Understand properties of solutions (TEAS 7)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
osmosis
a specific type of diffusion in which water moves across a semipermeable membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
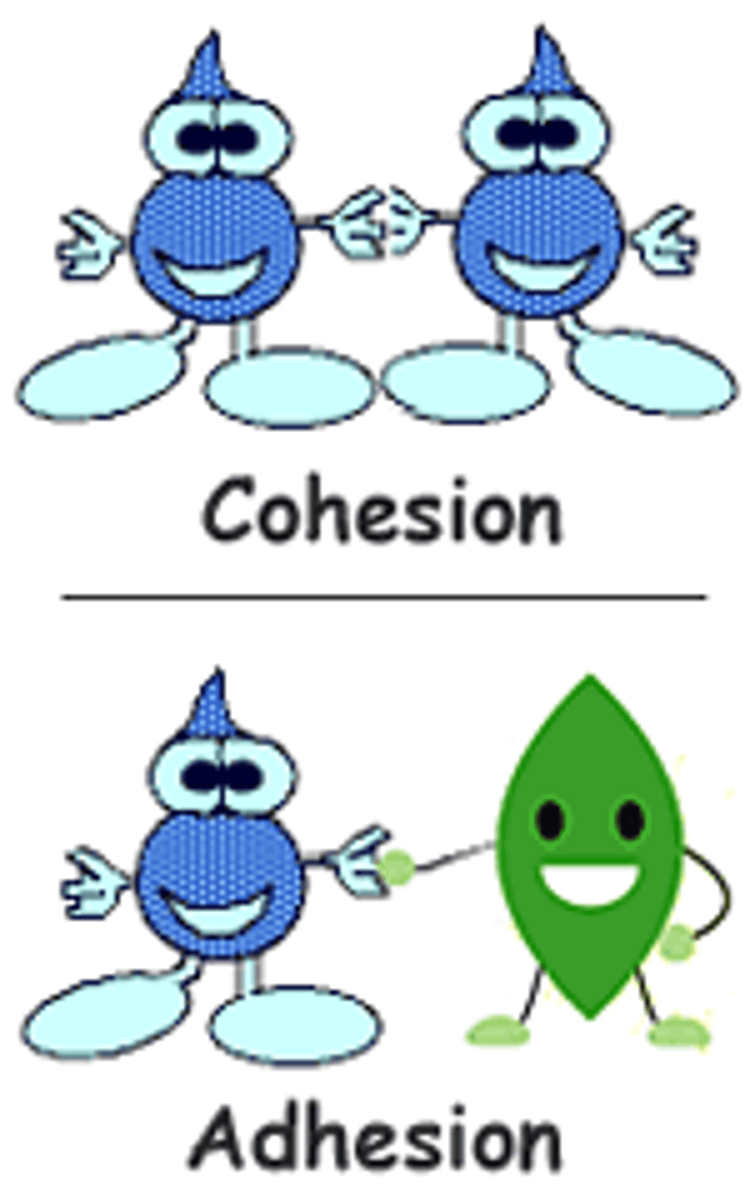
cohesion
the tendency of similar molecules to stick to each other or group together
