ap world unit 4
5.0(1)Studied by 72 people
0%Unit Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/85
Earn XP
Last updated 9:56 PM on 12/2/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
1
New cards
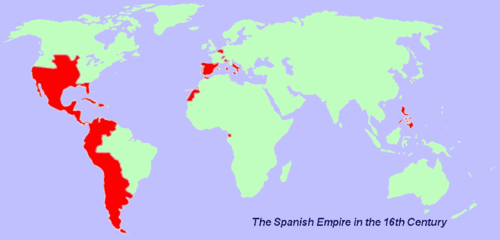
spanish empire
1400s- late 1900s. made up of territories and colonies in europe, africa, and asia controlled from spain. at its strongest, it was one of the biggest empires in world history according to how much land they had, and one of the 1st global empires. royalty from the castile and aragon kingdoms ruled it. christopher colombus led the first spanish exploration trip which led them to colonizing america.
2
New cards
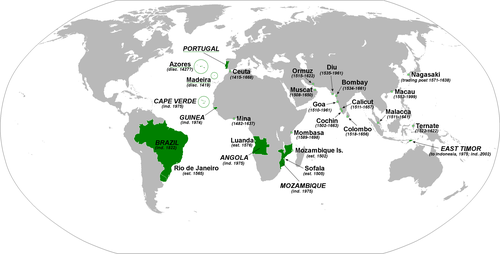
portuguese empire
bustling trade empire built throughout the indian ocean. extended control after defeating muslim fleet and captured goa which was made the capital of their trading empire. after this they seized the strait of malacca which gave them control of the moluccas also known as the spice islands.
3
New cards
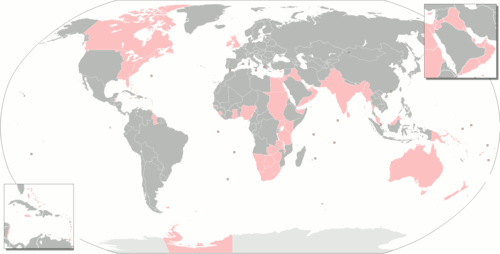
british empire
formerly the united kingdom and all the territories under its control.
4
New cards
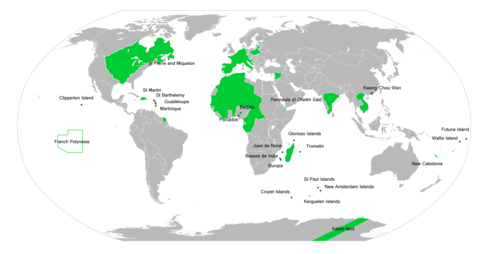
french empire
empire control in canada, ohio, and mississippi river valley with louisiana.
5
New cards
dutch empire
established by dutch east india company and soon replaced portugal as leader in spice islands introducing and maintaining monopoly on coffee and sugar and become only european allowed to trade with japan before empire declined b/c war w/ britain.
6
New cards
hernan cortes
1485-1547, spanish conquistador who defeated the aztecs and conquered mexico.

7
New cards
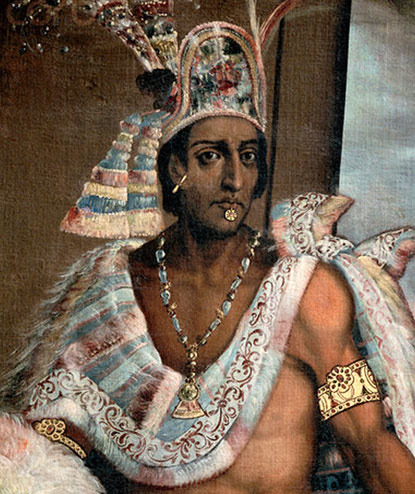
moctezuma I
(1466-1520) aztec ruler from 1502 to 1520; he was the emperor of the aztecs when cortés and his army conquered the empire. he was taken prisoner and killed during battle with the spanish army.

8
New cards
atahualpa
(1497-1533) an incan ruler who was kidnapped by pizarro during his attempt to keep the spanish from entering his territory. he offered to fill a room with gold and silver in exchange for his release. the ransom was accepted, but the ruler was strangled by the spanish.

