Geology: Final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:30 AM on 5/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
1
New cards
How is soil mainly produced?
through weathering
2
New cards
What is weathering?
physical and chemical breakdown of rocks
3
New cards
What is a soil profile?
collection of distinct layers parallel to the surface
4
New cards
how are soil profiles created?
vertical and horizontal movements
5
New cards
what is a soil horizon?
Layers in a soil profile
6
New cards
how can soil horizons distinguished?
Can be distinguished by soil color, texture and composition
7
New cards
How is soil color important?
Can be an important diagnostic tool for analyzing a soil profile, but can be misleading
8
New cards
what does a soils color mean?
The color is a function of its chemical and physical composition and processes within the profile
9
New cards
what does abundant organic material look like?
O and A horizons are dark
10
New cards
what does leaching of inorganic material (iron-bearing) look like?
E horizon is white
11
New cards
what does the presence of clay minerals and iron oxides look like?
B horizon varies from yellow-brown to light red-brown to dark red
12
New cards
what else can soil color indicate?
drainage
13
New cards
what does well drained soil look like?
red color \[air + water + iron -> iron oxide\]
14
New cards
what does poorly drained soil look like?
yellow color
15
New cards
what is soil texture?
fineness or coarseness of soils
16
New cards
whats the diameter of clay?
diameter < 0.004 mm
17
New cards
whats the diameter of silt?
0\.004 mm < diameter < 0.074 mm
18
New cards
whats the diameter of sand?
0\.074 < diameter < 2.0 mm
19
New cards
whats the diameter of gravel?
> 2.0 mm
20
New cards
smallest grain size to the largest?
Clay -> Silt -> Sand -> Gravel
21
New cards
what does saturated mean?
all the pore spaces in a block of soil are completely filled with water
22
New cards
what is moisture content?
amount of water in a soil
23
New cards
why is moisture content important?
Important to strength of soil and potential to shrink and swell
24
New cards
water flow: saturated vs unsaturated
Saturated flow if all the pores are filled with water, unsaturated flow otherwise (more common)
25
New cards
what is subsidence?
ground failure characterized by nearly vertical deformation or the downward sinking of earth materials
26
New cards
what is karst topography?
Dissolution of rocks beneath the surface
27
New cards
examples of subsidence?
Thawing of frozen ground, compaction of sediment, earthquakes and drainage of magma
28
New cards
why do soil volume changes occur?
Result from natural processes, changes in water content of soil, frost heaving
29
New cards
what are the typical forms of subsidence?
* Karst
* Thermokarst formation
* Frost Susceptible soils
* Sediment and soil compaction
* Earthquake
* Underground drainage of magma
* Expansive Soils
* Groundwater Removal
* Thermokarst formation
* Frost Susceptible soils
* Sediment and soil compaction
* Earthquake
* Underground drainage of magma
* Expansive Soils
* Groundwater Removal
30
New cards
what is karst?
refers to landscape characterized by dissolution of bedrock by groundwater (chemical weathering)
31
New cards
why does dissolution occur?
Dissolution occurs as surface water or groundwater flows through rock that is easily dissolved
32
New cards
where is karst formed? what does it dissolve in?
* formed in limestone, dolostone, marble, gypsum, and halite
* dissolve in water (or weak acid)
* dissolve in water (or weak acid)
33
New cards
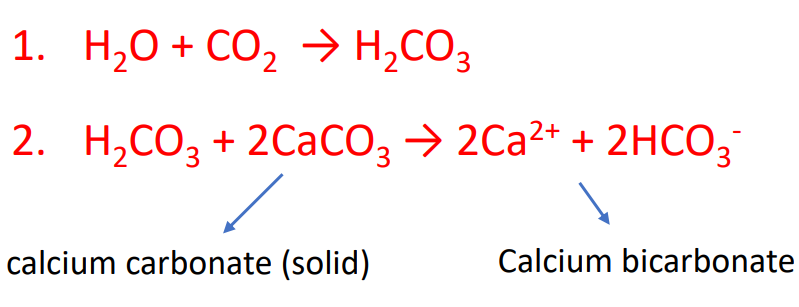
what is this?
