AP Music Theory
1/234
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
235 Terms
Tonic
scale degree 1, do
Supertonic
scale degree 2, re
Mediant
scale degree 3, mi
Subdominant
scale degree 4, fa
Dominant
scale degree 5, sol
Submediant
scale degree 6, la
Leading Tone
scale degree 7, ti
Order of Sharps
F C G D A E B
Order of Flats
B E A D G C F
C major
no sharps or flats
G major
1 sharp
D major
2 sharps
A major
3 sharps
E major
4 sharps
C♭/B major
7 flats/5 sharps
G♭/F♯ major
6 flats/6 sharps
D♭/C♯ major
5 flats/7 sharps
A♭ major
4 flats
E♭ major
3 flats
B♭ major
2 flats
F major
1 flat
C minor
E♭ relative major, 3 flats
G minor
B♭ relative major, 2 flats
D minor
F relative major, 1 flat
A minor
C relative major, no sharps or flats
E minor
G relative major, 1 sharp
C♭/B minor
D relative major, 2 sharps
G♭/F♯ minor
A relative major, 3 sharps
D♭/C♯ minor
E relative major, 4 sharps
A♭ minor
C♭ relative major, 7 flats
E♭ minor
G♭ relative major, 6 flats
B♭ minor
D♭ relative major, 5 flats
F minor
A♭ relative major, 4 flats
Simple Duple
2/2, 2/4
Simple Triple
3/4, 3/8
Simple Quadruple
4/4
Compound Duple
6/8, 6/4
Compound Triple
9/8
Compound Quadruple
12/8
Grave
very slow, solemn (25-45 bpm)
Largo
slow and broad (40-60)
Larghetto
slow, but faster than largo
Lento
slow (45-60 bpm)
Adagio
slow, with expression (66-76)
Andante
walking pace (76-108 bpm)
Andantino
slightly faster than andante
Moderato
moderately (108-120 bpm)
Allegretto
moderately fast (112-120 bpm)
Allegro
fast (120-156 bpm)
Vivace
lively (156-176)
Presto