9
New cards
mestizo
a new racial concept that developed in latin america following the intermixing that occurred between european colonists and the native american population.

10
New cards
tupac amaru
mestizo leader of indian revolt (1780-1781) in peru; supported by many in the lower social classes; revolt failed because of creole fears of real social revolution.

11
New cards
mulattoes
in colonial latin america, people of mixed spanish and african descent who were denied basic political, economic, and social rights due to their mixed heritage.

12
New cards
less racial mixing
in contrast to most latin american colonies, there were fewer children born of mixed-race parents in british north america and a sharply defined racial system developed.
13
New cards
pelts
the "soft gold" that drove russian expansion.
14
New cards
yasak
tribute that russian rulers demanded from the native peoples of siberia, most often in the form of fur.

15
New cards
catherine the great
(1762-1796) she is responsible for many positive changes in Russia, as well as securing the country a warm water port.

16
New cards
cossacks
the "vanguard" of russian expansion across siberia; bands of warriors consisting of peasants who had escaped serfdom.

17
New cards
russification
a tsarist program that required non-russians to speak only russian and provided education only for those groups loyal to russia.

18
New cards
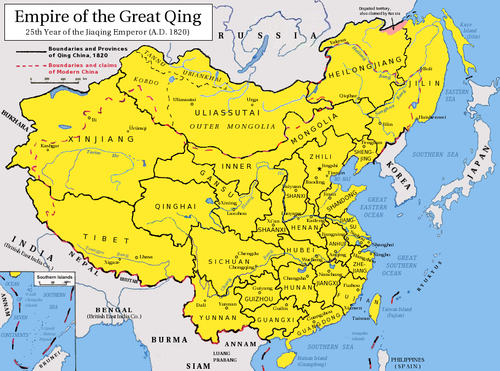
qing dynasty
(1644-1911 CE), the last imperial dynasty of china which was overthrown by revolutionaries; was ruled by the manchu people: began to isolate themselves from western culture.
19
New cards
manchuria
an area northeast of the great wall of china that conquered china and ruled during the qing dynasty.
20
New cards
zunghars
western mongol group that created a substantial state (1671-1760); their threat provoked qing expansion into central asia.

21
New cards
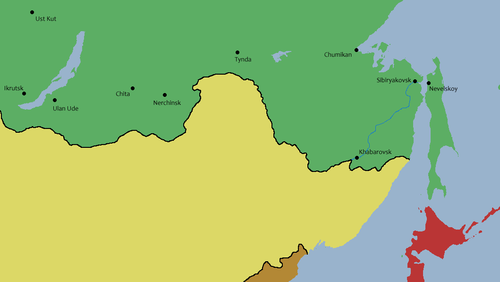
treaty of nerchinsk
the first treaty between china and russia that helped set the borders for the two nations (1689.)
22
New cards
court of colonial affairs
bureaucratic institution developed by the qing dynasty which helped manchus establish an identity; ruled the rest of china.

23
New cards
timur
timur through conquest gained control over much of central asia and iran.

24
New cards
akbar
(r. 1556-1605). he expanded the empire and pursued a policy of conciliation with hindus.; removed the special jizya tax on non-muslim people in south asia and restrained the more militant ulama.

25
New cards
rajputs
members of a mainly hindu warrior caste from northwest india

26
New cards
jahangir
akbar's son, promoted Islam in the empire, but was still tolerant of others.

27
New cards
shaykh ahmad sirhindi
(1564-1624) indian islamic scholar from punjab; claimed to want to "renew" authentic Islam in the mughal empire and strongly rejected the synthesis that akbar was bringing about in india between islam and hinduism; encouraged mughal emperors to enforce the jizya, impose sharia, and remove non-muslims from high office.

28
New cards
aurangzeb
(1658-1707) mughal emperor in india and great-grandson of akbar 'the great' - under whom the empire reached its greatest extent; mughal empire collapsed shortly after his death and was conquered by the british.

29
New cards
sati
a hindu practice where the widow of a fallen husband followed him to death by throwing herself on his funeral pyre.