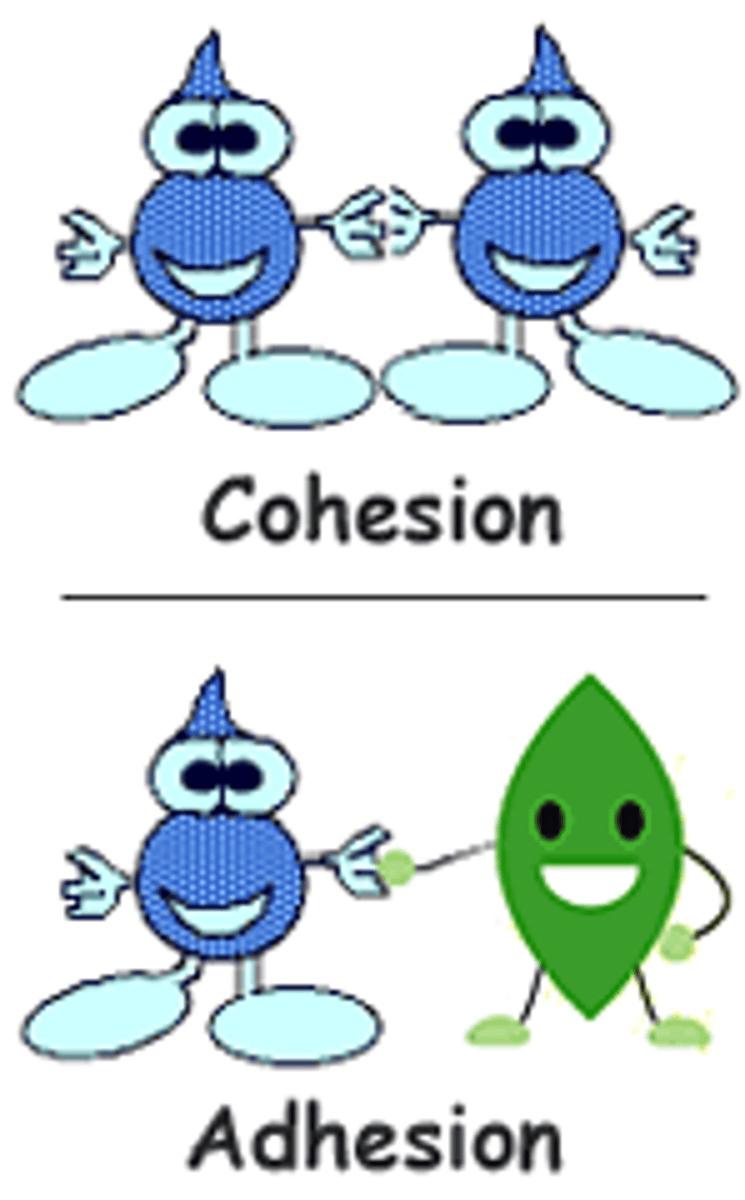
adhesiveness
a measure of how well dissimilar particles or surfaces cling to one another
solvent
the substance in which a solute is dissolved to form a solution
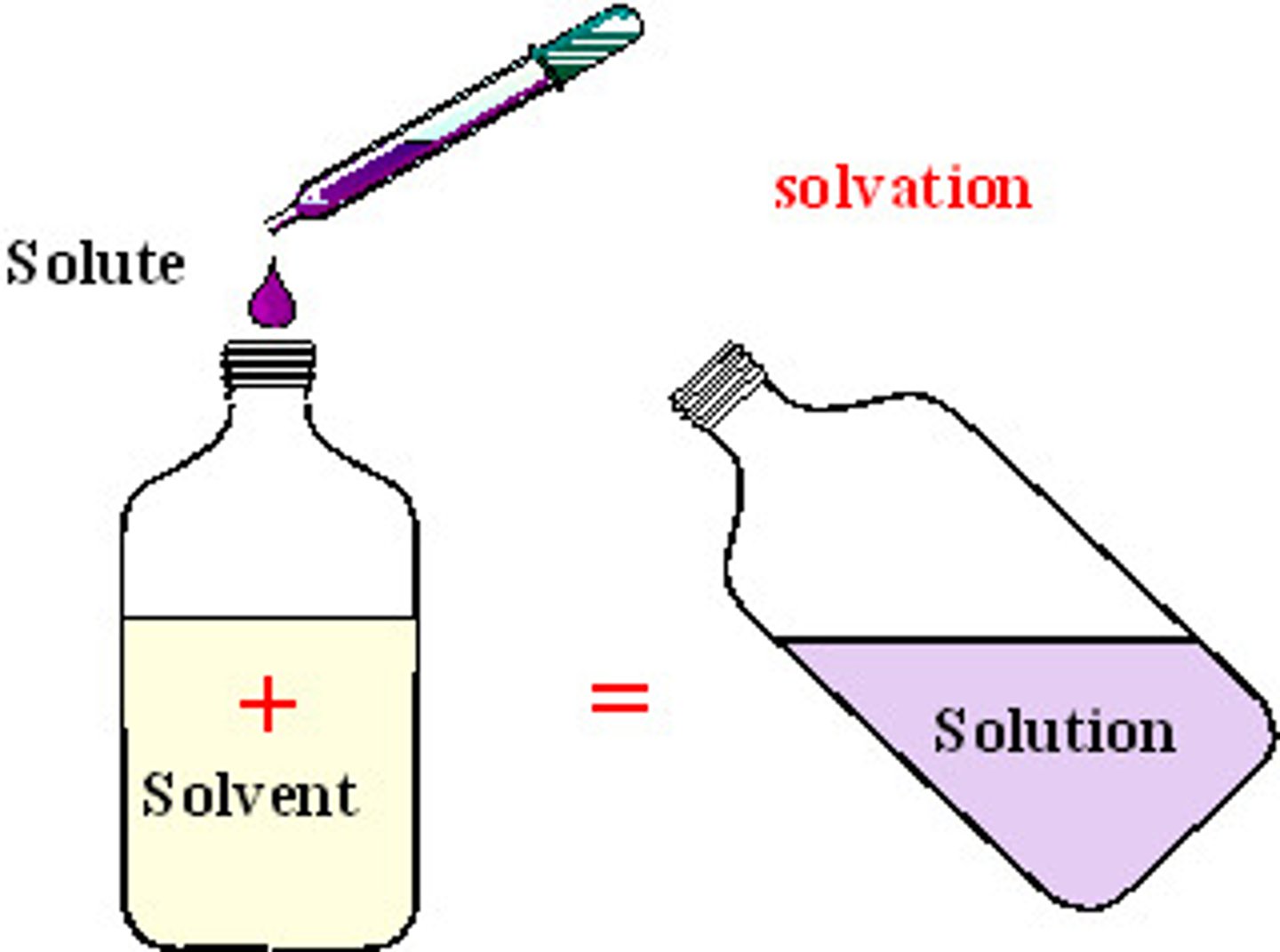
solution
a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances whose components are uniformly distributed on a microscopic scale
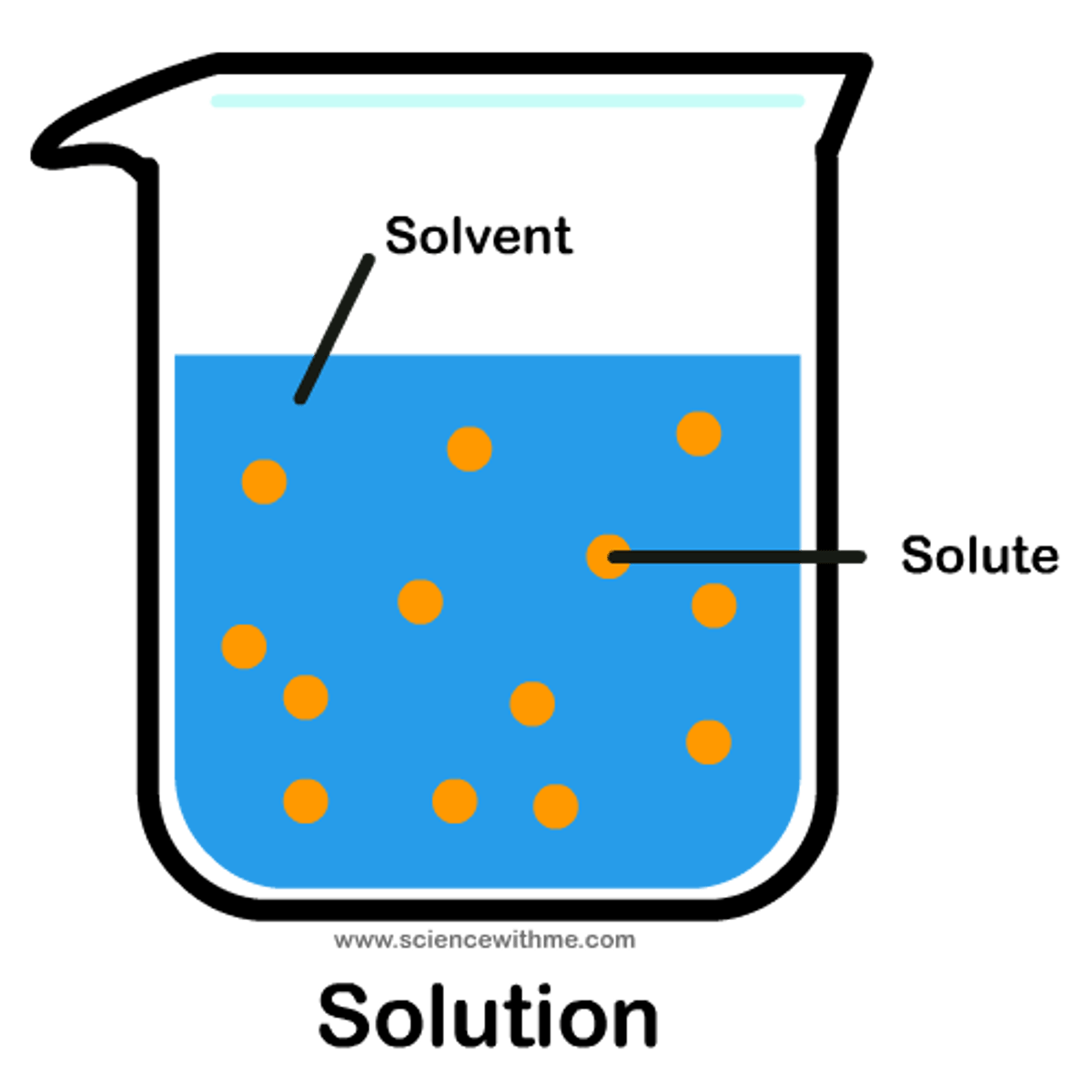
solute
the substance that dissolves in a solvent to form a solution.
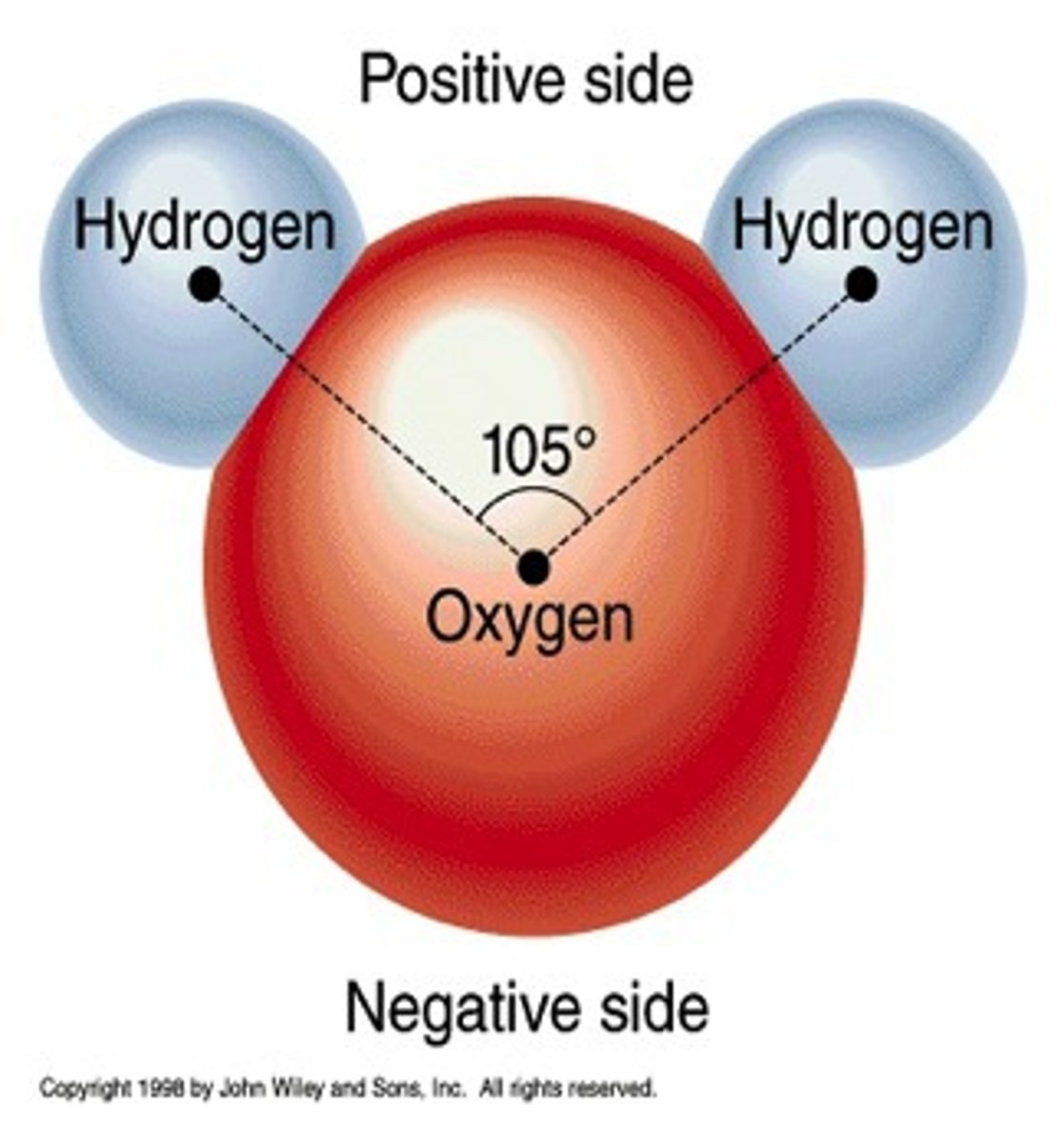
water is a polar molecule, which means
it has negatively charged (oxygen ends) and positively charged (hydrogen end) sides.
