CNS
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
parts of the CNS
brain
cerebral hemispheres
basal ganglia
brainstem
cerebellum
spinal cord
function of CNS
integrate, correlate, respond to a variety of sensory info
source of thoughts, emotions, and memories
parts of PNS
cranial nerves
spinal nerves
peripheral nerves
ganglia
functions of PNS
all somatic (sensory and motor) and autonomic processes carried out outside of CNS
what is the nervous system
collection of neurons throughout the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and sensory organs
orientation of CNS
above the midbrain:
anterior= rostral
posterior= caudal
superior= dorsal
inferior = ventral
below midbrain
anterior= ventral
posterior= dorsal
superior= rostral
inferior= caudal
Week 3 gastrulation produces 3 layers
ectoderm
mesoderm
endoderm
Ectoderm
nervous system: CNS+PNS
epidermis- outer layer of skin
teeth: enamel of teeth
hair, nails, sweat glands
lens of eye: cornea and retina
Mesoderm
musculoskeletal system: bones, muscles, CT
circulatory system: heart blood vessels, blood cells
reproductive system: gonads
excretory system: kidneys
dermis of skin: inner layer of skin
notochord: temporary rod- like structure that aids in vertebrate development
Endoderm
digestive system: lining of GI tract
respiratory system: lungs
urinary bladder+urethra
thyroid+parathyroid glands
thymus
lining of respiratory and digestive tracts: mucous membranes
Neurulation
neural tube forms by 4th week
forms 3 bulges to make 3 primary vesicles:
prosencephalon
mesencephalon
rhombencephalon
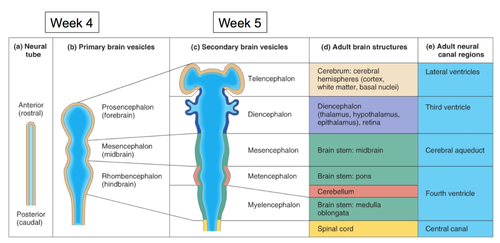
secondary vesicles
telencephalon
diencephalon
mesencephalon
metencephalon
myelencephalon
Prosencephalon
Telencephalon→cerebrum, cerebral hemispheres → lateral ventricle
diencephalon → diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus) + retina→ 3rd ventricle
Mesencephalon
mesencephalon → brain stem, midbrain → cerebral aqueduct
Rhombencephalon
metencephalon → brain stem, pons / cerebellum→ 4th ventricle
myelencephalon → brain stem: medulla oblongata→ 4th ventricle
Neural tube defects
spina bifida (lamina don’t fuse)
spina bifida occulta
mildest form, small gap in spine but no protrusion
meningocele
meninges protrude through gap
myelomeningocele
spinal cord and meninges protrude through gap → neurological complications
Anencephaly
cranial end of the neural tube fails to close → parts of brain and skull absent
infants w this are often stillborn or survive only a short time
encephalocele
portion of the brain and meninges protrude through opening in skull
severity depends on extent of protrusion and brain tissue involved
What vitamin decreases the chances of neural tube defects
Vitamin B9 (Folate/ Folic Acid)
folate is the active form
Neuron Anatomy
contain all traditional organelles
nucleus
mitochondria
ER (rough and smooth)
Golgi Apparatus
Ribosome
lysosomes
cytoskeleton
microtubules
microfilaments
cannot do mitosis
3 additional regions
dendrites
receivers of incoming info
body(soma)
packing+ sorting info
axon
small diameter and variable length projection that conducts nerve impulses away from soma to communicate with neighboring neurons or target tissues
myelin sheath
Synapse
regions at which neurons come nearly together to communicate (neuron or effector organ)
synaptic cleft
gap between neurons at synapse
synaptic vesicle
packets of neurotransmitters in presynaptic neuron
presynaptic neuron
neuron sending a signal before synapse
postsynaptic neuron
neuron receiving a signal after the synapse
neurotransmitter
substance used to communicate with the next cell
Types of synapses
By location
axodendritic
axon→dendrite
most common
axosomatic
axon → soma
inhibit neurons, spatial headstart on axon hillock
axoaxonic
axon → axon
least common
tamps down reaction as a last minute modulation
By physiology
chemical
most synapses are chemical
after action potential → release of NT into cleft → bind to next tissue (neuron or target organ)
electrical
less are electrical
use gap junctions
fast transmission without delay
not good for all bc we want a bit of back and forth between neurons
bidirectional signal transmission
either cell can send or receive signal
found in tissues that require synchronized activity
heart, lungs, eye control
Sensory neurons (afferent)
