Everything I didn't know from PMT
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/364
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:47 AM on 4/18/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
365 Terms
1
New cards
What is relative atomic mass
the mean weighted mass of an atom of an element compared with 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon-12
2
New cards
What is relative molecular mass
the mean weighted mass of a molecule compared with 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon-12
3
New cards
What is relative formula mass
the sum of the mean weighted masses of all atoms in the formula of a compound compared with 1/12th the mass of an atom of cabron-12
4
New cards
What is relative isotopic mass
the mass of an atom isotope compared with 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon-12
5
New cards
What is a mole
the amount of substance containing as many particles as there are atoms in 12g of carbon-12.
\
1 mole = 6.02 x 10^23 items
\
1 mole = 6.02 x 10^23 items
6
New cards
how is % yield calculated
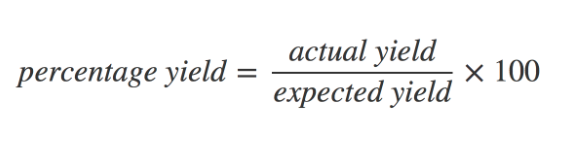
7
New cards
how is % composition by mass calculated
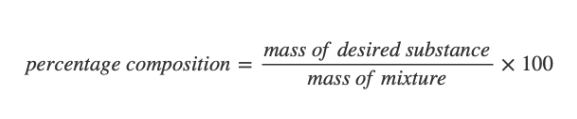
8
New cards
how is a standard solution prepared from a concentrated solution
* a certain volume of the concentrated solution is added to a volumetric flask in order to get the desired final volume
* distilled water is added to the volumetric flask up to the line on its neck
* distilled water is added to the volumetric flask up to the line on its neck
9
New cards
What are orbitals
regions in the space around an atom where electrons are most likely to be found, they can contain a maximum of two electrons
10
New cards
How are e- arranged in orbitals
* electrons fill from the lowest energy orbital first
* electrons will prefer to occupy orbitals by themselves, and will only pair with other electrons if no other lower energy orbitals are available to fill
* electrons will prefer to occupy orbitals by themselves, and will only pair with other electrons if no other lower energy orbitals are available to fill
11
New cards
How are orbitals filled on the energy level diagram drawn
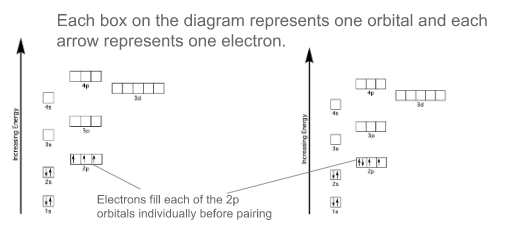
12
New cards
What did the Geiger-Marsden experiment show
it showed that the atom contained a very small, dense, positive nucleus
13
New cards
What is fusion
when two lighter nuclei collide and combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy
14
New cards
Why do giant covalent lattices have a much greater melting point than simple covalent molecules
the covalent bonds between the atoms in a covalent lattice are much stronger than the London forces between the simple covalent molecules
15
New cards
Why are ionic substances only conductive when dissolved
when ions are in a solid, they are unable to move so they cannot carry charge. dissolving the solid causes the ions to be mobile, so they are free to carry charge
16
New cards
Why do both covalent and ionic lattices have high melting points
both lattices contain atoms that have multiple strong bonds around them, these bonds take a lot of heat energy to break
17
New cards
All the bond angles
18
New cards
how do different numbers of bonded and lone pairs produce different shapes in molecules
lone pairs repel more than bonded pairs
19
New cards
How does bonding occur in an ionic lattice
the attraction between ions of different charges and the repulsion between ions of the same charge causes overall attraction in the lattice
20
New cards
what is first ionisation enthalpy
the enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of electrons is removed from one mole of gaseous atoms
21
New cards
why does first ionisation energy increase as we move across a period
the number of protons in the nucleus increases which increases the nuclear charge and thus the nuclear force felt by outer electrons it therefore takes more energy to remove them
22
New cards
what is the formula of a sulfate ion

23
New cards
what is the formula of a carbonate ion
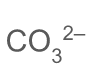
24
New cards
what is the formula of an ammonium ion
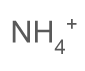
25
New cards
what is the formula of a hydrogencarbonate ion

26
New cards
Why does first ionisation energy decrease down a group
* the number of shells in the atom decreases, which increases shielding of outer electrons from the nucleus
* the nuclear radius also increases
* both of these factors mean that the attractive nuclear force felt by the electron is smaller, so it takes less energy to remove outer electrons
* the nuclear radius also increases
* both of these factors mean that the attractive nuclear force felt by the electron is smaller, so it takes less energy to remove outer electrons
27
