Ch 2 Chemistry of Life
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

41 Terms
Atom
Basic unit of matter
Element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
Ion
An atom or group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge.
ionic bond
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves SHARING a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
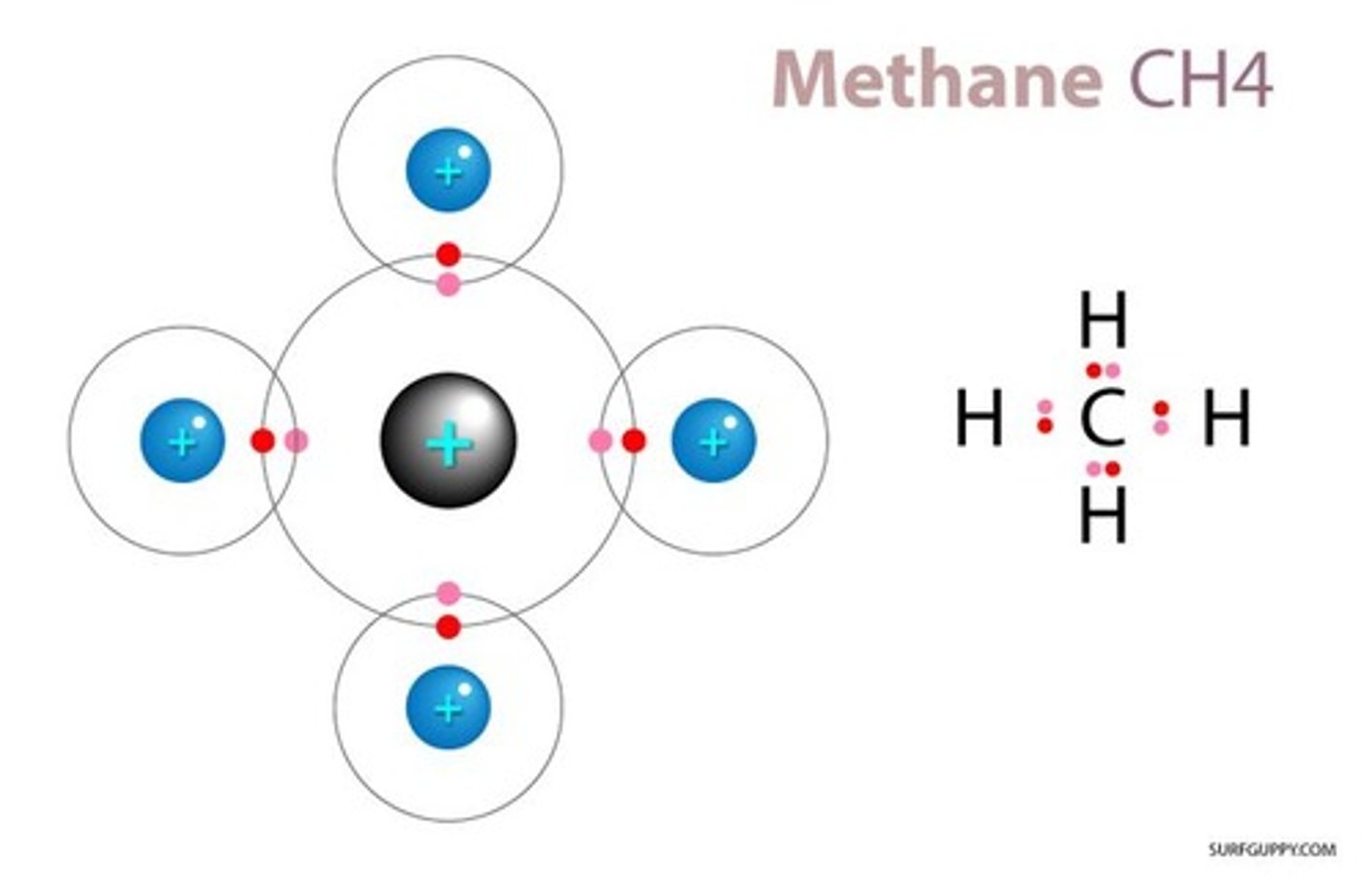
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together
Cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance

Adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances

Solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another.

Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances

Solute
the substance that is dissolved

Acid
A substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution. any compound that forms H+ ions in solution
Base
A substance that decreases the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
pH
a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution
specific heat
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celcius

Enzyme
protein that acts as a biological catalyst
Monomer
A simple compound whose molecules can join together to form polymers
Carbohydrates
the starches and sugars present in foods
Lipid
Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Protein
An organic compound that is made of one or more chains of amino acids and that is a principal component of all cells
nucleic acids
macromolecule made of a string of nucleotides
Reactant
a substance that takes part in and undergoes change during a reaction.
product
A substance produced in a chemical reaction
activation energy
Energy needed to get a reaction started
Exothermic reaction
A reaction that releases energy in the form of heat
endothermic reaction
A reaction that ABSORBS energy in the form of heat
acidic solution
A solution with a pH less than 7 is an
basic solution
a solution whose pH is greater than 7
Proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
Neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
stronger
Covalent bonds are STRONGER or WEAKER than ionic bonds
low
A substance that takes very little energy to change its temperature has a LOW or HIGH specific heat?
1) It can make 4 covalent bonds
2) It will bond with many elements
3) it can make three shapes of molecules
List three characteristics of carbon that may be why so many biomolecules are based on carbon
1) straight chain
2) branched chain
3) ring
What are the three SHAPES of molecules carbon can make?
1) Protein
2) Carbohydrates
3) Lipids
4) Nucleic Acids
List the four carbon based biomolecules that are the foundation of life
amino acids
What is the monomer that is linked together to make a protein?
DNA and RNA
What are two polymers of nucleic acid?
fatty acids
What is the monomer or building block for lipids?
bond energy
the energy required to break a chemical bond
Hydrogen
Because water is a polar molecule it can form __________________ bonds between different water molecules
peptide binds
What type of bond holds amino acids togther?