exceptionally fast (168-200)
Prestissimo
as fast as possible
Accelerando (accel.)
gradually faster
Ritardando (rit.)
gradually slower
Ritenuto (riten.)
immediately slower
Rubato
flexible tempo using slight variations of speed to enhance musical expression
Terraced Dynamics
describes the sharp, abrupt dynamic contrasts found in the music of the Baroque era
Subito
suddenly
Legato (tenuto)
smooth and connected
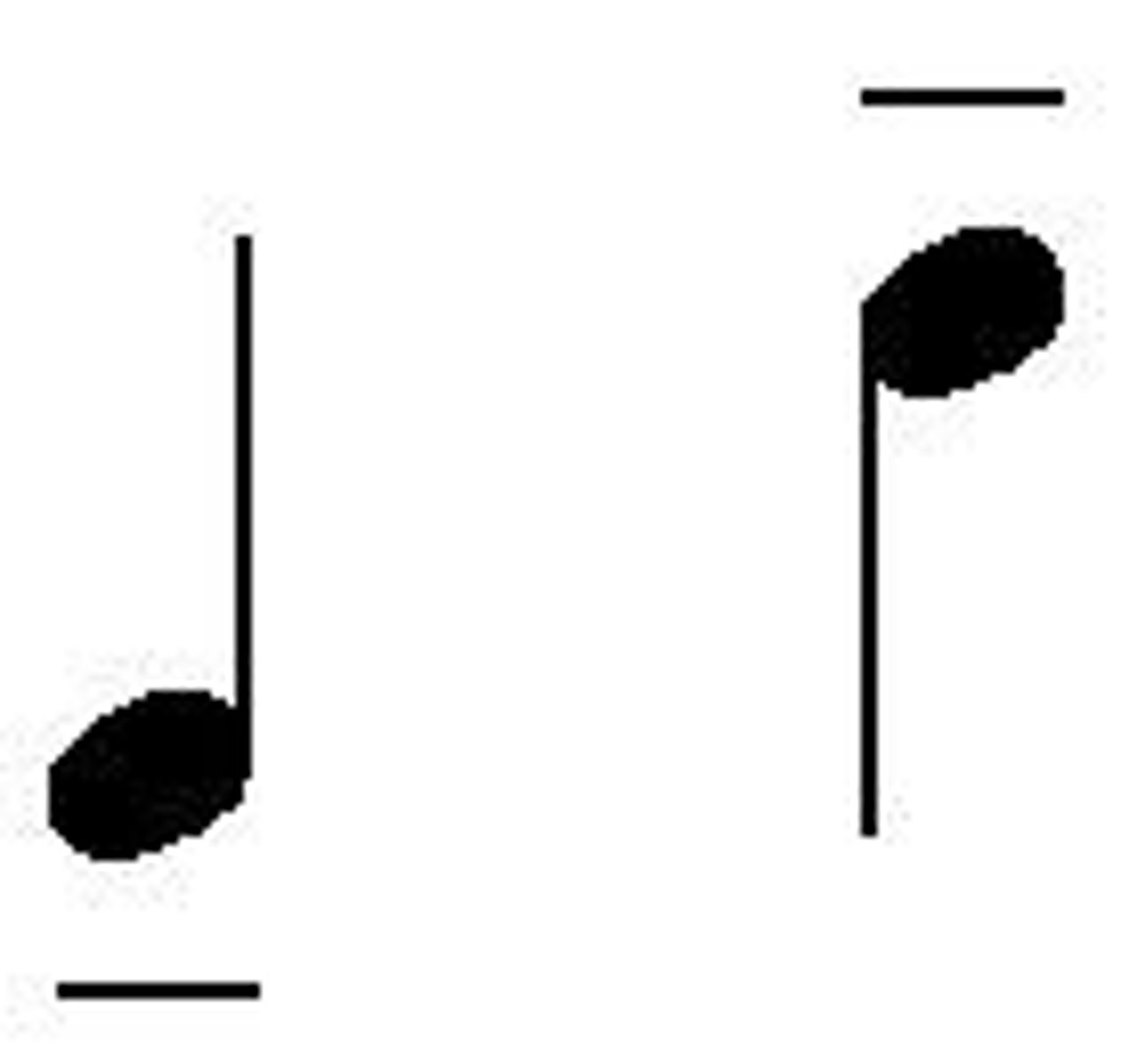
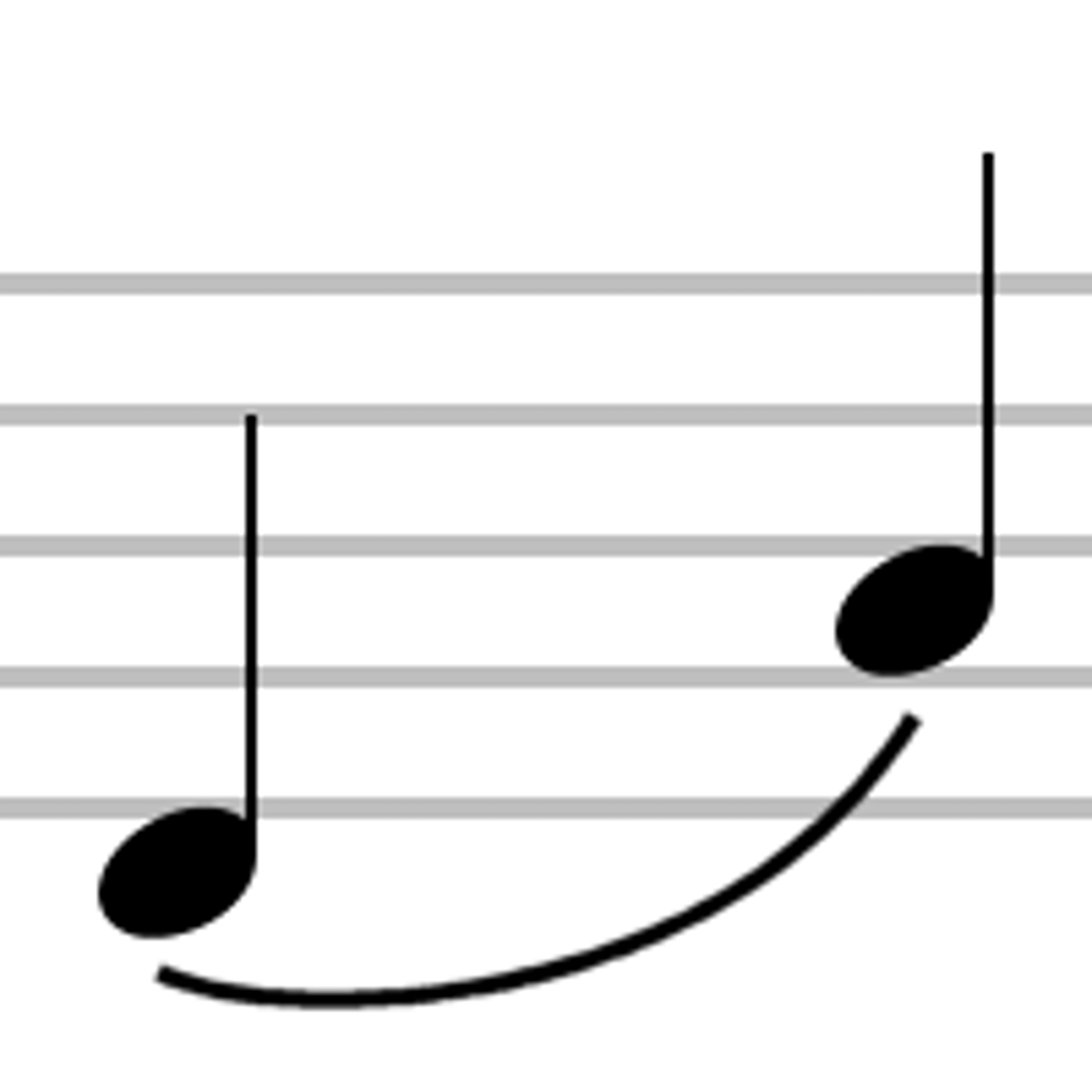
Slur
connected without rearticulating

Staccato
detached
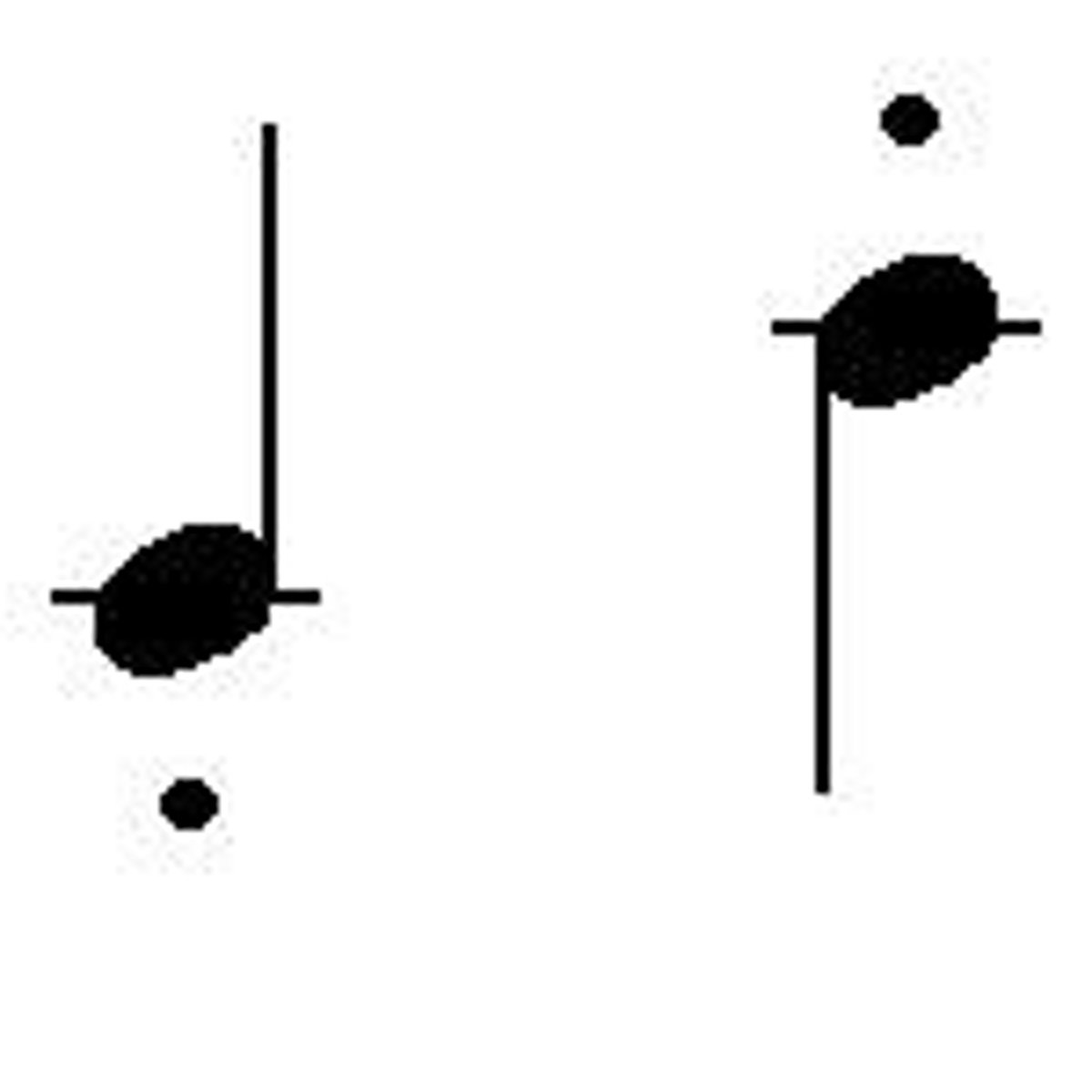
Accent
stronger attack
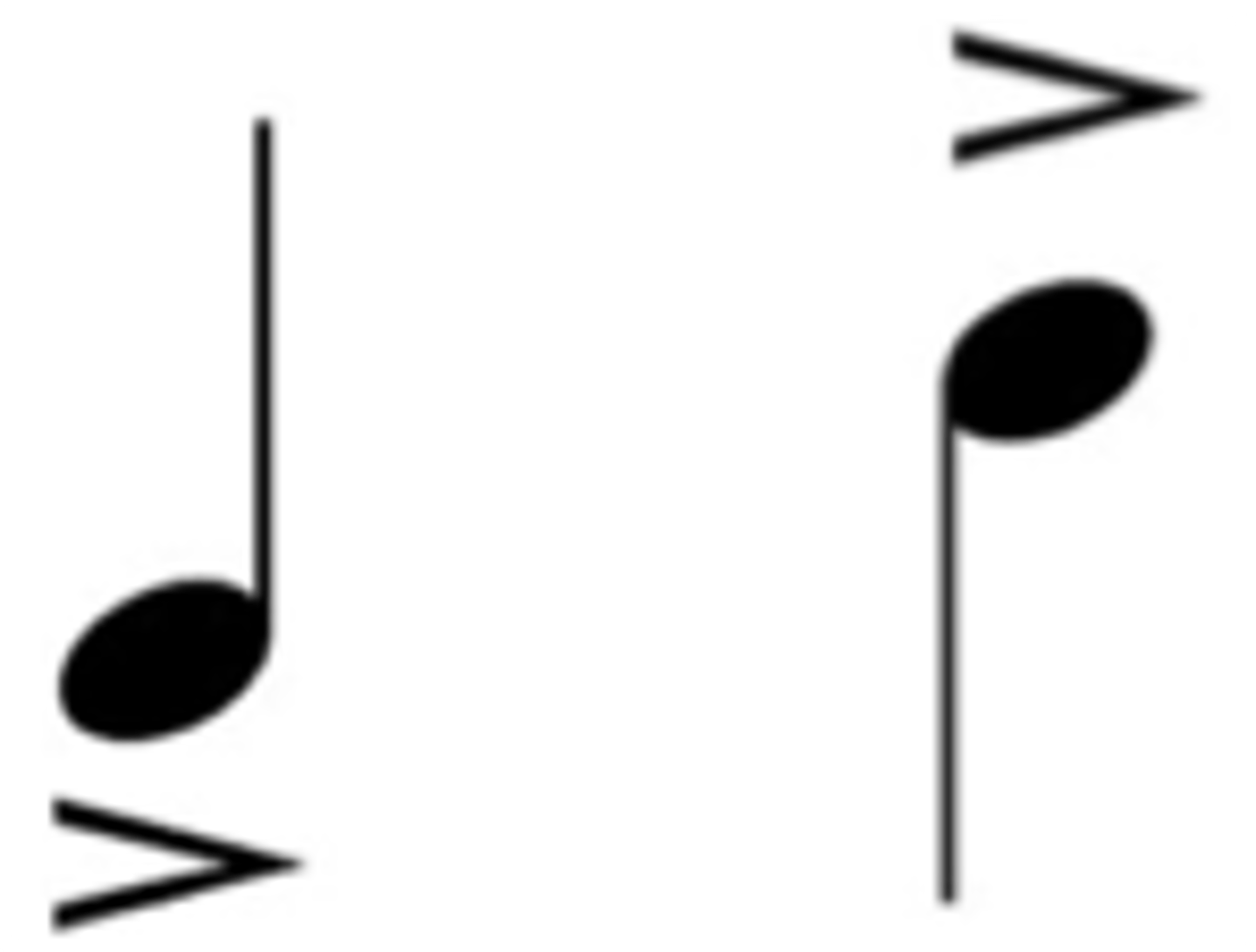

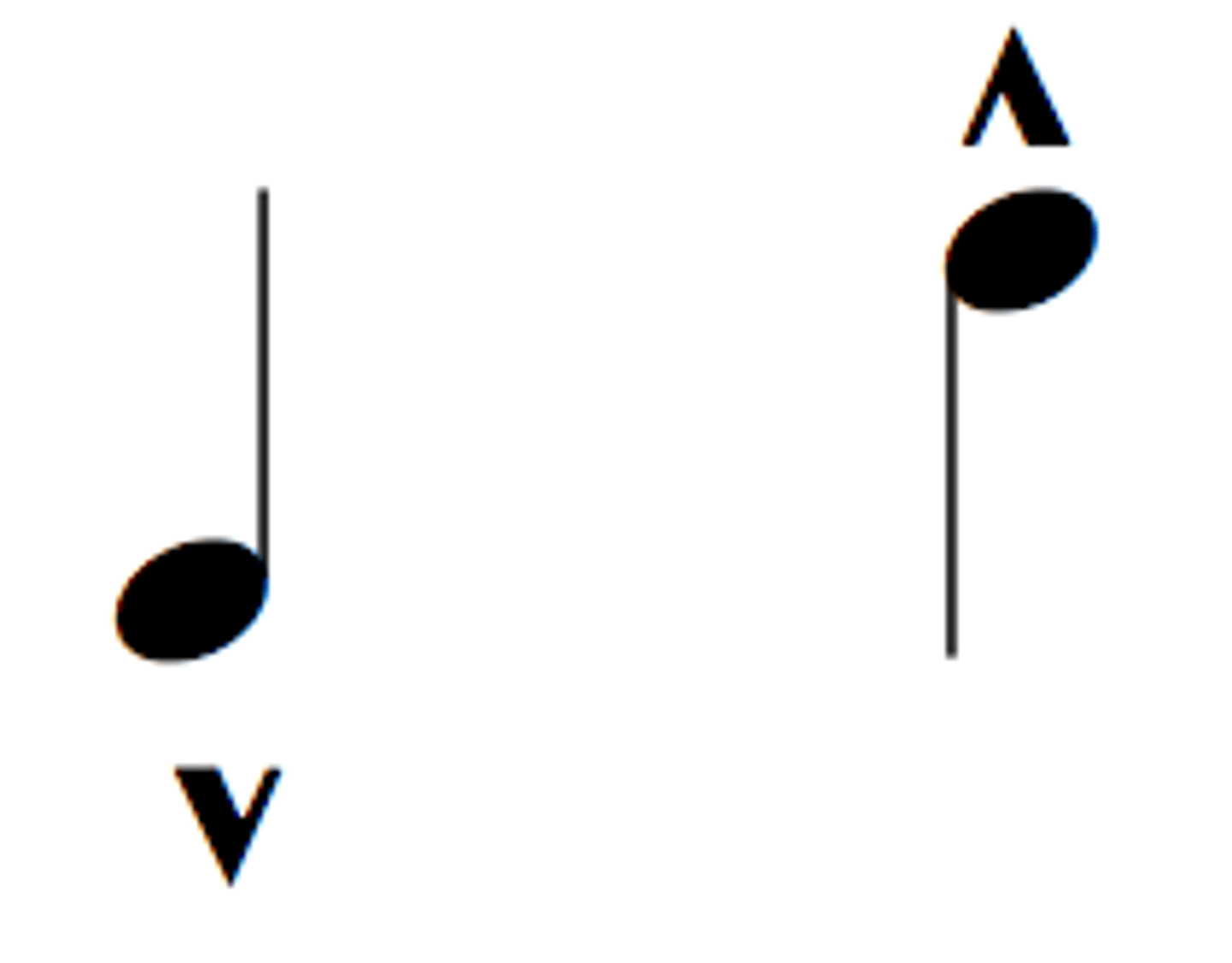
Marcato
heavily accented, clear separation before next note
Natural Minor