30
New cards

caravel
small, highly maneuverable used by the Portuguese and Spanish in the exploration of the Atlantic; used for long voyages at great speed from 15th - 17th centuries; used for exploration, not trade
31
New cards

carrack
large trading merchant ship operating in European waters (especially by the Portuguese) 14th- 17th century
32
New cards

fluyt
dutch sailing vessel that allowed them to control the baltic trade; designed to facilitate transoceanic delivery with max space and crew efficiency; used from 16th to 17th centuries
33
New cards
henry the navigator
(1394-1460) portuguese prince who promoted the study of navigation and directed voyages of exploration down the western coast of africa; sponsored seafaring expeditions to search for an all-water route to the east; imported enslaved africans
34
New cards
vasco da gama
portuguese explorer.; 1497-1498 he led the first naval expedition from europe to sail to india, opening an important commercial sea route for europeans
35
New cards
ferdinand magellan
portuguese navigator who led the spanish expedition of 1519-1522 that was the first to sail around the world.
36
New cards
trading post empire
imperial dominance based on control of trade rather than on control of subject peoples; practiced by europeans in the indian ocean as they took over trade from arab and muslim merchants
37
New cards
christopher columbus
italian navigator who discovered the new world (in 1492) in the name of spain while searching for a direct sea route to access indian ocean trade
38
New cards
columbian exchange
exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the americas and the rest of the world following columbus' voyages.
39
New cards
mercantilism
economic system where nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold/silver and by exporting more goods than they imported; colonies were crucial in the accumulation of wealth; prevalent from 16th - 19th centuries.
40
New cards
the great dying
the devastating demographic impact of european-borne epidemic diseases (like smallpox and measles) in the americas following european conquest; anywhere from 50-90% of indigenous peoples were killed by european diseases
41
New cards
chattel slavery
absolute legal ownership of another person, including the right to buy or sell that person; the form of slavery utilized in the Americas during the transatlantic slave trade
42
New cards
mita system
economic system in Inca society where Inca subjects paid "taxes" with their labor and what they produced for a set period of time each year; later exploited by the spanish as they forced incas to mine silver
43
New cards
indentured servitude
worker bound by a voluntary agreement to work for a specified period of years often in return for free passage to an overseas destination; before 1800 (19th century) most were europeans; after 1800 most indentured laborers were south or east asians
44
New cards
encomienda
grant of land made by spain to a spanish settler in the americas, including the right to use local indigenous peoples as laborers on the farm
45
New cards
hacienda
spanish estates in the americas that were often plantations; they represent the gradual removal of land from peasant ownership and a type of feudalistic order where the owners would have agreements of loyalty but would retain control over the actual land; continued into the 20th century.
46
New cards
joint-stock company
exploration company made up of a group of shareholders; each shareholder contributed money to the company and received some share of the company's profits and debts; used by european rulers to finance exploration and were used by rulers to compete against one another in global trade
47
New cards
royal chartered monopoly companies
groups of private investors who paid an annual fee to france and england in exchange for a monopoly over trade to indian ocean colonies
48
New cards
vodun (voodoo)
new world syncretic faith that combines the animist faiths of west africa with roman catholic christianity; evidence of the syncretism created when european and african beliefs merged in the americas
49
New cards
santeria
originated in cuba, a religion that blends african traditions and roman catholic beliefs/practices; evidence of the syncretism created when european and african beliefs merged in the americas
50
New cards

