DSA03 - Pediatric GI Anomalies
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
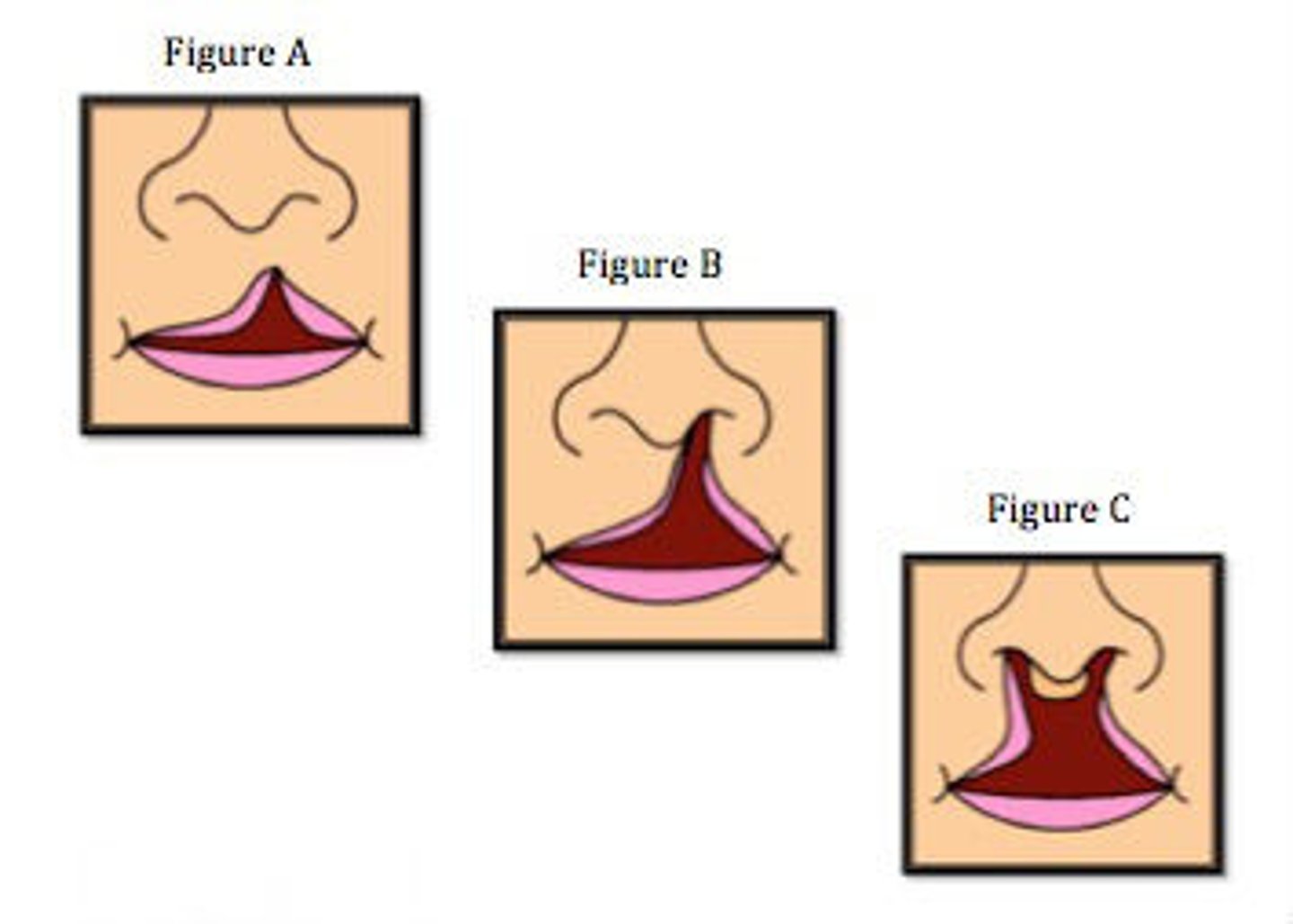
Cleft Lip
Define Condition:
Abnormal gap at upper lip
-Hx: Present at birth
-Path: When these do not fuse at 5 weeks gestation
> Median nasal processes merge --> Intermaxillary process
> Intermaxillary process merges w/ maxillary prominence & lateral nasal process ==> Upper Lip
-Sx/PE:
> Unilateral or Bilateral Defect
> May be complete (extends up to nostril) OR incomplete (extends only part way to nostril)
-Dx:
> Routine Prenatal Ultrasounds (20 weeks)
> Seen upon birth
-Tx: SURGERY
> Cut tissue near cleft and rearrange to close opening, then realign
-Prog: Can feed and develop normally
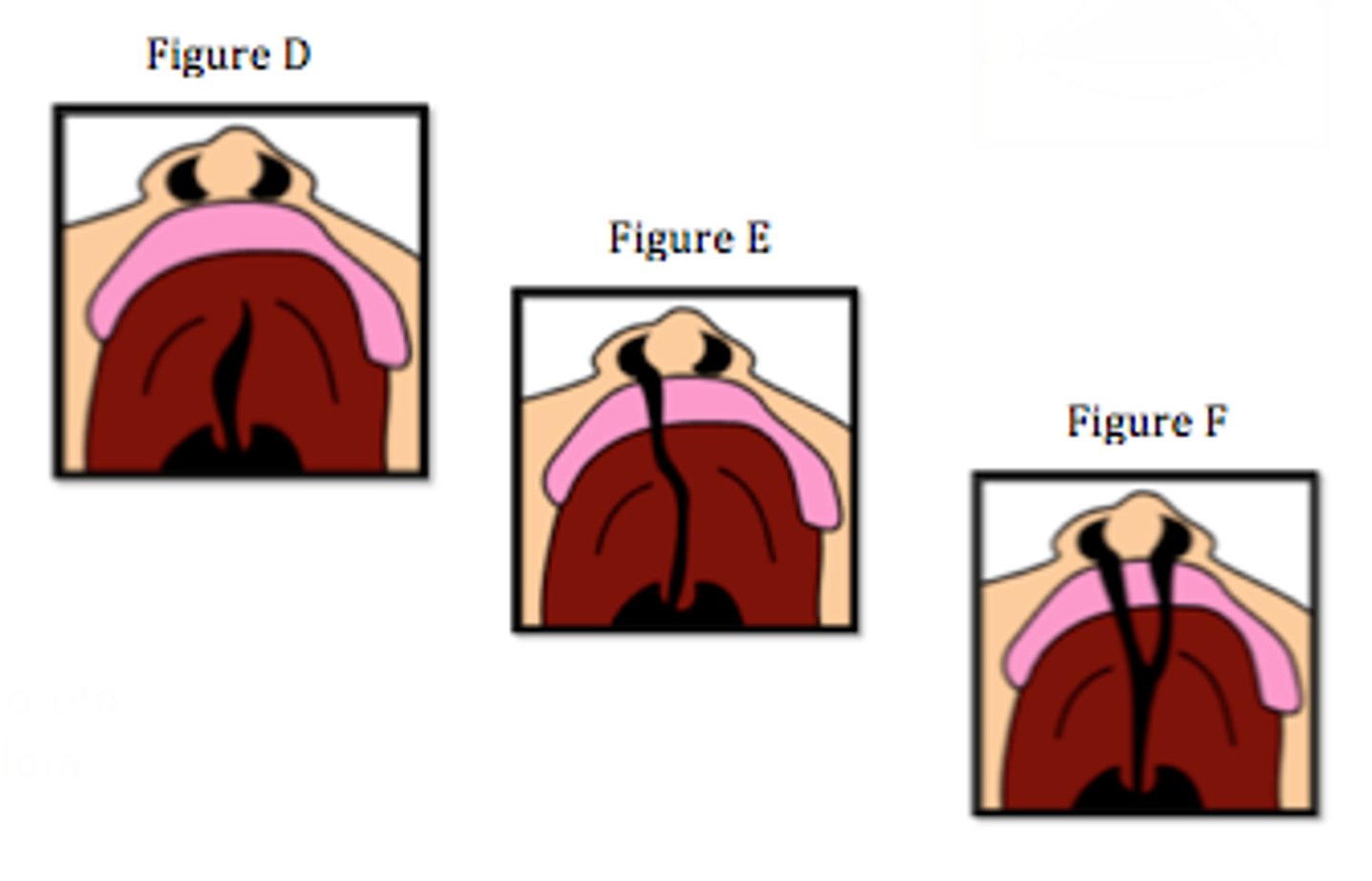
Cleft Palate
Define Condition:
Abnormal gap at roof of mouth
-Hx: Present at birth
-Path: When the primary palate (from intermaxillary process) & secondary palate (midline fusion of lateral palatine shelves from maxillary prominences) do not fuse normally by 8-12 weeks gestation
-Sx/PE:
> May be unilateral or bilateral
> May be complete (across whole palate) or incomplete (only part way across palate)
-Dx:
> Detected on first newborn PE after inserting finger into newborn's mouth (less on prenatal ultrasounds)
-Tx: SURGERY
> Cut and rearrange tissue around cleft to close opening
-Prog:
> Prevents from feeding (can't suction)
> Abnormal speech sounds
> Recurrent middle ear infex and effusions ==> HEARING LOSS
Cleft Lip; Cleft Palate
(Cleft Lip/Cleft Palate) is twice as common as (Cleft Lip/Cleft Palate)