Dissolution of bedrock by acidic water
34
New cards
which areas are vulnerable to dissolution?
Areas underlain by dense, thin-bedded, fractured, or well-jointed crystalline limestone are especially vulnerable to dissolution
35
New cards
what are sinkholes?
crater like depressions caused by roof collapse or dissolution
36
New cards
what are the 2 types of sinkholes?
solutional sinkholes and collapse sinkholes
37
New cards
what are the characteristics of karst?
* Sinkholes
* Disappearing streams
* Caves
* Springs
* Karst Tower
* Disappearing streams
* Caves
* Springs
* Karst Tower
38
New cards
when is a karst cave formed?
when dissolution produces a series of caves (groundwater moving)
39
New cards
what is a karst cave formation related too?
changing groundwater table as cave system tend to develop at or near the water table
40
New cards
what is frost heaving?
upward movement of soil particles and the land surface caused by volume increase
41
New cards
what happens during frost heaving?
soils containing water expand when frozen, moves the soil upward
42
New cards
what is permafrost? where does it occur?
Sediment remains frozen throughout the year, exists in polar or high altitude regions
43
New cards
what happens when permafrost melts?
it can create land subsidence
44
New cards
what does extensive melting create?
uneven soil called thermokarst
45
New cards
what has melted a large area over the past 5 decades?
Climatic warming
46
New cards
which soils and sediments can all possibly subside?
Rapidly deposited fine sediment, soil and sediment cemented with soluble minerals, and organic-rich soil
47
New cards
when does the rapidly deposited sediment compact?
when water is removed
48
New cards
when can compaction of sediment and soil occur?
naturally or as the result of human activities.
49
New cards
what do expansive soils do?
Expand during wet periods and shrink during dry periods
50
New cards
where is expansive soil common?
clay, shale, and clay-rich soil
51
New cards
what does expansive soil produce in surfaces?
Often will produce wavy landscape in surfaces, causing tilting and cracking of sidewalks, foundations of buildings
52
New cards
what causes expansive soils?
changes in its moisture content
53
New cards
Where does the majority of soil originate from?
It comes from weathered rock
54
New cards
What is the most important soil particle that characterizes expansive soils?
Clay minerals
55
New cards
What is the correct order of soil grain size from smallest to largest?
Clay, silt, sand, gravel
56
New cards
What does NOT cause ground subsidence?
Creation of permanently frozen ground where no thawing ever occurs
57
New cards
what is the coriolis effect?
earth rotates from west to east beneath the flowing air masses, caused a deflection or apparent change in motion of the wind
58
New cards
The unequal distribution of solar energy that reaches the surface of Earth leads to what?
temperature and pressure gradients that drive atmospheric circulation
59
New cards
how does the coriolis effect behave in the northern hemisphere?
it rotates in a counterclockwise manner => deflection is to the right
60
New cards
how does the coriolis effect behave in the southern hemisphere?
clockwise rotation => deflection is to the left
61
New cards
what is a cyclone?
an area or center of low pressure with rotating winds
62
New cards
how are cyclones classified?
* tropical or extratropical (extratropical: outside of the tropics) based on origin and core temperature
* both characterized by intensity, indicated by sustained wind speeds and lowest atmospheric temperature
* both characterized by intensity, indicated by sustained wind speeds and lowest atmospheric temperature
63
New cards
Tropical cyclones
* Form over warm tropical or subtropical ocean water (5°– 20° latitude)
* Not associated with fronts (warm/cold air boundaries)
* Have warm central cores
* Tropical depressions, tropical storms, hurricanes
* High winds, heavy rain, surges, and tornadoes
* Derive energy from warm ocean water and latent heat
* Not associated with fronts (warm/cold air boundaries)
* Have warm central cores
* Tropical depressions, tropical storms, hurricanes
* High winds, heavy rain, surges, and tornadoes
* Derive energy from warm ocean water and latent heat
64
New cards
Extratropical cyclones
* Form over land or water in temperate regions (30°–70° latitude)
* Related to fronts. Associated with fronts and cool central cores
* Strong windstorms, heavy rains, surges, snowstorms, blizzards
* Typically Less severe, most don’t produce severe weather
* Derive energy from temperature contrasts along fronts
* Related to fronts. Associated with fronts and cool central cores
* Strong windstorms, heavy rains, surges, snowstorms, blizzards
* Typically Less severe, most don’t produce severe weather
* Derive energy from temperature contrasts along fronts
65
New cards
What are hurricanes?