function
conduct impulses from receptors→ CNS
structural type
pseudounipolar
bipolar
role in NS
transmit info from external env. → CNS
Motor neurons (efferent)
function
conduct nerve impulse from CNS → effector organs
structural type
multipolar
golgi Type 1
role in NS
transmit info from CNS → muscle
interneurons (internuncial)
function
neurons completely contained within CNS
no direct contact w peripheral receptors or effectors
structural type
multipolar
golgi Type 1
Golgi type 2
role in NS
modification, coordination, integration, facilitation, and inhibition that must occur between sensory input and motor output
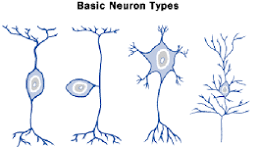
pseudounipolar
2 fused processes that appear as 1
central and peripheral process both function as axon
Bipolar
2 processes
1 axon + 1 dendrite
Multipolar Golgi Type 1
1 axon + 2 more dendrites
axons extend considerable distance to target cell
multipolar Golgi type 2
1 axon + 2 more dendrites
axons are short and stop close to cell body of origin
basic neuron types
Neuroglia
non-conducting support cells
capable of division
cannot do function of neuron but makes their job easier
Neuroglia of CNS
Ependymal cells
oligodendrocytes
astrocytes
microglia
neuroglia of PNS
satellite cells
Schwann cells / neurolemocytes
Astrocyte
part of CNS
most abundant neuroglial cell of CNS
structural support to surrounding neurons
form the blood brain barrier
stores glucose
produces scar tissue on damaged neurons → gliosis ( nerve tissue scarring)
influences NT release and clean- up
what can cross Blood Brain Barrier
oxygen and carbon dioxide
small and lipid soluble
water
osmosis
glucose
primary energy source of brain
specific transport system needed
lipid-soluble molecules
alcohol, hormones, certain drugs
some small molecules
amino acids
vitamins
ions
Oligodendrocyte
myelinating cell of CNS
2nd most numerous CNS glial cell
myelinate multiple neurons of CNS
Ependymal cells
found along floor of ventricles and central canal
help with CSF creation and appendages flow
Microglia
neuronal debris cleaners
immune response in CNS
phagocytic function
clear dead and damaged tissue
wall off damaged areas along w astrocytes
Schwann cells
uses entire cell to form an individual myelin sheath internode in PNS
similar to oligodendrocyte in CNS
assist in repair and regeneration of peripheral nervous tissue
satellite cell
similar to astrocyte in CNS
regulates chemical environment for the PNS
Demyelinating disorders
multiple sclerosis
attack oligodendrocytes
CNS
rapid or slow onset
affect optic nerves, sensation, corticospinal tract, cerebellar pathways, etc
Lhermitte sign
electric sensation down back / legs with neck flexion
Guillain Barre
attack Schwann cells
PNS
rapid onset
affect muscles+ autonomic instability
symptoms develop overs days - weeks
resolve over weeks/months
self-limiting
Regeneration
does not occur in CNS
no basement membrane/ endoneurial surrounding axons of CNS
axons in CNS don’t form neurolemomas → don’t survive axonal damage
damaged neurons in CNS rapidly turned into scar tissue (proliferation of astrocytes)
CNS oligodendrocytes have growth- inhibiting proteins to prevent CNS fiber regeneration
does occur in PNS
proximal tip of severed neuron → endoneurial tube that has Schwann basement membrane / endoneurium
to regen neurons must
be myelinated
have intact cell body
have functional schwann cell
axonal sprout growth rate of 1-4 mm/day
types of ion channels
ligand- gated
requires NT key to open
chemical
mechanically- gated
require physical pressure
voltage gated
require change in electrical charge to open
leaky/ passive
always open
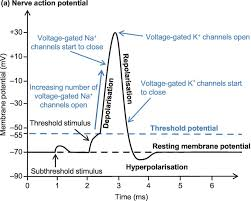
Resting Membrane potential
sum of the electrical charges of ions and negatively charged proteins
neurons have internal -70 mV charge → makes it polarized
Na+ and K+ movement
Na+ goes in and inside gets less neg
K+ leaves and inside gets more neg
Maintaining RMP
ions follow conc gradient
Na+ flows in
K+ flows out
to maintain polarity, active pump is used with the use of ATP
Graded Potentials
signal from previous neurons can be excitatory (closer to 0 and positive) or inhibitory (more negative)
at -55mV voltage-gated Na channels open → flood of (+) ions lead to depolarization → cause action potential
Action potentials
