531 Lec 24-25
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:50 AM on 4/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse
2
New cards
List of events for neurotransmitters
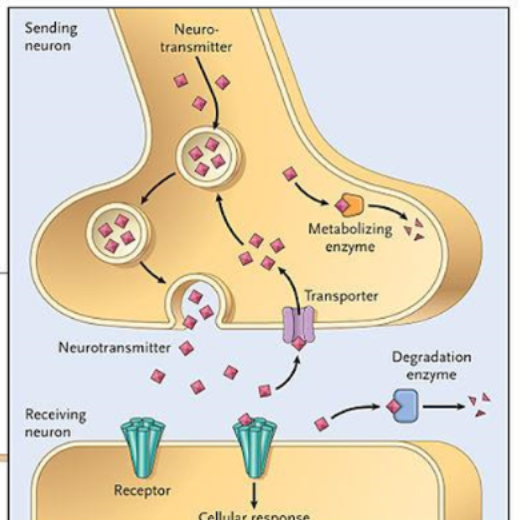
1)Usually synthesized in presynaptic neuron
2)Localized to vesicles
3)Impulse
4)Fusion of vesicle with presynaptic neuronal membrane
5)Release of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft
6)Interaction of messenger with post synaptic membrane receptors
7)Receptor-messenger engagement elicits biological response
8)Removal of NT from cleft
2)Localized to vesicles
3)Impulse
4)Fusion of vesicle with presynaptic neuronal membrane
5)Release of neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft
6)Interaction of messenger with post synaptic membrane receptors
7)Receptor-messenger engagement elicits biological response
8)Removal of NT from cleft
3
New cards
Amino Acid Neurotransmitters
Glutamate
GABA
GABA
4
New cards
Biogenic Amines NTs
Norepinephrine
Epinephrine
Dopamine
Serotonin
Histamine
Epinephrine
Dopamine
Serotonin
Histamine
5
New cards
Peptide NTs
Endorphins
6
New cards
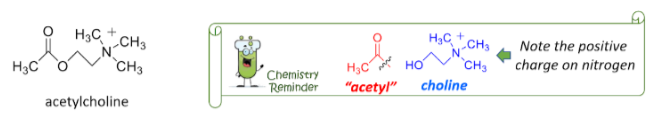
Acetylcholine
•Inhibits smooth heart muscle
•Constricts gastrointestinal muscles
•Extensively active throughout brain synapses
•Released at all vertebrate neuromuscular junctions
•Constricts gastrointestinal muscles
•Extensively active throughout brain synapses
•Released at all vertebrate neuromuscular junctions
7
New cards
Ach effects on periphery
Decreases heart rate
Increase Bronchoconstriction
Increased skeletal muscle contraction
Increased GI and urinary muscle contraction
Increase Bronchoconstriction
Increased skeletal muscle contraction
Increased GI and urinary muscle contraction
8
New cards
