Dendrology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Dendrology
Is the study of trees and includes taxonomy, identification, silivical characteristics, ranges, morphology, and ecology
Factors that make a Tree
Heights 4.5m (15ft) or more
Perenial
Single dominant woody stem
Capable of diameter growth
Factors that make a Shrub
Heights under 4.5m (15ft)
Perenial
Multi-stemmed
Capable of dianeter growth
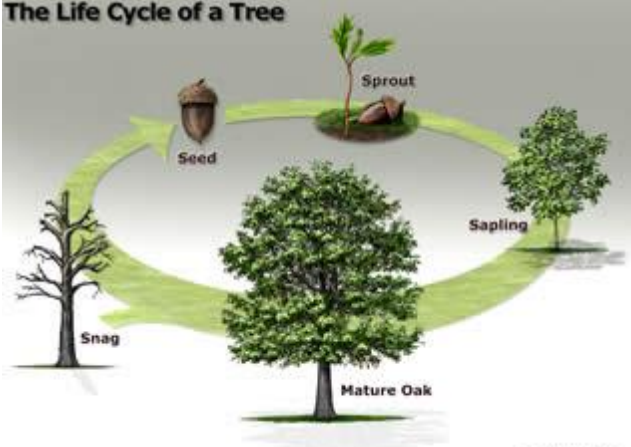
Tree Life Cycle
Seed → Sprout → Sapling → Mature → Mature Oak → Snag
Seed dispersal methods
Animals, wind, water, humans
How do seeds develope
Male & female parts of the tree producing fruits
Seeds are either in ______ like an acorm or in ______ like the black cherry
a prptective nut…. fleshy fruits
Seedling
Begins to develop woody characteristics
Stem harden, change color, & develop a thin protective bark
Roots are in the upper soil 4 water, nutrients, & air
Laeves/needles are adapted to shade but tilt toward light
Threats to seedlings
Fire, flood, drought, disease, insect attacks, animals
DBH
Diameter at Breast Height (4.5ft): Standard height to measure trees
Factors that make Sapling
1-4 in DBH
Not mature enough to reproduct
Branches develop
~Size of a nursery tree
Same competition as seedlings (Fire, flood, drought, disease, insect attacks, animals
Mature Tree
>4in DBH
FLowers develop, fruits form, seed dispersal can begin
Maximum environmental benefits
Benefits of a Snag
Provides habitat & food for wilflife
Returns nutrients to soil 4 other trees to use
Problems of a Snag
Fire Hazard/Fuel
Public Safety Hazard
Conifer
Needle shaped leaves
Cone-bearing
Evergreen
Gymnosperm
Pine

Gymnosperm
A plant that has seeds unprotected by an ovary or fruit
Deciduos
Broad, flat leaves
Seasonal
Angiosperm
Oak & Ash et all

Angiosperm
A flowering plant which forms seeds inside a protective chamber called an ovary.
Broadleaf, hardwood
Factors of Tree ID
Type
Arrangement
Shape
Margin
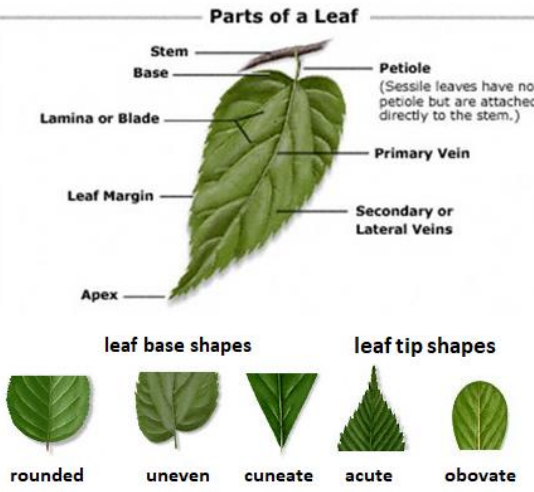
Leaf Shape
Simple Leaf Type
1 leaf blade
Joined by it's stalk to the woody stem

