Chapter 6: Internal Control in a Financial Statement Audit
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
what is the purpose of internal control (2)
midigate risk
prevent or detective
auditor or management
________has the responsibility to maintain controls that provide
reasonable assurance that adequate control exists over the entityʼs assets and records.
management
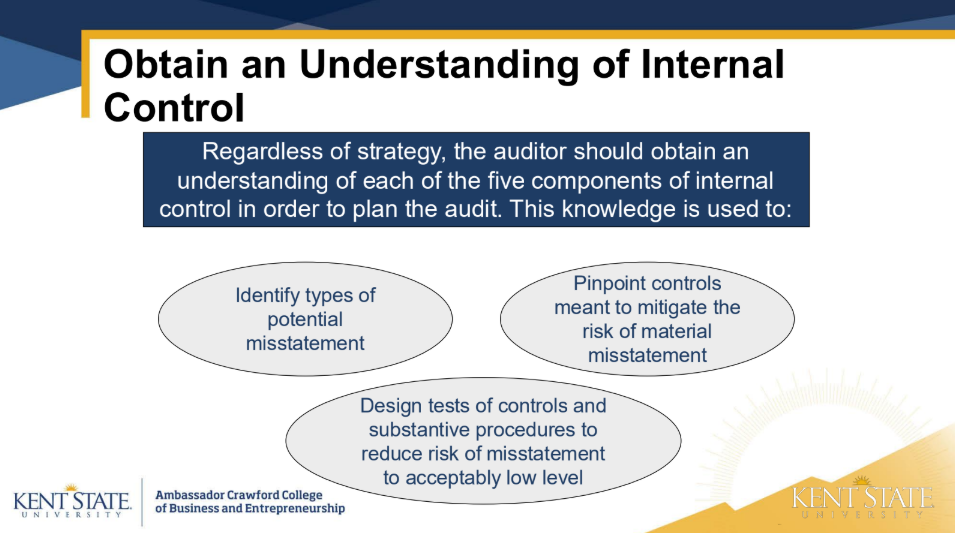
The auditor uses risk assessment procedures to: (4)
• understanding internal control
• Identify key controls
• types of potential misstatements
• Design tests of controls and substantive procedures
The auditor’s understanding of the internal control is a major factor in determining the overall audit strategy.
auditor or managerment responabilities
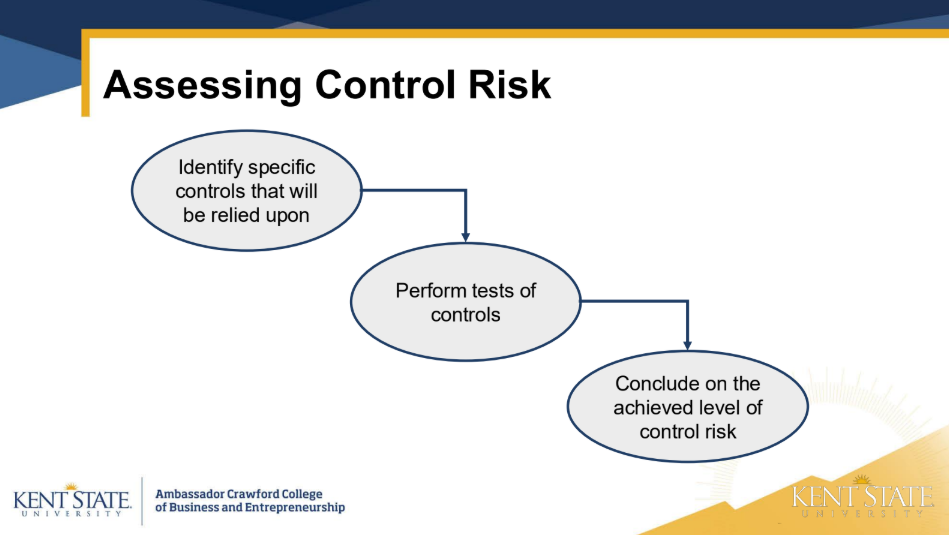
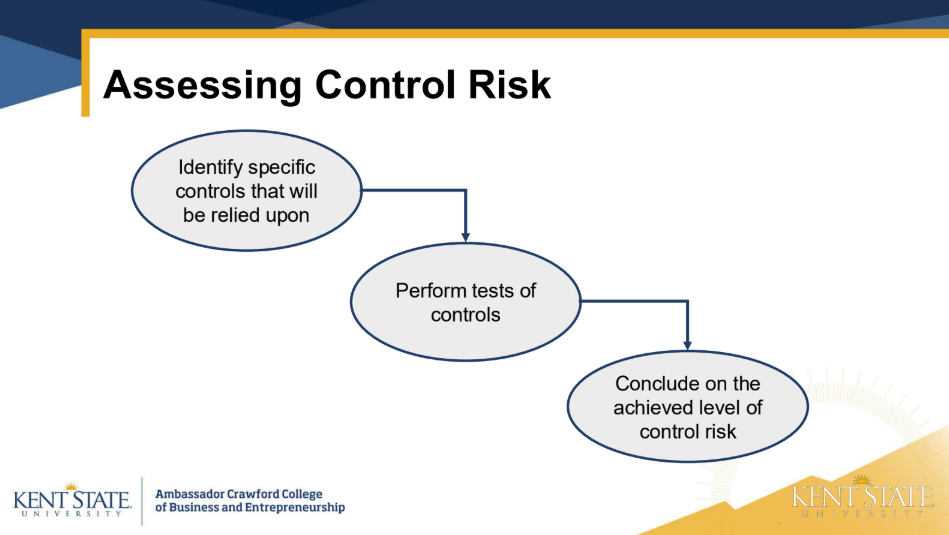
1) Obtain an understanding of internal controls
2) Assess control risk
auditor
An auditor’s primary consideration regarding an entity’s
internal controls is whether they
A.Prevent management override
B.Relate to the control environment
C.Reflect management’s philosophy and operating style
D.Affect the financial statement assertions
D.Affect the financial statement assertions
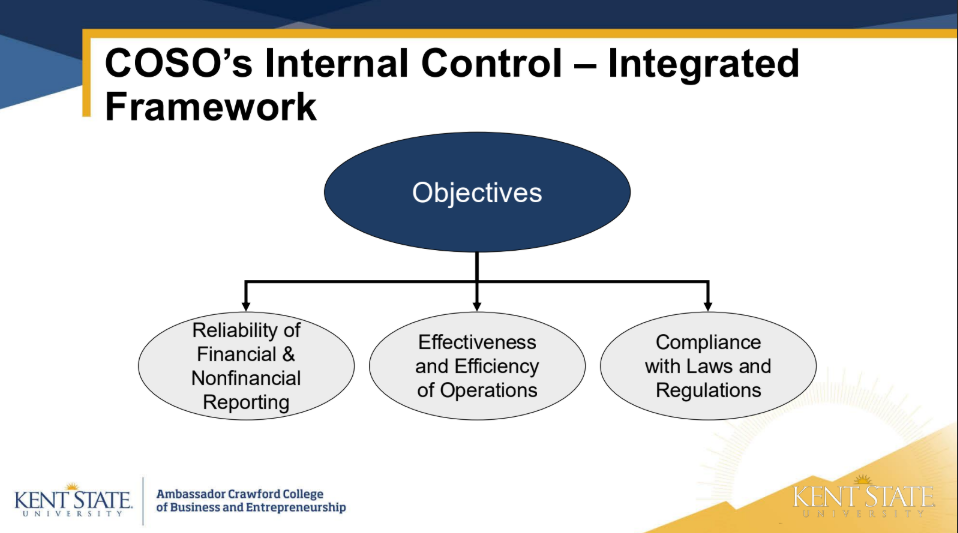
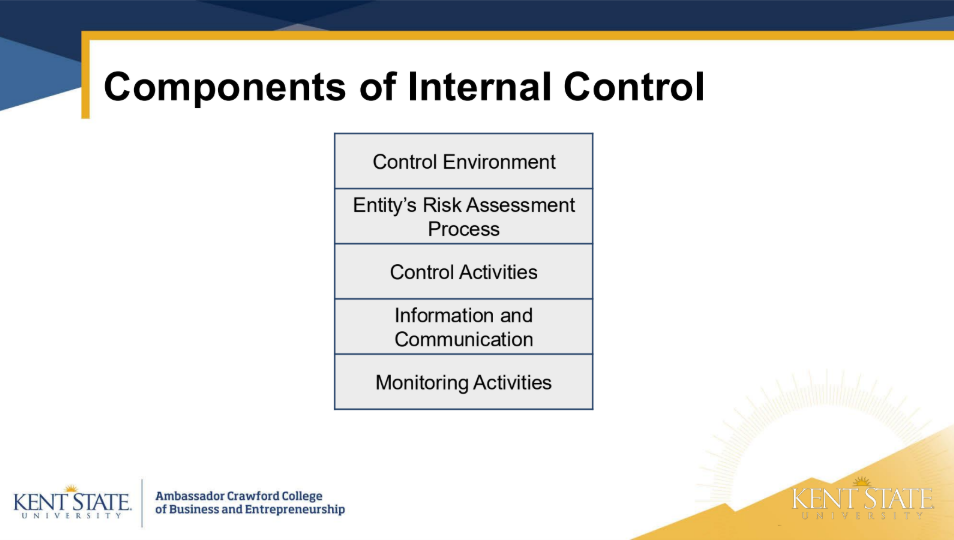
what is control environment
The control environment consists stuff form the foundation for internal control, set by the board and senior management