-water molecules are attracted to other water molecules.
the cohesiveness of water allows
it to travel through small capillaries without using energy
breaking up the multitude of hydrogen bond between water molecules requires a lot of energy so
water is said to have high specific heat and high heat of vaporization.
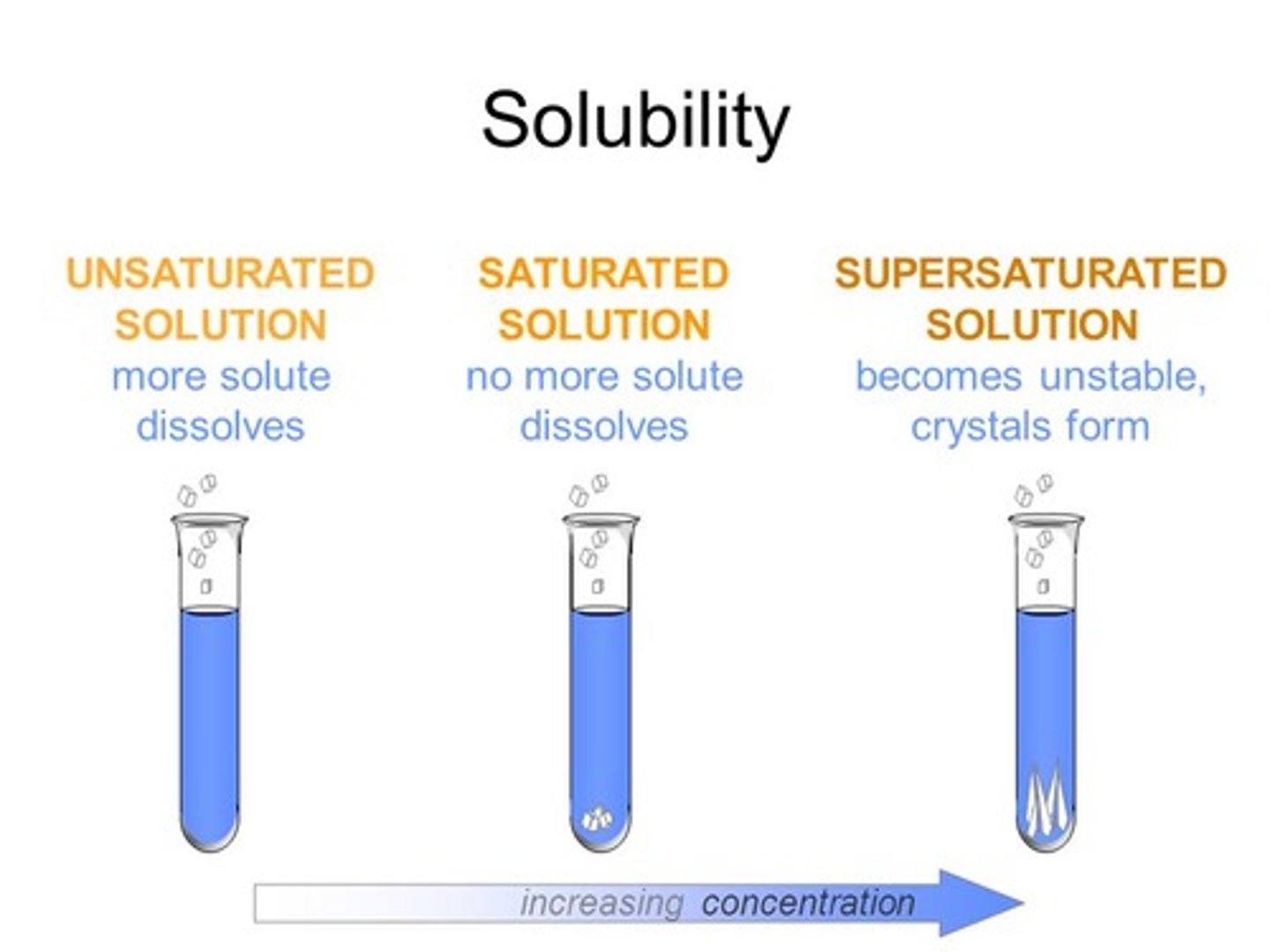
saturated solution
a solution containing the maximum possible amount of solute.
