Mid Term for Intro to Information System Management
1/144
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This midterm covers Chapter 2,4,5,6, and 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
145 Terms
3 Class of Computers
CPU(brain), Memory(storage), Input/output(sensory part)
Central Processing Unit(CPU)
It has 24 cores and its flexiable. Its good for general purpose however its much more limited.

Graphics processing unit(GPU)
it has 10000 cores and its for graphics(not flexblie). Its really good for proccessing and performing calulcation s and for 3D graphics
Single-user portable computers
Small enough to be carried and light weight Notebooks/Tablets/Nettops
Single-user nonportable computers
Fixed stationary computer that can do complex or specific task Desktops and Workstations
Server Farm
A large collection of servers that work togather to prcoess data and to handle task like running a website
Blade server
Compact, modular servers that include computer memory, storage, network connections, and often a cooling source. They are designed to save space in data centers.
1 and 2 tier for data center
Good for small busniess. if a busniess data center runs out it wont ber a bug disruption
3 and 4 data center
good for large organizations can have large hardware and has power-related devices and other power sources
Green Computing
environmentally design that focus on reducing hazardous material, lowing a company power-related cost, and can recyclinng computers and other equipment
Random Acccess Memory (RAM)
Temporary Hardware that stores currently being data. This allows a fast access and proccessor of different files and applications.
Read-only Memory(ROM)
Permanet Hardware. Data that has been pre-recorded. Allows a phone and computer to boot up without loosing its data Nonvolatile
Characteristics of quality data
Accessible, Accurate, Complete, Economical, Relevant, Reliable, Secure, Timely and verifiable
Why is is important for Quality data and information
It allows to make data backed up decisons.
It allows you to anaylsis __ easier which gives you make customers satisfaction high
Find your target audience
It enchances innovation. vecuse it allows people to work efficency, product and service quality
Raises Productivity allows employees to focus on the core mission instead of correcting the data errors
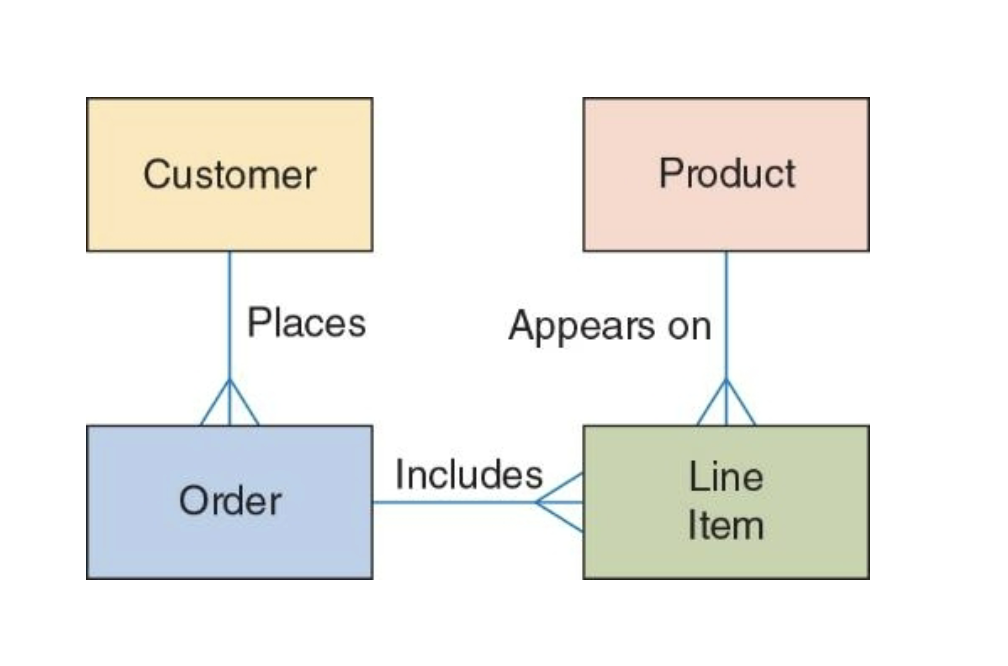
Entity-Relationships(ER)
A model that shows the structure of the database by showing the relation between entities(tables) and their attributes (characteristics) to others entities. This is used to anayze and communicate data needs
Data query language (DQL)
select data from a table in the database
Data definition language (DDL)
collections of intructions and commands used to define/describe the data and the relattionships
Data dictionary
collection of metadata that describe the data, format, stucture, and relationshops in a data base
Database Management System (DBMS)
Software to create/maintain/control the database by allowing user to intact with the data
Multiple-user computers
System that allows several users to have access and interact with the same computer and it shares resources like storage and processing power Mainframe computers / Mainframe computer, Supercomputer(largest),Blade servers, and Embedded computers
Data Warehouse
(older) Used as a storage for large datebase. its a hub for a organization complete analytical data throughout the enterprise.
