ACCY 202 Exam 1 & 2
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Accounting Equation

Accrual Basis: Revenue Recognition Principle
Revenue is recognized when good or service is provided to the customer and at the expected amount to be paid by the customer, regardless of when the cash is received (performance obligation is met)
Accrual Basis: Expense Recognition Principle (Matching Principle)
Expense is recognized in the same accounting period as the revenues that those expenses helped generate
Cash Basis Accounting
Revenue is recognized when cash is received and expenses are recognized when cash is paid
Return on Assets
NI/Average total assets
Net Income (Income Statement)
Revenue - Expenses
Ending Retained Earnings (Statement of RE)
Beg. RE + NI - Dividends
Balance Sheet
Assets = L + E
Debt Ratio
Total Liabilities/Total Assets
Normal Debit Balance
Dividends, Equity, Assets
Normal Credit Balance
Liabilities, Equity, Revenue
Operating Activities
Reflect cash generated by or consumed by a company’s day-to-day operations; relate to Income Statement and current assets/liabilities on the balance sheet
Financing Activities
Reflect the cash flow between a company and its owners (stockholders) and creditors (lenders) and how a company raises and repays capital; relate to changes in long-term debt and equity on balance sheet
Investing Activities
Reflect cash spent on or received from the purchase or sale of long-term assets (non-current) and other investments that affect long-term resources and growth; relate to PPE and long-term investments on balance sheet
Cash received from customers for sales of goods or services. |
Cash received from interest on loans (from a customer). |
Cash received from dividends (from an investment). |
Operating Inflows
Cash paid to suppliers for inventory. |
Cash paid to employees for wages and salaries. |
Cash paid to the government for taxes. |
Cash paid for operating expenses (rent, utilities, insurance). |
Cash paid for interest on debt/loan |
Operating Outflows
Cash received from selling equipment, buildings, or land. |
Cash received from selling investments in the stock or bonds of other companies. |
Cash collected on loans made to other parties. |
Investing Inflows
Cash paid to purchase new equipment, buildings, or land (Capital Expenditures, or CapEx). |
Cash paid to purchase investments in the stock or bonds of other companies. |
Cash paid to make loans to other parties. |
Investing Outflows
Cash received from issuing (selling) new stock. |
Cash received from issuing new bonds or taking out new long-term loans. |
Financing Inflows
Cash paid to shareholders as dividends. |
Cash paid to repay the principal amount of loans or redeem bonds. |
Cash paid to repurchase the company's own stock (Treasury Stock). |
Financing Outflows
Cash Basis Income
Cash receipts - cash payments
Deferred/Unearned Revenue
Cash paid in advance for goods and services provided in the future; debit as a liability, credit revenue when good/service is provided
Accrued Liabilities/Revenues
Costs that are incurred or revenues earned in a period that are both unpaid or not yet received in cash/assets and unrecorded
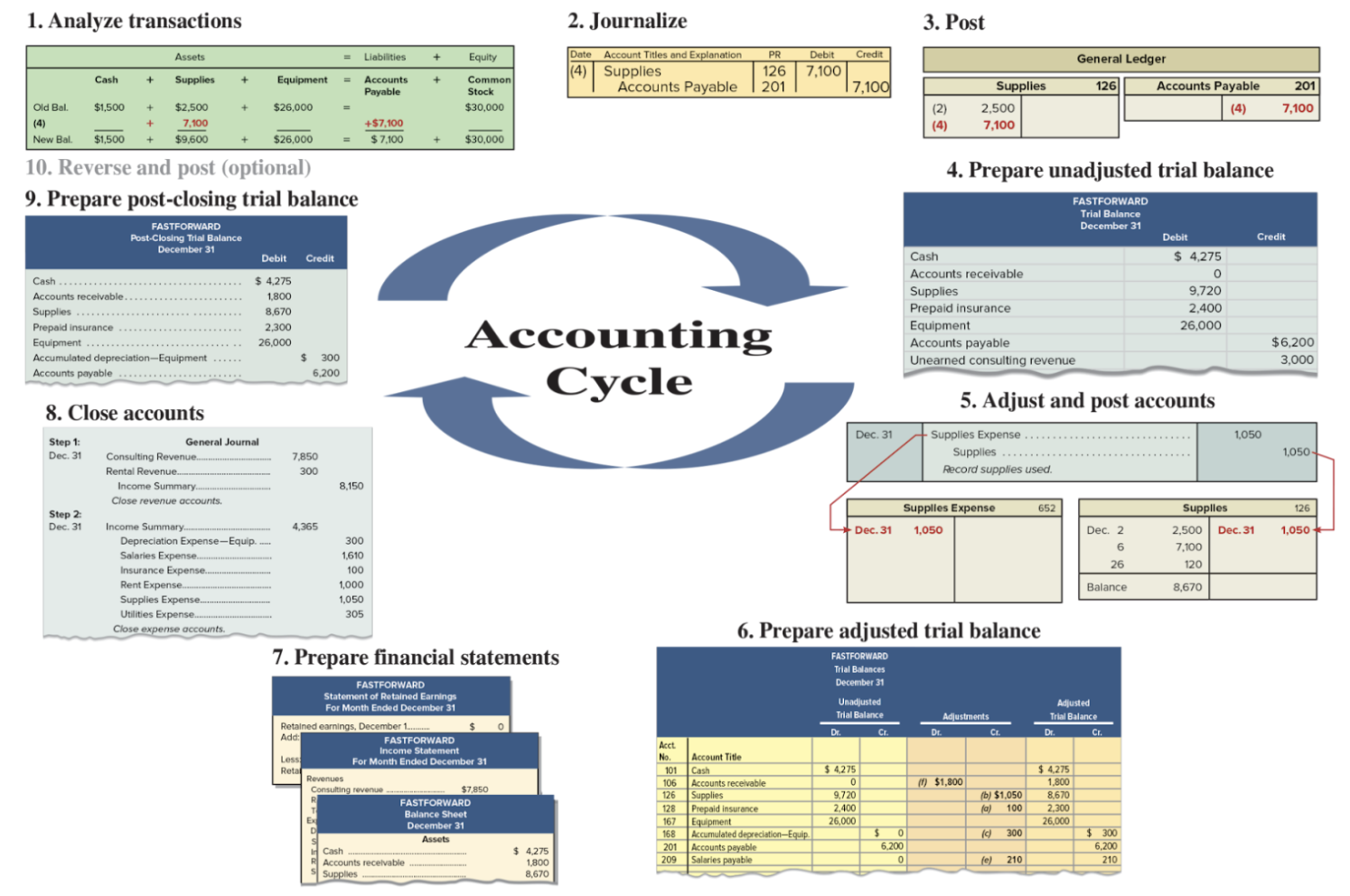
Accounting Cycle
Straight-Line Method of Depreciation
