Phys. Health: Arthritis and Lower Extremity Joint Replacement (Chap. 28)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Arthritis
Prevalence of Arthritis
Types of Arthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Osteoarthritis and Degenerative Joint Disease
Gout
Interventions for Arthritis
Arthritis InterventionsMedications:
NSAIDs – Reduce pain/swelling (e.g., ibuprofen).
DMARDs & Biologics – Slow autoimmune arthritis (e.g., methotrexate).
Corticosteroids – Short-term inflammation relief.
Gout meds – Lower uric acid (e.g., allopurinol).
Surgery:
Joint replacement – Used for severe arthritis (hip, knee).
Joint fusion – Stabilizes painful joints.
Arthritis in Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapists (OTs) and occupational therapy assistants (OTAs) use a multi-modal approach to help clients with arthritis by combining:
Joint protection techniques – Educating on ways to reduce joint stress.
Energy conservation strategies – Teaching how to pace activities and avoid fatigue.
Adaptive equipment – Recommending tools like jar openers and ergonomic utensils.
Exercise programs – Promoting gentle movements to maintain function.
Pain management – Using heat, cold, and relaxation techniques.
Environmental modifications – Adjusting home/work setups for easier access.
Occupational Therapy Treatment Process
Assessment of Occupational Performance
Interview – Discuss daily challenges.
Observation – Watch movement and function.
Assessments – Use tools to measure impact.
Activity Analysis – Identify task barriers.
Intervention Process
Education – Joint protection, energy conservation.
Adaptive Equipment – Tools for easier tasks.
Exercises – Improve mobility and strength.
Pain Management – Use heat, cold, relaxation.
Modifications – Adjust home/work setup.
Task Adaptation – Change activities for comfort.
What Is Arthritis?
Arthritis can be inflammatory, infectious, metabolic, or autoimmune
It can be progressive, static, or have periods of remission and exacerbation
Overall goals of OT intervention
Improve/prevent decline in function
Reduce/manage pain management
Preserve joint integrity
Improve quality of life (QoL)
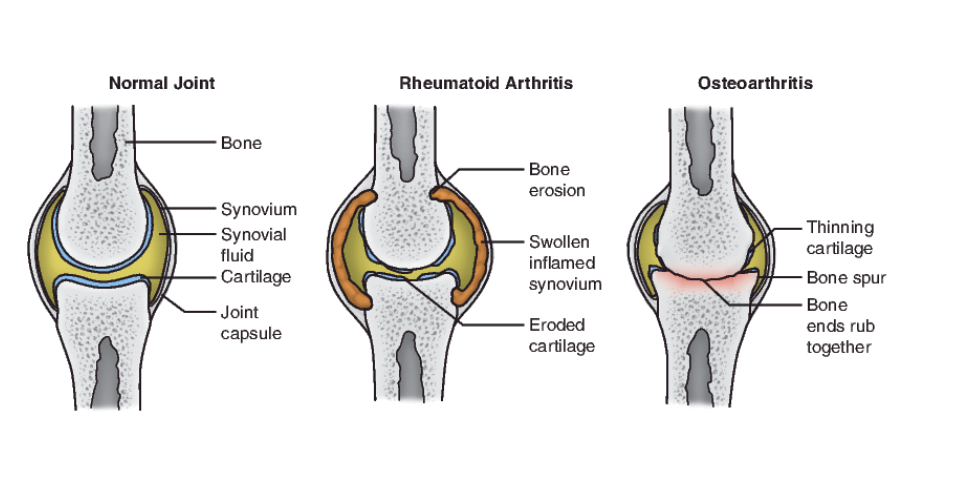
Osteoarthritis vs. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) or degenerative joint disease (DJD)
Articular cartilage wears away
Rheumatoid arthritis
Systemic, autoimmune
Also affects eyes & internal organs
Exacerbation/ remission
Comparison Chart
Characteristic | Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) | Osteoarthritis (OA) |
|---|---|---|
Age of Onset | Can begin at any age | Usually starts later in life |
Speed of Onset | Rapid (weeks to months) | Slow (years) |
Joint Symptoms | Painful, swollen, stiff joints | Achy, tender joints, little or no swelling |
Pattern of Affected Joints | Often symmetrical (both sides of the body) – hands, wrists, elbows, feet | Often asymmetrical – starts on one side, affects fingers (near nails), thumbs, hips, knees, or spine |
Duration of Morning Stiffness | Lasts over 1 hour, very difficult to get going in the morning | Lasts less than 1 hour, returns after activity |
Systemic Symptoms | Fatigue, general feeling of illness | No whole-body symptoms |
Osteoarthritis vs. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Signs & Symptoms
OA
Joint pain
Joint stiffness
Decrease ROM
Inflammation
Difficulty performing daily activities
Visible joint changes
Muscle weakness
RA
Tender, warm, swollen joints
Morning stiffness
Rheumatoid nodules
Fatigue, fever, and weight loss
Osteoarthritis vs. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Diagnosing
OA
Detailed health history
History of symptoms
Physical examination
X-ray/MRI
Ruling out other arthritic conditions
blood tests
joint aspiration
RA
Extensive history
Physical examination
Blood tests
Imaging studies
Osteoarthritis vs. Rheumatoid Arthritis
Treatment
OA:
Pain management
Improve function
Reduce the potential for long-term disability
Variable medical treatment (NSAIDs, pain relief)
