Neural Control and Coordination
Neural System:
- The neural system of all animals is composed of highly specialized cells called neurons that can ==detect, receive and transmit different stimuli.==
- The neural organization is elementary in lower invertebrates.
- For example, ==Hydra is composed of a network of neurons.==
- The neural system is better organized in ==insects==, where a brain and a number of ganglia and neural tissues are present.
- Vertebrates have a more developed neural system.
Human Neural System:
- The human neural system is divided into two parts
- The central neural system (CNS)
- The CNS includes the ==brain and the spinal cord== and is the site of information processing and control.
- The peripheral neural system (PNS)
- The PNS comprises all the ==nerves of the body== associated with the CNS (brain and spinal cord).
- The nerve fibers of the PNS are of two types:
- The ==afferent nerve fibers== transmit impulses from tissues/organs to the CNS
- The ==efferent fibers== transmit regulatory impulses from the CNS to the concerned peripheral tissues/organs.
- The PNS is divided into two divisions called:
- The Somatic neural system relays impulses from the ==CNS to skeletal muscles==
- The Autonomic neural system transmits impulses from the ==CNS to the involuntary organs and smooth muscles== of the body.
- The autonomic neural system is further classified into:
- The sympathetic neural system
- The parasympathetic neural system.
- The visceral nervous system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that comprises the whole complex of ==nerves, fibers, ganglia, and plexuses== by which impulses travel from the central nervous system to the viscera and from the viscera to the central nervous system.
Neuron as Structural and Functional Unit of Neural System:
A neuron is a microscopic structure composed of three major parts, namely, the cell ==body, dendrites, and axon.==
- The cell body contains cytoplasm with typical cell organelles and certain ==granular bodies== called ==Nissl’s granules.==
- ==Short fibers== which branch repeatedly and project out of the cell body also contain Nissl’s granules and are called ==dendrites.==
- These fibers ==transmit impulses toward the cell body.==
- The axon is a ==long fiber, the distal end of which is branched.==
- Each branch terminates as a ==bulb-like structure called a synaptic knob== which possesses synaptic vesicles containing chemicals called ==neurotransmitters.==
- The axons ==transmit nerve impulses away from the cell body== to a synapse or to a neuro-muscular junction.
- Based on the number of axons and dendrites, the neurons are divided into three types, i.e.
- Multipolar (with one axon and two or more dendrites; found in the ==cerebral cortex==)
- Bipolar (with one axon and one dendrite, found in the ==retina of the eye==)
- Unipolar (cell body with one axon only; found usually in the ==embryonic stage==).
- There are two types of axons, namely:
- The myelinated nerve fibers are ==enveloped with Schwann cells==, which ==form a myelin sheath== around the axon.
- The ==gaps== between two adjacent myelin sheaths are called ==nodes of Ranvier.==
- Myelinated nerve fibers are found in ==spinal and cranial nerves.==
- Nonmyelinated nerve fiber is enclosed by a Schwann cell that ==does not form a myelin sheath around the axon== and is commonly found in ==autonomous and somatic neural systems.==

Generation and Conduction of Nerve Impulse:
Neurons are excitable cells because their membranes are in a ==polarised state.==
Different types of ion channels are present on the neural membrane.
- These ion channels are ==selectively permeable== to different ions.
- When a neuron is not conducting any impulse, i.e., resting, the axonal membrane is comparatively ==more permeable to potassium ions (K+ ) and nearly impermeable to sodium ions (Na+ ).==
- Similarly, ==the membrane is impermeable to negatively charged proteins present in the axoplasm.==
- Consequently, the axoplasm ==inside the axon== contains a ==high concentration of K +== and negatively charged proteins and ==a low concentration of Na+.==
- In contrast, the fluid ==outside the axon== contains a ==low concentration of K +==, and a ==high concentration of Na+== and thus forms a concentration gradient.
- These ionic gradients across the resting membrane are maintained by the active transport of ions by the ==sodium-potassium pump== which transports ==3 Na + outwards for 2 K + into the cell.==
- As a result, the ==outer surface== of the axonal membrane possesses a ==positive charge== while its ==inner surface== becomes ==negatively charged== and therefore is polarised.