Ach effects on CNS
increased memory
increased thinking
increased thinking
9
New cards
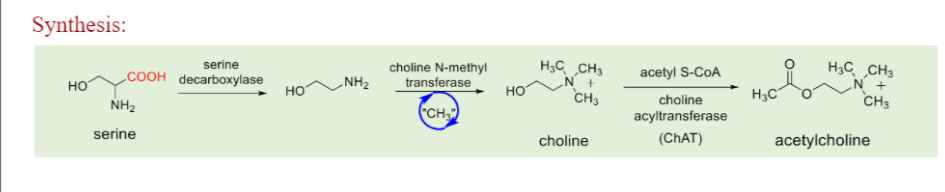
Ach Synthesis
1) Serine gets decarboxylated via serine decarboxylase
2)Choline is formed via choline N methyl transferase
3) Acetyl choline is formed via choline acyltransferase with acetyl COA as a co substrate
2)Choline is formed via choline N methyl transferase
3) Acetyl choline is formed via choline acyltransferase with acetyl COA as a co substrate
10
New cards
Ach breakdown
Acetylcholinesterase and water break Ach into acetic acid + Choline
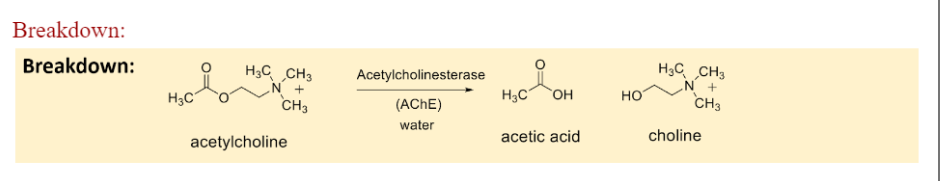
11
New cards
Ach Receptor signaling pathway
1)Impulse comes through axon
2)Impulse causes influx of calcium ion
3)Calcium oin binds an ACh vesicle
4)Vesicle fuses with membrane and releases Ach into synapse
5)Ach binds either nicotinic or muscarinic receptor on next neuron OR it can diffuse to a nicotinic autoreceptor or muscarinic autoreceptor on same neuron and get re uptaken OR hydrolyzed by AchE
2)Impulse causes influx of calcium ion
3)Calcium oin binds an ACh vesicle
4)Vesicle fuses with membrane and releases Ach into synapse
5)Ach binds either nicotinic or muscarinic receptor on next neuron OR it can diffuse to a nicotinic autoreceptor or muscarinic autoreceptor on same neuron and get re uptaken OR hydrolyzed by AchE
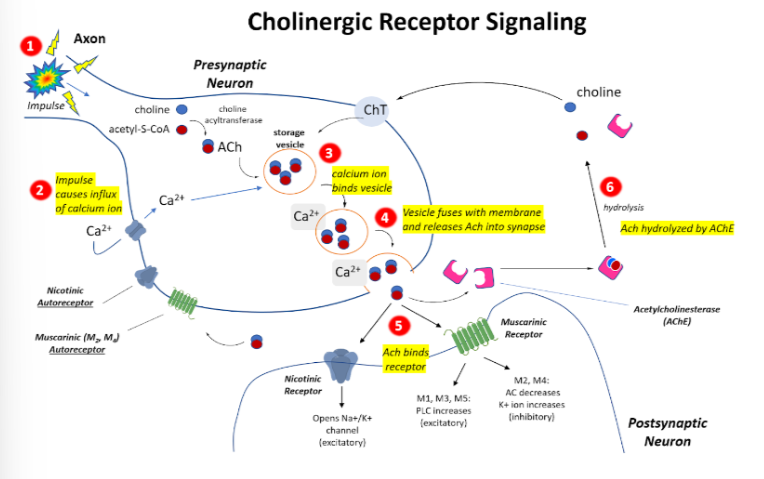
12
New cards
Muscarinic
• M1-M5
•G protein coupled receptors → second messenger cascade
•Natural ligand known as muscarine, low affinity for nicotine
•G protein coupled receptors → second messenger cascade
•Natural ligand known as muscarine, low affinity for nicotine
13
New cards
Nicotinic
•Nm- muscular
•Nn- neuronal
•Ganglionic
•Ion channels