Changes the same amount to each period of the asset’s useful life
Depreciable Cost of Asset
Cost - Salvage Value /
Useful Life in Periods
Net Book Value
Asset’s total cost - accumulated depreciation
Straight-Line Depreciation Alternative Equation
100%/number of periods in the asset’s useful life
Accumulated depreciation
Contra Asset; normal credit balance
Units of Production Method of Depreciation
1. Depreciation Per unit = Cost - salvage value / total units of production
2. Depreciation Expense = Depreciation per unit x Units produced in period
Accured Interest Expense Equation
Principal amount owed x Annual interest rate x Fraction of year since last payment
Change in Estimates/Revised SL Depreciation
Book Value - Revised Salvage Value /
Revised remaining useful life
If Sale Price = Book Value
No gain or loss
Sale price > book value
Gain
Sale price < book value
Loss
Total Asset Turnover
Net Sales/Average total assets
Add deposits in transit
1st Ex: Bank Balance Adjustment
Subtract outstanding checks
2nd Ex: Bank Balance Adjustments
Add or Subtract Bank Error Corrections
3rd Ex: Bank Balance Adjustments
Add interest earned and unrecorded cash receipts
1st Ex: Book Balance Adjustments
Subtract bank fees and NSF checks
2nd Ex: Book Balance Adjustments
Add or Subtract Book Error Corrections
3rd Ex: Book Balance Adjustments
Overstated Cash Balance (Book); ex. recorded a check for $800 instead of $80
Subtract
Understated Cash Balance (Book); ex. recorded a deposit for $100 instead of $1,000
Add
Overstated your Bank Balance; ex. the bank incorrectly added money to your account
Subtract
Understated your Bank Balance; ex. the bank incorrectly removed money from your account
Add
Net Change in Cash
Cash from Operating Activities + Cash from Investing Activities + Cash from Financing Activities
Ending Cash Balance
Beginning Cash Balance + Net Cash Provided by Operating Activities + Net Cash Provided by Investing Activities + Net Cash Provided by Financing Activities
Net cash flow
Cash inflow - Cash outflow
Investing & Financing
Identical for both Direct and Indirect Methods
In direct method for operating activities…
Convert Accrual Basis in Income Statement to Cash Basis for Statement of Cash Flows (ex. Wages Expense —> Cash paid to Employees)
Operating Cash Flow (Direct Method): Cash Received from Customers
Sales Revenue
+ Decrease in Accounts Receivable (cash inflow)
- Increase in Accounts Receivable (cash outflow)
Cash Paid to Suppliers
COGS + Change in Inventory - Change in Accounts Payable
(if A/P decreased, cash outflow —> + decrease in A/P)
Cash Paid for Rent
Rent Expense + Change in Prepaid Rent
(If Prepaid Rent increased, cash outflow —> +)
Cash Paid for Insurance
Insurance Expense + Change in Prepaid Insurance
Cash Paid of Utilities
Utilities Expense + Change in Utilities Payable
Cash Paid for Interest
No adjustment
Cash Paid
+ a decrease in payable or increase in prepaid
- an increase in payable or decrease in prepaid
Depreciation Per unit
Cost - salvage value / total units of production
Depreciation Expense
Depreciation per unit x Units produced in period
Retained Earnings
Rev - Exp - Div
Cash Balance per Bank Statement
Adjusted Cash Balance - Total Bank Adjustment
Credit Memoranda (CM)
