A&P Test 1-4
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Which organ system produces immune cells and has a role in fluid balance?
→ Lymphatic system
Which organ system protects organs, allows for support and movement, and also plays a key role in blood formation?
→ Skeletal system
Which type of tissue covers the body’s surface?
→ Epithelial tissue
Bone, cartilage, and adipose tissue are all types of what tissue?
→ Connective tissue
Sagittal
divides body into left and right
Frontal (coronal)
divides body into front and back
Transverse
divides body into top and bottom
Supine
lying face up
Prone
lying face down
Anterior (ventral):
front
Posterior (dorsal):
back
Medial
toward the midline
Lateral
away from the midline
Proximal
closer to point of origin
Distal
farther from point of origin
Superior
above
Inferior
below
Cranial cavity:
brain
Spinal cavity:
spinal cord
Thoracic cavity
heart and lungs
Abdominal cavity:
digestive organs
Pelvic cavity
bladder and reproductive organs
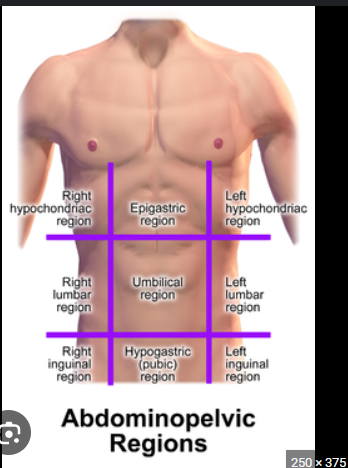
Hypochondriac region:
Upper left and right abdominal areas, below the ribs
These elements make up more than 96% of the human body:
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
These elements make up the greatest percentage of the body’s weight:
→ Oxygen and hydrogen (mainly in water)
What are covalent bonds?
Bonds where atoms share electrons
What is metabolism?
→ All chemical reactions in the body
What is catabolism?
→ Breaking down molecules to release energy
A person is in a catabolic state:
→ They're breaking down tissue or molecules (e.g., during illness, fasting)
Measure acidity or alkalinity:
pH scale
6 acidic, 7 neutral, 8 basic/alkaline
pH of human blood:
7.35 to 7.45
Four main organic compounds in the human body:
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Body’s main energy source:
Glucose (a carbohydrate)
How do cells acquire energy
Through cellular respiration of glucose, mainly in mitochondria
Cellular structure helps sweep particles along a path:
Cilia
Based on their function, where would you find microvilli
In the small intestine (for nutrient absorption)
Water pressure that develops in a solution as a result of osmosis:
→ Osmotic pressure
Which type of intravenous fluid would you expect most patients to receive?
→ Isotonic solution (e.g., normal saline)
What force drives the process of filtration in the body’s capillaries?
→ Blood (hydrostatic) pressure
Sodium-potassium pump and action:
Moves 3 sodium ions out and 2 potassium ions in, using ATP; helps maintain cellular electrical balance
What are nucleotides?
Building blocks of DNA and RNA
What determines genetic code?
The sequence of nitrogenous bases (A, T, C, G in DNA; A, U, C, G in RNA)
How does RNA differ from DNA?
RNA is single-stranded, has uracil instead of thymine, and uses ribose sugar
Chromosomes form during which phase of mitosis
Prophase
The chromosomes of a cell divide during which phase of mitosis?
Anaphase
What is the human microbiome?
The collection of microbes (bacteria, viruses, fungi) that live in and on the human body
Most common way that a person’s microbiome becomes disrupted:
Antibiotic use
The main finding of the Human Microbiome Project:
Healthy individuals have vastly different microbiomes, but key functions are shared
When does the most significant step in building a microbiome occur
At birth (especially during vaginal delivery)
Children born by Caesarean section and microbiomes:
They tend to have less diverse microbiomes and more skin bacteria early on
Critical period for establishing a microbiome to enhance neurodevelopment and lifelong health:
2 years old is the critical window for microbiome development.
Threats to the microbiome
Antibiotics, poor diet, lack of breastfeeding, over-sanitization, physiological stress
What advice would you give to a new mother considering breastfeeding?
Breastfeeding supports the baby’s immune system and helps build a strong, healthy microbiome
Exclusive breastfeeding for 6 months!!!
Capsid
keeps the virus from drying up and binding easier to the next host cell
Gram Positive
No outer membrane.
Easier for antibiotics to penetrate and break the cell wall
Staphylococcus
Spherical bacteria that grow in grape-like clusters.”
Sodium-Potassium Pump (Na+/K+)
Pumps 3 sodium ions (Na⁺) OUT of the cell
Pumps 2 potassium ions (K⁺) INTO the cell
-3 Sodium, +2 potassium
S=I—>O P=O—>I
Right Hypochondriac Region
Gallbladder