Leads to underdeveloped or missing pharynx --> Nasopharyngeal portion of eustachian tube can't open ==> middle ear can't drain
How does a Cleft Palate make a newborn more susceptible to Recurrent middle ear infections?
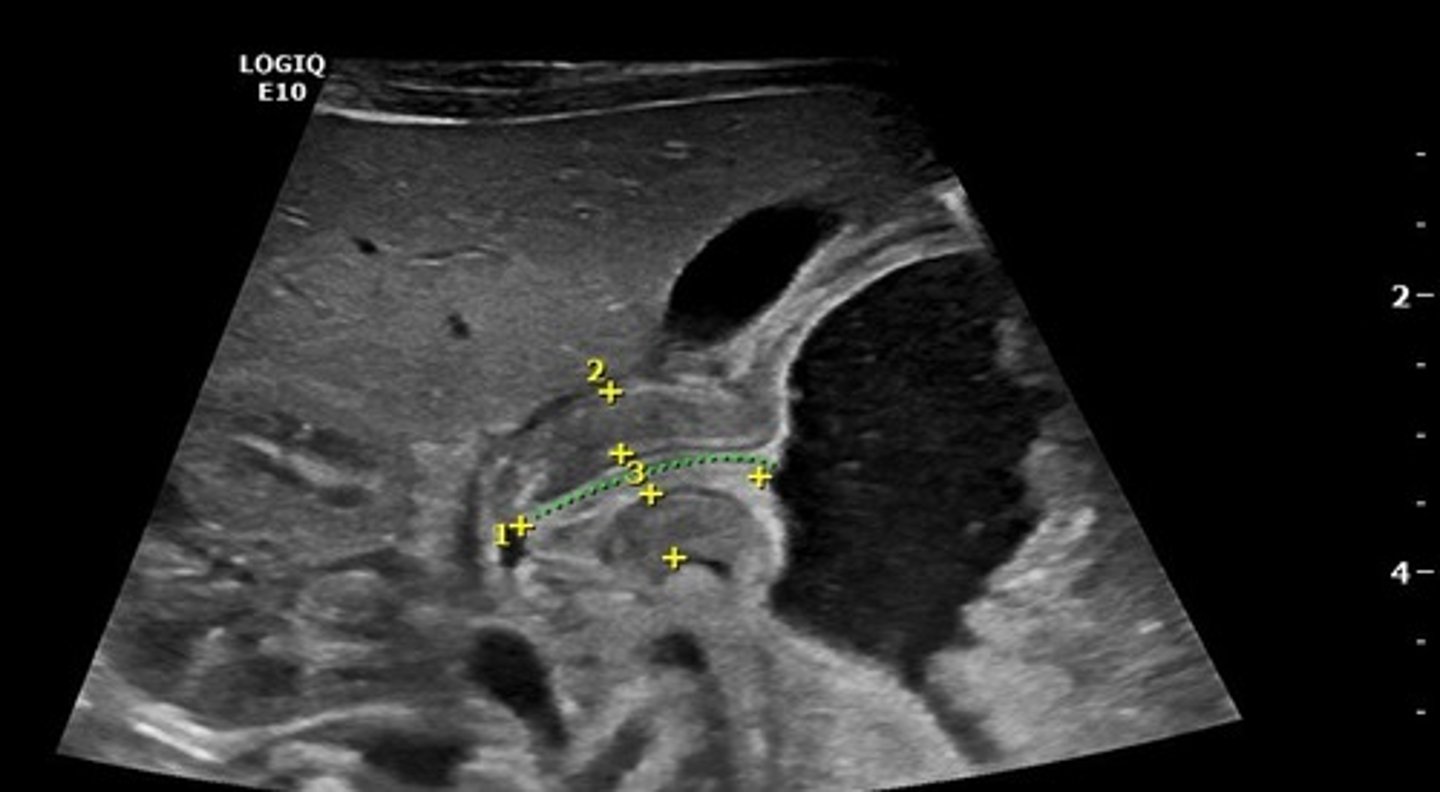
Infantile Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis (IHPS)
Define Condition:
Narrowed opening between stomach and duodenum
-Hx:
> Seen in INFANTS btwn 2 weeks and 6 weeks (MC in Firstborn children)
> MORE in MALES
-Path: D/t hypertrophy of pylorus --> near-complete obstruction of gastric outlet
> Genetics
> MATERNAL SMOKING
> When babies Txed w/ Erythromycin or Azithromycin
-Sx:
> PROJECTILE & FORCEFUL VOMITING
> Want to be fed RIGHT after vomiting (Hungry Vomiters)
> Dehydration & Wt Loss (if Untreated)
-PE:
> "Olive-like" Abdominal Mass in RUQ
> Peristaltic waves from left to right in abdomen (stomach trying to squeeze contents past obstruction)
> Dehydration (Dry mucous membranes, can't cry, diminished pulses)
> Low Wt/Thin
> WON'T Have Abdominal Distension OR High-Pitched Bowel Sounds
-Dx:
> 1st = Abdominal US
> Labs (if later)
>> Hypochloremia
>> Metabolic alkalosis
>> Hypokalemia (from volume depletion, since RAAS activated)
-Tx:
> 1st = CORRECT DEHYDRATION/ELECTROLYTE ABNS w/ IV FLUID
> Pyloromyotomy = Incision made to outer aspect of pylorus muscle --> inner portion bulges outward to relieve obstruction
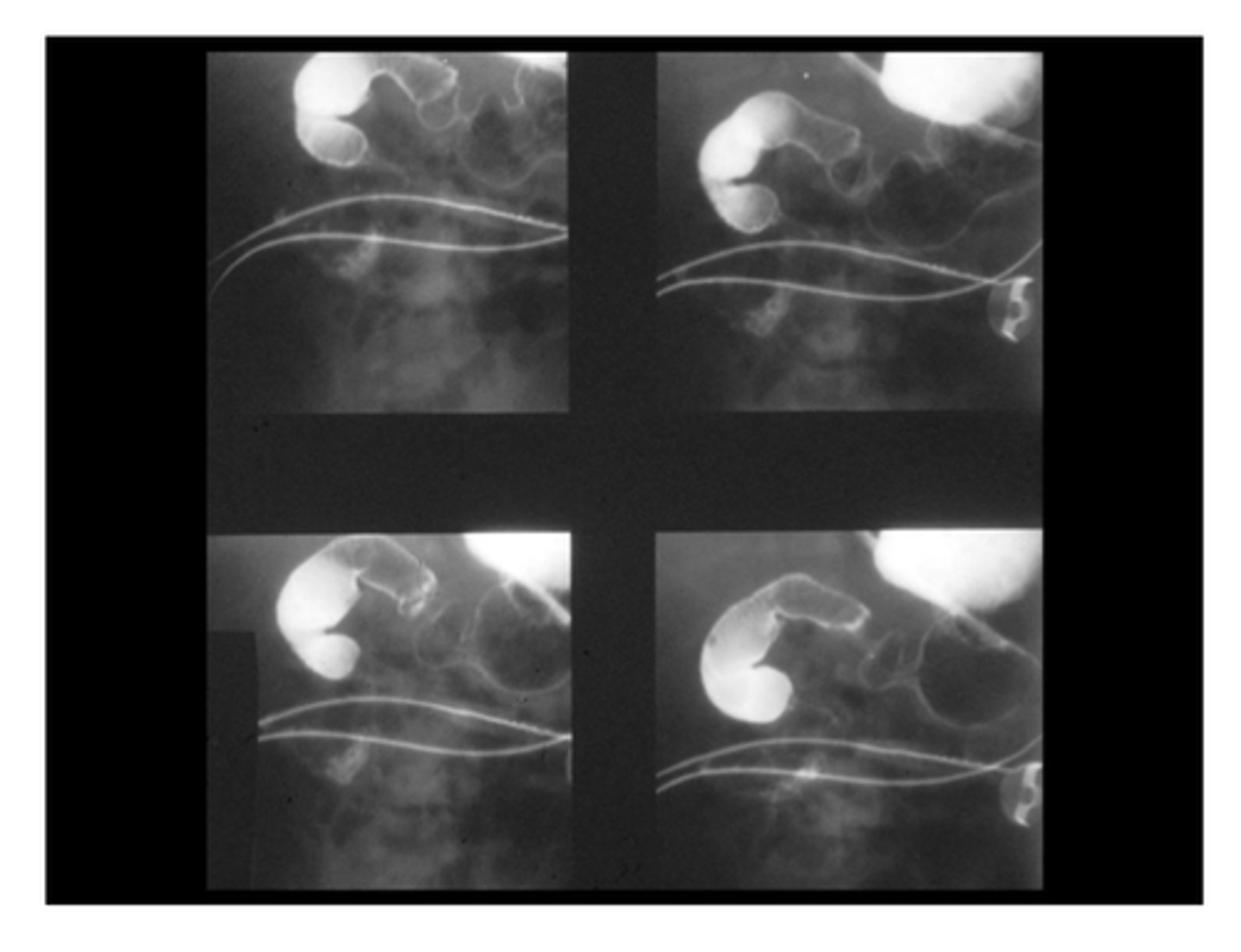
Small Intestinal Atresia
Define Condition:
Congenital discontinuity occurring in SI (segment of SI is absent/so narrow that nothing can pass through)