casta paintings
spanish-commissioned paintings that showed the racial mixing of new world families; illustrated the importance of European ancestry in the social hierarchy of latin america
51
New cards
mestizo
term used by spanish authorities to describe someone of mixed native american and european descent
52
New cards
mulatto
term used in spanish and portuguese colonies to describe someone of mixed african and european descent.
53
New cards
creoles
descendants of spanish-born but born in latin america; resented inferior social, political, economic status.
54
New cards
peninsulares
spanish-born upper class individuals who immigrated to latin america; highest social class and given special privileges and the highest political positions in latin american governments
55
New cards
the fronde
series of violent uprisings during the early reign of Louis XIV (1648 - 1653) caused by growing royal control and increased taxation; inspired Louis XIV to take total political control in fear of a future uprising
56
New cards
nat turner's rebellion
a rebellion of enslaved virginians that took place in southampton county, virginia led by former enslaved person nat turner in 1831; one example of resistance to existing authorities in the americas
57
New cards
british east india company
british joint-stock company that controlled most of India during the period of imperialism.; controlled the political, social, and economic life in india for more than 200 years.
58
New cards
dutch east india company
dutch-chartered joint-stock company that controlled the spice trade in the east indies.
59
New cards
triangular trade
three-way system of trade during 1600-1800s whereby africa sent enslaved people to the americas, the americas sent raw materials (like sugar, tobacco) to europe, and europe sent guns and rum to africa in exchange for enslaved africans
60
New cards
coercive labor
any labor system that involves force (slavery, chattel slavery, serfdom, spanish run mita system, and indentured labor)
61
New cards
bullion
gold and silver in the form of bars
62
New cards
Vasco da Gama’s 1497-1499 voyage
☆ from Portugal to Calicut, India
☆ motivation was spices like nutmeg, cinnamon, mace, cloves and pepper
(used as condiments, preservatives and aphrodisiacs)
☆ motivation was spices like nutmeg, cinnamon, mace, cloves and pepper
(used as condiments, preservatives and aphrodisiacs)
63
New cards
prester john
legendary Christian monarch ruling in Asia or Africa and wanted to continue the crusades
64
New cards
mexico and bolivia
silver deposits that were exploited by european countries
65
New cards
main ships
☆ caravel: easier to tack (which is wind with the wind in a zig-zag pattern), lateen sails, sponsored prince henry
☆ carrack: stable -> longer voyages, had larger cargoes
☆ galleon: like the carrack but larger and had weapons
☆ fluyt: a dutch ship that was cheaper to build and to operate because it had a small crew size, higher sails led to faster voyages, no weapons so x2 more cargo
☆ carrack: stable -> longer voyages, had larger cargoes
☆ galleon: like the carrack but larger and had weapons
☆ fluyt: a dutch ship that was cheaper to build and to operate because it had a small crew size, higher sails led to faster voyages, no weapons so x2 more cargo
66
New cards
example of a trading post empire where the main goal is to control trade not territories/populations
portugal
67
New cards
cartaz
a pass carried by all merchants, made by authorities in the East also made merchants pay duties of 6-10%
68
New cards
voyage of 1519-1521
☆ philippines first encountered (named after king philip the second)
☆ lead by ferdinand magellan, a portuguese mariner
☆ lead by ferdinand magellan, a portuguese mariner
69
New cards
takeover of the philipines
☆ small military operations with gunpowder weapons, alliances and gifts to chiefs and catholic rituals →basically peaceful takeover in 1565
☆ led to the philippines being an outpost for christianity in asia
☆ taxes, tribute and unpaid labor were common
☆ manila = new capital in 1600
☆ led to the philippines being an outpost for christianity in asia
☆ taxes, tribute and unpaid labor were common
☆ manila = new capital in 1600
70
New cards
manila
☆chinese and japanese merchants and artisans were living
☆ there was revolts because of discrimination which led to the spanish killing nearly all of the 20,000 chinese people living there
☆ there was revolts because of discrimination which led to the spanish killing nearly all of the 20,000 chinese people living there
71
New cards
europeans and japan
☆ when European merchants came to Japan, there was conflicts between daimyo
☆ they were welcomed bc of technology and there was ~300,00 converts to Christianity
☆ Japan unified politically in the early 17th century under a shogun fry, the Tokugawa clan
☆ they then saw europeans as a threat and forbade the practice of christianity
☆ 1650-1850: country was closed off because Japanese shoguns banned all European traders (except for Dutch because they weren’t really interested in spread christianity)
☆ they were welcomed bc of technology and there was ~300,00 converts to Christianity
☆ Japan unified politically in the early 17th century under a shogun fry, the Tokugawa clan