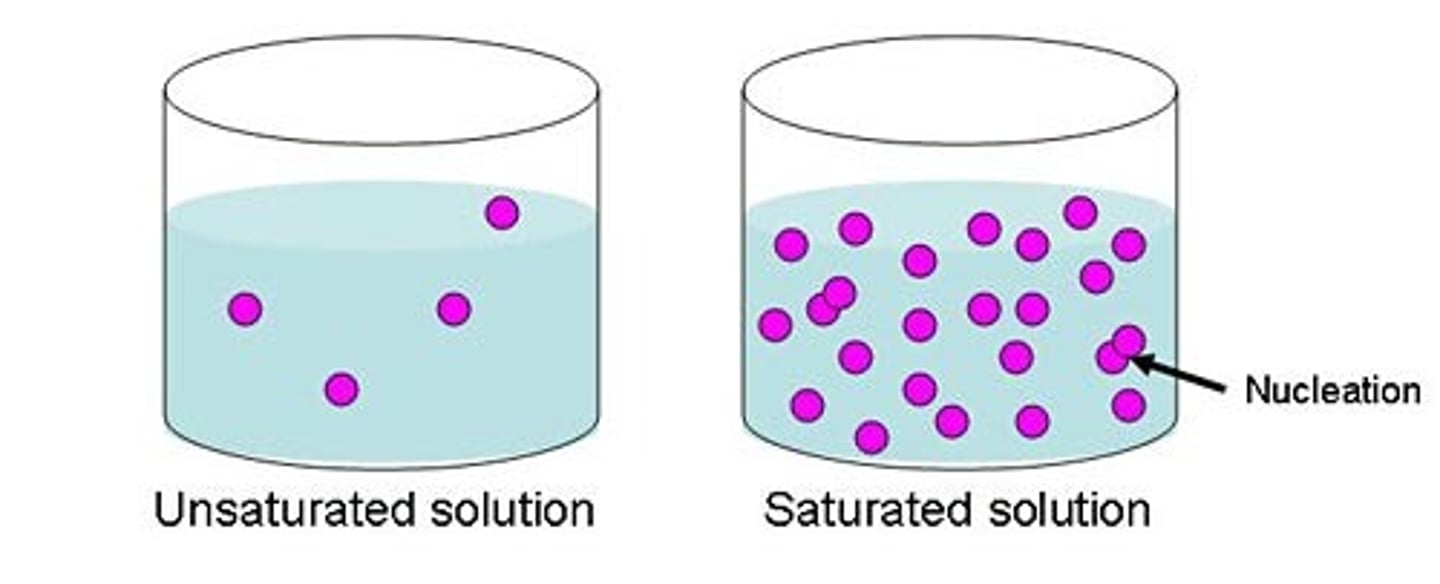
supersaturated solution
a solution that has been raised to a higher temperature in order to dissolve more solute than would be possible at room temperature
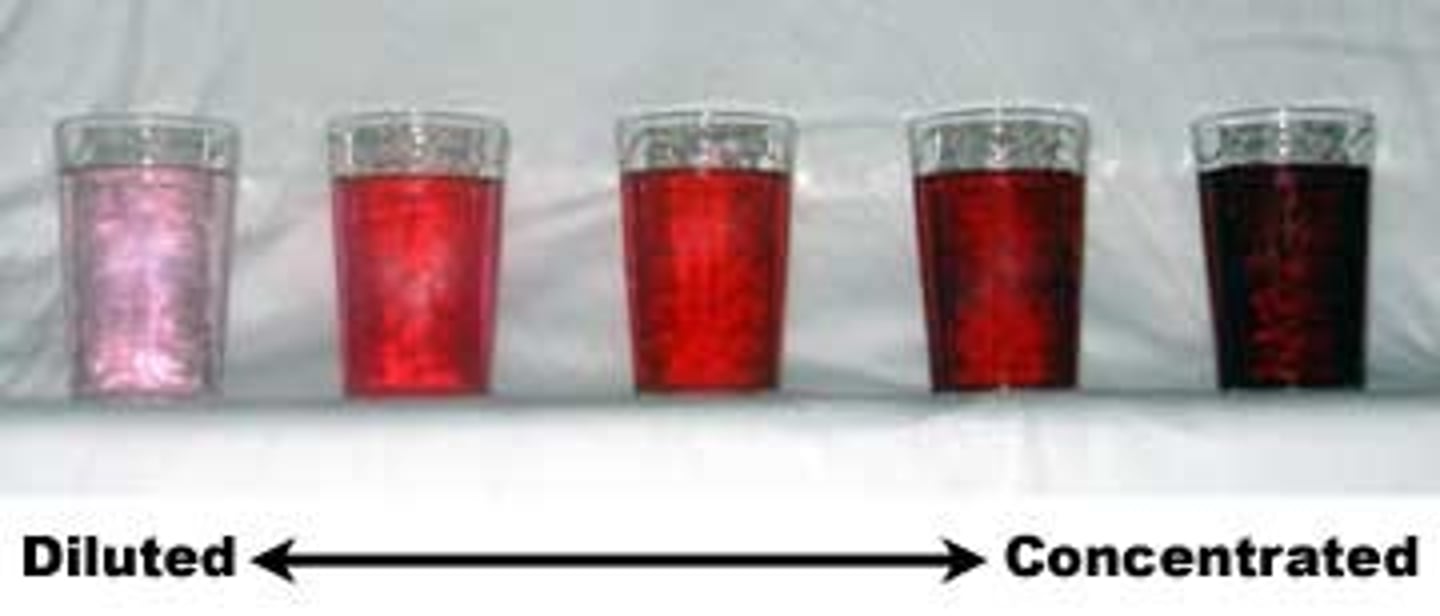
concentration of a solution
the quantity of solute in a given quantity of solution
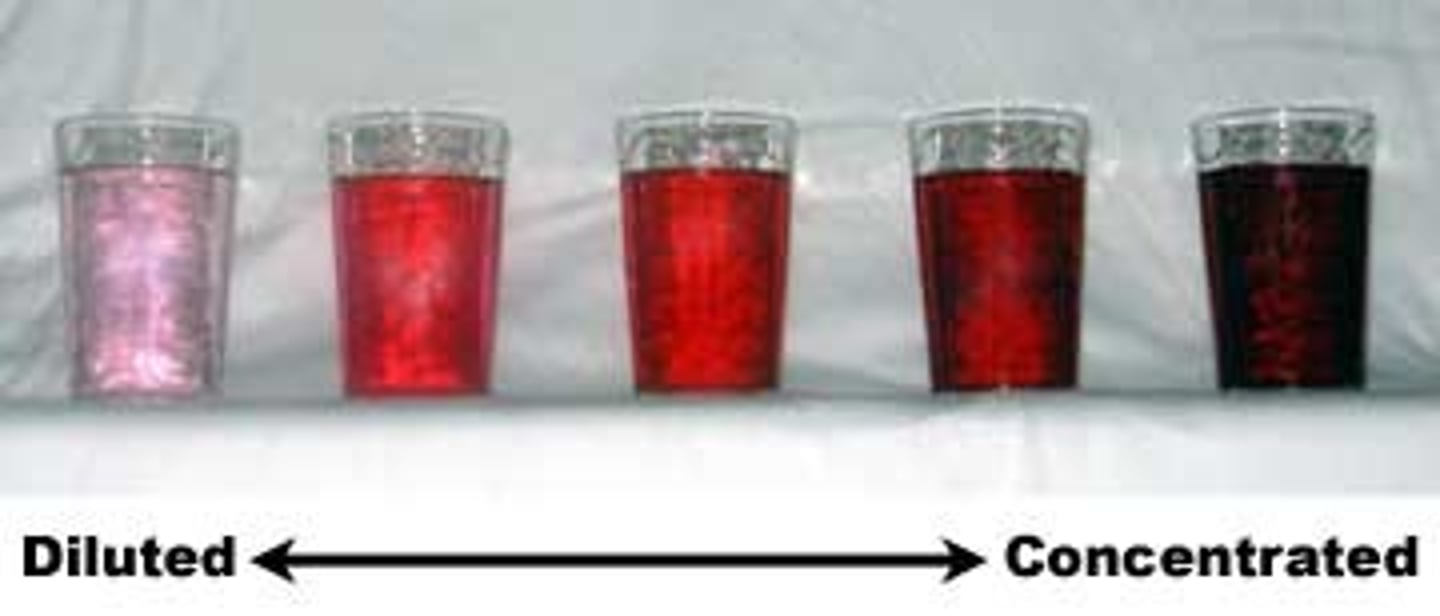