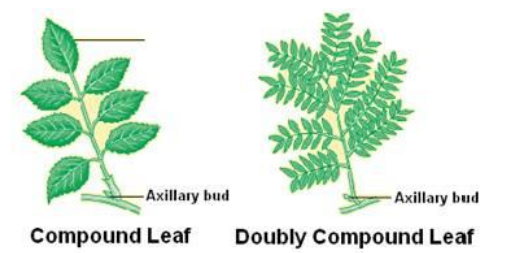
Compound Leaf Type
Made up of several leaflets
Leaflets are joined to non-woody midrib
Leaf Arrangment
Whorled, Opposite, Alternate
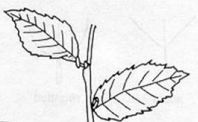
Alternate
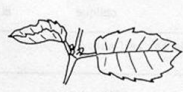
Opposite
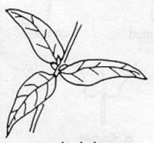
Whorled
Leaf Margin
Edges of leaves that can give clues to tree ID; Teeth (serrated, Lobed, Entire)

Entire

Serrate

Serrulate

Double Serrate
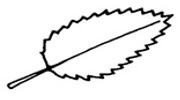
Dentate

crenate

undulate

Lobed
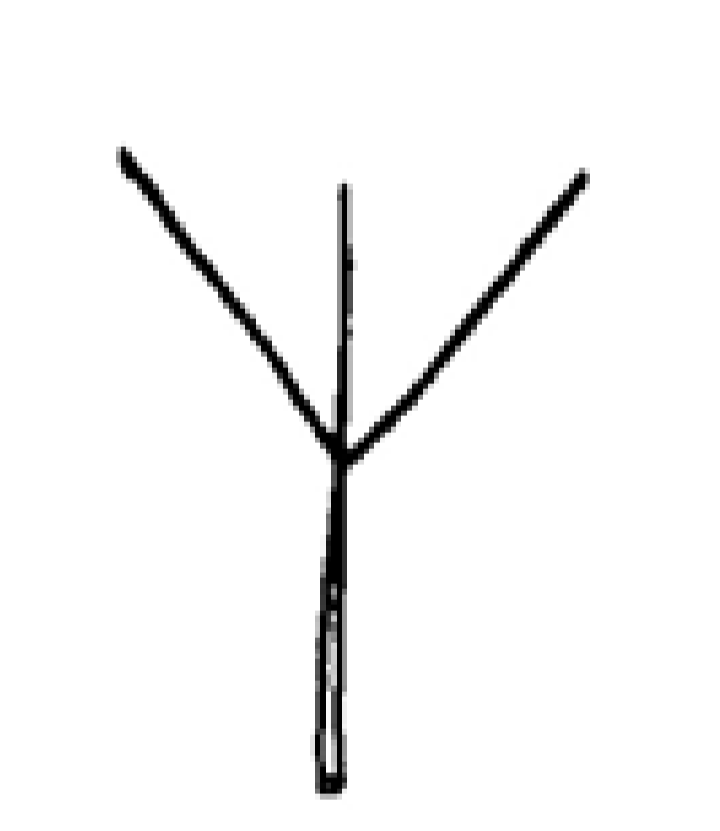
Acute
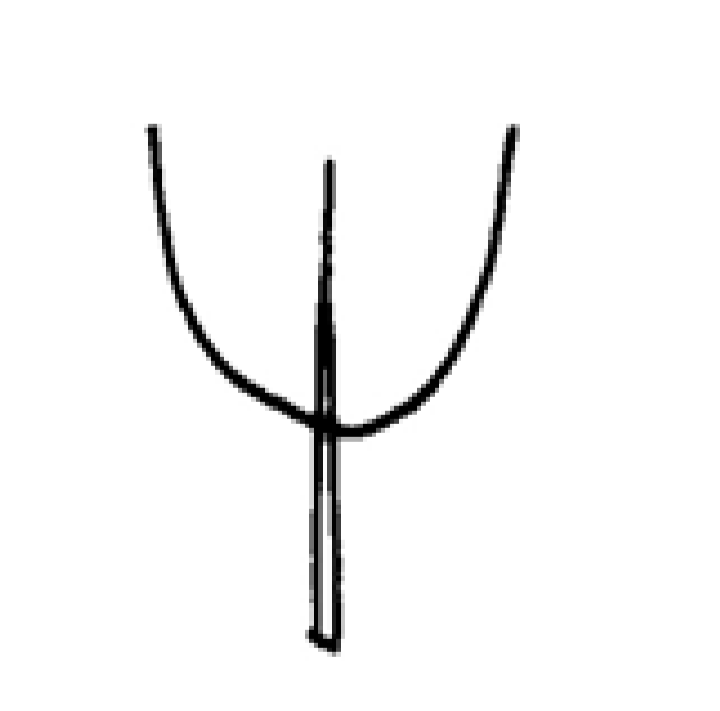
Rounded
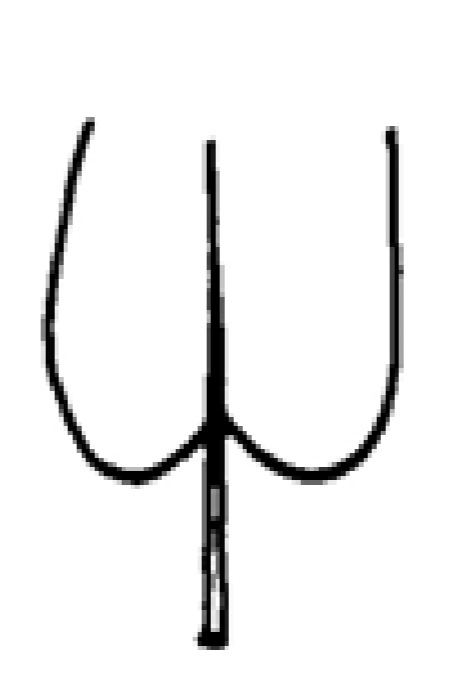
Cordate
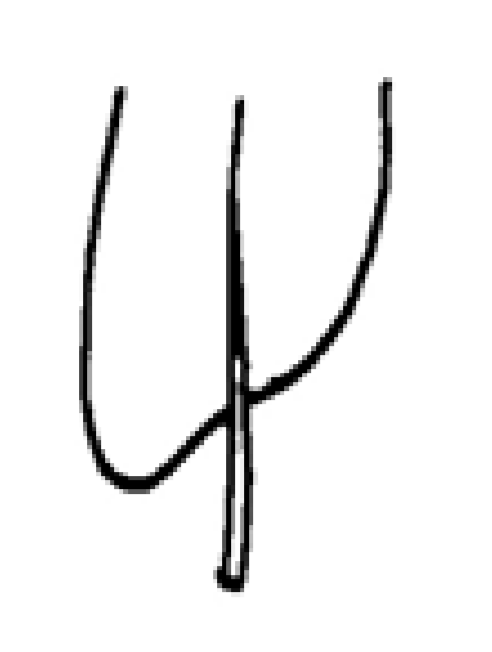
Oblique
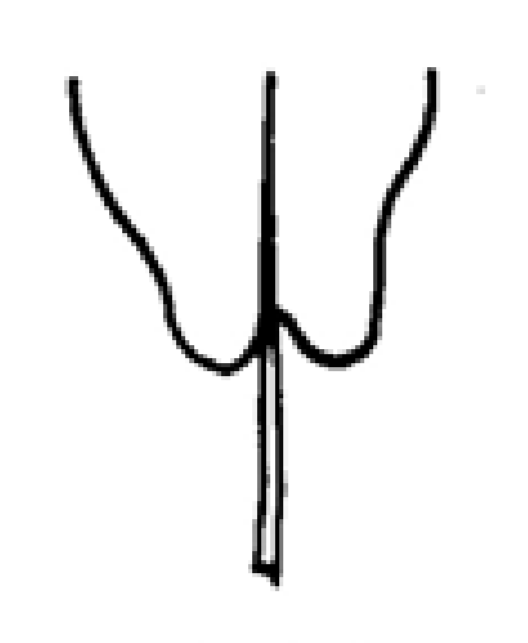
Auriculate
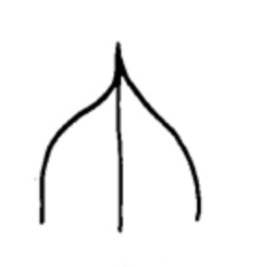
Acuminate