Neurotransmitters
glutamate
most common excitatory NT
GABA
most common inhibitory NT
Acetylcholine (ACh)
1st discovered
autonomic NS
adrenaline
fight /flight
noradrenaline
concentration
dopamine
self-pleasure
serotonin
mood
social hapiness
endorphins
euphoria
most neurons make a single NT→ package in vesicle → transport to axon terminal
as neuron receives AP NT released into synaptic cleft where NT can bind to next neuron → NT binding opens ion channels → affects next neurons RMP → excitatory or inhibitory effect
Sulci and Gyrus
sulcus= space
gyrus= ridge
more SA = more processing power
4 lobes of the brain
frontal
parietal
temporal
occipital
Frontal lobe
largest lobe w 4 main functional areas
primary motor cortex, all parts of body represented
premotor
supplementary motor areas
frontal operculum (Broca’s area) motor mechanisms of speech is formulated
speech production + mouth movement
mental activity, executive function, decision making
issues → voluntary motor function
Parietal lobe
somatosensory (pain, touch, position, localization)
main clearinghouse of somatosensory appraisal
postcentral gyrus
primary somatosensory cortex → somatosensory reception, integration, processing sensory info from surface of body + viscera
formulation of perception
superior parietal gyrus
body image
spatial orientations
inferior parietal gyrus
cortical association → integrates and processes sensory info from multiple modalities (audio+ visual info)
part of Wernicke’s area in inferior parietal lobe
issues = spatial awareness, touch localization, tactile based memory (agraphthesia/ astereognosis)
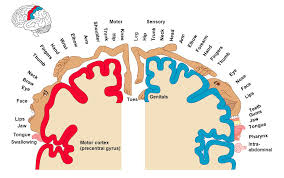
Homunculus
somatotopy: primary motor and somatosensory cortices have point for point correspondence of a specific area of body to a specific functional area of cortex
Temporal lobe
upper surface of the superior temporal gyrus → extend into lateral fissue
this is primary auditory cortex
caudal part of superior temporal gyrus → extens up to parietal cortex → forms part of Wernicke’s area
Wernicke’s area - processing the auditory info and comprehension of language
recall and memory
inferior part (occipitotemporal gyri) involved in visual and cognitive processing
medially = parahippocampal gyrus involved in learning and memory
Occipital lobe
visual
most caudal part of brain
lies on tentorium cerebelli and is made of several irregular lateral gyri
medial surface - calcarine fissure and parieto-occipital sulcus
contains primary and higher-order visual cortex
6 common laminae of the isocortex (external to internal)
lamina 1 molecular
gray matter
outermost layer closest to the pia mater
filled w synaptic activity between dendrites of pyramidal cells and axons of other cell types
integration center
lamina II- external granular lamina II
many small closely packed granular neurons
associative lamina
lamina III- external pyramidal lamina III
small pyramidal-shaped neuron cell bodies
associative lamina
axons extend out of the cortex to the white matter → return to the gray matter
projection, association, commissural fibers
Lamina IV- internal granular
receive external input
small cell bodies
well developed in sensory areas
most thalamic inputs arrive here
Lamina V- internal pyramidal (ganglionic)
large pyramidal-shaped neurons cell bodies
axons project to other brain and cord centers from here
corticospinal + corticobublbar fibers
famous for large pyramidal Betz cells
projection lamina
Lamina VI- multiform(fusiform)
a mix of incoming and outgoing projection fibers in this layer
projection lamina
Association fibers
connect different regions within the same hemisphere of the brain
long association fibers connect different lobes of the hemisphere to each other
short association fibers connect different gyri within a single lobe
link perceptual and memory centers of the brain
Commissures
bring 2 halves of brain together
commissural tracts cross from one cerebral hemisphere to the other through commissures
majority of the commissural tracts pass thru the large corpus callosum ( responsible for task-switching)
few tracts pass through anterior and posterior commissures commissures
internal capsule
superior to brain stem
tracts form a broad dense sheet = internal capsule
between thalamus + basal nuclei