-Hx: Prenatal or First 2 days of life
-Path:
> 60% = Duodenum
>> D/t failure of GI tract to "recanalize" (open up) during embryologic development during 8-10 weeks of gestation
> 20% = Jejunum/Ileum
>> D/t interruption of SI's vascular supply during fetal life (something preventing blood from fetus' distal SI)
-Sx/PE: If not seen on US
> BILIOUS EMESIS (obstruction DISTAL to Ampulla of Vater)
> Abdominal Distension
> Inability to pass meconium
-Dx:
> Routine Prenatal US (May also see Polyhydramnios b/c can't swallow amniotic fluid)
> CXR
>> Duodenum = Double Bubble Sign (distension of two anatomic locations proximal to obstruction = stomach & proximal duodenum)
>> Jejunal/Ileal = Dilated loops of small bowel with air-fluid levels
> Contrast Radiography/Fluoroscopy
>> Contrast will cease to flow once it reaches the site
-Tx: SURGERY
> Take two healthy ends of tract and connect them to each other (Duodeno-duodennostomy = duodenum connect to another portion of duodenum)
Annular (Ring-Shaped) Pancreas
Define Condition:
Congenital malformation in which Pancreas wraps circumferentially around descending portion of Duodenum
-Hx: First Few months of life
-Path: When ventral bud fails to rotate around GI tract (remains on OPPOSITE side from dorsal bud) --> fuse together AROUND duodenum
-Sx/PE:
> 2/3 = Asx (ring isn't causing enough narrowing to obstruct)
> 1/3 = DUODENAL OBSTRUCTION
>> NONBILIOUS Vomiting (obstruction is PROXIMAL to Ampulla of Vater)
>> Feeding Intolerance
>> Abdominal Distension
