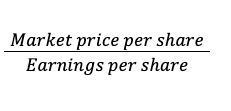CH 20 - Stockholders' Equity
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
LO 20-1 — Term & Def
Stockholders’ Equity
difference between recorded assets and recorded liabilities for a corporation.
LO 20-1 — Term & Def
Is Stockholders’ equity a claim on specific assets?
No, it’s a claim on total assets after liabilities are recognized.
LO 20-1
Stockholders’ equity is a ________ interest and has no existence without the presence of _______.
Residual; assets
LO 20-1
What are the five components of Stockholder Equity?
Paid-in Capital,
Retained Earnings,
Accumulated OCI,
Treasury Stock,
Noncontrolling interest.
LO 20-1
Paid-in Capital or contributed capital consists of…
Capital Stock (Preferred and Common Stock) and additional paid-in capital
LO 20-1 — Capital Stock Term:
Par Value
Value per share of stock designated in the articles of incorporation.
LO 20-1 — Capital Stock Term:
Authorized shares
Number of shares of stock that can be issued legally, as specifically in the charter of the corporation.
LO 20-1 — Capital Stock Term:
Issued shares
Number of shares of authorized capital stock that has been issued to stockholders.
LO 20-1 — Capital Stock Term:
Unissued shares
Number of shares of authorized capital stock that has not been issued – that is, the difference between authorized shares and issued shares.
LO 20-1 — Capital Stock Term:
Outstanding shares
Number of shares issued, less the number of shares repurchased and currently held by the company as treasury stock. Outstanding shares are used for earning per share calculations.
LO 20-1 — Capital Stock Term:
Treasury shares
Shares previously issued and later repurchased by the corporation that are still held (equal to the difference between issued shares and outstanding shares).
LO 20-1
Common Stock is the primary issue of shares. Ownership rights include: Vote in ________ meetings, Receipt of ________, share in asset distribution upon ________, and Right to a ____ _______ purchase of shares with new share offerings.
Shareholder; dividends; liquidation; pro rata
LO 20-1
Preferred stock has preferences that distinguish it from common stock. The most common preference is…
a priority of dividend claims.
LO 20-1
Additional Paid-in Capital reports the value of assets received above ____ or stated value.
Par
LO 20-1
Different types of additional paid-in capital accounts are ______ for reporting purposes. For example, Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par–Common Stock, Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par–Preferred Stock and Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par–Treasury Stock.
Combined
LO 20-1
Retained Earning is the accumulated net income/loss less ________ _______ and other amounts transferred to equity accounts, adjusted for any prior period adjustments (net of tax).
Accumulated dividends
LO 20-1
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income is…
Changes in equity defined as OCI, accumulated since a company’s inception.
LO 20-1
OCI is presented _____ of tax.
Net
LO 20-1
Treasury Stock is stock that has been issued, _______ by the issuer, but not resold or retired.
Reacquired
LO 20-1
What type of account is treasury stock?
Contra equity account
LO 20-1
Noncontrolling interest represents…
the amount of a company’s net assets (assets less liabilities) owned by outside investors in one of a company’s subsidiaries that are not part of the controlling stockholders’ interest (>50% interest).
LO 20-2
If stock is issued for noncash asset (ex. land), measure at ______ of the stock issued or the noncash _______ received, whichever is most reliably determinable.
FV; consideration
LO 20-2
What are the two methods for multiple securities issued for a lump-sum amount?
Proportional allocation and Incremental allocation
LO 20-2
Proportional allocation
Allocate lump sum based on the relative FV of each security when the FV of each individual security is known.
LO 20-2
Incremental allocation
When the FV of one security is known, allocate remainder of lump sum to security with unknown FV.
LO 20-2
What determines whether Proportional or incremental allocation is used?
Whether both FV is known or only one is known of a security
LO 20-2
What are stock issue costs?
Registration fees, underwriter commissions, attorney and accountant fees, printing costs, administrative costs and promotional costs
LO 20-2
When incurring a stock issue cost where do you record it?
Record a reduction to paid in capital in excess of par.
LO 20-3
What are motivations to reacquire common stock?
Satisfaction of stock compensation award, increase market price of stock, distribution excess cash to shareholders, and Thwart takeover attempt
LO 20-3
What is the journal entry for acquisition of treasury stock?