fibers → radiate in fan-like array to specific areas of cortex
basal ganglia
a group of nuceli of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit
base of forebrain + strongly connected w cerebral cortex, thalamus, other brain areas
act as braking system on motor control
direct= promote
indirect = inhibit
components: caudate +putamen(corpus striatum), Globus pallidus (internal + external) substantia nigra, and subthalamic nucleus
basal ganglia pathways
voluntary motor control, procedural learning relating to routine behaviors/ habits
bruxism
eye movement
cognitive
emotional functions
has inhibition and de-inhibition
increase basal ganglia activity = decreased movement (hypokinesis)
decrease basal ganglia activity = increased movement (hyperkinesis
Basal ganglia related disorders
Huntington’s disease
neurodegenerative disorder that affects muscle coordination and leads to cognitive decline and psychiatric problems
hyperkinetics - not enough basal ganglia activity
Putamen + GABA
Parkinson’s disease
chronic neurological disorder resulting in lack of control over movement, poor balance and coordination
hypokinesis - overactivation of basal ganglia
dopamine + substantia nigra
lateralization
2 hemispheres do different things
Left:
sensory stim from R body
motor control of R body
speech, language and comprehension
analysis +calculations
time and sequencing
recognition of words, letters, numbers
Right
sensory stim from left body
motor control of left body
creativity
spatial ability
contex/ perception
recognition of faces, place, and objects
Broca’s area
in frontal lobe of dominant hemisphere
responsible for speech production
broca’s apahasia (expressive)
can understand
words not formed properly
speech = slow and slurred
Wernicke’s area
comprehension / understanding of written and spoken language
Wernicke’s aphasia (affluent)
loss of ability to understand language
can speak clearly but words make no sense
Broca’s aphasia is also known as
expressive aphasia
wernicke’s aphasia is also known as
affluent aphasia
aphasia definition
a speech or language disorder - often caused by a stroke
diencephalon
interbrain
gives rise to posterior forebrain structures
diencephalon appears at the upper end of the brain stem (in between the cerebrum + brain stem)
diencephalon made up of
thalamus
subthalamus
hypothalamus
epithalamus
Thalamus
acts as a relay between a variety of subcortical areas and the cerebral cortex
everything except for smell
plays role in regulating states of sleep and wakefulness
regulating arousal, awareness level, and activity
Ventral posterolateral (VPL)
somatosensory (body) limbs
Ventral posteromedial (VPM)
somatosensory (face)
Lateral geniculate (LGN)
vision
Medial geniculate (MGN)
hearing
both sides have R/L input on each side
sensory relay nuclei
VPL
VPM
LGN
MGN
motor relay nuclei
Ventral anterior
Ventral lateral
ventral anterior (VA)
motor - power
basal ganglia
ventral lateral (VL)
motor- accuracy
cerebellum
anterior relay nuclei
limbic: emotion, memory
association nuclei
dorsomedial
pulvinar
dorsomedial
limbic: emotions, cognition, learning, memory
pulvinar
sensory integration
block out excess stimuli
epithalamus
consists of:
pineal gland (endocrine)
habenula ( connects limbic system to midbrain)
functions:
secretion of melatonin by the pineal gland
circadian rhythms
need to have 5 HTP/ smaller dose/Mg glycinate or theonate
regulation of motor pathways and emotions
hypothalamus
performs vital functions
linking NS to endocrine system via pituitary gland ( hypophysis)
controls body temp, hunger, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian cycles
turns on pituitary
Pituitary gland
anterior:
glandular tissue
makes + releases what hypothalamus needs
posterior:
neural tissue
ejects what hypo makes —doesn’t make anything
anterior pituitary hormones
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
in ovaries, stimulates egg maturation
in testes, produces spermatozoa
gametogenesis
gonadotropin
luteinizing hormone (LH)
in ovaries- produces progesterone to maintain uterine lining for potential fertilization and implantation
named for activity in ovaries
in testes- produce testosterone
gonadotropin
Growth hormone (GH)
grows and develops bones and tissues
Prolactin (PRL)
produces milk + storage
mammary glands