New cards
How do the charge densities of group 2 ions affect the thermal stability of their carbonates
smaller ions with the same charge have higher charge densities and distort the carbonate ion, so that the compound will decompose at a lower temperature
28
New cards
how can we test for Fe2+ ions
* add OH- ions
* the green solution will form a green precipitate
* the green solution will form a green precipitate
29
New cards
how can we test for Fe3+ ions
* add OH- ions
* the yellow solution will form an orange precipitate
* the yellow solution will form an orange precipitate
30
New cards
how can we test for Cu2+ ions
* add OH- ions
* the blue solution will form a blue precipitate
* the blue solution will form a blue precipitate
31
New cards
how can we test for NH4+ ions
* add NaOH (aq) to a boiling tube containing the NH4+ ions
* warm the boiling tube
* any vapours given off by the tube will turn damp red litmus paper blue if NH4+ ions are present
* warm the boiling tube
* any vapours given off by the tube will turn damp red litmus paper blue if NH4+ ions are present
32
New cards
how can we test for Al3+ ions
* add OH- ions
* the colourless solution will form a white precipitate
* the colourless solution will form a white precipitate
33
New cards
What should you add before adding AgNo3 in halide tests
* add a few drops of HNO3
* shake the test tube
* shake the test tube
34
New cards
how can we test for SO4 2- ions
* add Ba2+ ions
* a white precipitate should form
* a white precipitate should form
35
New cards
how can we test for CO3 2- ions
* add dilute nitric acid
* if effervescence occurs than CO3 2- ions are present
* if effervescence occurs than CO3 2- ions are present
36
New cards
How can we test for
* Li+
* Na+
* K+
* Ca+
ions
* Li+
* Na+
* K+
* Ca+
ions
* evaporate the water from the sample
* moisten a test wire and collect the solid residue from the evaporating dish
* pass this residue into a bunsen burner and record the colour of the flame
* moisten a test wire and collect the solid residue from the evaporating dish
* pass this residue into a bunsen burner and record the colour of the flame
37
New cards
Flame test colour of: Na+
orange
38
New cards
Flame test colour of:Ca+
brick red
39
New cards
Flame test colour of: Li+
red
40
New cards
how can we test for Pb2+ ions
* add OH- ions
* a white precipitate will form
* upon adding excess OH- ions, the precipitate will dissolve
* a white precipitate will form
* upon adding excess OH- ions, the precipitate will dissolve
41
New cards
What’s an alkali
a species that releases OH- ions in solution
42
New cards
What’s a base
a soluble alkali
43
New cards
What is neutralisation
when the proton on an acid molecule is replaced by a metal ion (or ammonia), forming a salt and water
44
New cards
how do group 2 oxide react with water
MO + H2O --→ M(OH)2
\
Group 2 oxides are therefore basic as they release OH- ions when dissolved
\
Group 2 oxides are therefore basic as they release OH- ions when dissolved
45
New cards
place the following in order of decreasing frequency:
Infra red
X-Rays
Microwaves
Gamma Rays
Infra red
X-Rays
Microwaves
Gamma Rays
* Gamma Rays
* X-Rays
* Infra red
* Microwaves
* X-Rays
* Infra red
* Microwaves
46
New cards
What is volume measured in in the ideal gas equation
m^3
47
New cards
How can you predict the yield of a reaction
* work out the number of moles of a reactant you have used
* multiply by the ratio between the chosen reactant and product
* multiply by the Mr of the product
\
\
* multiply by the ratio between the chosen reactant and product
* multiply by the Mr of the product
\
\

48
New cards
what is the difference between a pi and a sigma bond
* a sigma bond is caused by the direct overlap of the p-orbitals of carbon atoms
* pi bonds are caused by the indirect ‘leaning’ overlap of p-orbitals
* pi bonds are caused by the indirect ‘leaning’ overlap of p-orbitals
49
New cards
What is a double bond
consists of one pi bond and one sigma bond
50
New cards
what is the meaning of the term endothermic
* reactions that take energy in from the surroundings
* the energy needed to break the bonds is greater than the energy needed to make the bonds in the reaction
* the energy needed to break the bonds is greater than the energy needed to make the bonds in the reaction
51
New cards
what is the meaning of the term exothermic
* reactions that release energy into the surroundings
* the energy needed to break the bonds is less than the energy needed to make the bonds in the reaction
* the energy needed to break the bonds is less than the energy needed to make the bonds in the reaction
52
New cards
what are standard conditions
* pressure: 100 kPa
* temperature: 298 K (room temp)
* all solutions: a concentration of 1 mol dm^-3 for electrode potentials