-Dx:
> CXR = Double Bubble Sign (distension of stomach and proximal duodenum)
> Upper GI Series (shows contrast material can't pass beyond duodenum)
> Fluoroscopy
> Abdominal CT or MRI (DEFINITE)
-Tx:
> If SBO = CORRECTIVE SURGERY (Duodeno-Duodenostomy)
>> Cut duodenum in two locations (one above obstruction, one below obstruction)
>> Connect proximal duodenum to distal duodenum in a route that bypasses pancreas
Malrotation
Define Condition:
Congenital anatomic abnormality in which SI and LI are abnormally located in abdominal cavity
-Path: Intestines DO NOT rotate in counterclockwise direction during embryological development
> Duodenum compressed by fibrous attachment tissue
> Minimal attachment of intestines to posterior abdominal wall
> Cecum in RUQ (instead of RLQ)
-Sx/PE:
> Asx
> Abdominal Discomfort
> Vomiting (Bilious or Nonbilious, depending on obstruction location)
> Poor Feeding
> Poor Weight Gain
-Dx:
> Routine Prenatal US
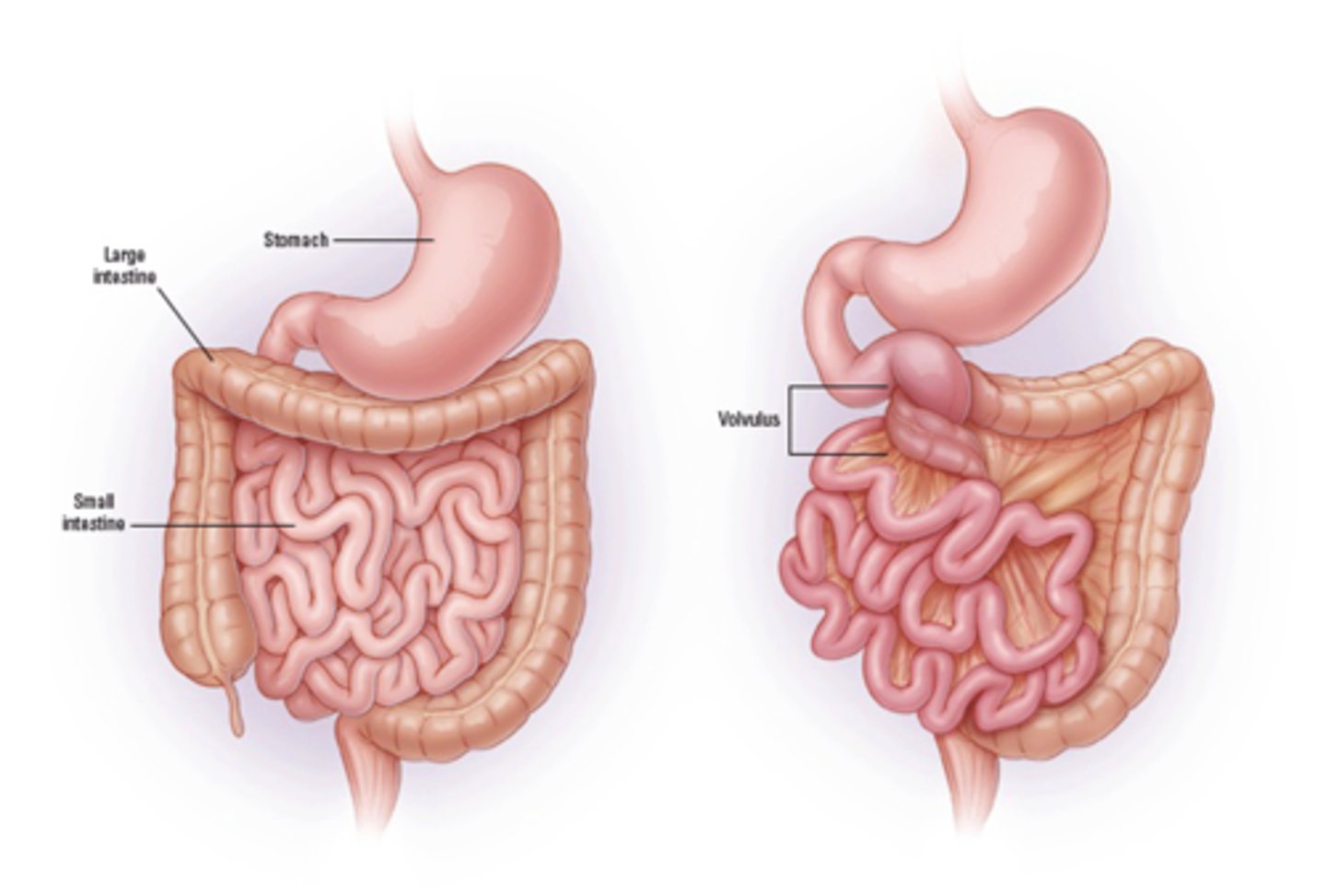
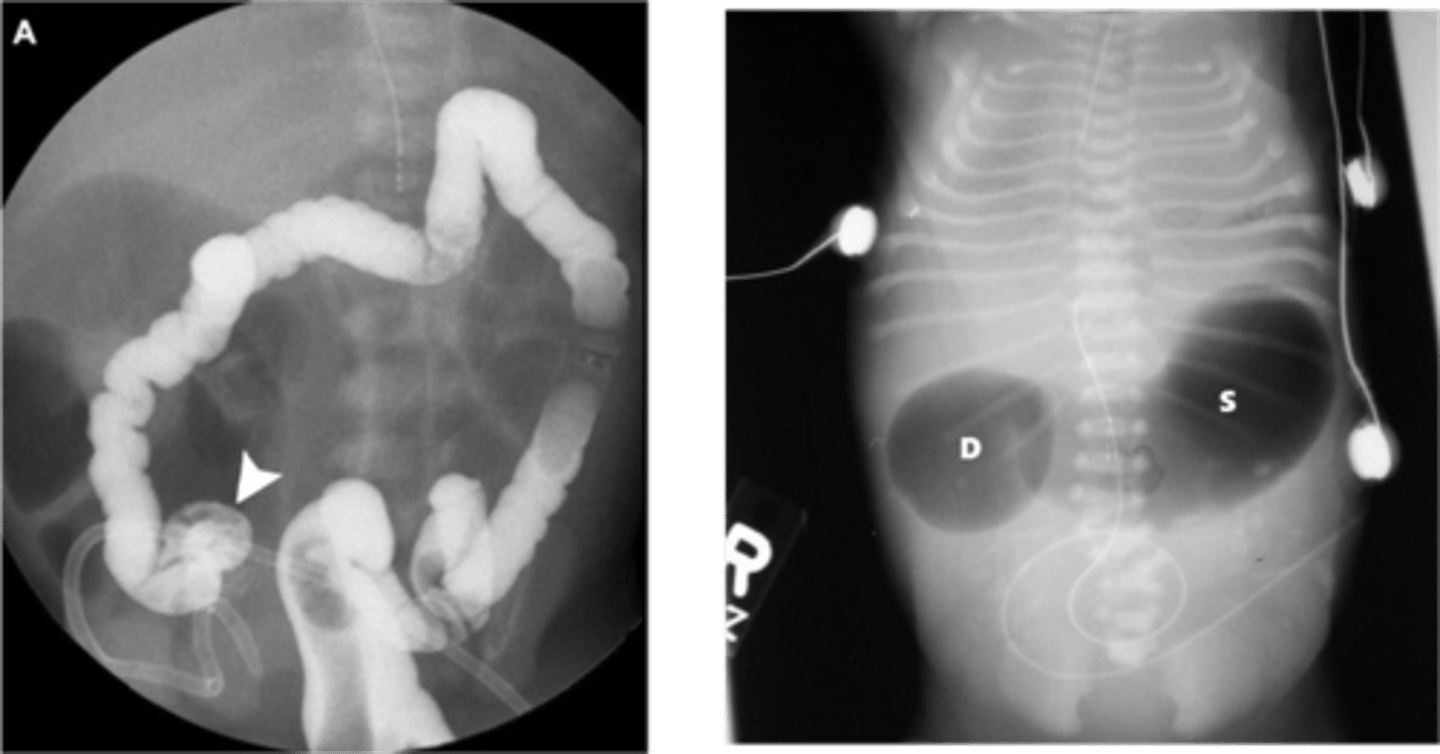
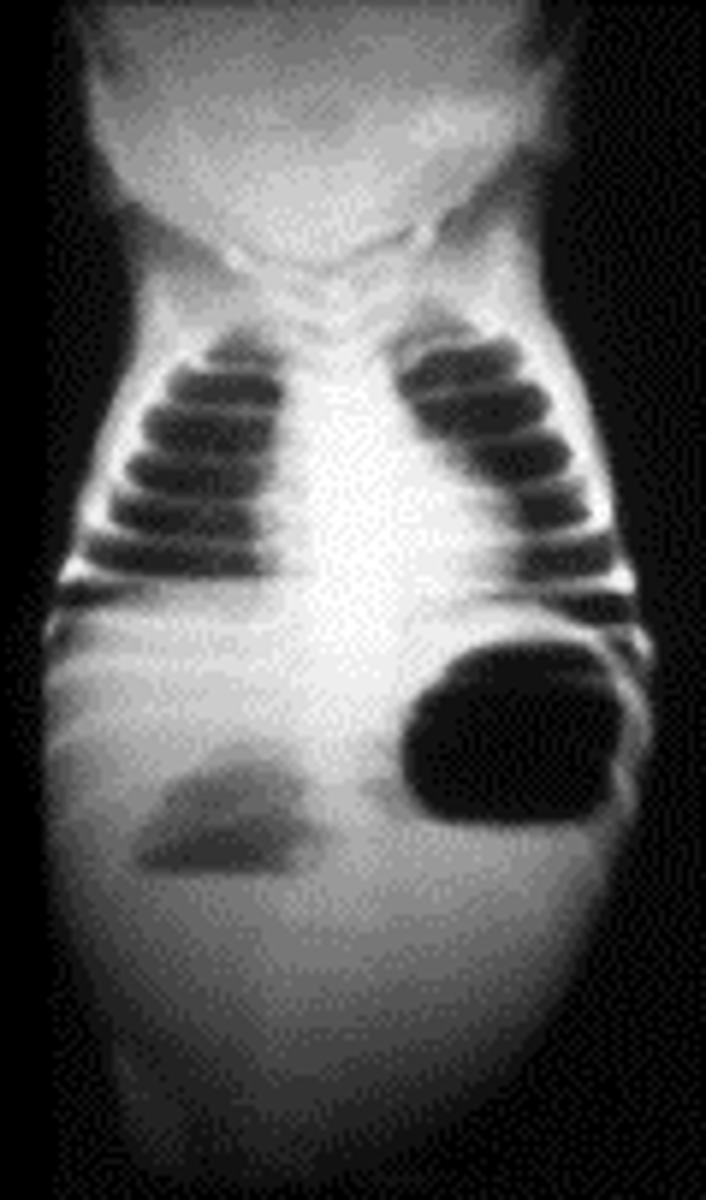
Midgut Volvulus
Define Condition:
When SI wraps around SMA
-Hx:
> MALROTATION (30%) --> babies in first months of life
-Path:
> SI squeezes SMA --> cuts off blood supply to SI and LI
> Coiling of SI (d/t poor attachment to posterior abdominal wall) ==> Bowel Obstruction
-Sx/PE:
> Sx of Malrotation
>> Asx
>> Abdominal Discomfort
>> Vomiting (Bilious or Nonbilious, depending on obstruction location)
>> Poor Feeding
>> Poor Weight Gain
> Ischemia
>> Severe & SUDDEN Pain