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
stimulates adrenal glands to release its own hormones
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
stimulates thyroid to release its own hormones
metabolism hormone
Posterior pituitary hormones
oxytocin (OT)
produces milk letdown / release
mammary glands
smooth muscle in uterus
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
causes kidneys to reabsorb water
limbic system description
pseudo lobe
bc it has structures from a variety of precursor structure
has variety of functions related to
emotion
behavior
memory
aid in response to stress + pleasure
components of limbic system
amygdala
processing fear, anger, and pleasure
especially as it relates to identification of threats
hippocampus
aids in formation of new memories
help convert short term to long term memories
hypothalamus
regulation of hunger, thirst, temperature, circadian rhythm
self-care
thalamus
relays signals in and out of cortex
helps regulate consciousness, sleep cycle, and alertness
cingulate gyrus
emotion forming, processing, learning, and memory
helps in processing emotional responses -especially relating to social environment
septal nuclei
involved in reward and reinforcement in learning and pleasure-seeking behavior
addictions
mammillary bodies
involved the memory/recall pathway between hippocampus and entorhinal cortex
fornix
major bundle highway between hippocampus and other parts of limbic system
parahippocampal gyrus
involved in encoding and retrieval of memory
entorhinal cortex
portion of temporal lob involved in memory pathways as well as navigation + time perception
3 components of brain stem
midbrain (mesencephalon)
associated w vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wake cycles, alertness, and temperature regulation
pons (metencephalon)
contains tracts that carry signals from the cerebrum to the medulla + to the cerebellum
also has tracts that carry sensory signals → thalamus
medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting, and vasomotor centers regulating heart rate, breathing, and blood pressure
*almost all cranial nerves originate from the brain stem
primary components of midbrain
CN III and IV
Tectum
comprised of colliculi (superior + inferior)
4 colliculi = corpora quadrigemina
superior = visual
inferior = auditory
tegmentum
extends from the substantia nigra to the cerebral aqueduct
dopamine output
substantia nigra
cerebral peduncles
located on either side of the midbrain + are its most anterior part
connect the brain and brainstem
act as connectors between the rest of the midbrain + thalamic nuclei
reticular formation
alertness and stress
circadian rhythm
periaqueductal gray
endorphin/ enkaphalin area
pain pathways + pain killing structure
Pons
posterior:
2 pairs of thick stalks = cerebellar peduncles
runs thru pons
connect the cerebellum to the pons and midbrain
cardiovascular effects+ respiration control
anterior / rostral to medulla:
4 cranial nerves
CN V: trigeminal nuclei
CN VI: abducens nuclei
CN VII: facial nuclei
CN VIII: vestibulocochlear nuclei
medulla oblongata
pyramid of medulla
elevated region between anterior median and anterolateral
decussation of pyramids
crossing fibers that obliterating the anterior median fissure
Medulla oblongata controls autonomic fins and connects they higher levels of the brain → spinal cord
gray -out
white- in
sensory fibers cross @ MO
Cranial nerves
CN I- olfactory
CN II - optic
CN III- oculomotor
CN IV- Trochlear
CN V- trigeminal
CN VI- abducens
CN VII- facial
CN VIII- Vestibulocochlear
CN IX- Glossopharyngeal
CN X- vagus
CN XI- Accesory
CN XII- Hypoglossal
olfactory CN I
originates from telencephalon
function: pure sensory
bypasses the thalamus for direct connection to the limbic system
immediate sense memories
smelling smoke when sleeping
conditions affecting function( can be obstructive/neural)
allergies -O
alzheimer’s - N
covid- O/N
rhinitis- O
foreign substances inhaled - O/N
deviated septum - O
blocked choanae - O
Optic nerve - CN II
originates from diencephalon
function
pure sensory
converts light to electrical messages to be sent to the brain
pupil reflex
see + feel light
received at the primary visual cortex ( calcarine sulcus) of occipital lobe
visual messages cross sides
LGN (thalamus) + superior colliculi (midbrain)