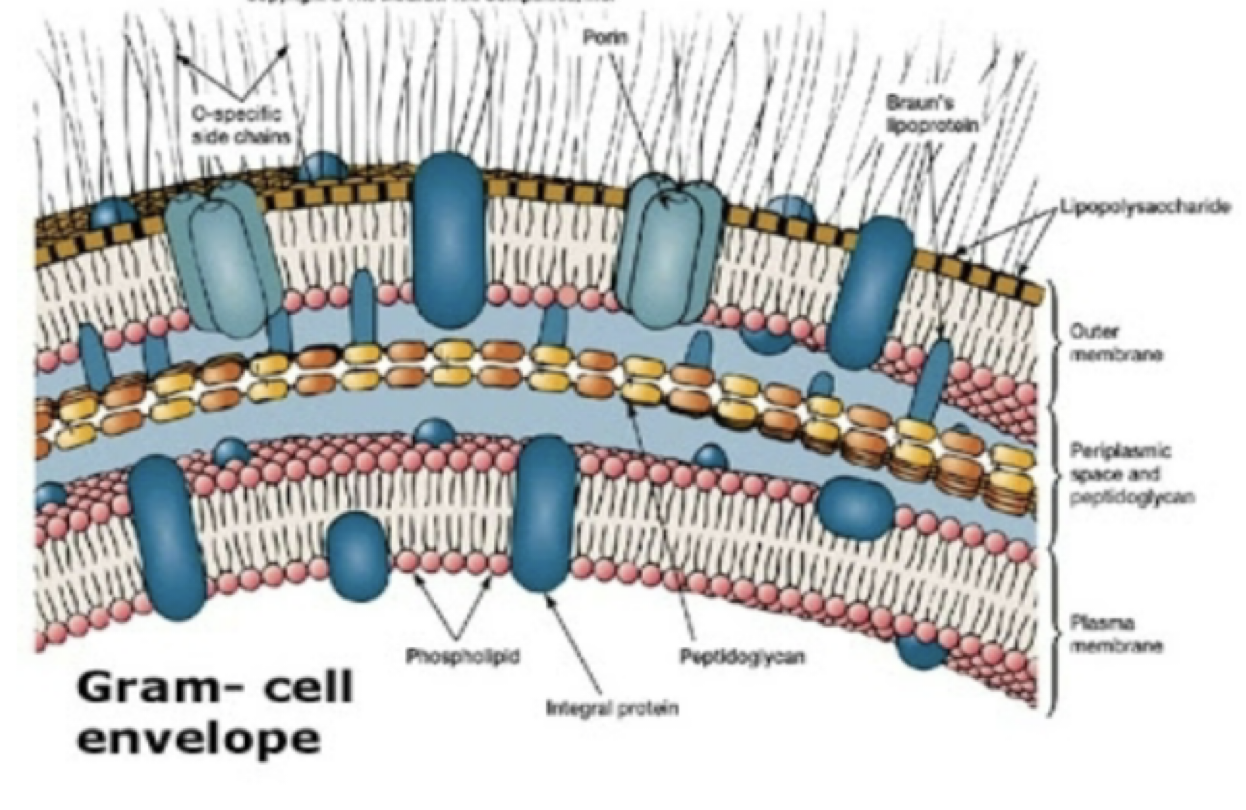
gram negative bacteria
cell wall is thinner
contain a thin layer of peptidoglycan (10%-20%) and no teichoic acid
have an outer membrane of lipopolysaccharides
primary dye removed by decolorizer
pick up counterstain
gram negative cell wall
gram stain procedure
Step 1) Slide is covered with crystal violet for 1 minute
all bacteria are purple
Step 2) Slide is covered with iodine for 1 minute
Large complex forms with the crystal violet and the iodine
All bacteria are purple
Step 3) Slide is covered with Gram’s alcohol (quick rinse)
gram positive cells remain purple