Acute
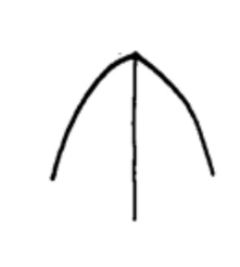
Obtuse

Truncate
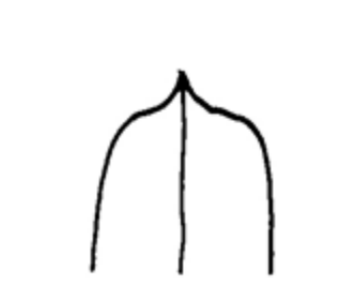
Cuspidate
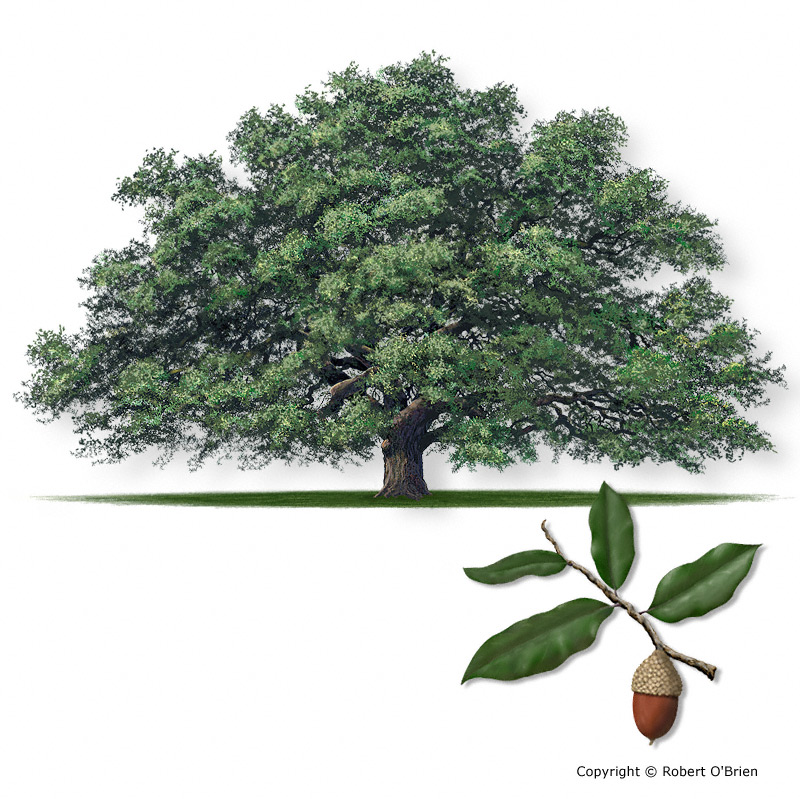