what is risk assessment
a dynamic process of identifying and analyzing risks to achieving objectives
what is control activities
actions taken by management's to reduce risks and help achieve objectives
what is information and communcation
what’s needed to run internal controls and meet objectives. Clear communication helps staff understand their roles and keeps management informed.
what is monitoring activities
Internal controls are monitored through ongoing or separate evaluations to ensure all components are working. Issues are reviewed and serious problems are reported to senior management and the board.
reason why control will be set at high
controls do not pertain to an assertion
controls are assessed as ineffective
testing the effectiveness of controls is inefficient
what is a reliance strategy
• Plan to rely on internal control and assess control risk at a
lower level
the level of control risk is set in terms of assertion about classes of transactions and event, and related disclosures, for the period under audit
Substantive vs. Reliance Strategy - How are they different?
• Substantive Strategy: Set CR at the max
• Reliance Strategy: Set preliminary CR below the max, test controls, then
adjust CR based on results of tests of controls
After obtaining an understanding of an entity’s internal control system, an auditor may set control risk at high for some assertions because the auditor
A.Believes the internal controls are unlikely to be effective
B.Determines that the pertinent internal control components are not well documented
C.Performs tests of controls to restrict detection risk to an acceptable level
D.Identifies internal controls that are likely to prevent material misstatements
A.Believes the internal controls are unlikely to be effective
how does entity size effect on internal control
All companies should have the five components of internal control, but in small or midsize businesses, they’re usually less formal than in large companies.
what are the 3 limitation of an entity’s internal control
management override of internal control
human errors of mistakes
collusion
Which of the following audit techniques would likely provide an auditor with the least assurance about the effectiveness of the operation of a control?
A.Inquiry of entity personnel
B.Reperformance of the control by the auditor
C.Observation of entity personnel
D.Walkthrough
A.Inquiry of entity personnel
what is control deficiency
A control deficiency exists when a control’s design or operation doesn’t let staff prevent or catch mistakes in time
what is significant
A control deficiency that's not severe but still important enough to report to those in charge.
what is material weakness
A control deficiency that could likely cause a material misstatement to go unnoticed or uncorrected in time.