Banks use CM to indicate an increase in the customer’s account balance
Debit Memoranda (DM)
Banks use DM to indicate an decrease in the customer’s account balance
Adjusted NI
NI - Depreciation Expense +/- Gain or Loss on Disposal
Total Cash Paid (interest)
Cash paid for Principal + Cash paid for Interest
Net Income for Merchandiser
Gross Profit - Expenses
Gross Profit
Net Sales - COGS
Net Sales
Sales - Discounts - Returns/Allowances
Gross Profit/Margin Ratio
Gross Margin / Net Sales
Merchandise Inventory
Current Asset not on company’s balance sheet and a product owned by company intended to be sold
Inventory Costs
Costs to buy goods, ship them, and make them ready for sale
Perpetual Inventory System
Records Costs of Goods Sold at the time of Each Sale
Merchandiser’s Operating Cycle
Purchases
Merchandise Inventory
Credit Sales
Accounts Receivable
Cash Collection
COGS (1)
GAFS - Ending Inventory
GAFS
Beg Inventory + Net Purchases
How to Read Credit Terms (ex. 2/10, n/60)
2% discount if paid within 10 days, otherwise entire amount is due within 60 days
Cash Discount for Sellers
Sales Discount
Cash Discount for Buyers
Purchases Discount
Payment within Discount Period
Debit Accounts Payable
Credit Merchandise Inventory and Cash
FOB Shipping Point (3 Parts)
Buyer accepts ownership when the goods depart the seller’s place of business
Buyer pays shipping costs, risk of loss in transit
Goods are part of the buyer’s inventory when they are in transit
FOB Destination
Ownership of goods transfers to the buyer when the goods arrive at the buyer’s place of business
Seller pays for shipping
Revenue is not recorded until goods arrive at the destination
Debits to Merchandise Inventory
Purchases
Transportation-In
Credits to Merchandise Inventory
1.Purchases Discounts
Returns
Allowances
Purchases allowances
Seller granting a price reduction (allowance) to a buyer of defective or unacceptable merchandise
Two Required Entires for Perpetual Accounting System
Revenue Recorded (and asset increased) from the customer
COGS incurred (and asset decreased) to the customer
Sales Discounts & Sales Returns and Allowances
Contra Revenue Account w/normal debit balance
Selling Expenses
Costs to market and distribute products and services
Selling Expenses Examples
Advertising, store supplies, rent, and delivery of goods to customers
G&A Expense
Costs to administer a company’s overall operations
G&A Expense Examples
Office salaries, office equipment, and office supplies
Consignment Goods (3 Parts)
Goods sent by the owner (consignor)
The consignor owns the consigned goods and reports them in its inventory
Consignee never reports consigned goods in inventory
Net Realizable Value (damaged or obsolete goods, always a loss if occurred)
Sales price - Cost of making the sale
FIFO
Assumes costs flow in the order incurred
LIFO
Assumes costs flow in the reverse order incurred
Weighted Average
assumes costs flow at an average of costs available
Rising Costs FIFO
Reports lowest COGS, yielding highest gross profit and net income
Rising Costs LIFO
Reports highest COGS, yielding lowest gross profit and net income
Rising and Falling Costs Weighted Average
Yields results between FIFO and LIFO
Falling Costs FIFO
(Opp of Rising) Reports highest COGS, yielding lowest gross profit and net income