Supercomputers
Large, fast, expensive used for complex math and tasks government or a world company has it, used for process large amount of data from space
Embedded computers
Sit on a the motherboard. Its very small and only has specific job —> cheap smartwatch that counts steps and heartbeat
Processors
Machine that processes something
Mainframe computers
Processes thousands of tasks simultaneously(consistently) Bank transactions
Quantum computing
a type of computing the is focus on quantum mechanics to perform calculations at a quick speed its an emerging computers
Magnetic Ink Character Recognition(MICR)
(Input) A technology used to verify the legitimacy or originality of paper documents and to assist in the processing of checks
Optical Character Recognition(OCR)
(Input) a technology that enables the conversion of different types of documents, such as scanned paper documents or PDFs, into editable and searchable data formats.
Optical Mark Recognition(OMR)
(Input) A technology used to capture and interpret human-marked data from forms such as surveya, ballots, and SAT
Speech recognition devices
(Input) Devices that convert spoken language into text or commands, commonly used in voice-activated systems
Plasma display
Uses small cells filled with gas that light up when electrically charged, creating bright and high-contrast images — often used in large TVs.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
Uses liquid crystals that block or allow light from a backlight to pass through, making it energy-efficient and ideal for thin screens like laptops and monitors.
LED (Light Emitting Diode)
A type of LCD display that uses LEDs instead of fluorescent lights for the backlight, offering brighter images, thinner screens, and lower power use.
OLED (Organic LED)
Each pixel produces its own light using organic materials, giving deeper blacks, faster response times, and flexible or curved screen designs. its the lowest consumption
Different types of Memory
RAM, ROM, and cache
Memory
Gives the processor with an area to store instructions and data
Input/Output
Provide data and instructions to the computer and it deals with results sent from the computer
Cache
High-speed memory, processor can access faster than the main memory
Cloud computing
Delivering on-demand computing services (servers, storage, databases, networking, software) over the Internet.Offers flexible resources, rapid innovation, and cost savings.
Utility computing
A service provisioning model where computing resources (like processing power or storage) are provided on demand and billed like a public utility. Allows users to pay only for the resources they consume.
Grid computing
collection of computers that work to solve a common problem
Parallel computing
A type of computing that divides a large workload among many processors to solve a problem
Web computing
gives a run applications and access data using the web browser over the internet
Data center
climate/access controlled housing computer hardware
Data mart
A subset of data warehouse that provide quick access to relevant data for a specific department
Data mining
Used to find hidden patterns, trends and etc which is important in large datasets to make data backed decision-making
Real-time
responds to input instantly
Multithreading
allows to open different thread(a set of instruction within an applications that is independent of others threads) of a single program
Multiprocessing
Supports running a program on more than one CPU.
