TOPIC 1 - Magnetic Confinement Fusion
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
C: Conceptual, D: Able to Derive, U: Able to use
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
C: How is the charged particle confined?
Charged particles in magnetic confinement fusion are confined using strong magnetic fields that create a toroidal or stellarator shapes.
C: Why is the toroidal field alone not a sufficient solution?
The toroidal field alone is not sufficient because it does not provide stability against particle drift and can allow some charged particles to escape.
C: Rotational Transform and safety factor
The rotational transform is a measure of the twist of magnetic field lines in a plasma, and it helps define the safety factor, which determines how well the magnetic configuration can confine the plasma and prevent instabilities. - Helical path.
D: Relationship between safety factor q and the angle l
q = #turns toroidally/ poloidal turn = 2pi/l
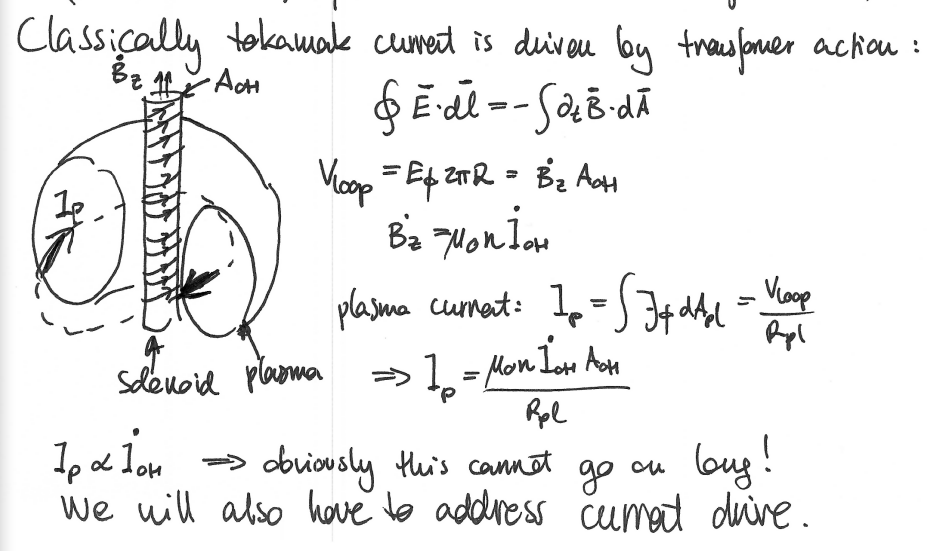
C: How is current driven in a tokamak?
Transformer Action
C: Gain Factor, Q and what is engineering Q?
Q = (Pout - Pin )/ Pin = (Pn+Palpha) / Pext = Pfusion / Pext
Q = 0; no fusion. Q = 5; burning plasma regime. Q=10;ITER. Q to infinity at ignition.