alcohol dissolves the lipopolysaccharide layer in the Gram-negative cell wall (Crystal violet washes out)
gram negative cells are now colorless
Step 4) Slide is covered with safranin for 1 minute
Gram positive cells are still purple
gram negative cells now red
Gram Variable Reactions
bacteria that stain both purple and red
due to:
age of culture
technique
genetics
media
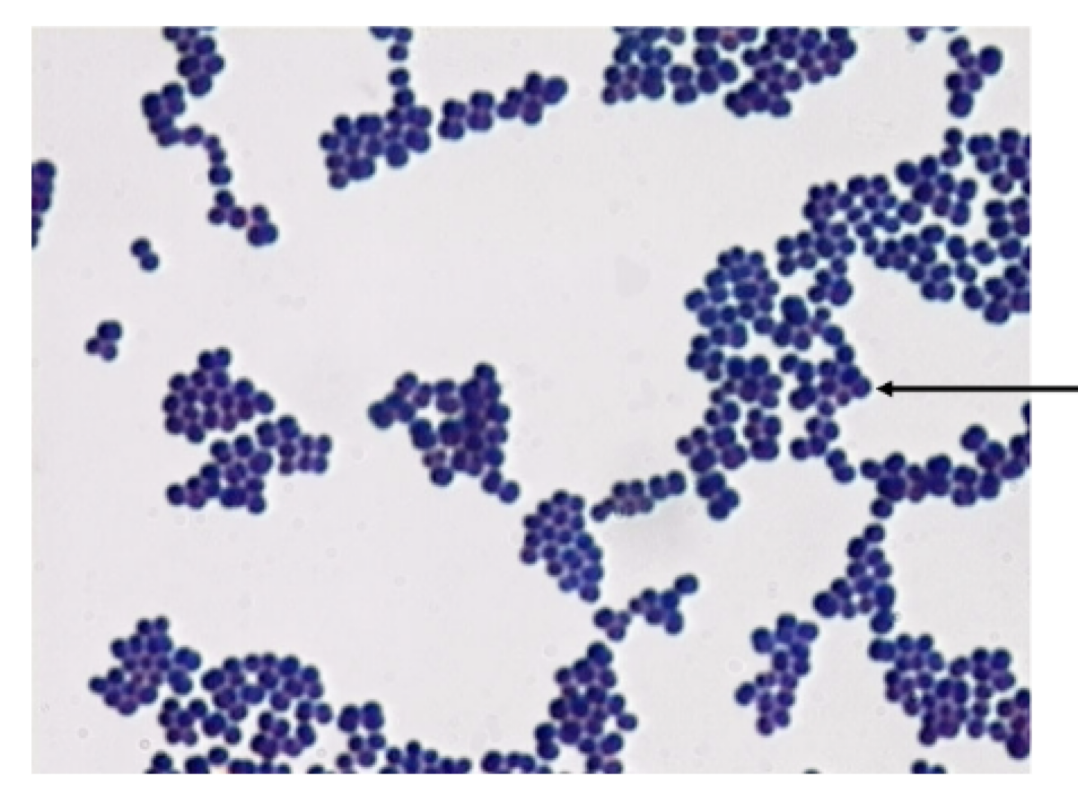
positive
cocci
staphylococcus
1) identify the grams stain reaction
2) identify this bacterial shape
3) arrangement
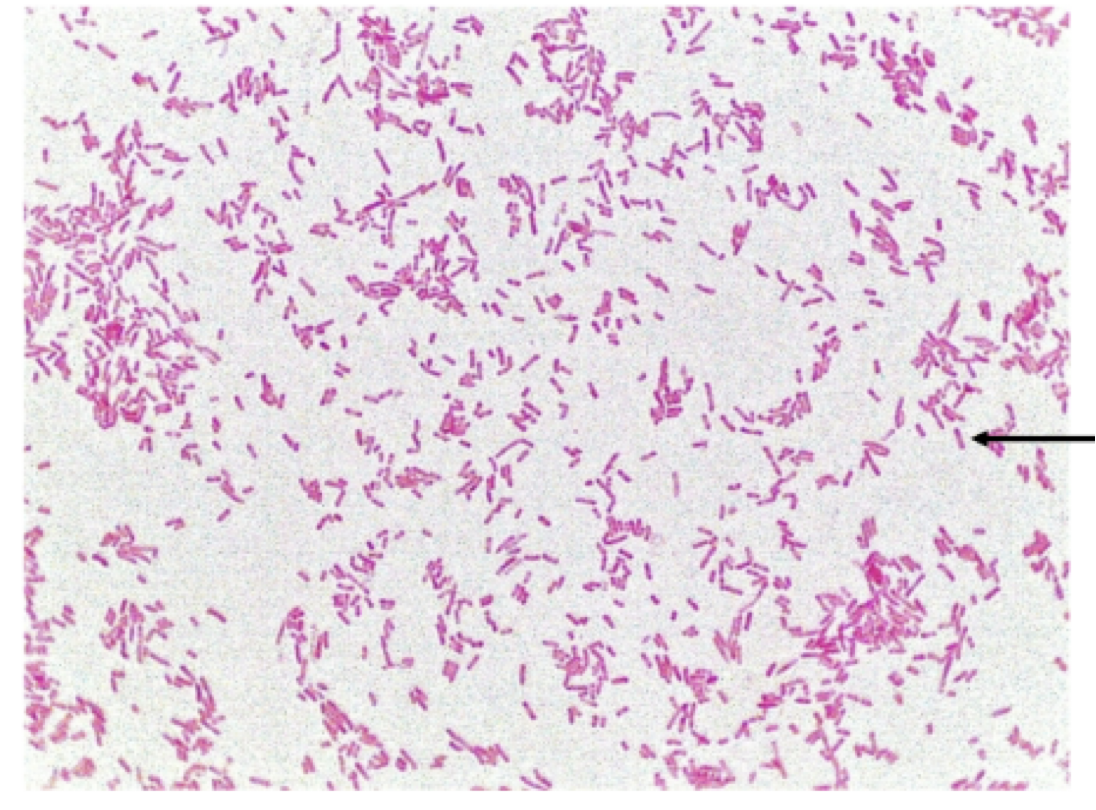
negative
bacilli
single, random, no specific arrangement
1) identify the grams stain reaction
2) identify this bacterial shape
3) arrangement