* temperature: 298 K (room temp)
* all solutions: a concentration of 1 mol dm^-3 for electrode potentials
53
New cards
\
define the standard enthalpy change of reaction
define the standard enthalpy change of reaction
* the enthalpy change that occurs when species are reacted in the molar ratios as defined by a chemical equation
* the reaction takes place under standard conditions with reactants and products in their standard states
* the reaction takes place under standard conditions with reactants and products in their standard states
54
New cards
define the standard enthalpy change of combustion
the enthalpy change that occurs when a species is reacted with one mole of oxygen under standard conditions with products and reactants in their standard states
55
New cards
define the standard enthalpy change of formation
the enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states under standard conditions
56
New cards
define the standard enthalpy change of neutralisation
the enthalpy change that occurs when one mole of water is produced from a neutralisation that happens under standard conditions
57
New cards
What is average bond enthalpy
the energy needed to break one mole of the stated bond under standard conditions
58
New cards
what relation does bond enthalpy have to bond strength
* the greater the bond enthalpy, the greater the bond strength
* as the bond strength increases the length of the bond decreases
* as the bond strength increases the length of the bond decreases
59
New cards
Is bond breaking exo or endo
endothermic
60
New cards
Is bond making exo or endo
exothermic
61
New cards
what does each term mean in q=mc△T
q= the energy absorbed by the material (normally water) in J
m= the mass of material being used in g
c= the specific heat capacity of the material used
△T= the change in temperature of the material
m= the mass of material being used in g
c= the specific heat capacity of the material used
△T= the change in temperature of the material
62
New cards
what is a catalyst poison
a substance that reduces the effectiveness of the catalyst by permanently bonding to the active sites
63
New cards
What does the heterogeneous catalyst look like
the reactants form partial bonds with the catalyst, adsorbing onto the surface, because the reactants are in close proximity, successful collisions are more frequent
64
New cards
What are some common simple molecular pollutants
* CO2, CO, NOx, SOx
* unburnt hydrocarbons
* unburnt hydrocarbons
65
New cards
what are some methods of reducing co2 emissions
using renewable sources of electricity such as solar or wind power as well as using electric or hydrogen powered cars can be methods of reducing CO2 emissions
66
New cards
what are some methods to reduce CO and unburnt hydrocarbons
using more efficient engines and catalytic converters in cars
67
New cards
how can NOx and SOx emissions be reduced
modifications to engines and the fuels used can reduce NOx and SOx emissions
68
New cards
What's an aliphatic hydrocarbon
a hydrocarbon that does not contain any aromatic rings and is a straight or branched chain hydrocarbon
69
New cards
What is a functional group
a group of atoms on a carbon chain that gives the molecule its properties
70
New cards
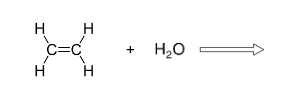
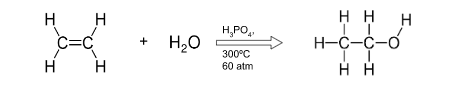
Complete with conditions- H2C2H2 + H2O
\
\
\
\
conditions:
H3PO4
300 degrees celcius
60 atm
\
\
H3PO4
300 degrees celcius
60 atm
\
\
71
New cards
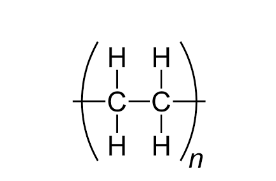
What is the name of this polymer (-C-C-)n
\
\
\
\
poly(ethene)
72
New cards
What is an electrophile
a species that accepts a lone pair of electrons in a reaction
73
New cards
What is a carbocation
a hydrocarbon that contains a positively charged carbon atom, it is normally unstable and occurs as an intermediate in electrophilic additions
74
New cards
How are organic mechanism confirmed empirically
the products of the reaction are analysed when different anions are used in the reaction
75
New cards
What are structural isomers
hydrocarbons with the same molecular formula, but different structural formulae
76
New cards
What are stereoisomers
hydrocarbons with the same structural formula, but different arrangements of their atoms in 3D space
77
New cards
Why does stereoismerism occur around a double bond
free rotation is restricted around the double bond. when each carbon has two different groups attached to it different arrangements are possible about the C=C bond
78
New cards
What is cis-trans isomerism
a type of E-Z isomerism that occurs when each carbon in the double bond has one group in common
79
New cards
what are some benefits of using fossil fuels
* fossil fuels are readily available due to all the infrastructure to use them already being in place
* fossil fuels are cheaper than alternatives
