Muscular
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
Functions of the muscular system
hold body erect
movement
generates 85% of body heat
move food through digestive system
aid blood flow through veins
move fluids through ducts and other systems
muscle fibers
long, slender cells make up muscles
each muscle consists of a group of fibers bound together by connective tissue
fascia
flexible band of connective tissue
envelops, separates or bids together muscles
myofascial
pertaining to muscle tissue and fascia
tendon
narrow band of nonelastic, dense, fibrous connective tissue
attach muscle to bone
aponeurosis
sheet-like fibrous connective tissue resembling a flattened tendon
serves as a fascia to to bind muscles or connect to bone
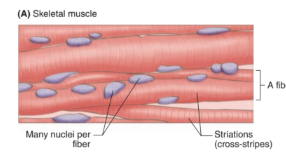
skeletal muscle
Voluntary control
striated
smooth muscle
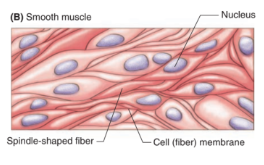
visceral muscles
involuntary
unstriated
visceral muscles
in the walls of internal organs, blood vessels, and ducts from glands
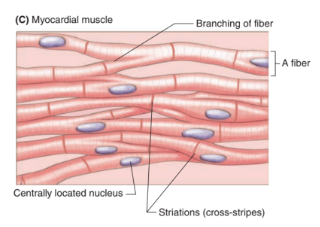
myocardial/cardiac muscle
striated
involuntary
constant contraction and relaxation causes heartbeat
innervation
simulation of a muscle by an impulse transmitted by a motor nerve
antagonistic muscle pairs
one muscle contracts
opposite relaxes
contraction
tightening, becoming shorter and thicker, enlarged muscle belly
relaxation
longer thinner
abduction
movement of a limb away from the midline
adduction
movement of a limb toward the midline
flexion
decreasing the angle between 2 bones by bending limb at joint
extension
increasing the angle by straightening limb
rotation
circular movement around an axis
circumduction
circular movement at the far end of a limb
supination
turning limb so that palm/sole is turned forward/upward
pronation
turning limb so that palm/sole downward/backward
dorsiflexion
bending foot upward at ankle
plantar flexion
bending foot downward at ankle
frontalis
muscle in the forehead
raises and lowers eyebrows
temporalis
muscle moves the lower jaw up and back to close the mouth
masseter
muscle moves the lower jaw up to close the mouth when chewing
pectoralis major
bulk of the chest in males
lies under breast in females
external and internal oblique
in abdomen
flex and rotate the torso and spine
rectus abdominis
helps flex the trunk
assists in breathing
supports the spine
transverse abdominis
on side of abdomen
engaged with laughs or coughs
deltoid
forms the muscular cap of the shoulder
trapezius
muscle moves the head and shoulder blade
biceps brachii
in anterior upper arm
flexes the elbow
triceps brachii
in posterior upper arm
extends the elbow
rectus femoris
extends the leg at the knee
quadriceps femoris
four muscles
flex and extend the leg at the knee
gastrocnemius
calf muscles that flexes the knee and bends the foot downward
exercise physiologist
specialist working under the supervision of a physician
develop, implement and coordinate exercise programs
administer tests
neurologist
physician specializing in treating causes of paralysis and similar disorders
physiatrist
physician specializing in physical medicine and rehab with the focus on restoring function
sports medicine physician
specializes in treating sport-related injuries of the bones joints and muscles
fasciitis
inflammation of a fascia
fibromyalgia syndrome
debilitating chronic condition
characterised by fatigue, diffuse or specific pain
tenosunovitis
inflammation of the sheath surrounding a tendon
tendinitis
inflammation of the tendons
from excessive or unusual use of joint
chronic fatigue syndrome
debilitating and complex disorder
unknown cause
profound fatigue
adhesion
band of fibrous tissue that holds structures together abnormally
atrophy
weakness/wearing away of body tissues and structures
myalgia
tenderness or pain in muscles
myocele
herniation of muscle substance through a tear in the surrounding fascia
hernia
protrusion of a part of a structure through the containing tissue
myolysis