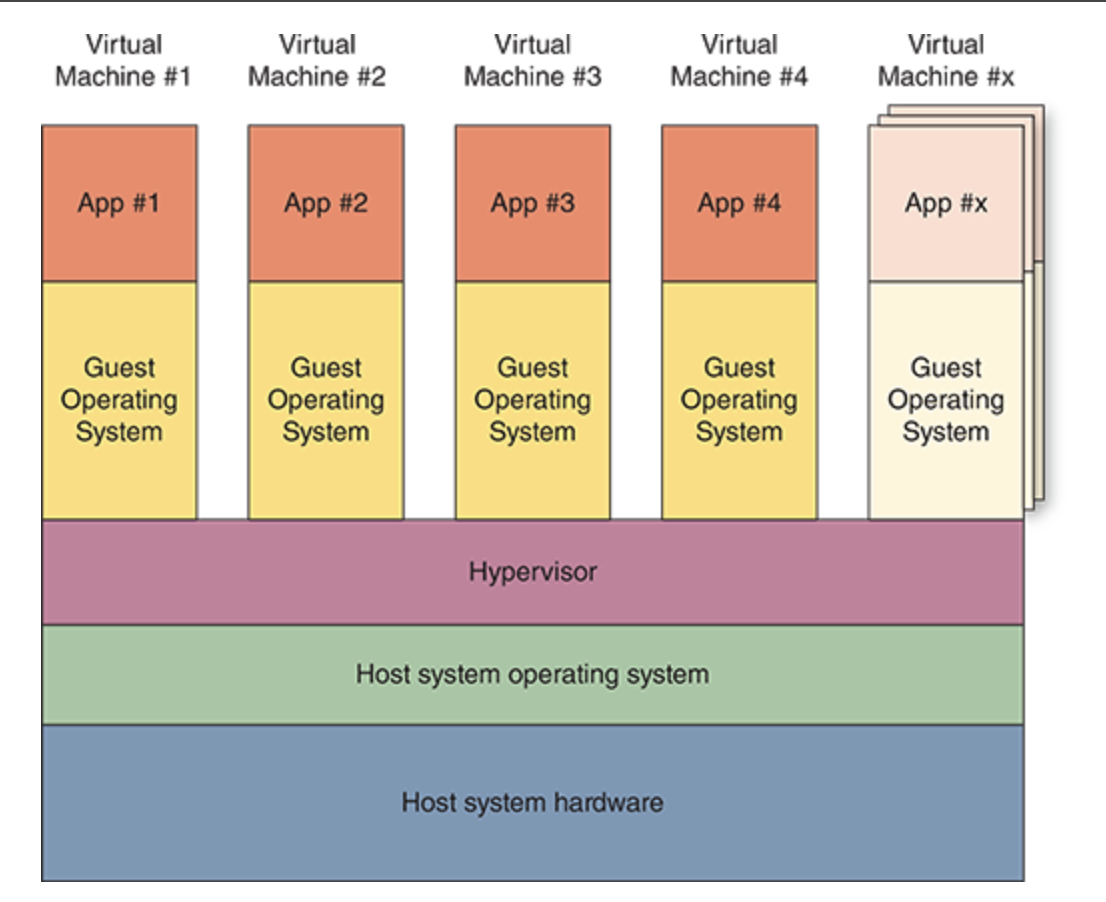
Server virtualization
is a way to divide one physical server into several smaller virtual servers. Each virtual server works like a separate computer, even though they all share the same physical hardware. This can improive hardware usage
5 approach of task mangement
Multi-user, multiprocessing, multitasking, multihreading, and real-time
Operation System
a set of programs that controls the computer’s hardware and acts like an interface wiith the applications
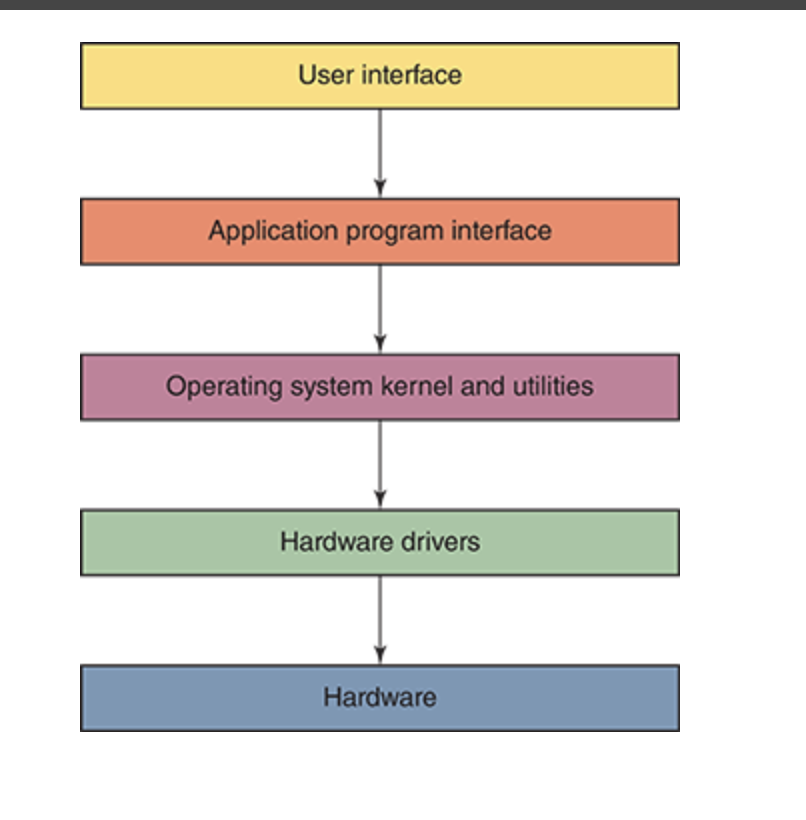
kernel
heart of the operation systems that control the most critical process
Secondary Storage
Store large amounts of informations more permanetly than main memory
Secondary Storage characteristics
Access method, capacity, and portability
Portability
Ability of a software to be transferred to another
Backward compatibility
Key feature of the mainframe. means that new computers or software can still run older programs that were made for earlier versions.