Q enginerring is for electrical power and is always less than Q. The engineering Q for ITER is around 2.
Power Balance
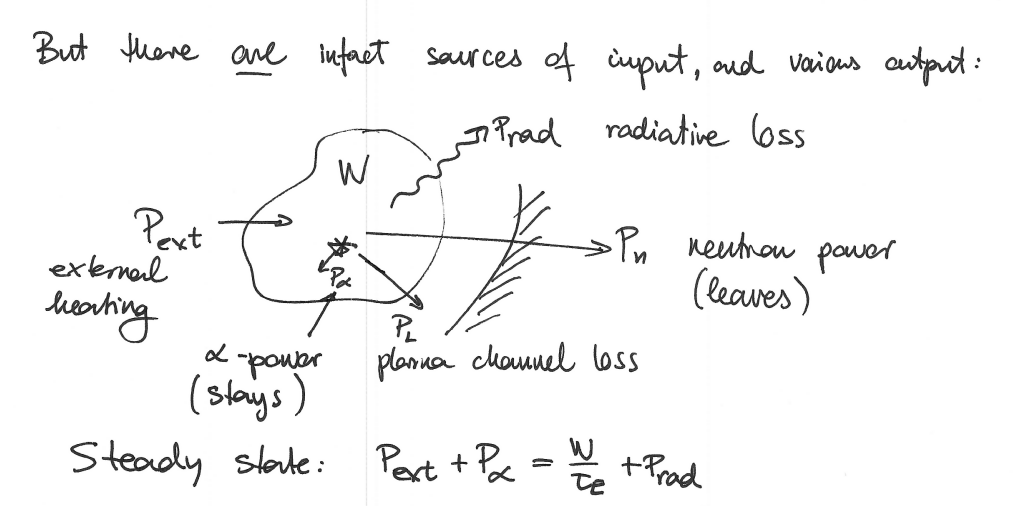
Confinement time tauE
tauE = W / PL where PL is the - change in stored energy W
P-bremmstrahlung proportionalities and Z-effective
P_br = const Z² ni ne T1/2
Z-eff = 1/ne \sum nj Zj2
Lawson Criteria
nT \tauE > 3×1021 m-3 KeV s
n \tauE > 12T/(<ov>E_alpha )
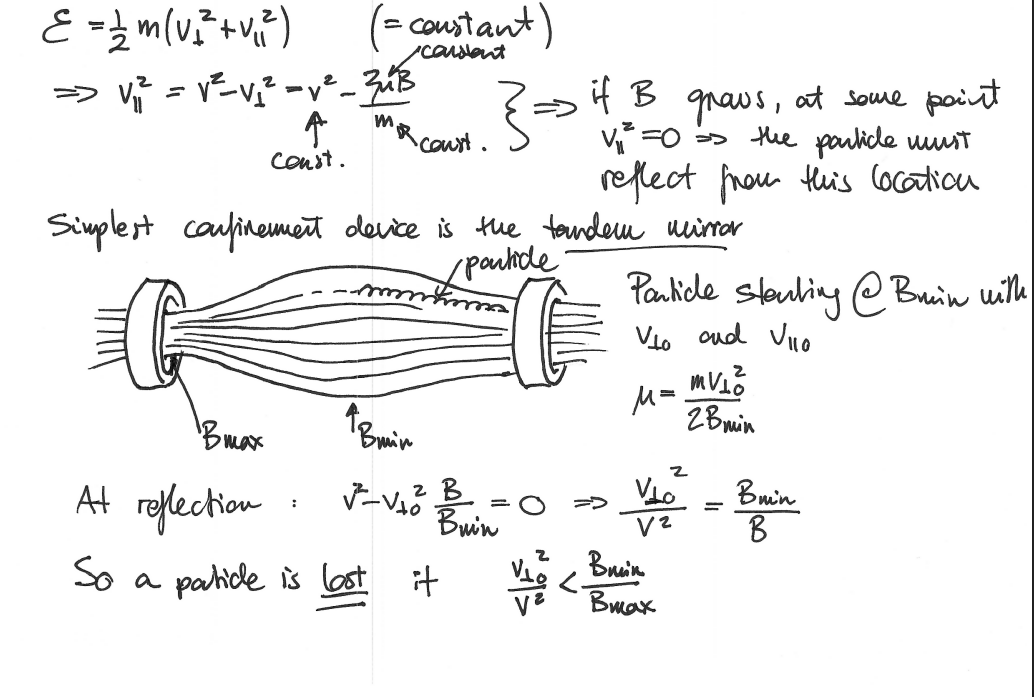
Magnetic Moment Expression
mu = mvperp2 / 2B is an adiabatic invarirent
When is a particle lost? - Magnetic Mirror
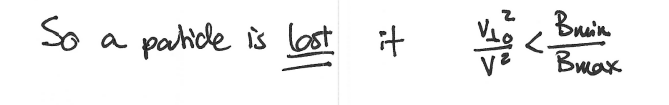
Magnetic Mirror Trapping Condition Derivation
Loss Cone
The loss cone refers to a region in velocity space of plasma particles where their motion leads to escape from confinement due to magnetic field gradients, particularly in magnetically controlled environments.

Grad B Drift Velocity
V-gradB = mvperp2 /2qB³ (B X gradB)
Curvature Drift Velocity
V-R = mvparallel2 /qB³ (B X gradB)
Consequence of grad B and curvature drifts
Drifts are charge dependent → Ions and electrons drift in opposite direction → E-field → EXB /B² drift produced that is parallel to R, so the particles are lost in the walls
FIX: Add polloidal field