dilution
the addition of solvent to decrease the concentration of solute in a solution
molarity
moles of solute/liters of solution (mol/L)
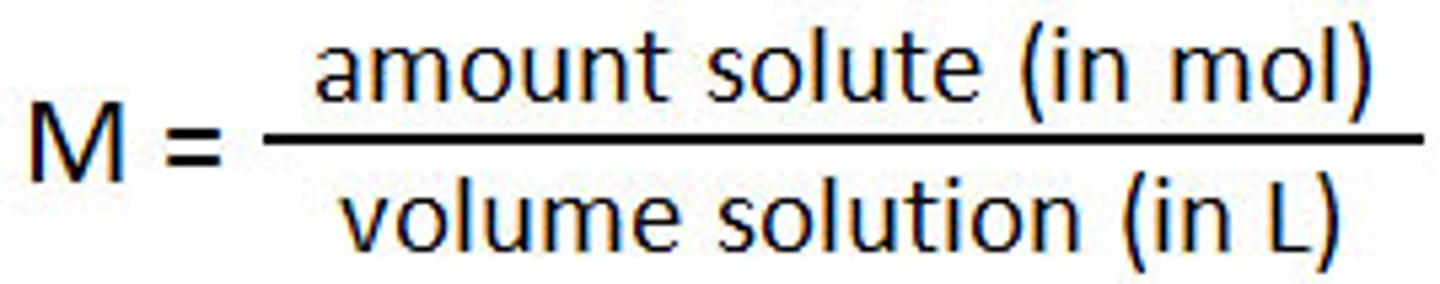
mole fraction equation
moles of solute/ total moles present
(mol/mol)
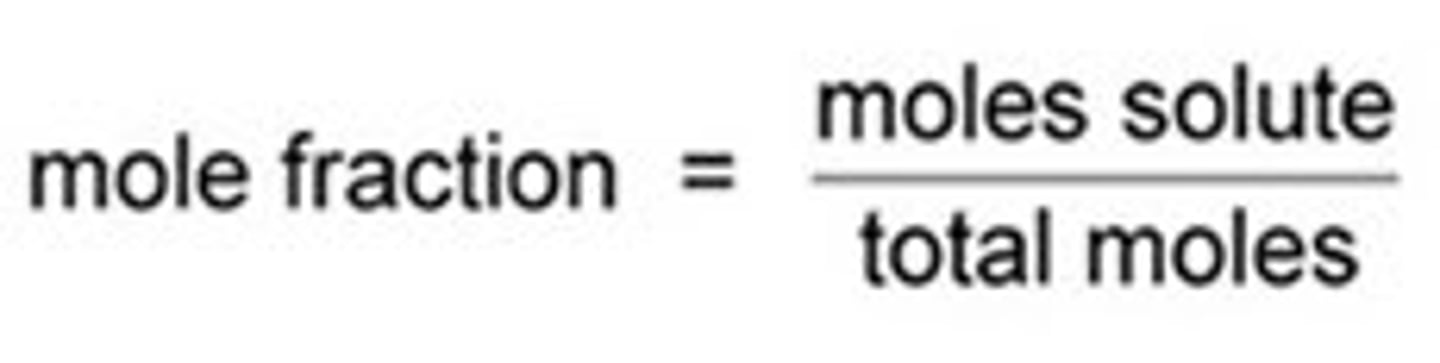
molality
moles of solute/kg of solvent (mol/kg)

mass percentage