Dr. Treasury Stock and Cr. Cash
LO 20-3
What is the journal entry for sale of treasury stock?
Dr. Cash and Cr. Treasury Stock (+ DR/CR of Paid-in Capital–Treasury Stock)
LO 20-3
In the sale of treasury when cash received is greater than acquisition cost, the difference is ______ to paid-in capital–Treasury Stock.
Credited
LO 20-3
In the sale of treasury when cash received is less than acquisition cost, the difference is ______ to paid-in capital–Treasury Stock if the prior credit balance in that account is sufficient to absorb the debit. Any excess is ______ to Retained Earnings
Debited
LO 20-3
What is the journal entry for retirement of treasury stock?
Dr. Common Stock and Additional Paid in Capital. Cr. Treasury Stock. Balance with paid-in Capital–Treasury Stock (and possibly Retained Earnings)
LO 20-3
What is the journal entry for direct retirement?
Dr. Common Stock and Additional Paid in Capital. Cr. Cash (and DR/CR to Paid-in Capital–Retired Stock)
LO 20-3
In the direct retirement when cash paid is greater than original issuance price, the difference is ______ to paid-in capital–Retired Stock.
Credited
LO 20-3
In the direct retirement when cash paid is greater than original issuance price, the difference is ______ to paid-in capital–Retired Stock if the prior credit balance in that account is sufficient to absorb the debit. Any excess is ______ to Retained Earnings.
Debited
LO 20-4
What are some features of Preferred stock?
Callable,
Redeemable,
Mandatorily redeemable,
Convertible
Cumulative dividend preference.
LO 20-4 — Terms & Def
Callable
Allows the issuer the option to recall (buy back) shares at a specified price.
LO 20-4 — Terms & Def
Redeemable
Allows the stockholder the option to redeem stock (return stock to issuer for payment) at a specified price.
LLO 20-4 — Terms & Def
Mandatorily redeemable
Any of various financial instruments issued in the form of shares that embody an unconditional obligation requiring the issuer to redeem the instrument by transferring its assets at a specified or determinable date (or dates) or upon an event that is certain to occur.
LO 20-4 — Terms & Def
Convertible
A security that is convertible into another security based on a conversion rate. For example, convertible preferred stock that is convertible into common stock on a two-for-one basis (two shares of common for each share of preferred).
LO 20-4 — Terms & Def
Cumulative dividend preference
Requires dividends not declared in a given year to accumulate at the preference rate for the stock. The issuer must pay cumulative dividends in full before dividends can be paid on common stock. If preferred dividends are not declared in a given year, they are said to have been passed and are called dividends in arrears on the cumulative preferred stock.
LO 20-5
What are the three dividends touched upon in LO-5?
Cash Dividends, Property Dividends and Liquidating Dividends
LO 20-5
What does Cash Dividends reduce?
Retained Earnings
LO 20-5
What does Property Dividends reduce?
Retained Earnings
LO 20-5
What does Liquidating Dividends reduce?
Additional paid-in capital
LO 20-5
Date of declaration by the board of directors
Increase liabilities and decrease retained earnings
LO 20-5
Ex-Dividend date
No journal entry. Stockholders from the date forward do not receive the declared dividend. AKA the cut-off day.
LO 20-5
Date of record.
No journal entry. Stockholders on the date of record will receive the dividend.
LO 20-5
Date of cash payment to shareholders
Decrease liabilities and decrease assets. Current dividends on preferred stock (and any cumulative dividends in arrears) paid before common shareholders are paid.
LO 20-6
What is a stock dividend?
Proportional distribution of additional shares of a company’s own stock to its shareholders.
LO 20-6
Before a stock split the company has 400 shares of stock and wants a stock dividend of 10%, how much total stock is after this split?
440 shares. (400*110%=440)440 shares. (400*110%=440)
LO 20-6
After a stock split, will the ownership percentage change?
No. the ownership percentage will stay the same as everyone gets the stock split.
LO 20-6
What are the motivations for stock dividends?
To continue dividend distributions without disbursing needed cash for operations, to increase the number of shares outstanding; reducing the market price per share and possibly increasing trading of shares on the market; to convey that a portion or earnings will remain permanently in the business
LO 20-6
What are small stock dividends?