Live Oak (Quercus virgniana)
Charcteristics of Live Oak
3-5 acorn clusters
enclosing 1/3 of nut;
Alt, simple, evergreen, entire margin
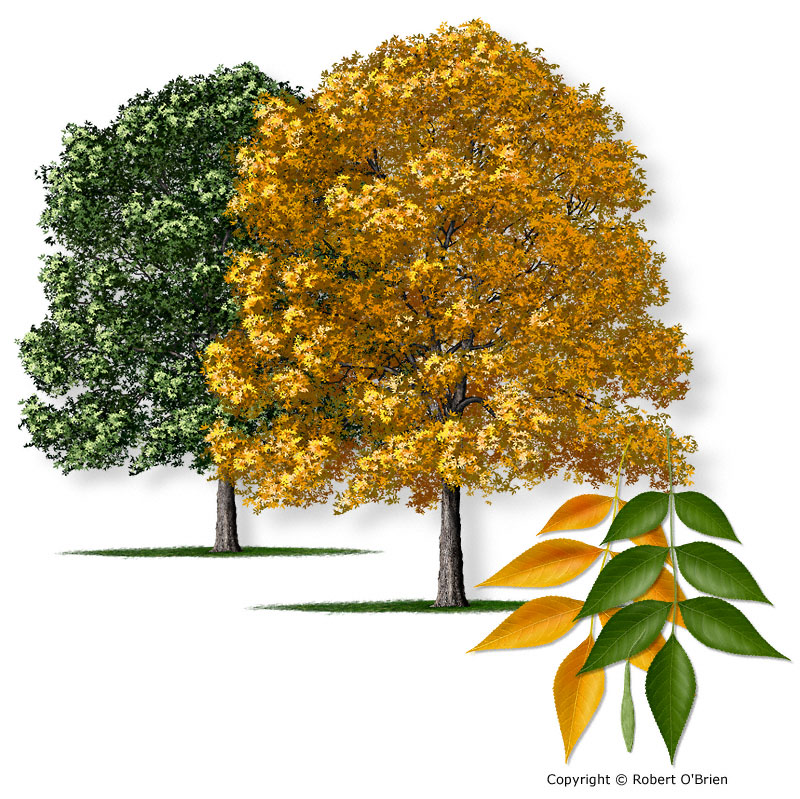

Green Ash (Fraxinus pennsylvania)
Characteristics of Green Ash
Opposuite, pinnately compound leaves
Single Samaras
Green Ash Fun Fact
The most widespread ash species in North America.
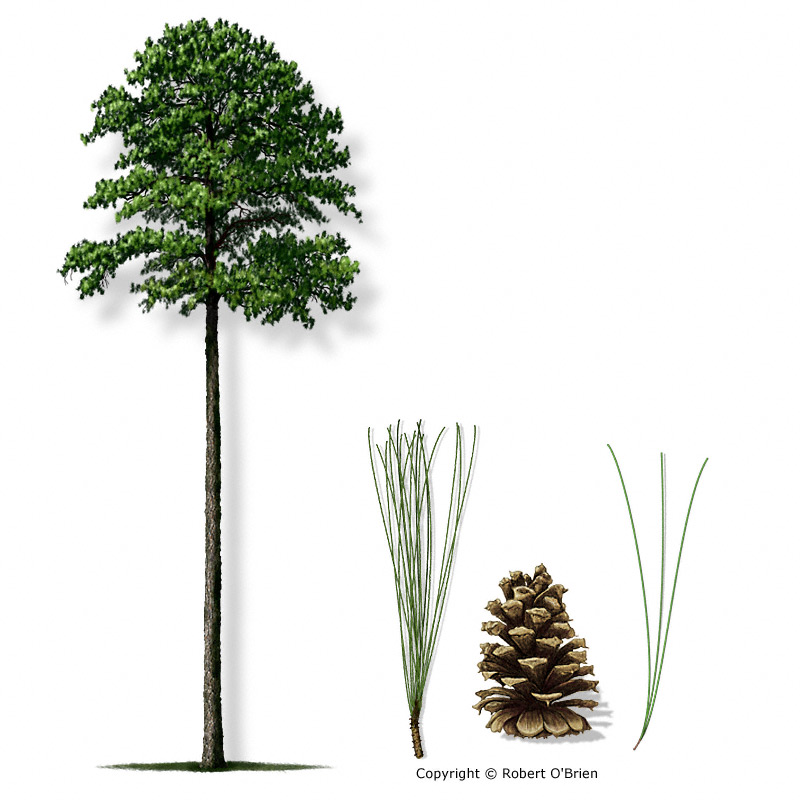

Loblolly Pine (Pinus taeda)
Charcteristics of Loblolly
Open spreading crown
Grayish cone
3-2 needles
Loblolly Fun Fact
"loblolly" comes from a slang word used by English seamen for the lumpy gruel they were served at sea.