Scalability
ability that computer has handling alot of current users smoothly
Workstations
Mainly used to support engineering and technical users that perform with heavy math computing
3D
used to make solid objects from powder or filaments
Data Center
Climate/controlled building that house computer hardware that delivers organization’s data and information services. They also have air-cooing systems to adjust to the heat created by the processors
Thin client
Low cost. Manged computer with no internal/external attached drives for data storage. They have a limited capabilites
tier 1 and tier 2 characteristic
may be appropriate for small organizations where a business disruption of several hours to a few days would not have a serious business impact and critical activities could be managed manually without computer assistance
tier 3 and 4
dependant on computers to manage manufacturing operations
Green computing Main goals
Reduce hazardous material
lower power cost
Recycling and enable safe disposal of computers
Instruction and execution phases
Fetch instruction, decode instruction, execute instruction, and store results.
Clock Speed
Porduce a series of electronic pulses at a predetermined rate
Criteria to classify data centers into four tiers?
to enable organizations to quantify and qualify their ability to provide a predictable level of performance based on expected annual downtime, fault tolerance, and power outage protection.
Multicore microprocessor
Combines two or more independent processors into a single computer so they can share the workload.
System Software
Operating systems and utility programs that manage hardware and software.
Application Software
Programs designed to perform specific user tasks (e.g., word processing, web browsing).
Nettop
inexpensive desktop for email, web and document processing
Operating Systems
Set of programs that controls a computer’s hardware and acts as an interface with application software. The activities pefform by it are managing files and system memory.
Entity
is a person, place, or thing (object) for which data is collected, stored, and maintained Student and Product
Attribute
a property or characteristic of an entity Name or Age
Data item
the smallest piece of data a single value or field
Information
Processed or organized data that has meaning.
Knowledge
understanding or insights derived from information.
Hierarchy of data
Organzied arragement of data from its smallest unit to the largest container .data item → attribute → record → file → database
Schema
blueprint of a database
Open-source operating system
Free and distributed with a available of the source code Limit: eople need to br trained with it as well it needs to be protected. Linux and Python
4 Different objects in database
Queries, forms, report and table.
Database
Where you keep information. You can changing/inserting/retrieving/removing files in it
What makes a good database
Accessible, accurate, complete, economincal, relevant, reliable, secure, and timely and vertiable
Primary key
is a set of columns that uniquely identifies each row in that table
Foregin Key
Is a field in one table that refers to the primary key in another table
4 commons types of business analytics
Describe, Diagnosiyoc, predictive, prescriptive
Characteristics of Big Data
Volume, Velocity, variety, veracity, and value
Big Data
Describe data collections that are big and complex that traditional data management software, hardware and analysis processes can’t deal with them
Extract, Transform, and load(ETL)
a process that takes data from different sources that it tranforms it into a format for analysis and stores it in a data container. Doesnt need a data lake but a warehouse
Why do business use ETL
Having analysis data allows people to identity important insights whole decision making in the company uses it to make organizational decisions
NoSQL
Stores data in a non structure query —> not all database need to have structure. In simple terms this mean that if theres a new entity or attribute it doesn’t need a predefined schema because its meant to just be added. Its really good for analyzing interconnections, location, events, transactions and also. they have good greater horizontal scaling capability.
IMDB
Database management system that stores the entire database in random access memory(RAM) —> this allows faster access to data
Query
a request for data or information from a database.
SQL
the main language used to interact with databases.
DaaS
An arrangement where the database is stored on a service.
The pros of DaaS
it reduce cost that relates to hardware, software, and staffing. it can have more or less of the capacity based on the individual changing needs
Data
Raw facts or figures without context.
Data manipulation language
is a subset of SQL, used to manage/manipulate data within tables (e.g., SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE).
Applications software
Specific Purpose. to allow users to perform specific tasks such as playing games and/or opening documents Adobe photoshop,Spreadsheet, Google Chrome