The electrical potential difference across the resting plasma membrane is called the r==esting potential.==
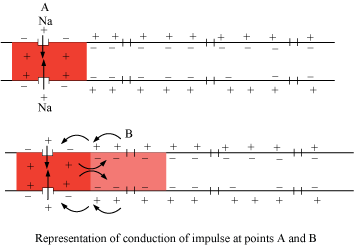
When a stimulus is applied at a site on the polarised membrane, the membrane at site A becomes freely permeable to Na+.
- This leads to a ==rapid influx of Na+ followed by the reversal of the polarity== at that site, i.e., the outer surface of the membrane becomes negatively charged and the inner side becomes positively charged.
- ==The polarity of the membrane at site A is thus reversed and hence depolarised.==
The electrical potential difference across the plasma membrane at site A is called ==the action potential, which is in fact termed a nerve impulse.==
At sites immediately ahead, ==the axon (e.g., site B) membrane has a positive charge on the outer surface and a negative charge on its inner surface.==
- As a result, a current flows on the inner surface from site A to site B.
On the outer surface, current flows from site B to site A to complete the circuit of the current flow.
- Hence, the ==polarity at the site is reversed,== and an action potential is generated at site B.
- Thus, the ==impulse (action potential) generated at site A arrives at site B.==
The sequence is repeated along the length of the axon and consequently, the impulse is conducted.
- The rise in the stimulus-induced permeability to Na+ is extremely short-lived.
- It is quickly followed by a rise in permeability to K+.
Within a fraction of a second, K+ diffuses outside the membrane and restores the resting potential of the membrane at the site of excitation and the fiber becomes once more responsive to further stimulation.
Transmission of Impulses:
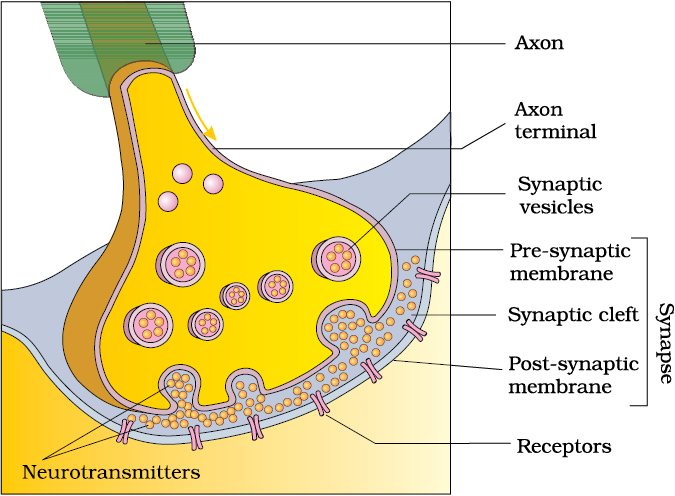
A nerve impulse is transmitted from one neuron to another through junctions called ==synapses.==
- A synapse is formed by the membranes of a ==pre-synaptic neuron and a post-synaptic neuron==, which may or may not be separated by a gap called the ==synaptic cleft.==
- There are two types of synapses, namely, electrical synapses and chemical synapses.
- At electrical synapses, the membranes of ==pre-and post-synaptic neurons are in very close proximity.==
- Electrical current can flow directly from one neuron into the other across these synapses.
- The transmission of an impulse across electrical synapses is very similar to impulse conduction ==along a single axon.==
- Impulse transmission across an electrical synapse is ==always faster than that across a chemical synapse.==
- Electrical synapses are ==rare== in our system.
- At a chemical synapse, the membranes of the ==pre-and post-synaptic neurons are separated== by a ==fluid-filled space== called the synaptic cleft.
- ==Chemicals called neurotransmitters== are involved in the transmission of impulses at these synapses.
- The axon terminals contain vesicles filled with these neurotransmitters.
- When an impulse (action potential) arrives at the axon terminal, it ==stimulates the movement of the synaptic vesicles== towards the membrane where they fuse with the plasma membrane and ==release their neurotransmitters in the synaptic cleft.==
- The released neurotransmitters ==bind to their specific receptors==, present on the post-synaptic membrane.
- This binding opens ion channels allowing the entry of ions which can generate a new potential in the post-synaptic neuron.