☆ they then saw europeans as a threat and forbade the practice of christianity
☆ 1650-1850: country was closed off because Japanese shoguns banned all European traders (except for Dutch because they weren’t really interested in spread christianity)
72
New cards
spanish america produced ___ of the world's silver and _____was the capital for shipments
85%, manila
73
New cards
1570s and taxes in china
☆ chinese authorities made taxes that were required to pay in silver
☆ higher demand → value increased and foreigners could buy more of china’s goods
☆ Chinese, Portuguese and dutch traders went to manila to sell Chinese goods in exchange for silver
☆ higher demand → value increased and foreigners could buy more of china’s goods
☆ Chinese, Portuguese and dutch traders went to manila to sell Chinese goods in exchange for silver
74
New cards
Bolivia and silver
a city called Potosi became the largest city in the americas because of the silver there
75
New cards
piece of eight
the spanish silver coin being used by merchants in North America, India, Russia and Africa
76
New cards
japan and trading
☆ Japan used the silver production to unify Japan under the Tokugawa shoguns
☆ merchants created a market-based economy, investing in agriculture and industrialization
☆ slowing of population growth (contraception), no ecological crisis (restoring forests) and a highly commercialized economy
☆ merchants created a market-based economy, investing in agriculture and industrialization
☆ slowing of population growth (contraception), no ecological crisis (restoring forests) and a highly commercialized economy
77
New cards
china and trading
☆ even more commercialization and regionally specialized
☆ more land being devoted to cash crops → loss of half the forest cover
☆ role in silver trade = asian centrality of the global economy
☆ europeans acted as middlemen, American silver to asia
☆ Chinese and Indian textiles > European textiles
☆ more land being devoted to cash crops → loss of half the forest cover
☆ role in silver trade = asian centrality of the global economy
☆ europeans acted as middlemen, American silver to asia
☆ Chinese and Indian textiles > European textiles
78
New cards
the fur industry
☆ 1500 - number of animals that had fur were decreasing
☆ little ice age only made it worse because people wanted fur for warmth
☆ price of a pelt quadrupled in France between 1558 and 1611
☆ little ice age only made it worse because people wanted fur for warmth
☆ price of a pelt quadrupled in France between 1558 and 1611
79
New cards
natives and the fur industry
☆ most Europeans made the natives get the pets and in exchange gave the natives goods like blankets and guns
☆ cheap labor, not really coerced
☆ their role in trade protected them from enslavement
☆ natives being depended on European goods → traditional crafts being lost
☆ alcohol being introduced to native societies was very problematic
☆ fur trade, disease, dependence, guns and alcohol = the decline of native societies
☆ cheap labor, not really coerced
☆ their role in trade protected them from enslavement
☆ natives being depended on European goods → traditional crafts being lost
☆ alcohol being introduced to native societies was very problematic
☆ fur trade, disease, dependence, guns and alcohol = the decline of native societies
80
New cards
1664-1763
French-british rivalry made natives choose sides and fight
81
New cards
russian tribute
☆ the abundance of fur animals in Siberia made Russia rich
☆ Russians got fur from tribute: every able-bodied Siberian male from 18-50 must give them pelts
☆ they took Siberian hostages to ensure more pelts
☆ Russians got fur from tribute: every able-bodied Siberian male from 18-50 must give them pelts
☆ they took Siberian hostages to ensure more pelts
82
New cards
1500-1866 atlantic slave trade
12.5 million people taken from African societies as part of trade
83
New cards
the shift from slavic to african people as slaves
most slavic people were slaves, but in 1453 when the ottomans took Constantinople the supply of slavic slaves was cut off, at the time Portuguese mariners were exploring the African coast
84
New cards
foods that went to africa
maize and manioc (aka cassava)
85
New cards
Benin kingdom
☆ monarch called oba, who controlled trade
☆ avoided involvement in slave trade (1516 began restricting it, then banned the export of male slaves)
☆ but in the eighteenth century it resumed the trade
☆ avoided involvement in slave trade (1516 began restricting it, then banned the export of male slaves)
☆ but in the eighteenth century it resumed the trade
86
New cards
Aja-speaking people/kingdom of dahomey
☆ highly authoritarian
☆ tried to limited external slave trade, tried to import European craftsmen and develop plantation agriculture but failed
☆ because of this failure they participated in the slave trade under royal control
☆ annual slave raids → essential revenue
☆ tried to limited external slave trade, tried to import European craftsmen and develop plantation agriculture but failed
☆ because of this failure they participated in the slave trade under royal control
☆ annual slave raids → essential revenue