major scale with flat 3rd, 6th, and 7th scale degrees
Harmonic Minor
natural minor scale with raised 7th scale degree
Melodic Minor
natural minor scale with raised 6th and 7th scale degrees ascending, natural minor scale descending
Relative Keys
major and a minor scale with the same key signature
Parallel Keys
major and a minor scale with the same tonic
Closely Related Keys
keys that differ by no more than one accidental
Distantly Related Keys
key signatures that differ by more than one accidental
Chromatic Scale
scale of half steps (sharps when ascending, flats when descending)
Whole-Tone Scale
all whole steps
Major Pentatonic Scale
1st, 2nd, 3rd, 5th, 6th of a major scale
Minor Pentatonic Scale
1st, 3rd, 4th, 5th, 7th of a natural minor scale
Interval
distance between two pitches
Harmonic Intervals
distance between simultaneous pitches
Melodic Intervals
distance between successive pitches
Interval Size
number of lines/spaces/letter names between two pitches
Interval Quality
perfect, major, minor, augmented, diminished
Perfect Interval
unison, 4th, 5th, or octave
Major Interval
2nds, 3rds, 6ths, and 7ths
Diminished Interval
minor or perfect interval lowered by a half step
Minor Interval
2nds, 3rds, 6ths, and 7ths lowered by a half step
Augmented Interval
major or perfect interval raised by a half step
Inverted Interval
reversal of the two notes of an interval
Simple Interval
octave or less
Transposing Instrument
sounds at a different pitch than the written note
Timbre
distinctive "coloristc" quality of a sound
Range
total span of pitches than a instrument or voice can produce
Register
specific portion of range (lower register/upper register)
Tessitura
range in which a voice or instrument is most comfortable and produces its most characteristic timbre
Melodic Contour
shape of a melody (ascending, descending, conjunct, disjunct)
Conjunct Motion
stepwise
Disjunct Motion
leaps
Syllabic
one note per syllable
Melismatic
many notes per syllable
Melodic Transposition
melody or melodic segment is moved to a new pitch level, while keeping its intervallic and rhythmic content
Texture
how musical components combine simultaneously to form an overall sound
Monophony
one melodic line (unaccompanied)
Homophony
one melodic voice is prominent over the accompanying lines or voices