>> Bloody Stool
>> CV Issues (tachycardia, hypotension, sepsis)
-Dx:
> Ultrasounds (risk of false negatives)
> Upper GI Series (more accurate)
-Tx:
> Manual Detorsion (Untwist) of SI
> Cut fibrous connection between posterior abdominal wall and duodenum
> Reposition intestines to prevent Volvulus
Intussusception
Define Condition:
One portion of intestine slides inside adjacent part of intestine (telescopes)
-Hx:
> 3 mos to 3 y/o
> ACUTE VIRAL INFEX
-Path:
> Acute Virus = Enlargement of Peyer's patches/lymphatic tissue in intestines
> 90% = ILEOCECAL JUNCTION!!
-Sx:
> EPISODIC severe abdominal pain (inconsolable during, "pull legs towards chest") - last 15 to 20 mins
> BILIOUS VOMITING
> 20% = Bloody stool (red currant jelly stool) = GI blood + sloughed mucosal cells
-PE:
> SAUSAGE (tube)-shaped abdominal mass (90%) d/t being at Ileocecal Junction
> Lead Point (10%) = mass w/n lumen of intestine (like polyp/tumor/diverticulum); may move forward with peristalsis OR will move part of intestine with it if attached
-Dx:
> US = Target Sign/Bull's Eye Sign/Donut Sign/Coiled Spring Sign (one segment of bowel w/n another segment)
> Contrast (Barium) Enema
-Tx:
> Therapeutic Enema
>> Tube in rectum --> Air/Saline/Contrast forced in to "un-telescopes" in intestines
> Abdominal Surgery (if enema fails)
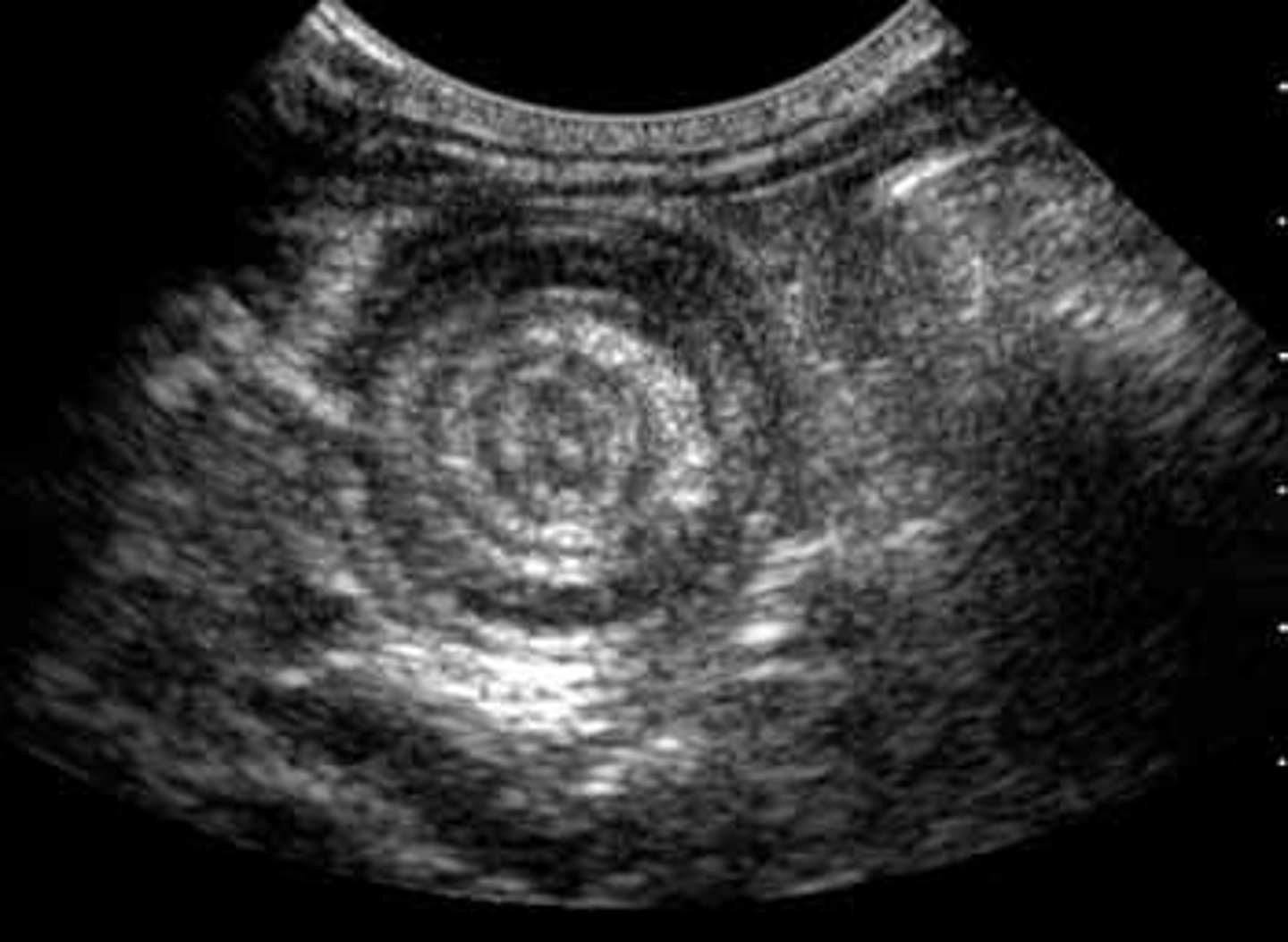
Meckel's Diverticulum
Define Condition:
Congenital outpouching of SI in ILEUM (w/n 2 feet of ileocecal valve)
-Hx:
> MC Congenital Anomaly of GI tract
> More common in Males
> W/n first 2 years of life