Generally < 20-25% of outstanding shares. Recognized at fair value. No net impact of SE unless fractional shares are paid in cash
LO 20-6
What is the entry upon declaration of small stock dividends?
Dr. RE (at fair value) Cr. Common Stock Dividend Distributable (at par) Cr. Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par (Remainder)
LO 20-6
What is the entry upon distribution of small stock dividends?
Dr Common Stock Dividends Distributable Cr. Common Stock
LO 20-6
What are stock split effected in the form of a dividend (large stock dividend)?
Generally > 20-25% of outstanding shares. Recognized at par value. No impact of Stockholders’ equity.
LO 20-6
What is the entry upon declaration of large stock dividends?
Dr. RE (at par value) Cr. Common Stock Dividend Distributable (at par)
LO 20-6
What is the entry upon distribution of large stock dividends?
Dr Common Stock Dividends Distributable Cr. Common Stock
LO 20-6
Does stock splits require a journal entry?
No.
LO 20-6
What is a 2-for-1 stock split?
Doubles shares and reduces par value by one-half. Results in an increase in the number of shares and a decrease in market price per share.
LO 20-6
In a 2-for-1 stock split, what happens to one share of common stock at $1 par per share?
Turns into one share of common stock at $0.50 par per share.
LO 20-6
What is a reverse 2-for-1 stock split?
Drops the number of shares by one-half and doubles the par value per share. Results in a decrease in the number of shares and an increase in the market price per share.
LO 20-6
In a reverse 2-for-1 stock split, what happens to two one share of common stock at $0.50 par per share?
Turns into one share of common stock at $1 par per share.
LO 20-7
What is included in Comprehensive Income?
Net Income and Other Comprehensive Income
LO 20-7
Is it OCI? Unrealized holding gain or loss on AFS debt securities.
Yes.
LO 20-7
Is it OCI? Gain or loss related to postretirement benefit plans.
Yes.
LO 20-7
Is it OCI? Gain or loss from foreign currency translation adjustments.
Yes.
LO 20-7
Is it OCI? Gain or loss from adjustments to a cash flow hedge.
Yes.
LO 20-7
What are the two ways to present the Statement of Comprehensive Income?
One single continuous statement or two statements of income and comprehensive income.
LO 20-7
Is it OCI? Unrealized Gains/Losses on Trading Securities
No. These go directly to the income statement.
LO 20-7
Is it OCI? Realized Gains/Losses on Any Investments
No. Once an investment is sold, gains/losses go through net income.
LO 20-7
Is it OCI? Interest Income and Dividend Income
No. Always included in net income
LO 20-7
Is it OCI? Impairment Losses on Assets.
No. Run through the income statement.
LO 20-7
Is it OCI? Operating Expenses and Revenues
No. (Sales, COGS, SG&A, etc.)
LO 20-8
The following are examples of Equity Disclosures: Number of shares _______, issued or outstanding, and par value. Changes in ________________ account and in the number of shares of equity securities. Rights and privileges associated with the company’s securities such as __________ and __________ preferences, participation rights, call prices, and conversion rates. Restrictions to retained earnings.
Authorized; stockholders’ equity; dividend: liquidation
LO 20-8
What are the Equity Ratios?
Book Value per Share,
Payout ratio,
return on equity
price-to-earnings ratio.
LO 20-8
What does a Book value per share ratio tell us?
Measures common shareholder investment per share
LO 20-8
What is the equation for Book value per share ratio?
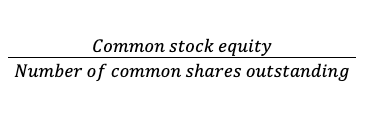
LO 20-8
What does a Payout ratio tell us?
Computes proportion of income paid as dividends
LO 20-8
What is the equation for Payout ratio?

LO 20-8
What does a Return of equity ratio tell us?
Computes the return on investment by owners
LO 20-8
What is the equation for Return of equity ratio?
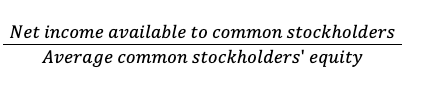
LO 20-8
What does a Price-to-earnings ratio tell us?
Measures market price per dollar of EPS
LO 20-8
What is the equation for Price-to-earnings ratio?