Body mechanics, lifestyle changes
Adaptive equipment and environmental modifications
RA:
NSAIDs, DMARDs, and pain medication
Joint protection and orthoses
Pain/inflammation management
Adaptive equipment during exacerbation
Remission phase: gentle progressive exercise
Adaptive Equipment
OA:
Orthopedic supports (knee or wrist braces) to stabilize joints
Ergonomic tools (specialized kitchen tools, utensils with larger grips)
Canes or walkers to assist with mobility and reduce joint strain
Reachers/grabbers to avoid bending or stretching
Sock aids and buttonhooks for easier dressing
Shower chairs and handheld shower heads for bathing comfort
RA:
Splints or orthoses to protect joints, especially during flare-ups
Ergonomic tools (similar to OA, but with more focus on reducing joint strain during daily activities)
Adaptive writing tools (pens with cushioned grips)
Assistive devices for opening jars, doors, or bottles (easy-grip aids)
Wheelchairs or power mobility aids for when walking becomes too painful
Splinting for joint stability during exacerbations
Fibromyalgia - a type of arthritis
Symptoms:
Pain
Fatigue
Memory and concentration problems ("fibro fog")
Sleep issues, mood changes, headaches
Diagnosing:
No specific test
Diagnosed using ACR criteria (pain, fatigue, tenderness)
Treatment:
Pain relief (NSAIDs, meds)
Exercise (low-impact)
Acupuncture, massage therapy
Stress management (biofeedback, meditation)
Dietary supplements (e.g., vitamin D, magnesium)
Causes
Genetics
Infections
Physical/emotional trauma
Lupus - arthritic disease
Symptoms:
Painful, swollen joints
Extreme fatigue, unexplained fever
Butterfly-shaped rash, photosensitivity
Anemia, abnormal clotting
Headache, confusion, memory loss
Raynaud’s phenomenon, chest pain, edema
Can affect multiple body systems
Diagnosing:
Blood tests
Urinalysis (UA)
Other clinical assessments
Causes:
Genetic predisposition + environmental factors
Medication-induced lupus
Treatment:
Medications for symptom management
Alternative treatments
Orthoses for joint protection
Gout
Symptoms:
Intense pain, swelling, redness
Warmth in the affected joint
Joint stiffness, deformity
Tophi (uric acid crystal deposits)
Causes:
Family history
Male gender, obesity
Alcohol abuse
High-purine foods
Enzyme defects, organ transplants
Lead exposure
Diagnosing:
Blood test (uric acid levels)
X-rays (bony changes)
Joint fluid test (uric acid crystals)
Family history, medication review
Treatment:
Dietary modifications
Medications (e.g., uric acid-lowering drugs)
Lifestyle changes (weight loss, hydration)
Patient education
Pharmacological Treatment of Arthritis
Corticosteroids
OTC analgesics
Opioids
DMARDs/biologics
Antidepressants
Low dose seizure
Antimalarial
Immunosuppressant
Drugs that affect uric acid
Surgical Treatment of Arthritis
Arthrodesis (Joint Fusion)
Reduces pain, increases stability
Common in ankle, wrist, thumb, fingers
Arthroplasty (Joint Replacement)
Used for hips, knees, shoulders, ankles, wrists, elbows, MCP joints
Osteotomy (For OA)
Cuts and repositions bone to correct defects
Improves weight-bearing in lower extremity (LE) long bones
Resection
Removes all/part of a bone
Reduces pain, improves function
Synovectomy (For RA)
Removes diseased synovium
Decreases pain and swelling
Psychosocial Impact and Safety Concerns
Arthritis & Psychosocial Well-Being
Pain and fatigue → depression, anxiety, isolation
Loss of function → low self-esteem, frustration
How OT Helps
Pain management (joint protection, pacing)
Energy conservation
Assistive devices
Coping strategies
Skills to Teach
Joint protection
Adaptive strategies
Self-advocacy
Why Independence in ADLs/IADLs Matters
Boosts confidence
Reduces dependence
Encourages engagement
Why "No Pain, No Gain" Is Wrong
Can worsen joint damage
Teach pacing, graded exercise, and activity modification instead
OT Interventions
Decreasing pain
Improving function
Environmental and lifestyle modifications
Decreasing the risk of deformity or disability
Client Education
Decreasing pain
Improving function