-Path: Remnant of vitelline duct (omphalomesenteric duct - connects midgut to yolk sac)
> DOESN'T Obliterate at Week 7 of Gestation
-Sx/PE:
> MOST (95%) as Asx
If contains Ectopic gastric tissue (w/n 1st 2 years of life)
> PAINLESS DARK RED GI BLEEDING (d/t injury of ileal mucosa from gastric acid)
> "Lead Point" of intestines (if found, will see Sx of Intussusception)
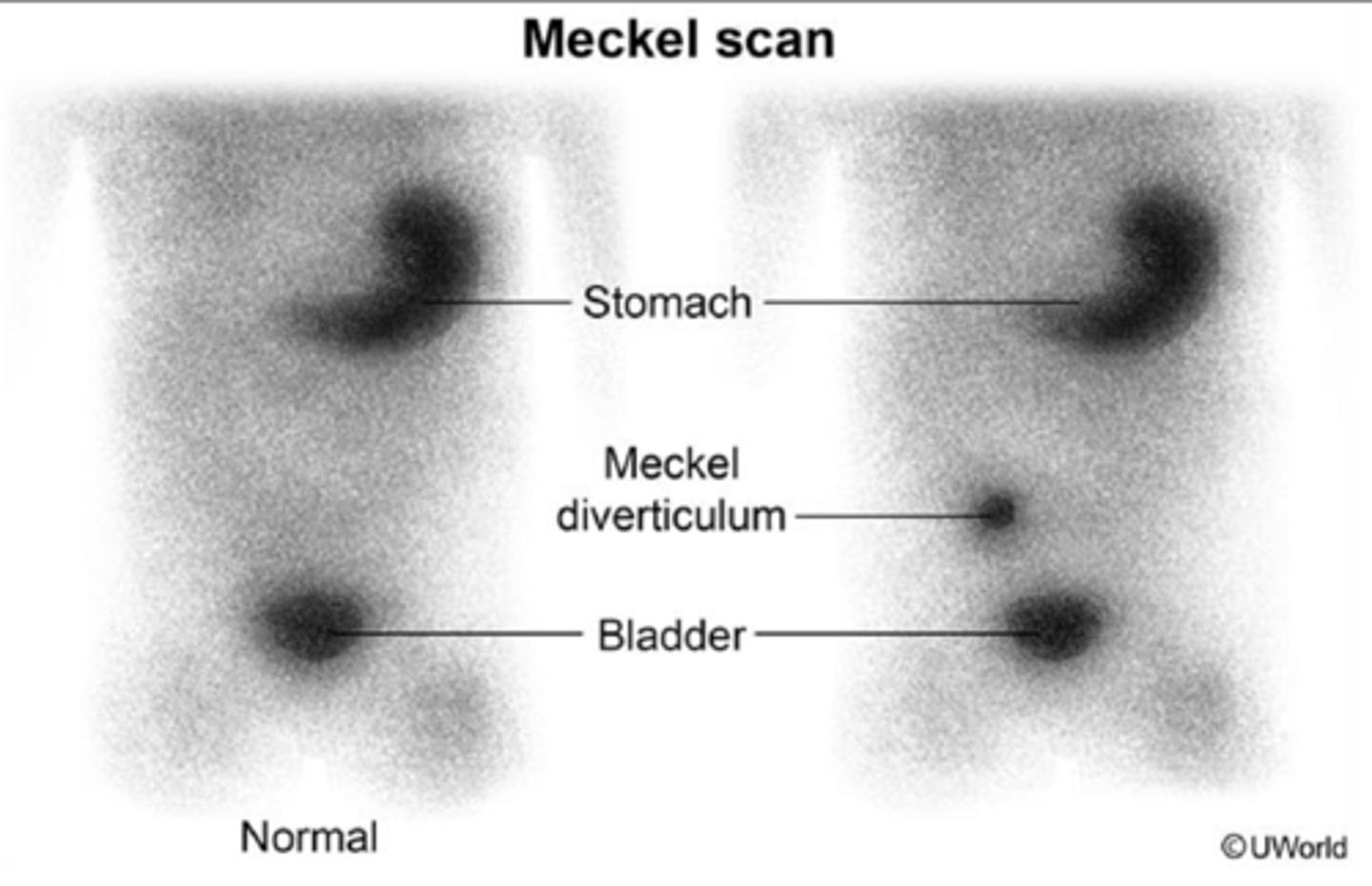
-Dx: Meckel Radionuclide Scan
> Radiotracer (99m Technetium pertechnetate) administered via IV
> Tracer taken up by gastric mucosal cells --> Gamma camera used to detect tracer ==> Tracer detected in SI if it contains ectopic gastric tissue
-Tx:
> Asx = None
> Sx = Cut out (Diverticulotomy)
Hirschprung Disease (Congenital Aganglionic Megacolon)
Define Condition:
Congenital GI disorder in which certain nerve cells are missing from distal colon --> Failure of Peristalsis
-Hx:
> From BIRTH
> More in MALES
> 10% = Down Syndrome
-Path:
> Failure of neural crest cells (precursors to enteric ganglion cells) to migrate completely during embryologic intestinal development
> Enteric Ganglion cells ABSENT from distal colon ==> Intestinal Wall can't relax (functional bowel obstruction)
-Sx/PE:
> LIFELONG CONSTIPATION (can't pass meconium w/n first 48 hrs of life)
>> May not be Dxed until 7-1o y/o if length of aganglionic segment of bowel is short (MILD Constipation)
> Abdominal Distension
> Bilious Vomiting
-Dx:
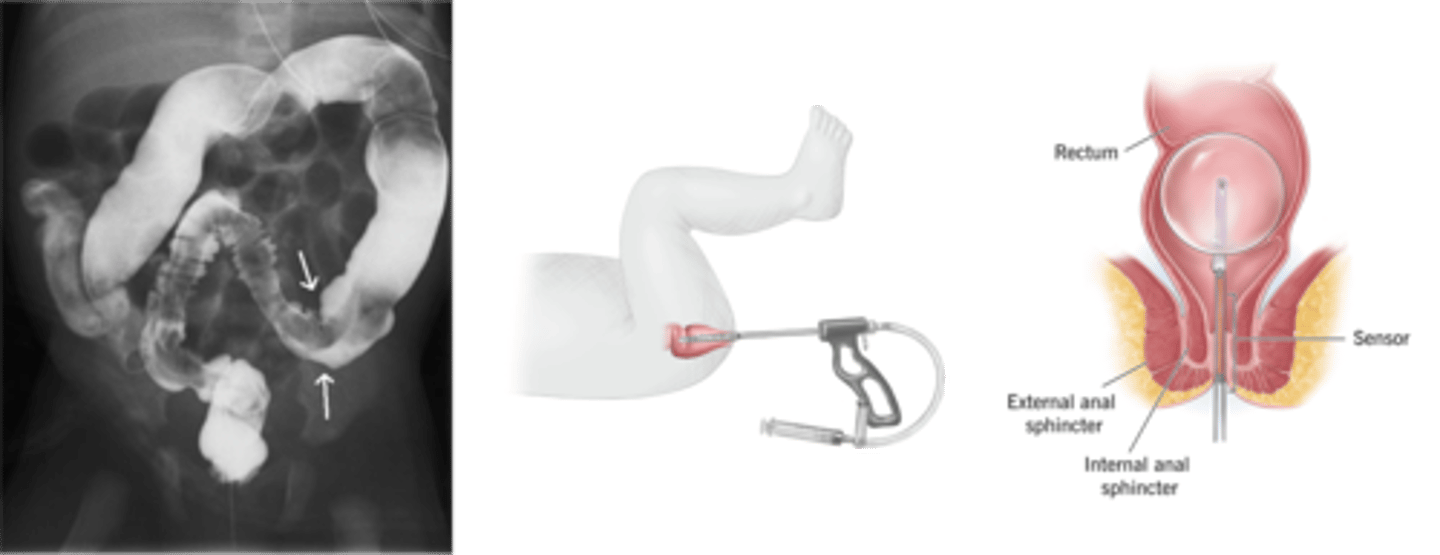
> Contrast Enema
>> Bowel segment just proximal to affected area will be dilated
>> May result in FALSE NEGATIVES