mass of solute (g) / mass of solution (g) x 100

parts per thousands (ppt)
g solute/ kg solution
parts per million (ppm)
mg solute/kg solution
parts per billion (ppb)
mcg solute/ kg solution
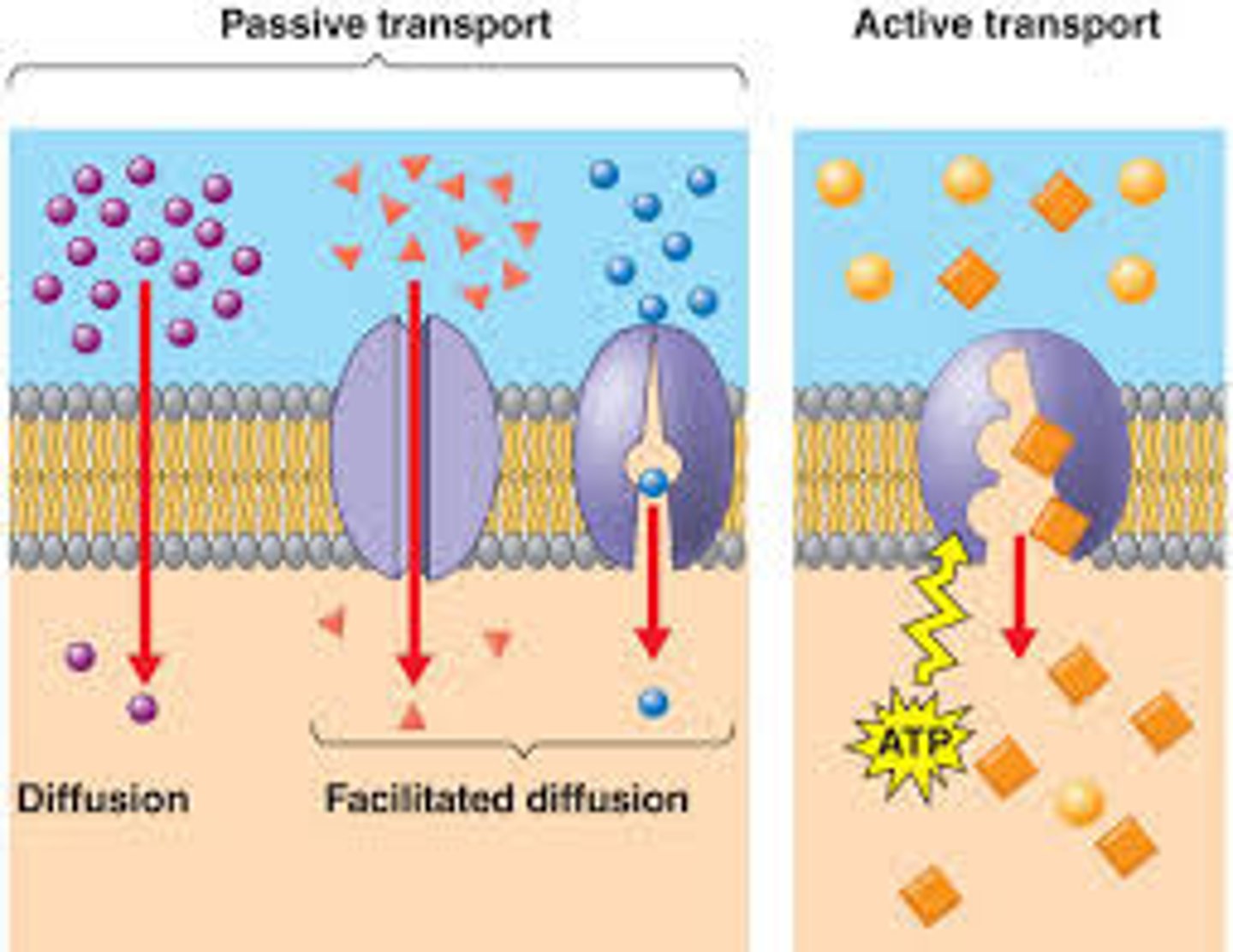
Diffusion
is the movement of any substance from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
ex. when perfume is sprayed in a room.