Environmental and lifestyle modifications
Decreasing the risk of deformity or disability
Client education addresses all these areas through instruction and application of principles of:
Home exercise programs and modalities
Joint protection techniques
Pain management
Stress management/relaxation training
Adaptive Equipment
To Decrease Pain & Protect Joints
Jar openers – Reduce grip strain
Large-handled utensils – Easier to hold
Button hooks, zipper pulls – Reduce finger stress
Lever door handles – Easier than twisting knobs
To Improve Function & Independence
Reachers/grabbers – Avoid excessive bending/reaching
Sock aids, dressing sticks – Assist with dressing
Built-up pens, and ergonomic keyboards – Reduce hand strain
To Modify Environment & Lifestyle
Shower chairs, and grab bars – Increase safety
Raised toilet seats – Reduce knee/hip strain
Voice-activated devices – Reduce hand use
To Reduce Deformity & Disability Risk
Splints/orthoses – Support joints to prevent deformity
Compression gloves – Reduce swelling, improve circulation
Orthoses/Splints
Goals of Orthoses:
Decrease pain by allowing joints/tissues to rest
Improve function by supporting weak joints
Modify environment/lifestyle by enabling safe movement
Reduce deformity risk by preventing or limiting damaging forces
How Orthoses Help:
Protect weak/damaged joints → Allows rest and healing
Support safe joint use → Increases occupational engagement
Prevent/correct deformities → Reduce long-term disability
Edema
Goals:
Decrease pain by reducing swelling
Improve function by addressing edema
Environmental/lifestyle modifications to prevent swelling
Reduce the risk of deformity caused by swelling
How Management Helps:
Controlling swelling → Reduces pain and improves movement
Lifestyle modifications (e.g., wrist elevation, avoiding overuse) → Prevent future swelling
Thermal & physical agent modalities (e.g., cold packs, compression, massage) → Used in-clinic for edema control
Home-use techniques (e.g., contrast baths, elevation) → Clients can manage swelling independently
Therapeutic Exercises and Activities
Goals:
Decrease pain with movement
Improve function by increasing strength and range of motion
Modify lifestyle with exercise
Prevent deformity by maintaining joint health
How It Helps:
Graded exercises → Increase intensity gradually
Home exercise programs → Encourage consistency
Land & aquatic exercises → Support joint movement
Leisure activities → Keep clients engaged while improving health
Knowledge Assessment
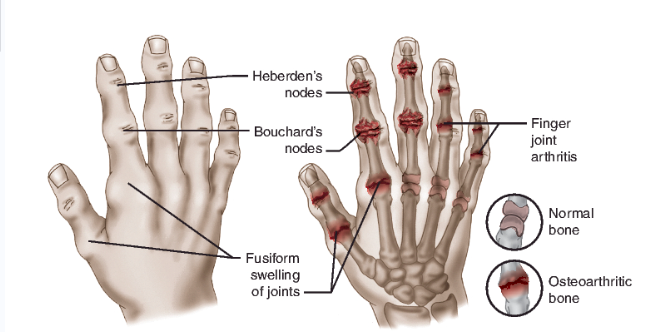
Bone Spurs – Osteoarthritis
Bouchard’s Nodes – Osteoarthritis (middle joints of fingers)
Boutonniere Deformity – Rheumatoid Arthritis
Facial Rash – Lupus (butterfly-shaped rash)
Fatigue – Common in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Lupus, Fibromyalgia
Fusiform Swelling – Rheumatoid Arthritis (swelling in fingers)
Heberden’s Nodes – Osteoarthritis (end joints of fingers)
Swan Neck Deformity – Rheumatoid Arthritis
Tophi – Gout (urate crystals)
Trigger Points – Fibromyalgia
Impact of Arthritis & OT Solutions
ADLs: Pain and stiffness make daily tasks harder.
OT: Use adaptive tools and joint protection strategies.Sexual Activity: Pain, movement limits, and fatigue affect intimacy.
OT: Teach positioning, energy conservation, and communication strategies.IADLs: Difficulties with cooking, cleaning, and finances.
OT: Offer adaptive tools, energy conservation, and task simplification.Health Management: Pain and medication management can overwhelm clients.
OT: Help organize routines and use reminders or planners.Leisure: Physical limits affect hobbies and social activities.
OT: Provide adaptive equipment and suggest alternate activities.Education/Work: Difficulty with tasks at school or work.
OT: Adjust ergonomics and modify tasks.Rest/Sleep: Pain or stiffness disrupts sleep.
OT: Teach sleep hygiene and relaxation strategies.Social Participation: Pain and fatigue limit social involvement.
OT: Use energy conservation and encourage group participation.