> Anorectal Manometry
>> Pressure sensor inserted into rectum to measure contraction strength --> inability for affected to relax
>> May result in FALSE POSITIVES
> Rectal biopsy
>> GOLD STANDARD, but invasive
>> Instrument inserted into rectum (tip has blade to collect small sample of intestinal wall --> suction force withdraws tissue)
>> No ganglion cells = CONFIRMS
-Tx: CUT OUT AGANGLIONIC SEGMENT --> Proximal segment surgically connected to distal rectum
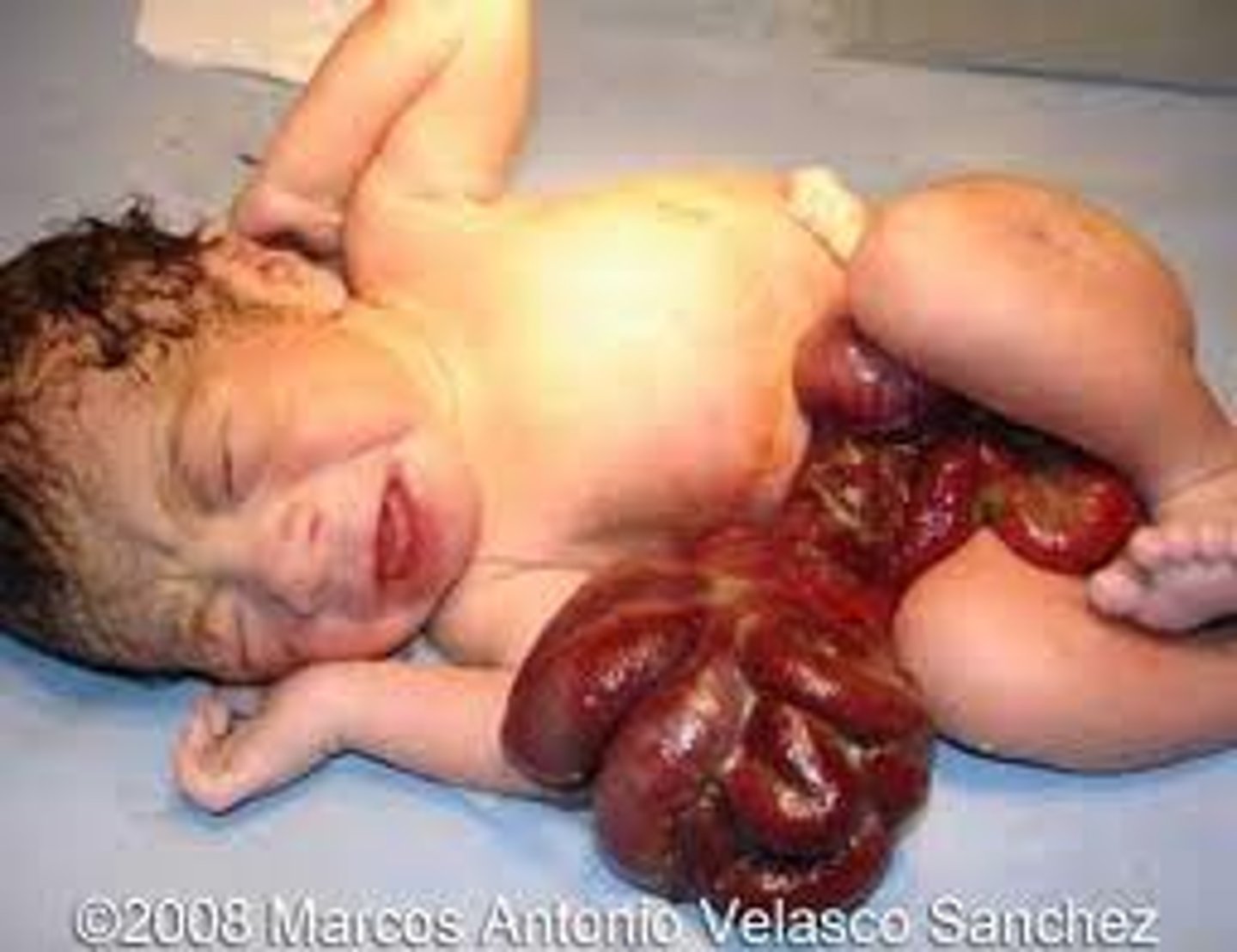
Gastroschisis
Define Condition:
Congenital defect with hole in abdominal wall LATERAL TO UMBILICUS --> extrusion of abdominal contents to the RIGHT side
-Hx:
> PRENATAL
> No underlying genetic syndrome
-Path: Failure of the two lateral folds at 6 weeks gestation to fuse in the midline may result in an abdominal wall defect
-Sx/PE:
> Malrotation
> Atresia
> Obstruction
> Perforation
-Dx: ROUTINE PRENATAL US @ 20 wks gestation
-Tx: Surgery to push contents back into cavity & close cavity + Treat other issues
Omphalocele
Define Condition:
Congenital defect with hole in abdominal wall AT THE BASE OF THE UMBILICUS --> Umbilical cord inserts at apex of membrane ==> extrusion of MEMBRANE COVERED abdominal contents (but membrane may rupture during fetal life)
-Hx:
> PRENATAL
> Underlying genetic syndrome (Aneuploidy - trisomy 18, trisomy 13, trisomy 21, Turner syndrome)
-Path:
> Failure of developing gut to returns to its cavity after 12 weeks of gestation
> Failure of lateral fold closure
-Sx/PE:
> OTHER anatomic defects in other organ systems (Ex: Cardiac, GU, CNS)
> Malrotation
> Atresia
> Obstruction
> Perforation
-Dx: ROUTINE PRENATAL US @ 20 wks gestation
-Tx: Surgery to push contents back into cavity & close cavity + Treat other issues
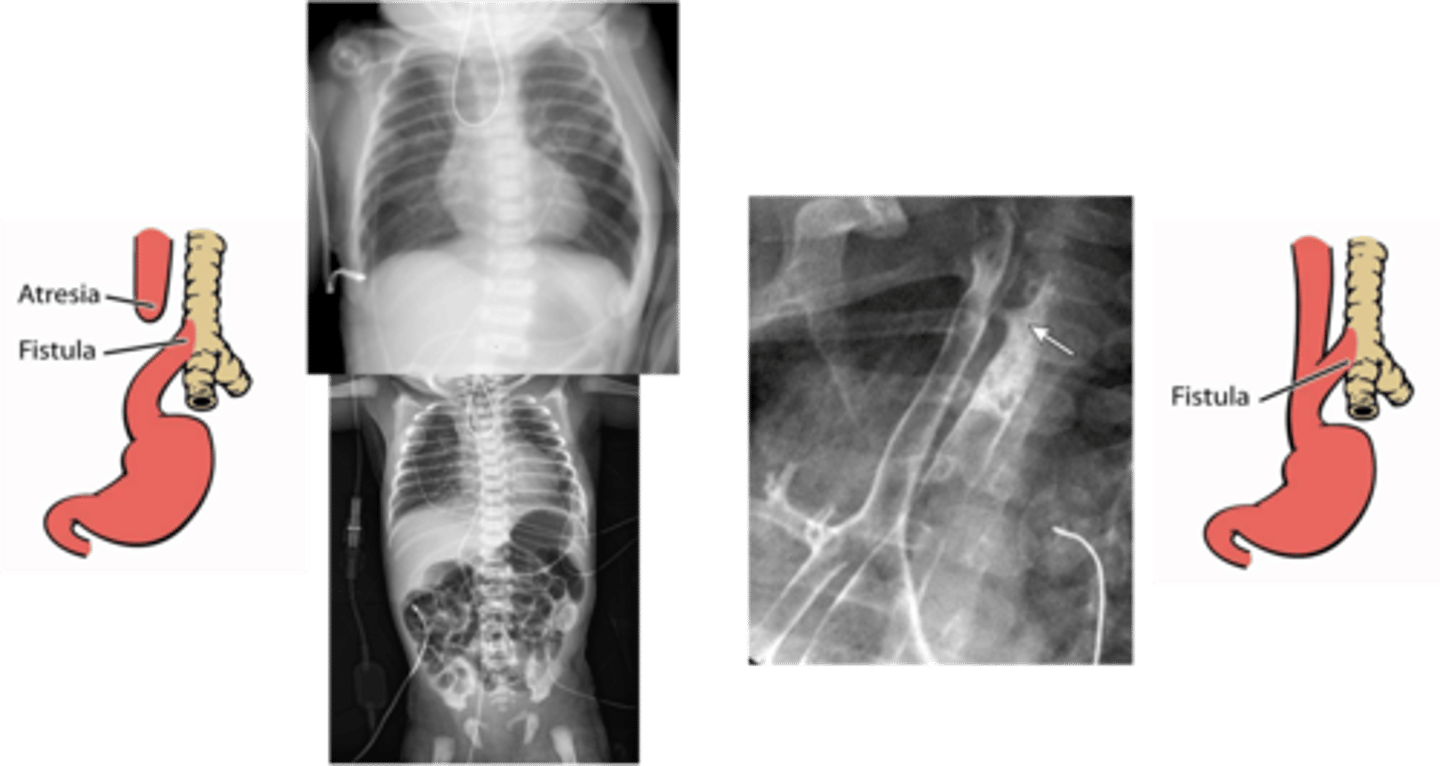
Tracheoesophageal Fistula (TEF)
Define Condition:
Congenital anatomic abnormality in which there is a connection between the trachea and the esophagus
-Hx: AFTER BIRTH (first few days of life)
-Path:
> 85% = Esophageal Atresia + Distal TEF
> 4% = Pure TEF (H-Type)
-Sx/PE:
BOTH: (VACTERL) - 50% of pts have one or more of these:
> Vertebral Anomalies
> Anal Atresia
> Cardiac Malformations
> TEF
> Renal Anomalies
> Limb Defects (radius and/or thumb)
Esophageal Atresia (d/t EXTREMELY short GI tract)
> Choking
> Drooling
> Inability to Feed
> Abdominal Distension (stomach & intestines filled with air)
> Gastric Acid Reflux (may cause Aspiration Pneumonia & Respiratory Difficulties)
Pure TEF (H Type)
> Milk/Formula/Gastric Secretions move into Trachea ==> Coughing, Choking, Resp Distress, Aspiration Pneumonia
> BURPING (Gas moves easily through INTACT esophagus)
-Dx:
Esophageal Atresia (d/t EXTREMELY short GI tract)
> Prenatal Ultrasound
>> Esophageal Atresia = POLYHYDRAMNIOS
> CXR & Catheter
>> Coiling = atresia of Esophagus
> Plain CXR
>> Esophageal Atresia + Gas-filled GI Tract = EA-TEF
Pure TEF (H Type)
> Water-soluble contrast study
> Endoscopy/Bronchoscopy
-Tx:
> Pure TEF = Opening in esophagus and trachea sewn closed
> EA-TEF = Esophageal segments surgically connected to each other