* fossil fuels are very efficient at producing energy: they have a high energy density
* fossil fuels are cheaper than alternatives
* fossil fuels are very efficient at producing energy: they have a high energy density
80
New cards
what are some risks of using fossil fuels
* burning fossil fuels causes greenhouse gases to be released which contribute greatly to global warming
* burning fossil fuels causes air pollutants to be released which pose a health risk to humans
* fossil fuels reserves are limited, and may start to run out in the near future
* burning fossil fuels causes air pollutants to be released which pose a health risk to humans
* fossil fuels reserves are limited, and may start to run out in the near future
81
New cards
how is atom economy calculated

82
New cards
what are the benefits of a high atom economy
* less waste is produced from the reaction, which makes it cheaper
* the reaction requires less natural resources so it is more sustainable
* the reaction requires less natural resources so it is more sustainable
83
New cards
What is electrolysis
the breaking down of a substance using electrical energy
84
New cards
How is electrolysis done in a lab
two non-reactive electrodes are connected to the power supply and placed in the solution, the power is turned on and electrolysis starts
\
use the following setup
\
use the following setup
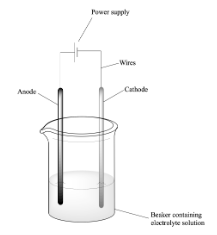
85
New cards
How does electrolysis work
* the cations are attracted to the cathode and are reduced
* the anions are attracted to the anode and oxidised
* the compound is therefore broken up as the two ions do not need each other to be stable
* the anions are attracted to the anode and oxidised
* the compound is therefore broken up as the two ions do not need each other to be stable
86
New cards
½ equations for electrolysis of NaCl
2Cl- (aq) ---→ Cl2 (g) + 2e-
2H+ (aq) + 2e- ----→ H2 (g)
2H+ (aq) + 2e- ----→ H2 (g)
87
New cards
What is an oxidising agent
a substance that removes electrons form other species by accepting electrons and getting reduced
88
New cards
What is a reducing agent
a substance that donates electrons to other species by getting oxidised
89
New cards
What does bromine look like under standard conditions
a red-brown liquid
90
New cards
What does iodine look like under standard conditions
a violet solid
91
New cards
Why does reactivity decrease down G7
* the number of electron shells increase, this increases the shielding from the nucleus as well as the atomic radius
* both of these factors decrease the nuclear attraction of outer electrons, making it harder for the halogen to gain electrons
* both of these factors decrease the nuclear attraction of outer electrons, making it harder for the halogen to gain electrons
92
New cards
Why does volatility decrease down G7
* halogens only have intermolecular london forces between their molecules
* as we move down the group the number of electrons in the halogen molecule increases, thus the london forces between the molecules become stronger, taking more energy to break
* as we move down the group the number of electrons in the halogen molecule increases, thus the london forces between the molecules become stronger, taking more energy to break
93
New cards
Why are halogens more soluble in cyclohexane than water
halogen molecules are non-polar, so they do not dissolve very well in polar solvents like water, but they will dissolve readily in non-polar solvents like cyclohexane
94
New cards
What are the solubilities of silver halide precipitates in ammonia
* AgCl: soluble in dilute ammonia
* AgBr: soluble only in concentrated ammonia
* AgI: insoluble in dilute and concentrated ammonia
* AgBr: soluble only in concentrated ammonia
* AgI: insoluble in dilute and concentrated ammonia
95
New cards
How are hydrogen halides prepared
X- + H3PO4 ---→ HX + H2PO4-
\
\
\
\
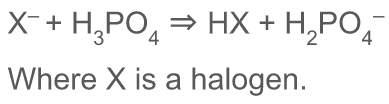
96
New cards
How are hydrogen halides prepared
97
New cards
how does HBr react with H2SO4
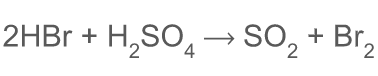
98
New cards
Why is HF a weaker acid than HCl
the F- ion forms ionic bonds with the H3O+ ions in solution, which means there is an equilibrium between the bound and unbound forms of the acid
\
\
\
\

99
New cards
what are some uses of chlorine
* sterilisation of water
* bleaching for use in the paper or textiles industry
* bleaching for use in the paper or textiles industry
100
New cards
what are some risks associated with the storage and transport of chlorine
* chlorine is extremely toxic and can cause irreversible lung damage and eye damage upon exposure
* some chlorine compounds, such as those made when exposed to water, are carcinogenic
* some chlorine compounds, such as those made when exposed to water, are carcinogenic