degeneration of muscle tissue
myorrhexis
simultaneous inflammation and weakening of voluntary muscles in many parts of the body
sarcopenia
loss of muscle mass, strength and function with aging
muscle tone
the state of balanced muscle tension
atonic muscle tone
lacking normal tone or strength
dystonia muscle tone
abnormal muscle tone that caused impairment of voluntary movement
hypotonia muscle tone
diminished tone of skeletal muscles
ataxia
lack of muscle coordination during voluntary movement
contracture
permanent tightening of fascia, muscles, tendons, ligaments or skin
occurs when elastic connective tissues are replaced with nonelastic fibrous tissues
intermittent claudication
pain in leg muscles during exercise
spasm
sudden, involuntary contraction of muscles
cramp
painful localized muscle spasm often named for its cause
spasmodic torticollis
stiff neck due to spasmodic contraction of the neck muscles that pull the head toward the affected side
bradykinesia
extreme slowness in movement
dykinesia
distortion/impairement of voluntary movement
hyperkinesia
abnormally increased muscle function/activity
myoclonus
sudden involuntary jerking of muscles
nocturnal myoclonus
myoclonus when a person is falling asleep
singultus
myoclonus of the diaphragm causing hiccup with each spasm
myasthenia gravis
chronic autoimmune disease affecting the neuromuscular junction and producing serious weakness of voluntary muscles
muscular dystrophy
over 30 genetic diseases
progressive weakness and degeneration of skeletal muscles without affecting the nervous system
duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
most common
primarly affects boys aged 3-5
progressses rapidly
becker muscular dystrophy (BMD)
similar but less sever than DMD
repetitive stress disorders
result from repeated motions
repetitive stress disorders- compartment syndrome
compression of nerves and blood vessels
due to swelling within muscle compartment
overuse injuries
minor tissue injuries that have not been given time to heal
overuse tendinitis
inflammation of tendons caused by excessive or unsual use of a joint
stress fracture
myofasical pain syndrome
chronic pain disorder
affecting muscles and fascia throughout the body
myofasical pain syndrome - trigger points
tender areas
commonly develop where facia comes into contact with muscle
myofasical pain syndrome - referred pain
originates in one area but is felt in another
rator cuff injuries- impingement syndrome
inflamed and swollen tendons are caught in the narrow space between shoulders and joints.
rator cuff tendinitis
inflammation of tendons of the rotator cuff
may lead to ruptured rotator cuff
carpal tunnel syndrome
tendons passing through the carpal tunnel are chronically oversued
become inflamed and swollen
carpal tunnel release
surgical enlargement of the carpal tunnel or
cutting of carpal ligament to relieve pressure
ganglion cyst
harmless fluid-filled swelling
occurs most commonly on the outer surface of the wrist
epicondylitis
inflammation of the tissues surrounding the elbow
heel spur
calcium deposit in the plantar fascia near attachment to the calcaneus bone
can cause plantar fasciitis
sprain
injury to a joint occuring when a ligament is wrenched or torn
strain
injury to the body of the muscle or to the attachment of a tendon
shin splint
painful condition caused by the tibialis anterior muscle tearing away from the tibia
achilles tendinitis
painful inflammation of the achilles tendon caused by excessive stress
iliotibial band syndrome
overuse injury of the iliotibial band rubbing against bone
incomplete spinal cord injury
some function below the level of injury
complete spinal cord injury
complete loss of sensation and muscle control
paralysis
loss of sensation and voluntary muscle movement in a muscle through disease or injury to its nerve supply
myoparesis
weakness or slight muscular paralysis
hemiparesis
slight paralysis affecting one side of the body
hemiplegia
total paralysis affecting one side of the body