Tropical cyclones in Atlantic and eastern Pacific Oceans (what we call them)
66
New cards
What are typhoons?
Tropical cyclones in Northwest Pacific Ocean (west of International Dateline and north of the equator)
67
New cards
What are cyclones (regional name)?
Tropical cyclones in Indian Ocean
68
New cards
What are nor’easters?
Extratropical cyclone that moves northward along East Coast of the U.S. and Canada
69
New cards
what is the Saffir-Simpson Scale?
Saffir-Simpson Scale classifies hurricanes based on wind speed and its damage-potential, developed by two meteorologists in 1970s
70
New cards
what are extratropical storms named after?
sometimes named after their origins
71
New cards
who names hurricanes?
Tropical storms and hurricanes given names established by international agreement through World Meteorological Organization
72
New cards
what are the rules for naming a hurricane?
* Named once winds exceed 63 km (39 mi.) per hour
* Names assigned sequentially each year from a previously agreed-upon list for each origin
* Male/female names alternated
* Names are reused every 6 years
* Names of big storms are retired (example: Katrina, Harvey)
* Names assigned sequentially each year from a previously agreed-upon list for each origin
* Male/female names alternated
* Names are reused every 6 years
* Names of big storms are retired (example: Katrina, Harvey)
73
New cards
what is a tropical disturbance?
* Most hurricanes starts out as TD
* Typically 200 - 600 km (120 to 370 mi.)
* An organized mass of thunderstorms persisting for > 24 hours
* Associated with elongated area of low pressure (trough)
* Has a weak rotation due to Coriolis effect
* Typically 200 - 600 km (120 to 370 mi.)
* An organized mass of thunderstorms persisting for > 24 hours
* Associated with elongated area of low pressure (trough)
* Has a weak rotation due to Coriolis effect
74
New cards
what are tropical disturbances formed by?
* Lines of convection similar to squall lines
* Upper-level low pressure troughs OR
* Cold front remnants
* Easterly waves of converging and diverging winds, such as Atlantic Ocean hurricanes
* Upper-level low pressure troughs OR
* Cold front remnants
* Easterly waves of converging and diverging winds, such as Atlantic Ocean hurricanes
75
New cards
what are tropical depressions?
Tropical disturbance wind speeds increase and begins to spin, a low-pressure center is formed
76
New cards
what are tropical storms?
* Not all tropical depressions develop into tropical storm
* Sustained winds increase to 63 km (39 mi.) per hour
* Storm is given a name
* Wind speeds are not at hurricane strength, but rainfall can be intense
* Sustained winds increase to 63 km (39 mi.) per hour
* Storm is given a name
* Wind speeds are not at hurricane strength, but rainfall can be intense
77
New cards
how are hurricanes classified?
Classified when winds reach 119 km (74 mph)
78
New cards
what are the environmental conditions of a hurricane?