- The new potential developed may be either ==excitatory or inhibitory.==
Central Nervous System:
The brain is the central information processing organ of our body, and acts as the ‘==command and control system’.==
- It controls:
- Voluntary movements
- Balance of the body
- Functioning of vital involuntary organs (e.g., lungs, heart, kidneys, etc.),
- Thermoregulation
- Hunger and thirst
- Circadian (24-hour) rhythms of our body
- Activities of several endocrine glands
- Human behavior.
- It is also the site for ==processing vision, hearing, speech, memory, intelligence, emotions, and thoughts.==
The human brain is well protected by the skull.
Inside the skull, the brain is covered by ==cranial meninges== consisting of:
an outer layer called ==dura mater==.
a very thin middle layer called ==arachnoid==.
an inner layer (which is in contact with the brain tissue) called ==the pia mater.==

The brain can be divided into three major parts:
- Forebrain
- Midbrain
- Hindbrain
Forebrain:
- The forebrain consists of the cerebrum, thalamus, and hypothalamus.
- The cerebrum forms the major part of the human brain.
- A deep cleft divides the cerebrum longitudinally into two halves, which are termed the ==left and right cerebral hemispheres.==
- The hemispheres are connected by a tract of ==nerve fibers called the corpus callosum.==
- The layer of cells which covers the cerebral hemisphere is called the ==cerebral cortex== and is thrown into prominent folds.
- The cerebral cortex is referred to as ==grey matter== due to its greyish appearance.
- The neuron cell bodies are concentrated here giving the color.
- The cerebral cortex contains ==motor areas, sensory areas, and large regions that are neither clearly sensory nor motor in function.==
- These regions called association areas are responsible for complex functions like ==intersensory associations, memory, and communication.==
- Fibers of the tracts are covered with the ==myelin sheath==, which constitutes the ==inner part of the cerebral hemisphere.==
- They give an opaque white appearance to the layer and, hence, are called ==white matter.==
- The cerebrum wraps around a structure called ==the thalamus, which is a major coordinating center for sensory and motor signaling.==
- Another very important part of the brain called the ==hypothalamus lies at the base of the thalamus.==
- The hypothalamus contains a number of centers that control ==body temperature, the urge for eating and drink.==
- It also contains several groups of ==neurosecretory cells==, which secrete hormones called ==hypothalamic hormones.==
- The inner parts of cerebral hemispheres and a group of associated deep structures like the ==amygdala, hippocampus, etc., form a complex structure called the limbic lobe or limbic system.==
- Along with the hypothalamus, it is involved in:
- the regulation of sexual behavior
- Expression of emotional reactions (e.g., excitement, pleasure, rage, and fear)
- Motivation.
Midbrain:
- The midbrain is located between the thalamus/hypothalamus of the forebrain and the pons of the hindbrain.
- A canal called the ==cerebral aqueduct passes through the midbrain.==
- The dorsal portion of the midbrain consists mainly of ==four round swellings (lobes) called corpora quadrigemina.==
Hindbrain:
- The hindbrain comprises ==pons, cerebellum, and medulla== (also called the medulla oblongata).
- Pons consists of fiber tracts that interconnect different regions of the brain.
- Cerebellum has a very convoluted surface in order to provide additional space for many more neurons.
- The ==medulla of the brain is connected to the spinal cord==.
- The medulla contains centers that control
- Respiration
- Cardiovascular reflexes
- Gastric secretions.
- Three major regions make up the brain stem; mid-brain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
- The ==brain stem forms the connections between the brain and spinal cord.==
Reflex Action and Reflex Arc:
The entire process of response to peripheral nerve stimulation, that occurs involuntarily, i.e., without conscious effort or thought, and requires the ==involvement of a part of the central nervous system== is called a reflex action.
The reflex pathway comprises at ==least one afferent neuron (receptor) and one efferent (effector or excitator)== neuron appropriately arranged in a series.
- The afferent neuron receives a ==signal from a sensory organ and transmits the impulse via a dorsal nerve root into the CNS== (at the level of the spinal cord).
- The ==efferent neuron then carries signals from CNS to the effector.==
The stimulus and response thus form a reflex arc as shown below in the ==knee jerk reflex.==