•Natiral ligand known as nicotine , low affinity for muscarine
•Nn- neuronal
•Ganglionic
•Ion channels
•Natiral ligand known as nicotine , low affinity for muscarine
14
New cards
Acetylcholine Binding with Muscarinic Receptors
•Hydrogen bonding: ester and Asn-617
•Hydrophobic interactions of ethyl middle section
•Ionic bonding: quaternary amine and Asp311
•Methyl groups fit into small pockets
•Hydrophobic interactions of ethyl middle section
•Ionic bonding: quaternary amine and Asp311
•Methyl groups fit into small pockets
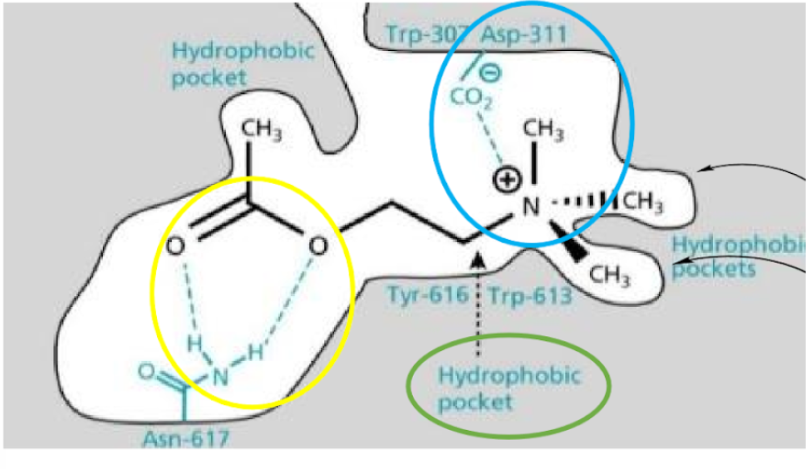
15
New cards
Ach Binding with AChE
Cation Pi interaction
Hydrogen bonding
\
Serine, histidine, glutamic acid
Hydrogen bonding
\
Serine, histidine, glutamic acid
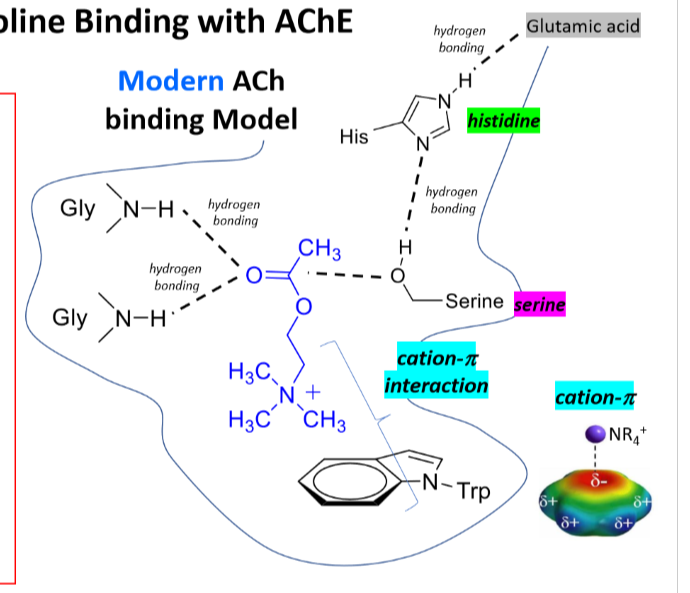
16
New cards
Therapeutic Uses of ACh
stimulates muscle contraction, involved in REM sleep, cognition and neuroplasticity
→Excessive Ach at the neuromuscular junctions and synapses cause symptoms of both muscarinic and nicotinic toxicity; cramps, increased salivation, lacrimation, paralysis, diarrhea, blurry vision, muscular fasiculation
→Low levels of ACh can lead to muscle weakness, memory, focus, thinking issues and other neuologica conditions
→Excessive Ach at the neuromuscular junctions and synapses cause symptoms of both muscarinic and nicotinic toxicity; cramps, increased salivation, lacrimation, paralysis, diarrhea, blurry vision, muscular fasiculation
→Low levels of ACh can lead to muscle weakness, memory, focus, thinking issues and other neuologica conditions
17
New cards
SLUDGE

18
New cards
Structure Activity Relationships (SARs):
an approach designed to find relationships between chemical structure (or structural-related properties) and biological activity (or target property) of studied compounds.