* Thick layer of warm ocean water, at least 26 °C (\~80 F) & depth of 46 m (\~150 ft)
* Steep vertical temperature gradient, atmosphere must cool quickly with increasing altitude, which allows moist air to continues to be unstable and uplift
* Weak vertical wind shear (wind speed change), shear: Strong winds aloft prevent hurricane development
* Disturbance is far enough away from the equator, coriolis effect is strong enough to cause rotation around the region of low pressure
* Steep vertical temperature gradient, atmosphere must cool quickly with increasing altitude, which allows moist air to continues to be unstable and uplift
* Weak vertical wind shear (wind speed change), shear: Strong winds aloft prevent hurricane development
* Disturbance is far enough away from the equator, coriolis effect is strong enough to cause rotation around the region of low pressure
79
New cards
what are rain bands?
clouds that spiral inward around center, contains numerous thunderstorms, counter-clockwise in Northern Hemisphere, increase in intensity towards the center of the hurricane
80
New cards
what is the eyewall?
innermost band of clouds, contain the greatest winds and rainfall, constantly changing as the storm progresses
81
New cards
what is the eye of a hurricane?
area of calm at center of the hurricane, strong surface winds that converge towards the center never reach it, narrow at surface and wider at top, diameters range from 3 to more than 37 mi
82
New cards
where do tropical cyclones have the greatest impact?
Tropical cyclones have the greatest impact on coastal areas with warm offshore waters, such as the Gulf of Mexico and the Gulf Stream along the East Coast.
83
New cards
which area of the US has a higher risk for hurricanes and why?
The East and Gulf Coasts of the United States have the highest risk for tropical storms and hurricanes in North America, moving direction: tend to move west-northwest, temperature: 80s F vs 70s F
84
New cards
which is more active: Northwest pacific or north Atlantic
Northwest Pacific is much more active than North Atlantic (3X)
85
New cards
why do the South Atlantic and southeast Pacific rarely have hurricanes?
because of cold ocean water
86
New cards
why do hurricanes not form close to the equator?
because of the absence of the Coriolis effect
87
New cards
whats the risk of extratropical cyclones in the US?
* Severe weather from extratropical cyclones is greater in the interior of the continent but may also occur in coastal areas.
* Creates winter storms along Pacific Coast and snowstorm in Nevada, Rocky Mountains
* Spring and summer thunderstorms and tornadoes in United States and Canada
* Creates winter storms along Pacific Coast and snowstorm in Nevada, Rocky Mountains
* Spring and summer thunderstorms and tornadoes in United States and Canada
88
New cards
What is a typhoon?
A hurricane in the Western Pacific Ocean, such as Japan and China
89
New cards
What is the primary difference between a tropical depression and a tropical storm?
Wind speed
90
New cards
What is the correct order of tropical cyclone development (least to most developed)?
Tropical disturbance, tropical depression, tropical storm, hurricane
91
New cards
Which of the following locations has the least risk for hurricanes: Florida, Texas, California, New Jersey?
California
92
New cards
What is climate?
characteristic atmospheric conditions over a long period of time (years or decades)
93
New cards
What is weather?
atmospheric conditions over a short period of time (days or weeks)
94
New cards
What is the atmosphere comprised of?
mainly of nitrogen and oxygen with smaller amounts of other gases
95
New cards
What are permanent gases?
* Gasses whose proportions stay constant
* Nitrogen(N2 ), Oxygen(O2 ) and Argon(H2 )
* Have little effect on atmospheric dynamics
* Nitrogen(N2 ), Oxygen(O2 ) and Argon(H2 )
* Have little effect on atmospheric dynamics
96
New cards
What are variable gases?
* Gasses whose proportions vary with time and space
* Play important roles in atmospheric dynamics
* Carbon dioxide, water vapor, ozone et.
* Play important roles in atmospheric dynamics
* Carbon dioxide, water vapor, ozone et.
97
New cards
What are aerosols?
* Microscopic particles whose proportions vary with time and space
* Not a gas, but microscopic liquid or solid particles (from dust, or fossil fuels)
* Not a gas, but microscopic liquid or solid particles (from dust, or fossil fuels)
98
New cards
What is a cryosphere?
* The part of the hydrosphere where water stays frozen year-round
* Permafrost, sea ice, ice caps, and glaciers
* Permafrost, sea ice, ice caps, and glaciers
99
New cards
Where do glaciers flow?
Glaciers flow from high areas to low areas under the weight of accumulated ice
100
New cards
What is a glacier input?
new snow forms ice at high elevations