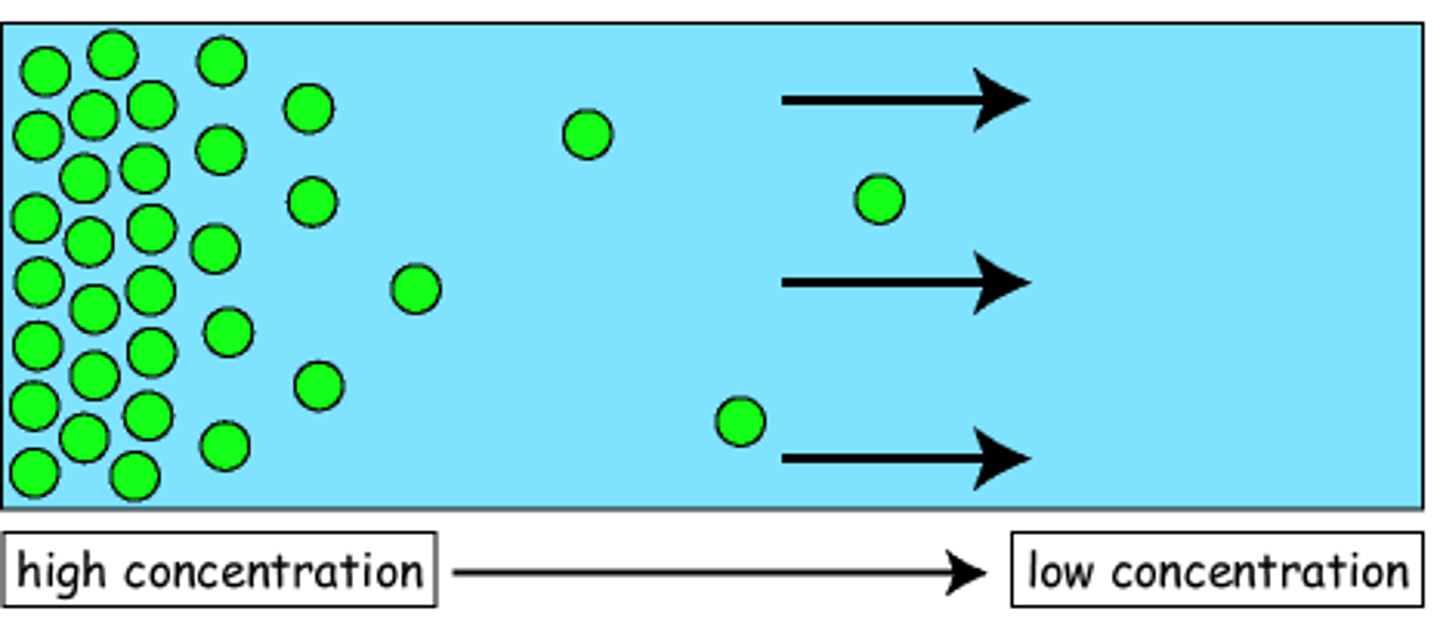
osmosis
is a specific type of diffusion referring to water moving from an area of high concentration to low concentration.
active transport
movement across a cell membrane that travels against the concentration gradient and thus requires energy
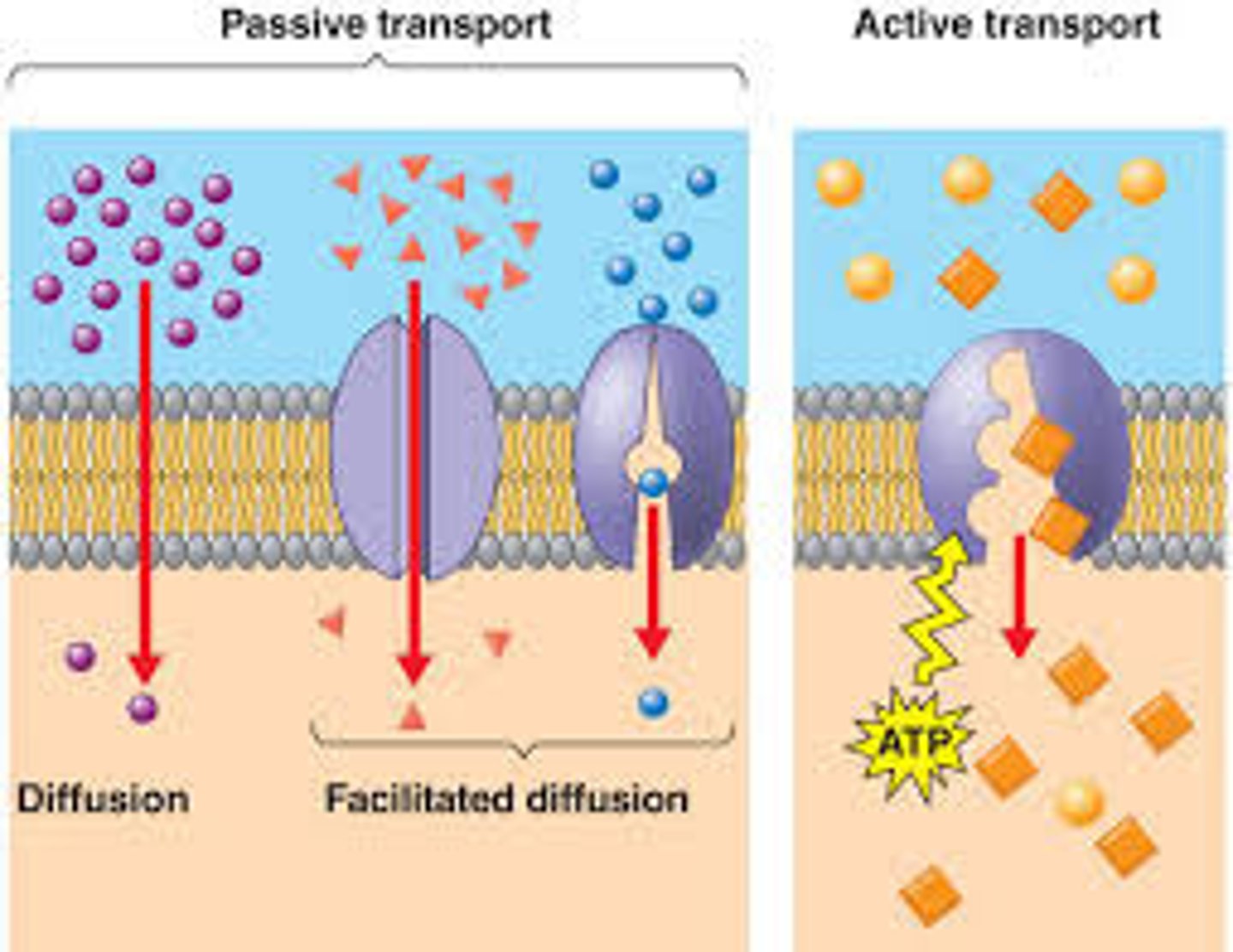
passive transport
The movement of materials through a cell membrane without using energy