Text Editing Terms
1/32
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Acronyms
Words formed from the first letters of a phrase, pronounced as a word.
Abbreviations
Shortened forms of words or phrases. i.e Dr. (Doctor)
Active Voice
occurs when the subject of the sentence performs the action of the verb.
Passive voice
occurs when the subject is the recipient of the action.
Ambiguity
A sentence or phrase can be interpreted in mor than one way.
Example: “I saw her duck” Is duck an animal or an action?
Antonyms
Words with opposite meanings

Apostrophe use
Possession
Contractions: “don’t” do not
Clichés
Overused expressions that have lost originality
Comma Splice
Occurs when two independent clauses are incorrectly joined by a comma.

Concord
Subject-Verb agreement: Singular subject take singular verbs, and plural subjects take plural verbs.
Pronoun agreement: Pronouns must agree with the noun they refer to in number and gender.

Degrees of comparison
Positive: Describes one thing (fast)
Comparative: Compares two things (faster)
Superlative: Compares more than two things (fastest)
Dashes
Used to create a break in sentence, often for emphasis.
3 types of dashes:
hyphen -
em dash —
en dash –
Direct and Reported Speech
Direct speech: Exact words spoken by someone.
Reported speech: Paraphrasing someone’s words.
Double Negative
Occurs when two negative words are used in a sentence, which leads to confusion or incorrect meaning.
Generalization
When broad statements are made without considering exceptions.

Homonyms
Words that are spelled the same and pronounced the same but have different meanings.
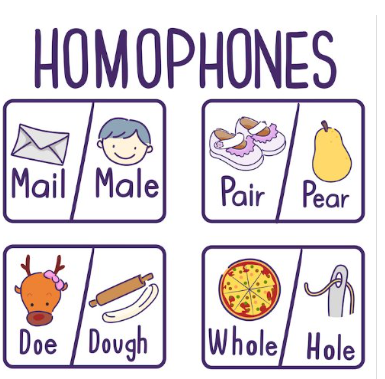
Homophones
Words that sound the same but have different meanings and spellings.
Hyphens
Used to join words together or indicate word breaks, i.e’ mother-in-law’
Inconsistent use of Pronouns
When pronouns do not match the noun they refer to in terms of a number or gender.

Literal and Figurative language
Literal language: words mean exactly what they say.
Figurative language: Words are used in a symbolic or non-literal sense

Malapropism
The mistaken use of a word in place of a similar-sounding one, often with humorous results.
Misrelated Participle/Dangling Participle
A participle that doesn’t logically relate to the subject in the sentence.

Phrases and Clauses
Phrases: A group of words without a subject and ver, acting as a single part of speech.
Clauses: A group of words with a subject and verb that can be independent( complete sentence) or dependent( needs an independent clause).
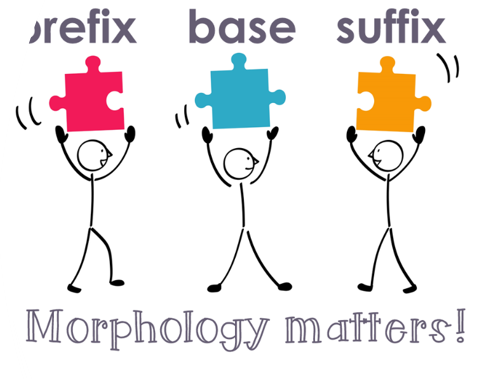
Prefixes and Suffixes
Prefixes: Added to the beginning of a word to change it’s meaning.
Suffixes: Added to the end of a word to change it’s form.

Redundancy
The unnecessary repetition of ideas or words.
Register
Refers to the level of formality in language use, appropriate to the context

Spoonerisms
are accidental transpositions of sounds in two words
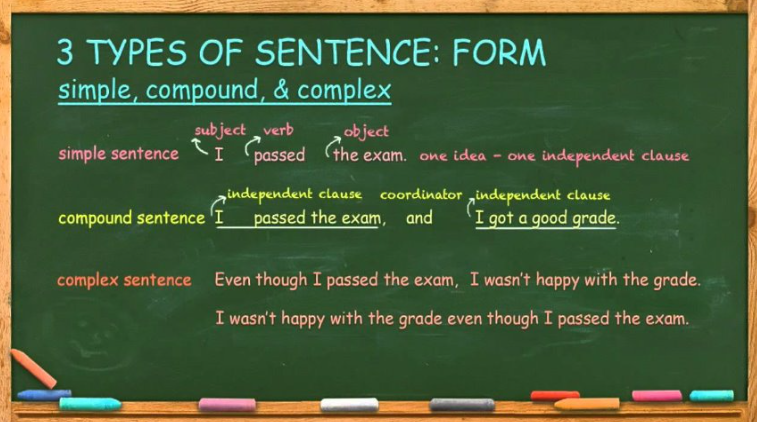
Simple, Compound and Complex Sentence
Simple sentence: Contains one independent clause.
Compound sentence: Contains two independent clauses joined by a conjunction.
Complex sentence: Contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
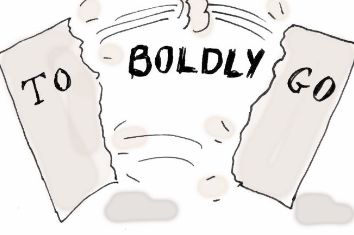
Split infinitive
An adverb is placed between “to” and the verb
Synonyms
Words with similar meanings
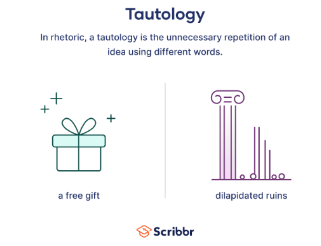
Tautology
The unnecessary repartition of an idea.

Tense Errors
When the verb tenses in a sentence are inconsistent.

Verbosity
The use of more words than necessary