19
New cards
SARs for Muscarinic Drugs
1)Ing’s Rule of 5
2)The molecule must possess a nitrogen atom capable of bearing a positive charge, preferably a quaternary ammonium salt
3)For maximum potency, the size of the alkyl groups substituted on the nitrogen should not exceed the size of a methyl group
4)The molecule should have one oxygen atom, preferably an ester like oxygen capable of participating in an Hbond
5)There should be a two carbon unit between the ester oxygen atom and the nitrogen atom
2)The molecule must possess a nitrogen atom capable of bearing a positive charge, preferably a quaternary ammonium salt
3)For maximum potency, the size of the alkyl groups substituted on the nitrogen should not exceed the size of a methyl group
4)The molecule should have one oxygen atom, preferably an ester like oxygen capable of participating in an Hbond
5)There should be a two carbon unit between the ester oxygen atom and the nitrogen atom
20
New cards
Ing’s Rule of 5
Max cholinergic activity occurs when there is no more than 5 atoms from nitrogen to the terminal hydrogen atom on the acyloxy group
21
New cards
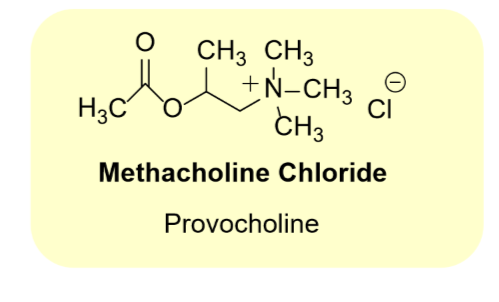
Methacholine chloride
•Muscarinic receptor selective
•Muscarinic agonist
•Low activity at nAChRs
•Bronchiospasm test for asthma
•Inhaled powder
•Muscarinic agonist
•Low activity at nAChRs
•Bronchiospasm test for asthma
•Inhaled powder
22
New cards
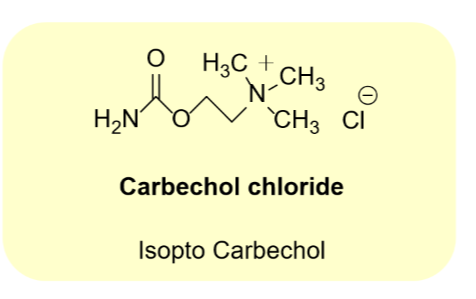
Carbechol chloride
•Binds mAChRs and nAChRS- agonist
•More restsant to base, acid that ACh
•More resistant to AChE than ACh
•Weak inhibitior of AChE
•Longer duration of action
•Use: glaucoma
•UseL Induce miosis during surgery
•Opthalmic solution
•More restsant to base, acid that ACh
•More resistant to AChE than ACh
•Weak inhibitior of AChE
•Longer duration of action
•Use: glaucoma
•UseL Induce miosis during surgery
•Opthalmic solution
23
New cards
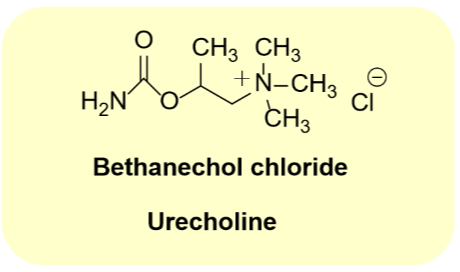
Bethanechol Chloride
•Carbamate analog of metacholine
•Muscarinic receptor selective
•Muscarinic agonist
•Virtually no activity at nAChRs
•Use: treat postsurgical urinary retention
•Use: treat postsurgical abdominal distention
•Oral drug
•Muscarinic receptor selective
•Muscarinic agonist
•Virtually no activity at nAChRs
•Use: treat postsurgical urinary retention
•Use: treat postsurgical abdominal distention
•Oral drug
24
New cards
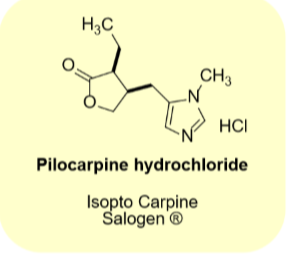
Pilocarpine hydrocholirde
•Natural product
•M3 receptor selective agonist
•Penetrates the eye well
•Use: Glaucoma
•Use: dry mouth due to radiation therapy
•Tablet, opthalmic solution, gel
•M3 receptor selective agonist
•Penetrates the eye well
•Use: Glaucoma
•Use: dry mouth due to radiation therapy
•Tablet, opthalmic solution, gel
25
New cards
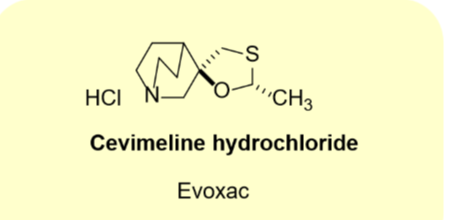
Cevimeline hydrochloride
•Natural product
•M1 receptor and M3 receptor selective agonist
•Use: dry mouth due to radiation therapy
•Oral tablet
•M1 receptor and M3 receptor selective agonist
•Use: dry mouth due to radiation therapy
•Oral tablet